Female Pelvis Anatomy
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
The Pelvic Skeleton
4 bones
2 Innominate bones (coxal)
Sacrum - Posterior wall
Coccyx - Posterior wall
True (Lesser / Minor) Pelvis
Area below pelvic brim
Contains uterus and ovaries
False (Greater / Major) Pelvis
Above the pelvic brim
Contains mostly bowel
True and False Pelvis
True and false pelvis divided by imaginary line called the iliopectinal line that runs from the sacral promontory to the symphysis pubis
Obturator Internus Muscle (Internal Obturator Muscle)
Covers the Innominate Bones
Appear lateral to the ovaries - may mimic appearance of ovaries
parallel and adjacent to the lateral pelvic wall
easily missed with high gain
True pelvis
Piriformis Muscle
Posterior wall of true pelvis
Travels from sacrum to greater trochanter of femur
triangular shaped muscle
usually obscured by overlying bowel gas in the sigmoid colon
Most likely muscle to mistake for ovary
Levator Ani Muscles
Make up the innermost layer of muscles to form the floor
make up middle and anterior floor
Lateral borders of the levator ani muscles cover the obturator internus muscle
Resists intraabdominal pressure (from coughing and straining)
holds pelvic organs in place
Levator ani muscles are composed of:
Iliococcygeus
Pubococcygeus
Puborectalis
The Pelvic Muscles
Filled bladder acts as a window to visualize three major muscle groups
Obturator Internus
Pelvic Floor Muscles
Iliopsoas Muscle
Muscles may be mistaken for ovaries, fluid collection, or masses
a symmetric bilateral arrangement indicates they are muscles
Levator Ani U/S appearance:
Best seen in transverse w/ caudal angulation at the most superior aspect of the bladder
Hypoechoic, hammock-shaped area that is medial, caudal, and posterior to the obturator internus
Iliopsoas Muscle
In false pelvis → never truly enters true pelvis, but courses along the border
discretely marginated and hypoechoic
both long and transverse images obtained through bladder midline with lateral angulation
Too deep to see TV
The Perineum
Area below the pelvic floor
Diamond shaped and consists of skin and muscle
The Perineum is divided into 2 sections:
Anterior Urogenital Triangle
Contains orifice for urethra and vagina
Posterior Anal Triangle
Contains anus
The Urinary Bladder
Smooth, hollow, thick-walled, musculo-membranous highly distendable collapsible muscular sac
reservoir for urine
retroperitoneal
located along the pelvic floor - posterior to the symphysis pubis
between symphysis pubis and vagina
lined with mucous membrane
rugae in the wall - allow the bladder to expand
Bladder wall layers:
Mucous membrane (transitional epithelium)
allows bladder to expand
Submucosa (connective tissue)
Muscle layer (Detrusor)
Adventitia (Fibrous)
The Vagina
Lies between the bladder and rectum
muscular tube composed mostly of smooth muscle
measures approximately 7-10 cm in length
Vaginal Anatomy:
half of vagina lies in the perineum while lower half lies above pelvic floor
fornix is found near cervix
anterior, lateral, and posterior fornices
urethra located in anterior vaginal wall
Uterus
Mobile, hollow, muscular, pear-shaped structure partially covered by peritoneum
Located between bladder and rectum in the true pelvis
Average nulliparous uterus measures about 7-8 cm long x 5.5 cm wide x 3 cm thick
multiparity may increase size by 1-2 cm in all dimensions
Four parts of uterus:
fundus
body
isthmus
cervix
Fundus
uppermost part of uterus
dome shaped region narrows at outer and lateral margins to form the cornua
fallopian tubes arise laterally from cornua
Body (Corpus) of Uterus:
Largest region
houses the uterine cavity (endometrium)
allows for dynamic changes during normal menstrual cycle and pregnancy
Isthmus of Uterus:
Marks transition from corpus (body) to cervix
known as uterine “waist”
most flexible part of uterus
called lower uterine segment during pregnancy
Cervix of Uterus:
Neck of the Uterus
2-3 cm long in non-pregnant uterus
Should be 3-4 cm long in pregnant women
Endocervical canal
Internal os: Communicates w/ uterus
External os: Communicates w/ vagina
Uterine Layers:
Serosa (Perimetrium)
Myometrium
Mucosa (Endometrium)
Serosa (Perimetrium)
Outermost layer of uterus
thin
not routinely visible. on TA U/S
Better visualized TV
Myometrium
thick middle layer of uterus
smooth muscle surrounded by connective tissue
forms bulk of uterus
Mucosa (endometrium)
mucosal lining of uterine cavity
varies in thickness throughout menstrual cycle
continuous with lining of vagina
Uterus U/S appearance:
Myometrium should be homogenous
Smooth walled borders
Arcuate vessels seen in periphery of uterus
Normal pre-puberty uterus measurements:
2.5-3.5 cm long x 1-2 cm AP thickness
Normal nulliparous uterus measurements:
7-8 × 5.5 × 3 cm
Normal multiparous uterus measurements:
8-9 x 5-6 × 5 cm
Normal post-menopausal uterus measurements:
3.5-6.5 × 1-2 × 2 cm
Broad Ligament
Not a true ligament → double fold of peritoneum
largest of all pelvic ligaments
fat, vessels, and nerves in between the two layers
minimally suspends the uterus
Supports the ovaries due to the fact that they adhere to the posterior side of the ligament
Round Ligament
Fibromuscular cords that hold uterine fundus in a forward position
Extend from the cornua
Provides anterior support
Keep uterus in anteverted position
Cardinal ligaments AKA:
Transverse cervical ligaments
Cardinal ligaments
Wide bands of ill-defined fibromuscular tissue
Connect the cervix to the pelvic side wall and sacrum
Maintain location of the cervix in the midline of the body
Uterosacral Ligament
Connects the cervix to rectum and sacrum
Provides posterior support
Maintains midline placement of cervix
Helps maintain anteverted position of the uterus
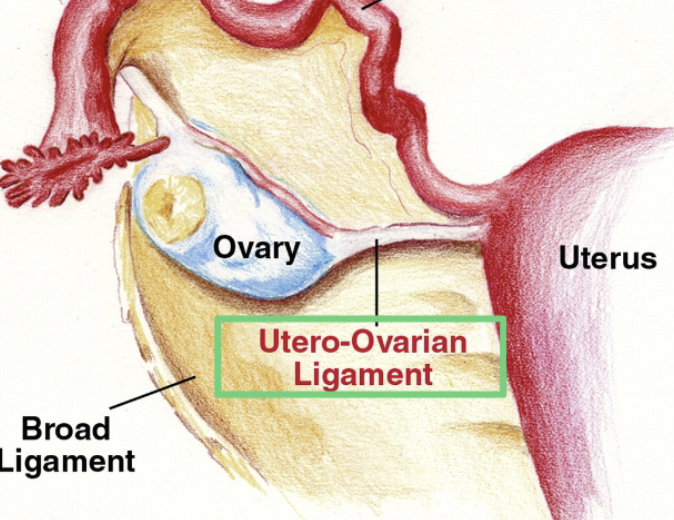
Ovarian Ligament AKA:
Utero-ovarian ligament
Ovarian Ligament
Extends from each ovary to the lateral sides of uterus
Fibromuscular cords within the broad ligament
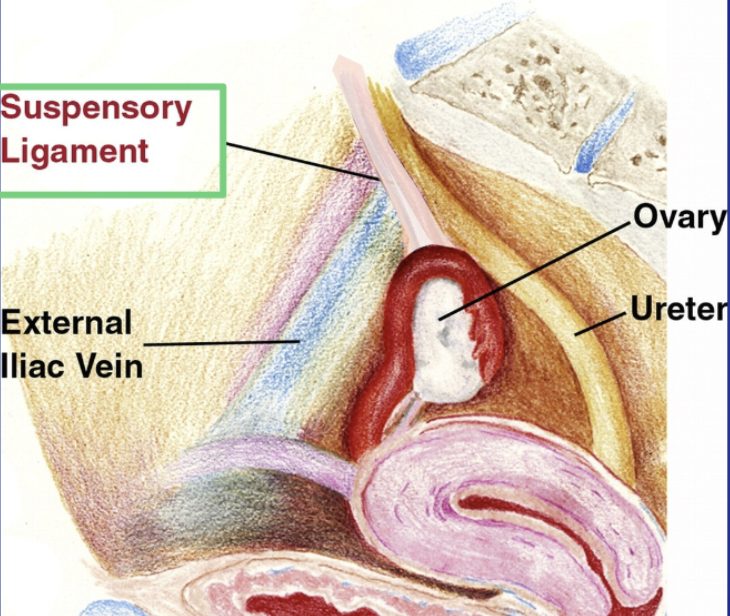
Suspensory Ligament AKA:
Infundibulopelvic ligament
Suspensory Ligament (Infundibulopelvic ligament)
Fold of peritoneum
Connects ovary and fallopian tube to pelvic wall
Extends up and over the iliac vessels
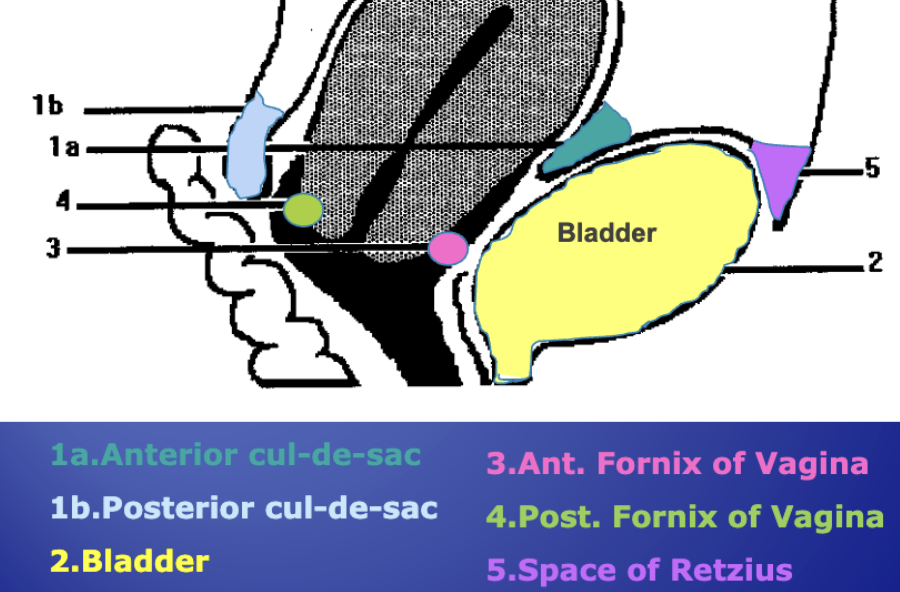
Anterior Cul-de-sac AKA:
Vesico-Uterine Pouch
Anterior Cul-de-sac (Vesico-Uterine Pouch)
Lies between the anterior wall of uterus and the bladder
Posterior Cul-de-sac AKA:
Recto-Uterine Pouch
Pouch of Douglas
Posterior Cul-De-sac
Most posterior and dependent portion of the pelvic cavity
First place to visualize fluid in the pelvis
Space of Reitzius AKA:
Prevesical / Retropubic space
Space of Reitzius
Space between bladder and pubis
Contains mostly fat
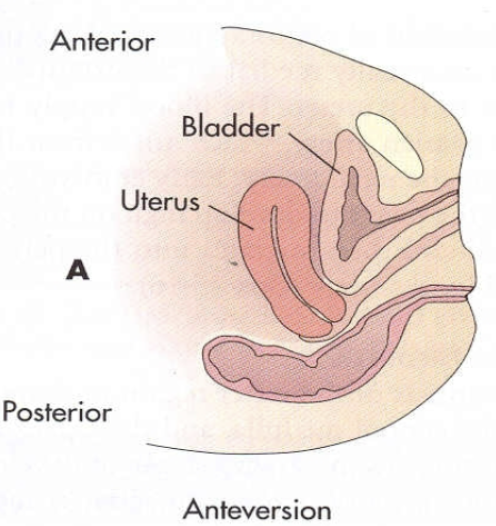
Anteverted uterine position:
Most common
Forward tilt of uterus maintaining 90° between cervix and vagina
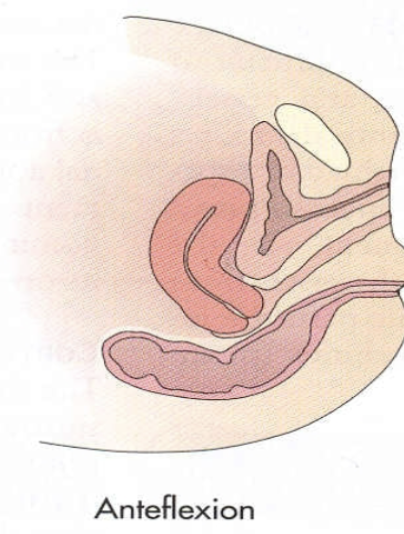
Anteflexed uterine position:
A forward bend of the uterine body on the cervix
occurs at the isthmus
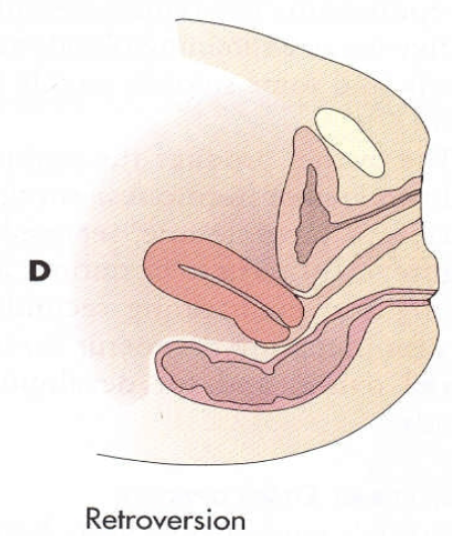
Retroverted uterine position:
A tipping backward of the uterus without a bend between the cervix and body
Approx. 10% of population
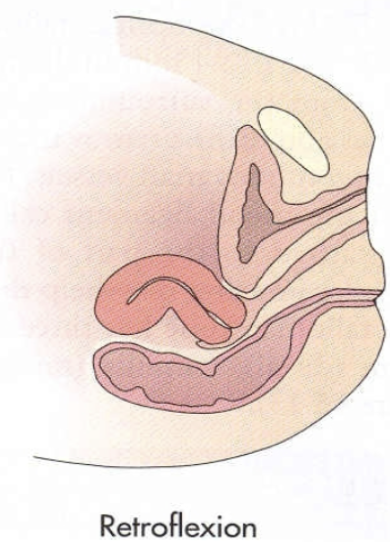
Retroflexed uterine position:
Bending backward of the uterine body on the cervix resulting in a sharp angle where it bends
The Fallopian Tubes AKA:
Oviducts
Salpinges (Salpinx)
Fallopian Tubes (Oviducts)
Extend from the uterine fundus (cornua) toward the ovaries
About 7-14 cm in length
Internal (lumen) dimensions:
Intramural - 1 mm
Ampulla - 6 mm
Contained in a specific fold of the broad ligament called the mesosalpinx
3 layers of fallopian tube wall:
Outer - serosa
Middle - muscular
Inner - mucosa
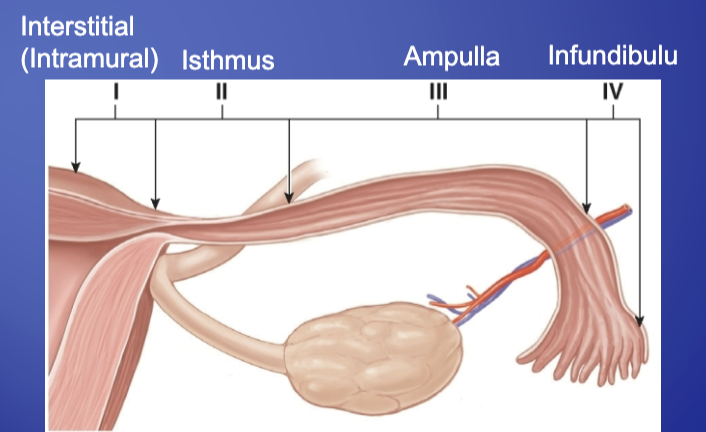
The fallopian tubes are divides into 4 regions:
Interstitial (Intramural)
Isthmus
Ampulla
Infundibulum
The Ovaries
Paired, solid, almond-shaped glands that secrete hormones
Not covered by peritoneum
Ovary measurements:
Adult ovary = 2.5-5 × 1.5-3 × 0.6-2.2 cm (avg. 3 × 2 × 2 cm)
Post-menopausal ovary - 2 × 1 × 1 cm
Should calculate ovarian volume → L x W x H / 2 = cm3
Average volume during reproductive years is 6-9 cm3
Layers of the ovaries:
Outer layer composed of germonal epithelium
Thin fibrous layer - tunica albuginea
Cortex - contains primordial follicles
Medulla (Zona vasculosa of Waldeyer) - forms from embryonic mesenchyme and contains blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves
The ovaries location:
When the urinary bladder is empty, the ovaries are located in the ovarian fossa just beneath the pelvic brim adjacent to the iliac vessels and ureters
Ovaries U/S appearance:
“swiss cheese” appearance
low-level amplitude with follicles
may be difficult to identify
reduce gain
TV > TA
Look anterior and medial to the iliac vessels
may have to press bowel out of the way
Pelvic Vasculature
Common Iliac A’s bifurcate to internal and external iliac A’s
External Iliac A’s and V’s supply and return blood to and from legs
Internal arteries feed the pelvis and divides into anterior and posterior trunks
Ovaries are anterior to Internal Iliac Artery
IIV’s are posterior to the arteries
Pelvic Arterial Flow Order:
Aorta → Common Iliac A → Internal Iliac A → Uterine A → Arcuate A’s → Radial A’s → Straight A’s → Spiral A’s
Pelvic Venous Flow Order:
Spiral V’s → Straight V’s → Radial V’s → Arcuate V’s → Uterine V’s → Internal Iliac V → Common Iliac V → IVC
Ovarian Vasculature Pathway:
Aorta → R/L Ovarian A → Ovary → R/L Ovarian V → IVC