CARIES & EROSION PROTECTION - GIVING DIET ADVICE
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
what is dental caries
demineralisation of the tooth surface caused by bacteria - bacteria produce acid which leads to enamel demineralisation
how can the risk of dental caries be reduced
identification of risk factors and targeted actions
define diet
diet: refers to the customary allowances of food and drink taken by any person from day to day - varies within families and cultures
what is the effect of diet on the mouth
diet may exert a local effect in the mouth by reacting with the enamel surface and as a substrate for cariogenic microorganisms (acidogenic/ aciduric)
which sugar is the most cariogenic
sucrose is the most cariogenic sugar - disaccharide made up of glucose and fructose
which sugars are not a threat to the dentition
lactose - in milk
intrinsic sugars - in fruits and vegetables
» not a threat to dental decay
which sugars are a threat to the dentition
added sugars
non-milk extrinsic sugars
free sugars (FS)
» major threat to dental decay
what happens to the pH of dental plaque after ingestion of free sugars (FS)
soon after the ingestion of FS the pH of dental plaque drops below the critical pH (5.5)
this is the pH at which enamel demineralises
Stephan Curve (1940)
why does the pH of dental plaque drop after FS ingestion
bacteria metabolises the FS taken in ≈ 10 minutes after ingestion therefore pH drops
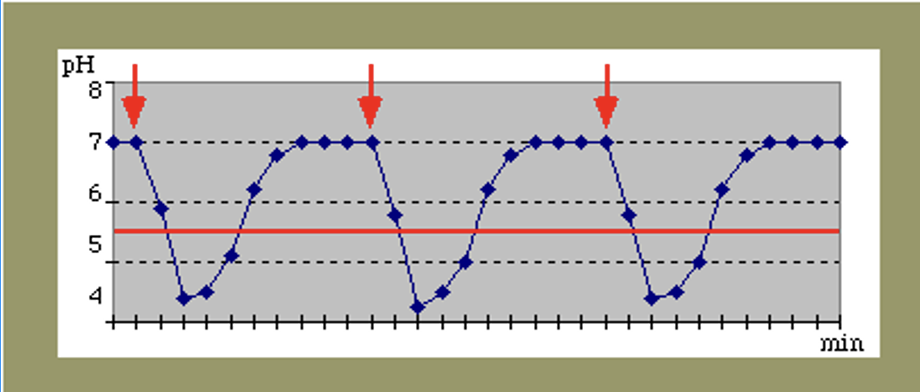
what does this graph show
Stephan Curve
the more frequently food is ingested the more frequent and longer the pH of plaque remains below the critical pH of 5.5
this results in repeated demineralisation
the gradual rise in pH overtime is due to the cleansing of oral cavity or a drink
how can the Stephan Curve be applied to clinical advice
caries can be reduced by:
fewer intakes of food
select foods that lead to a smaller drop in pH
in what two ways can sugars be eliminated in the mouth
chewing
rinsing effect of saliva
what is the clearance time of sugar dependent on (5)
salivary flow rate - older patients tend to have drier mouths
age
adhesive nature of food e.g. fudge, caramel
causes longer period of metabolisation by bacteria » longer period of demineralisation of enamel
concentration of sugar in food
time of day - mouth becomes drier around bed time therefore sugary intakes around nighttime will cause longer periods of metabolisation by sugar
which foods reduce the cariogenic potential of carbohydrates (4)
phosphates - found in cereal
cheese - has a neutralising effect but high in fat
fluoride - added to foods/ toothpastes
xylitol - artificial sweetener in chewing gum is antibacterial
what should diet advice encourage
general physical wellbeing
what should meals be based on
diet advice should be based on:
starchy foods
5 a day
fish
» cut down on saturated fats, salt and sugar
pointers when giving diet advice
advice should be personalised/ tailored
resources should be targeted at those who are at greatest risk of caries
be constructive, understanding and non-judgemental
encourage healthier foods by suggesting alternatives - instead of just telling patients what they should not be having
appreciate cultural norms
specific diet advice to give
reduce frequency and amount of sugar
restrict sugars to mealtimes
avoid snacking
avoid processed foods if possible e.g. cakes, fizzy drinks, dried fruits
encourage sugar free gum consumption
encourage tooth brushing x2 daily for 2 minutes
do not brush immediately after eating/ drinking/ vomiting
brush last thing at night and at one other time
what can parents be advised to do to monitor their child’s diet
record a diet diary
what should be recorded in a diet diary
3 day diary - 2 weekdays and 1 weekend
time of day
amount of food
types of food
what is dental erosion
dental erosion: the irreversible loss of dental hard tissue due to a chemical process of acid dissolution
does not involve dental bacterial plaque like dental caries
not directly associated with mechanical/ traumatic factors or caries
can be extrinsic or intrinsic
dental caries VS dental erosion
the acid produced in dental caries is bacterial related
in dental erosion, the acid is associated with the ingestion of acidic food and drinks
dental caries and dental erosion are often found together within one patient
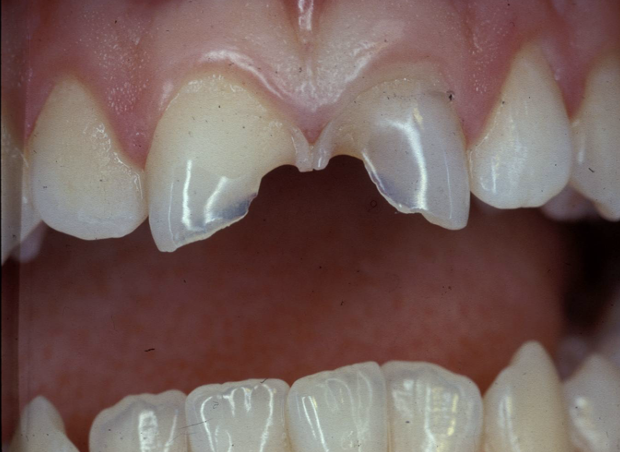
what does this image show
dental erosion
due to the ingestion of fizzy drinks through a straw
thin enamel around incisal tips
state extrinsic sources of acid
foods - citrus fruits, pickled foods, ketchup, vinegar, some crisps
drinks - carbonated drinks, alcopops, fruit juice, wine, herbal teas, smoothies
lifestyle - mood enhancing drugs
environmental - swimmers, wine tasters, battery acid workers
state intrinsic sources of acid
medical - gastric acid reflux, vomiting, rumination
psychological - anorexia, bulimia nervosa
what ingredients in soft drinks are erosive
phosphoric acid
citric acid
» plunges pH of mouth to < 5.5 - critical pH
image of dental erosion with dentine exposure
LL6
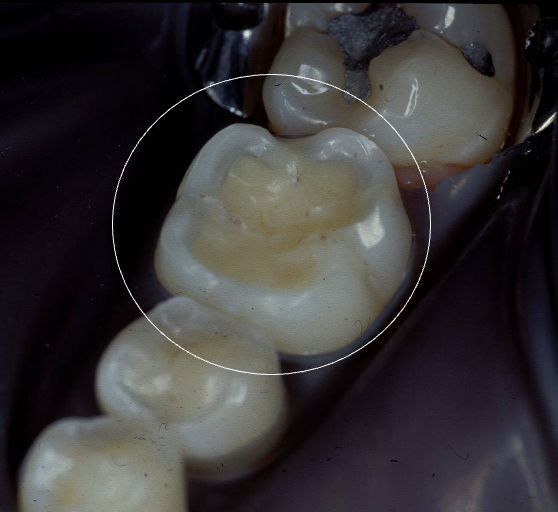
what is an important thing to do prior to dental treatment
tackle aetiological factors of the condition
what food has quite a lot of sugar in it
baked beans
why is sugar more likely to stick to teeth for longer during nighttime
our mouths are drier during nighttime due to the circadian rhythm