GI Anatomy complete set
1/200
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
201 Terms
Name the unpaired branches off abdominal aorta (how many are there?)
3
celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery, inferior mesenteric artery
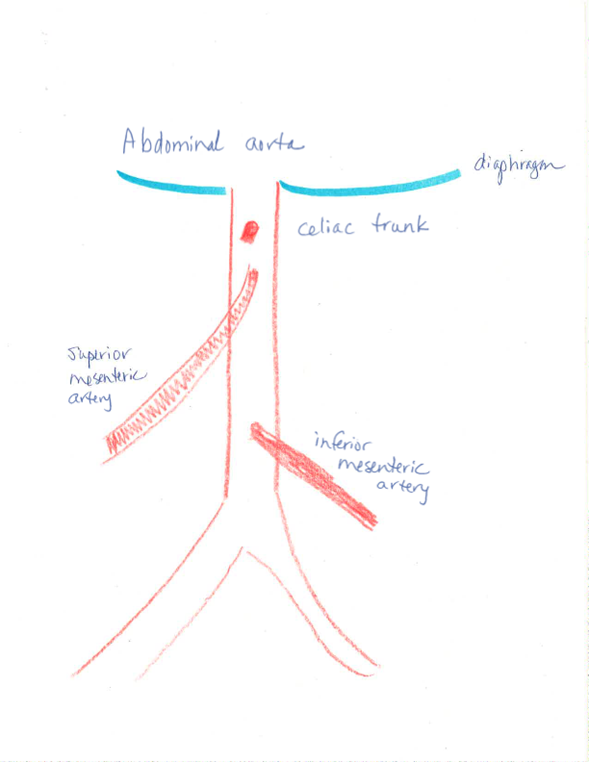
what are the three branches off the celiac trunk?
left gastric a, splenic a, common hepatic a
what does the left gastric a supply?
lesser curvature of stomach; it forms an anastomosis with the right gastric a
splenic artery supplies…
spleen, pancreas, stomach
common hepatic artery supplies the…
liver, stomach, duodenum, pancreas
what are some branches of the splenic artery?
short gastric arteries (supply fundus of stomach)
left gastro-omental artery (left gastro-epiploic a; supplies greater curvature of stomach; forms an anastamosis with the right gastro-omental a)
pancreatic arteries
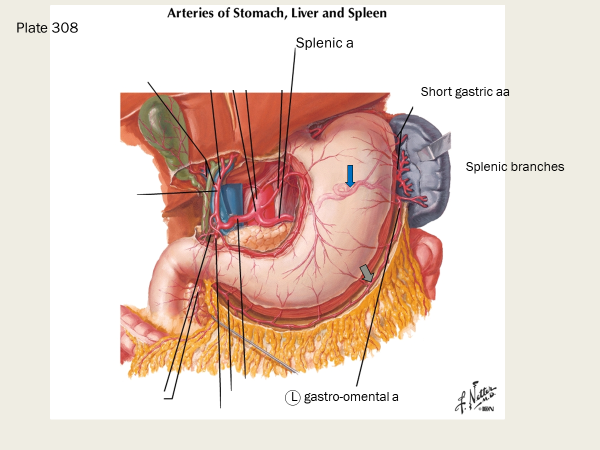
what do the short gastric arteries supply (and what do they branch from)?
they supply the fundus of the stomach
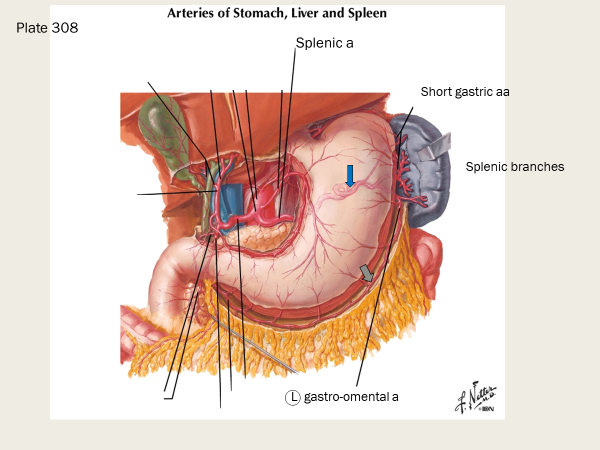
what does the left gastro-omental artery (also known as the left gastro-epiploic a) supply?
greater curvature of stomach
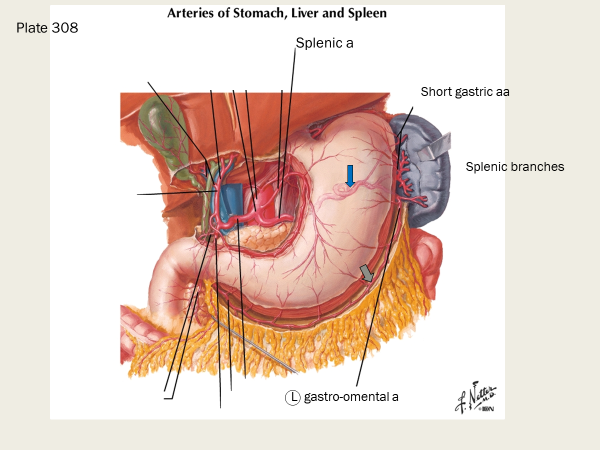
what does the proper hepatic artery branch off of?
it’s a branch of the common hepatic a
common hepatic artery —> proper hepatic artery —→ _____________
right gastric artery, supplies the lesser curvature of the stomach; it forms an anastamosis with the left gastric artery which also supplies the lesser curvature of the stomach)
which arteries supply the lesser curvature of the stomach?
the right and left gastric artery
what does the gastroduodenal artery supply, and what are two branches off of it?
supplies stomach and duodenum
both the right gastro-omental a and the superior pancreaticoduodenal arteries branch off of the gastroduodenal arteries
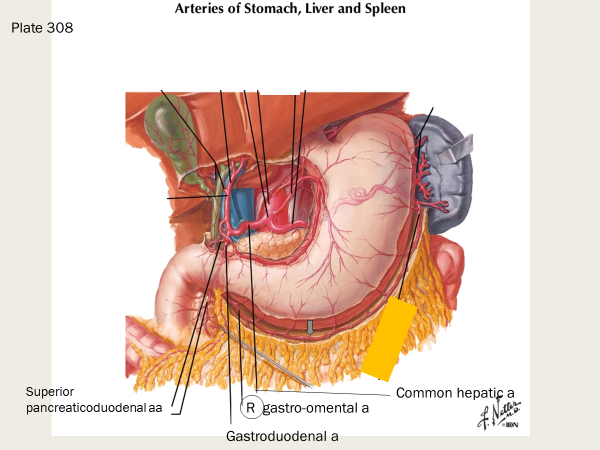
the right gastro-omental a and the superior pancreaticoduodenal arteries are branches of the…
gastroduodenal artery
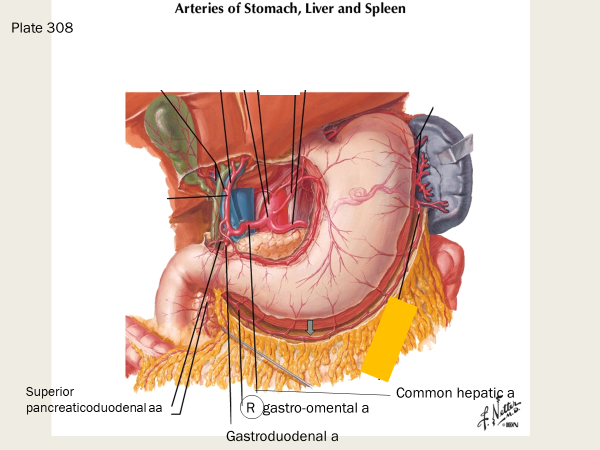
There are several branches off the superior mesenteric artery, including:
many intestinal arteries, inferior pancreaticoduodenal arteries, ileocolic artery, right colic artery, and ______________
middle colic artery
Remember III RM
(Colic 3, intestinal, and pancreaticoduodenal)
Intestinal
Inferior pancreaticoduodenal arteries
Ileocolic
Right colic a
Middle colic a
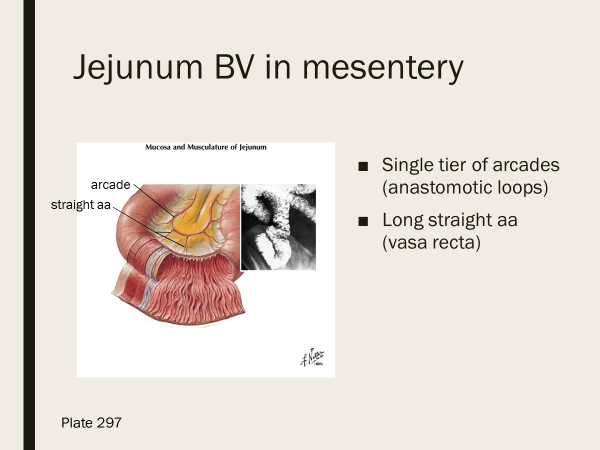
The Jejunum has how many tiers of arcades? Are the straight arteries of the jejunum long or short?
single tier, long straight aa jejunum
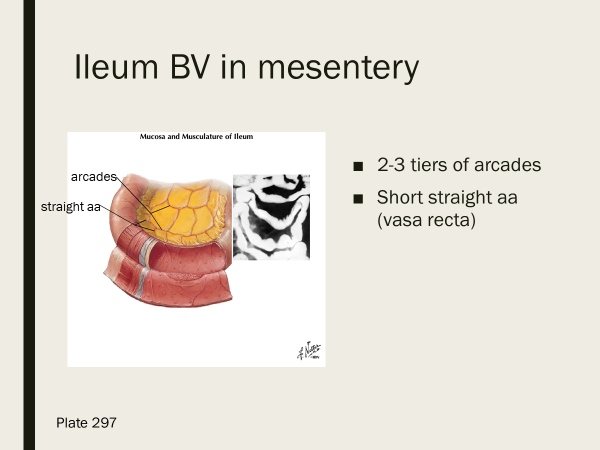
the ileum has how many tiers of arcades? short or long vasa recta?
2-3 tiers; short vasa recta
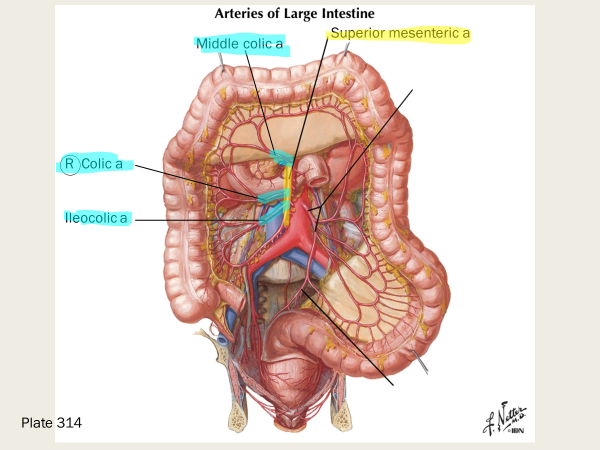
Which 3 branches of the superior mesenteric a (hint: they’re easy to group together) all contribute to the marginal artery anastamosis?
the colic arteries:
ileocolic a, right colic a, and middle colic a
What are three branches off the inferior mesenteric artery?
left colic artery, sigmoid arteries, and superior rectal artery
which arteries form the marginal artery anastomosis that supply the entire length of the colon?
ileocolic, right colic, middle colic, left colic, and sigmoid arteries all contribute to the marginal a anastamosis
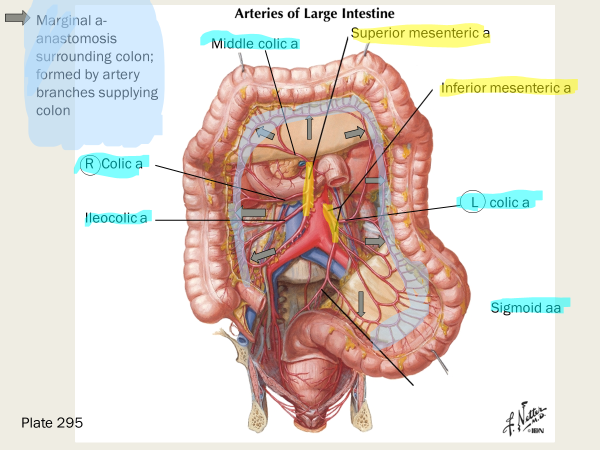
the left colic artery supplies the —- and the sigmoid aa supply the …
descending, and sigmoid colon respectively
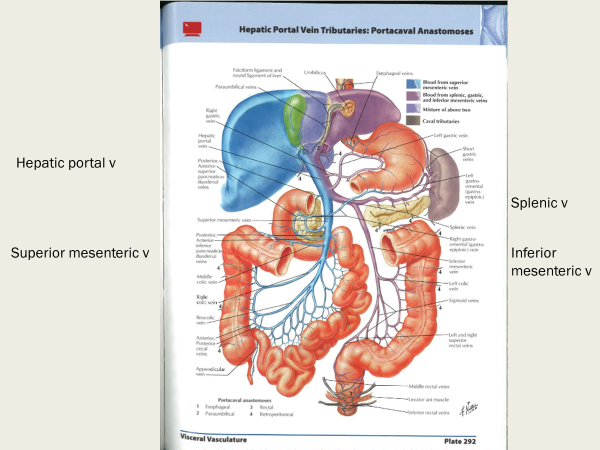
the portal triad is made up of the…
proper hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein, and the common bile duct
Hepatic artery - A branch of the common hepatic artery that originates from the celiac trunk
Portal vein - The main drainage site for the small and large intestines and spleen, carrying nutrient-rich but oxygen-poor blood
Common bile duct - A tube-like structure that carries bile from the gallbladder to the duodenum
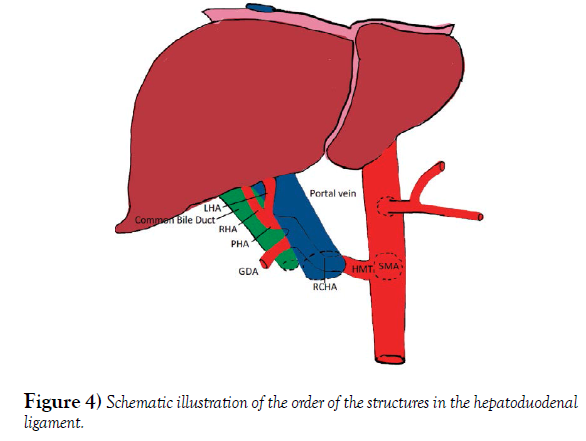
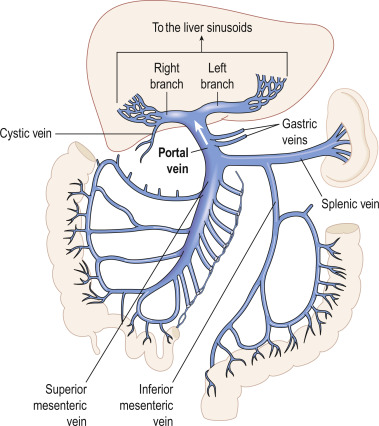
explain the dual capillary system of the portal system (blood flow from GI system/spleen to liver to IVC)
nutrients in capillary beds of GI tract and spleen are absorbed —>
nutrient rich blood flows into hepatic portal vein to liver —> liver processes nutrients —> blood collects in hepatic veins —> IVC
the _____ ___________ are microscopic blood vessels in the liver that transport blood and facilitate the exchange of nutrients and oxygen between the blood and the liver
hepatic sinusoids
the inferior mesenteric v empties into the _______ v
splenic vein
which three veins join to form the hepatic portal vein? Where does the blood from hepatic portal vein drain into?
splenic v + superior mesenteric v + gastric veins
drains into hepatic sinusoids
true or false: the gallbladder produces bile
FALSE; bile is produced by hepatocytes in the liver
what structure in our bodies produces cholesterol?
liver
what organ stores fat-soluble vitamins?
liver
why is bile important for digestion of fats?
it emulsifies lipids
what structure of the liver is a remnant of fetal circulation?
round ligament of liver/ligamentum teres; a remnant of the umbilical vein
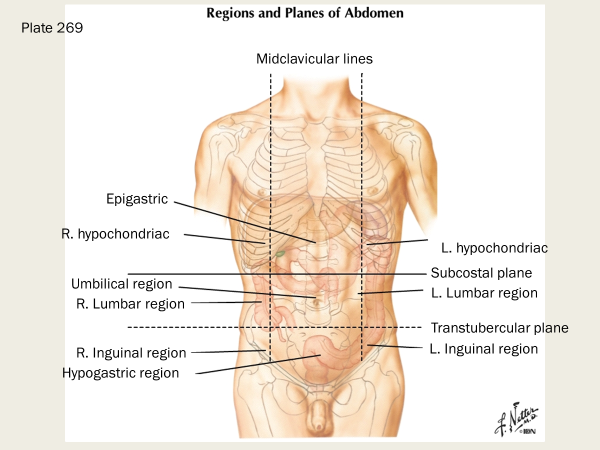
label these areas that lie superior to the subcostal plane:
right and left hypochondriac region and epigastric region
what ligaments anchor the liver to the diaphragm?
coronary ligaments (peritoneal ligament)
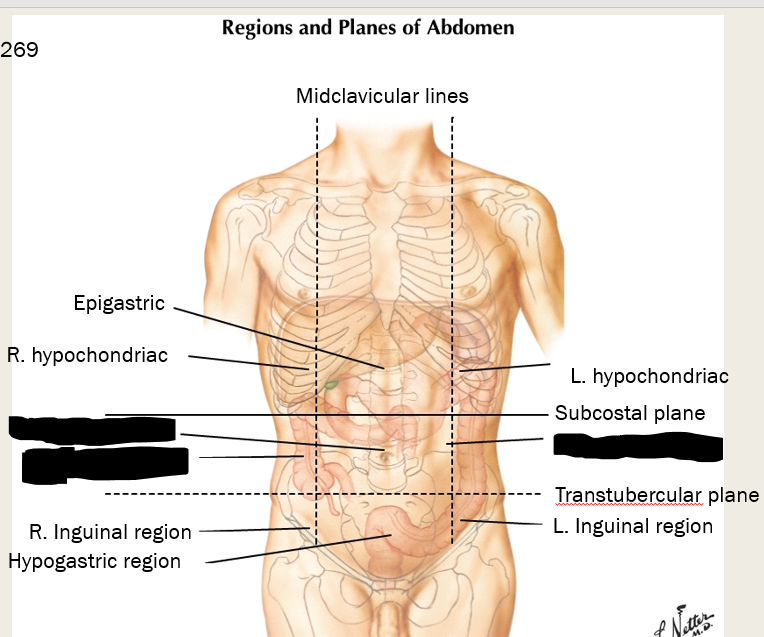
label these three regions between the subcostal and transtubercular planes
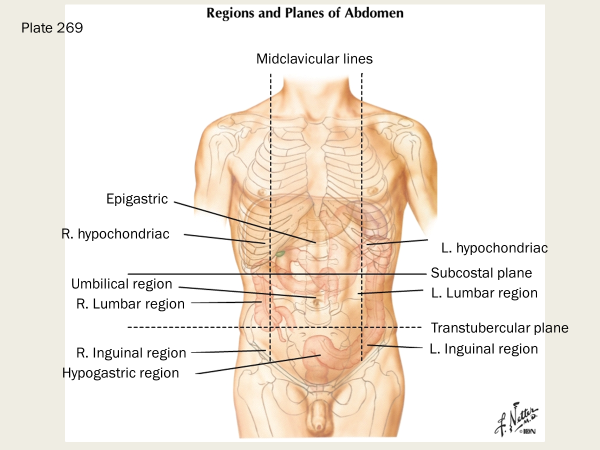
what are the three regions below the transtubercular plane on the anterior side?
right inguinal region (iliac), hypogastric region (pubic), and left inguinal region (iliac)
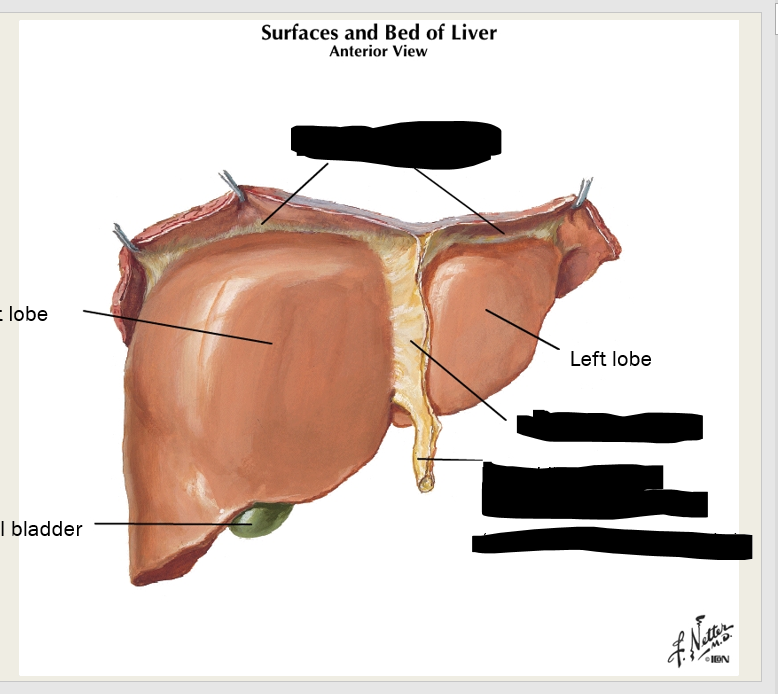
label these three ligaments
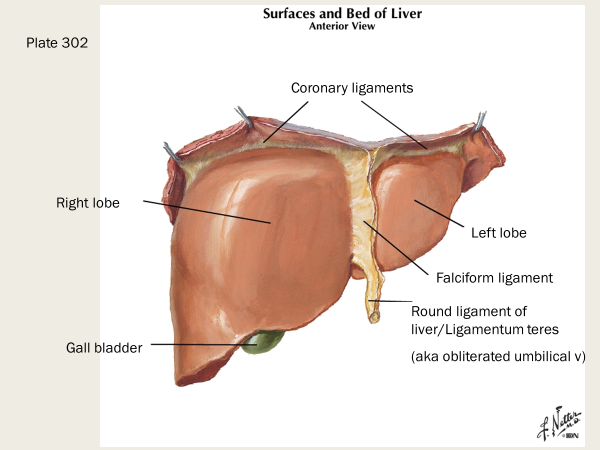
what is the bare area of the liver?
not lined with periotoneum; the superior end of the liver that sits on the inferior side of the diaphragm
what are the three cell types in the liver (that we need to know) and what are their functions?
hepatocytes - most functions of liver
Kupffer cells - macrophages that filter blood
Ito cells (stellate cells) - store fat
function of ito cells (stellate)
store fat
function of Kupffer cells in liver
macrophages that filter blood
the portal triad is made up of the…
Proper hepatic artery
Hepatic portal vein
Common hepatic duct: from liver, prior to cystic duct OR common bile duct: into duodenum
where is the gallbladder located, and what connects the gallbladder to the common hepatic duct?
Located on posterior surface of liver between right and left lobes
Cystic duct- connects gallbladder to common hepatic duct
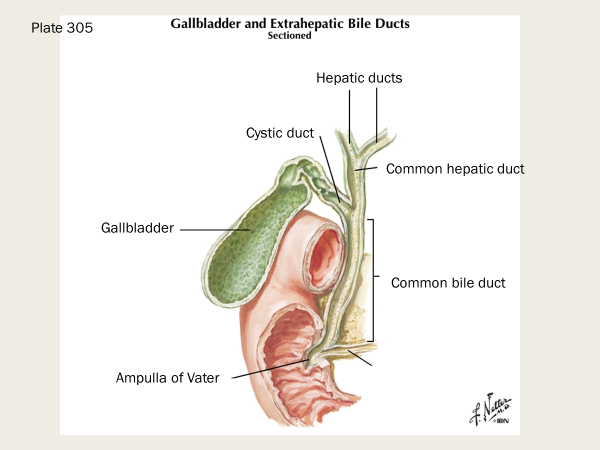
What is the ampulla of Vater?
The ampulla of Vater is a small, flask-shaped reservoir in the digestive system where the pancreatic and bile ducts meet and empty into the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine
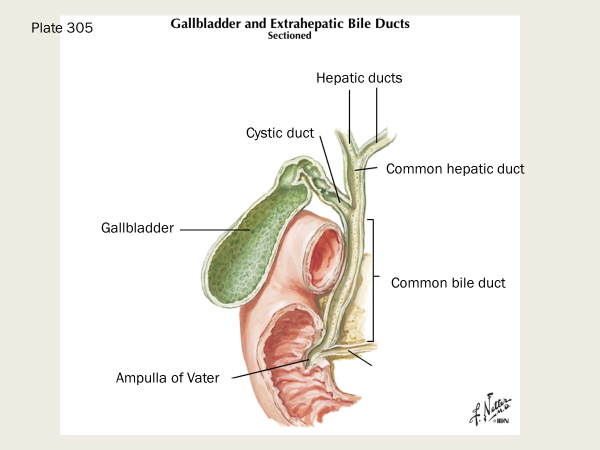
What are the boundaries for the cystohepatic trigone? Surgical significance of this? What are the contents of the cystohepatic trigone?
boundaries: common hepatic duct, cystic duct, inferior surface of liver
it’s a surgical landmark during laparoscopic cholecystectomy
contents include: cystic artery which supplies the gallbladder, and the lymph node of Lund, which is the primary lymph node draining the gallbladder
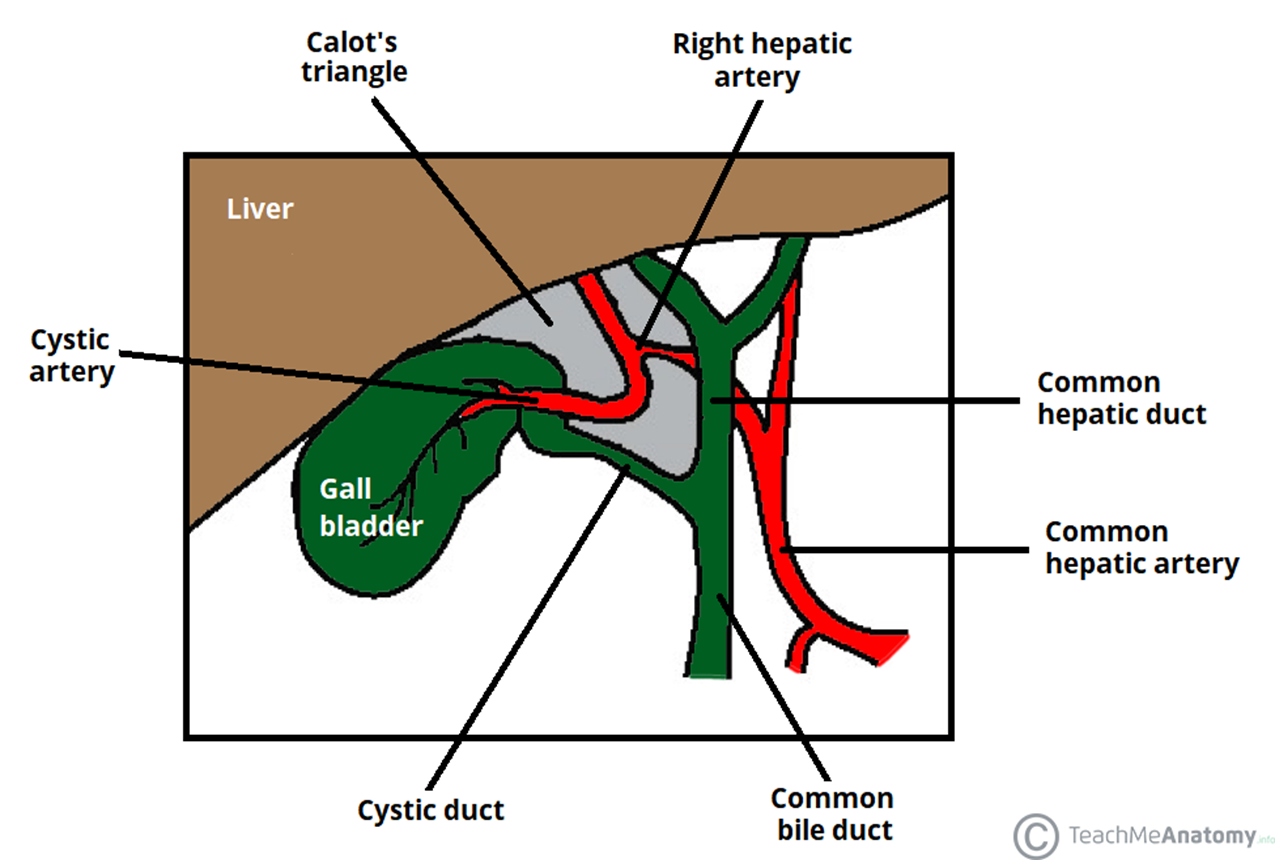
What is the sentinel lymph node of the gallbladder that increases in size in cholecystitis and cholangitis?
Lund’s node - removed with the gallbladder in cholcystectomy
the head of the pancreas is adjacent to the ___ and the tail is adjacent to the ___
the head fits into the C shape of duodenum, and the tail is next to the spleen
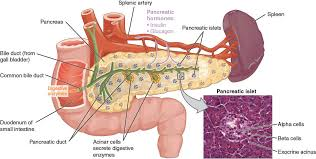
what are the exocrine functions of the pancreas?
digestive enzymes are released (amylase, lipase) and bicarb ions through main pancreatic duct into the duodenum
this organ is the site of erythrocyte production in the fetus, and the storage site for platelets (not just in the fetus)
spleen; it also filters blood, is important for immune response and lymphocyte proliferation, and stores erythrocyte breakdown products
The superior border of the pancreas is the….
inferior border is the …
and the anterior border is the …
superior border - gastric
inferior border - renal
anterior border - celiac (GI)
true or false- pain from the liver, gallbladder, and duodenum can cause referred pain to the right shoulder
true
True or False - The parietal and visceral peritoneum are mucous membranes
FALSE; they are serous membranes.
remember: Mucus is a thick, sticky, gelatinous fluid. Serous fluid is a watery fluid that resembles blood serum.
Mesothelium is made up of what type of epithelial cells?
simple squamous epithelial cells; serous peritoneum membrane (a continuous membrane that includes both the parietal and visceral peritoneum) is mesothelium
true or false- the peritoneum (both parietal and visceral) is continuous and highly convoluted
true; convoluted means twisted or coiled
what is the mesentery? (What does it have in it?)
Double layer of peritoneum (parietal and visceral) enclosing organ; attaching to abdominal wall. Has thin layer of loose CT between layers
Have BV, lymphatics, lymph nodes, nerves, fat
mesogastrium surrounds
the stomach
transverse mesocolon surrounds… and the sigmoid mesocolon surrounds
transverse colon and sigmoid colon
what surrounds the small intestine?
the mesentery
… provides neurovascular communication between the abdominal wall and abdominal organs
the peritoneum (mesentery/mesogastrium/mesocolon)
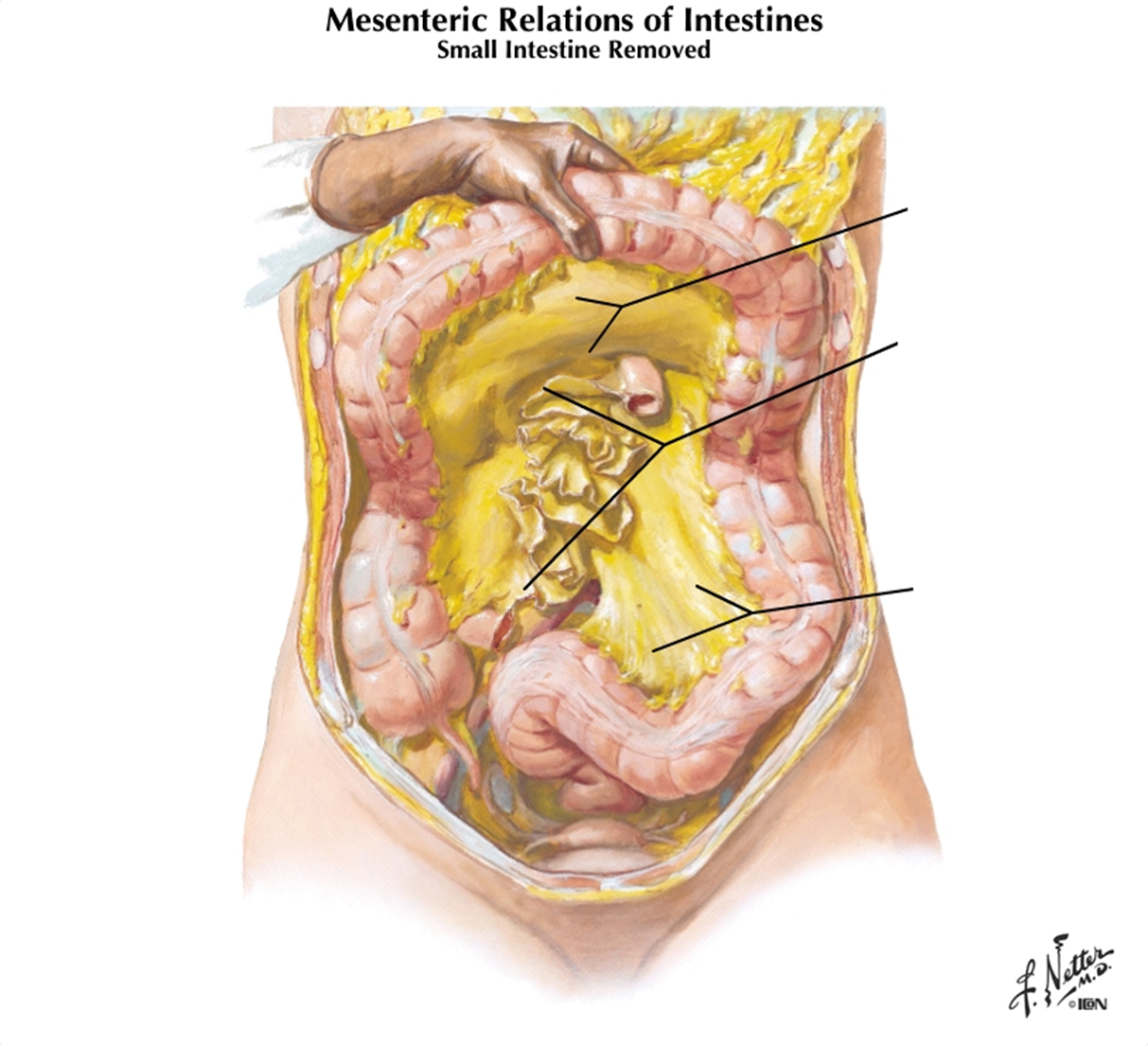
what structure is the double sheet of peritoneum from stomach and duodenum to adjacent organs
omentum (there are two- greater and lesser)
“omentum” means apron
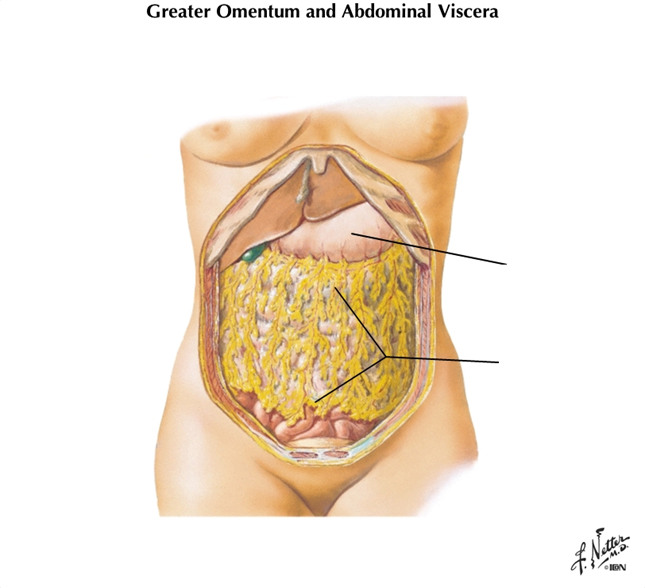
What is the position of the greater omentum?
Hangs off greater curvature of stomach and transverse colon
what is known as the “policeman of the abdomen” and why?
greater omentum, because it can move to wall off infections
what structure attaches to lesser curvature of stomach and proximal duodenum to liver?
lesser omentum
T or F - omentum is peritoneum
true
what two ligaments make up the lesser omentum? Which one contains the portal triad?
hepatoduodenal ligament and hepatogastric ligament
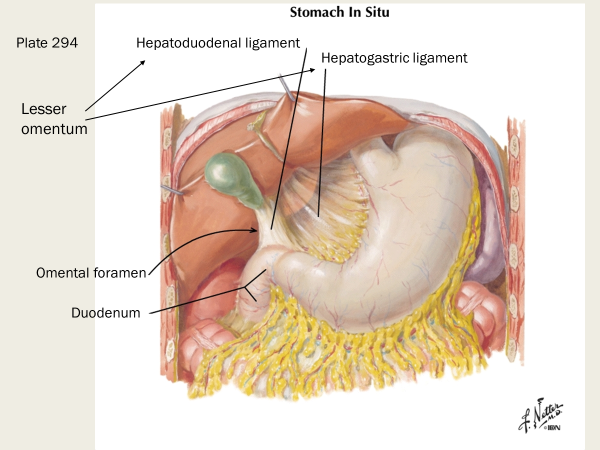
The hepatoduodenal ligament contains the portal triad
true or false - The Peritoneal ligament consists of double layer of peritoneum that connects an organ with an organ or to abdominal wall
true
What is the omental bursa?
A sac-like cavity between stomach/lesser omentum and posterior abdominal wall where infections can persist
the omental bursa is a sac-like cavity between the ________ and posterior abdominal wall
stomach (or lesser omentum)
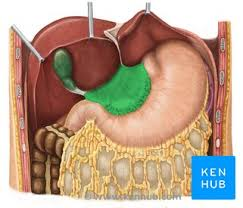
what is the purpose of the omental bursa? What is one clinical significance of this site?
allows free movement of stomach on posterior structures, and communicates with peritoneal cavity through omental foramen
This is an area where an infection can persist

What is the opening posterior to free edge of hepatoduodenal ligament?
omental (epiploic) foramen
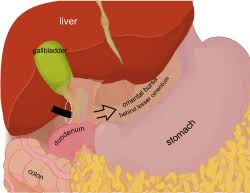
what are the boundaries of the omental foramen? (Ant, Post, Sup, and Inf)
Ant: hepatoduodenal ligament containing the portal triad (hepatic portal v, proper hepatic a, common bile duct)
Post: IVC; R crus of diaphragm
Sup: Caudate lobe of liver
Inf: first part of duodenum and portal triad
True or False - the posterior surface of retroperitoneal organs are covered in peritoneum
False; it is the anterior surface of retroperitoneal organs that are covered in peritoneum
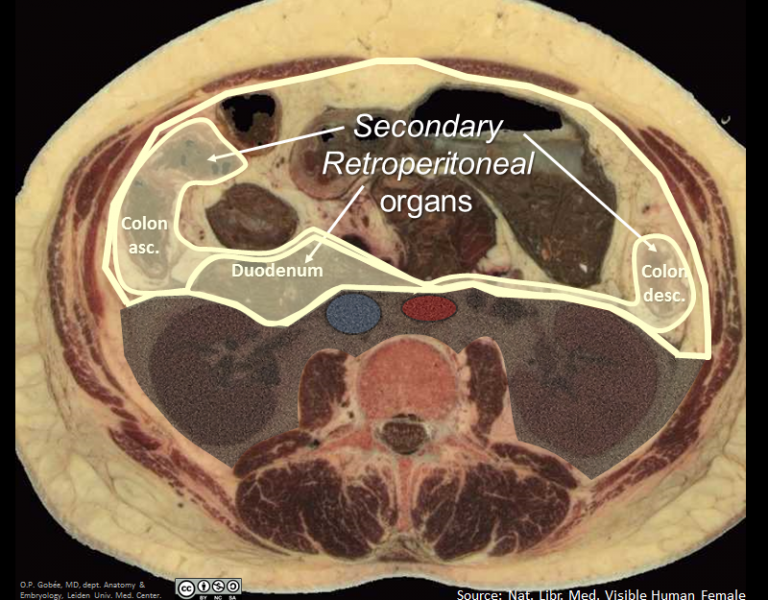
Name 6 retroperitoneal organs
days are passing, keep up always DAPKUA
Duodenum (mostly; the first part of the duodenum, however, is intraperitoneal)
Ascending/descending colon (NOT THE TRANSVERSE COLON)
Pancreas
Kidneys, suprarenal (adrenal glands)
Ureters
Aorta and Inferior vena cava

true or false - the parietal peritoneum is supplied by the same somatic nerves as the region of wall that it lines
true; For this reason it is sensitive to pressure, pain, heat, cold, laceration
is the esophagus posterior or anterior to the trachea?
the esophagus is located posteriorly to the trachea
are the c-shaped rings of the trachea positioned posteriorly or anteriorly?
anteriorly
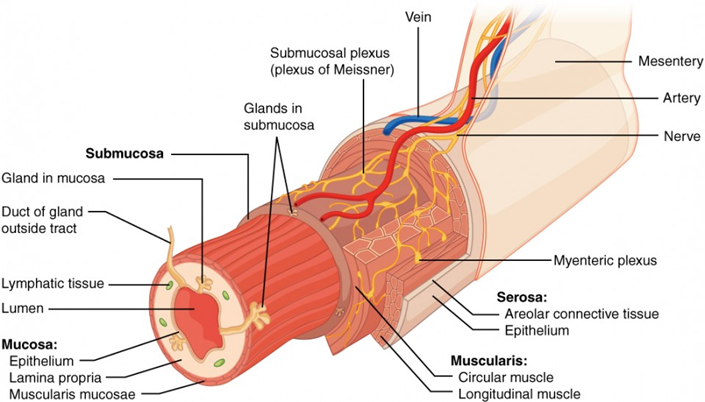
Put these layers of the digestive system in order from internal to external:
muscularis externa
mucosa
serosa
lumen
submucosa
Lumen (technically this isn’t a layer; this is actually just an open space through which material passes through the digestive tract)
Mucosa
Submucosa
Muscularis externa
Serosa
what are the three sublayers of mucosa
epithelium, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosa
what type of epithelial cells make up the mucosa?
mostly simple columnar with goblet cells
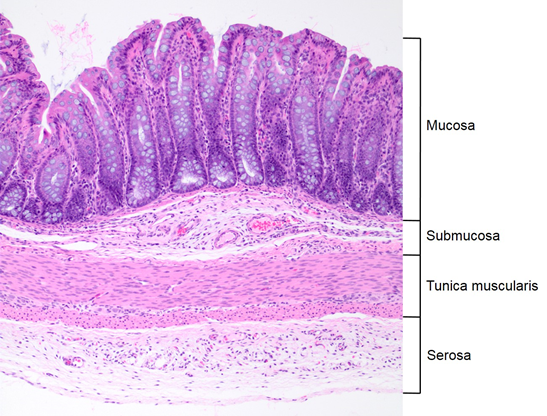
what is the lamina propria?
sublayer of mucosa made up of loose CT (either areolar or reticular)
mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue are here
where is MALT located?
in the lamina propria of mucosa
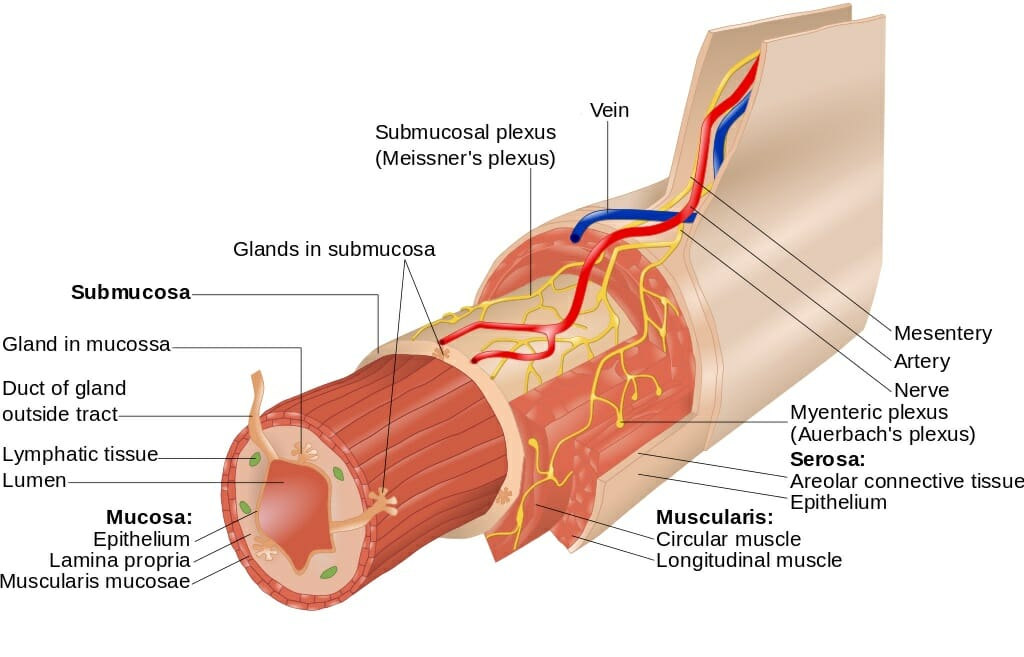
what are the layers of the muscularis externa?
inncer circular layer and outer longitudinal layer of smooth muscle
the serosa is made up of ____ CT covered with ______
Areolar CT covered with mesothelium (simple squamous epithelium
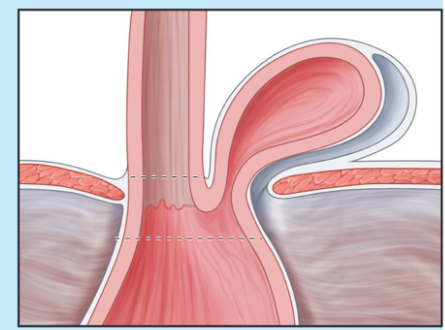
what is pictured here?
hiatal hernia
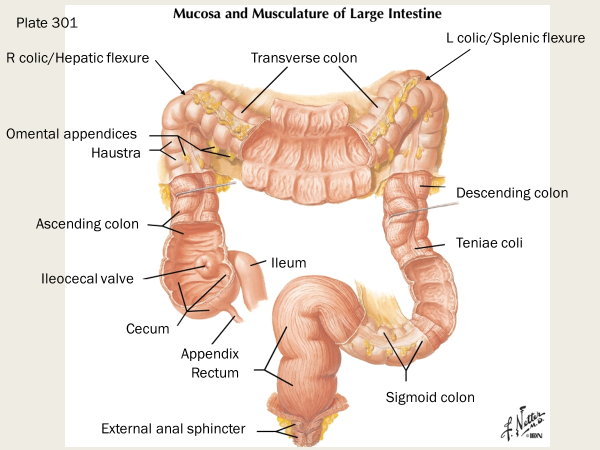
tinea coli
longitudinal bands of smooth muscle that run the length of the colon
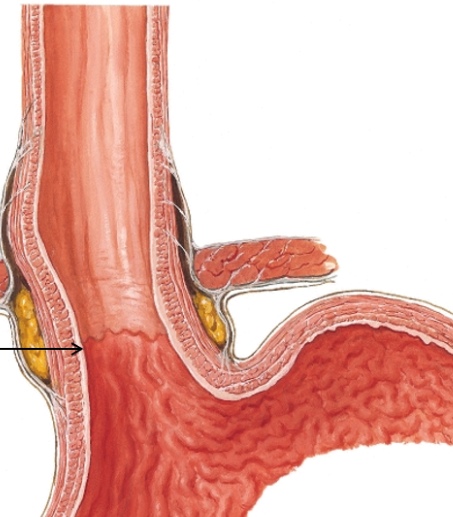
what is this?
esophagogastric junction
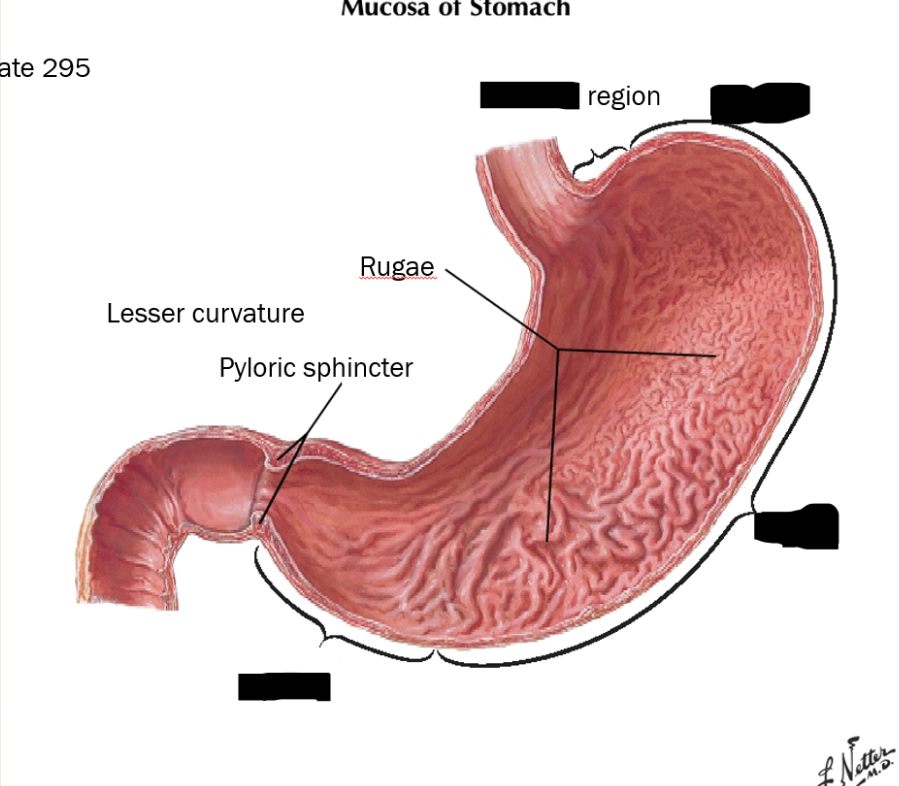
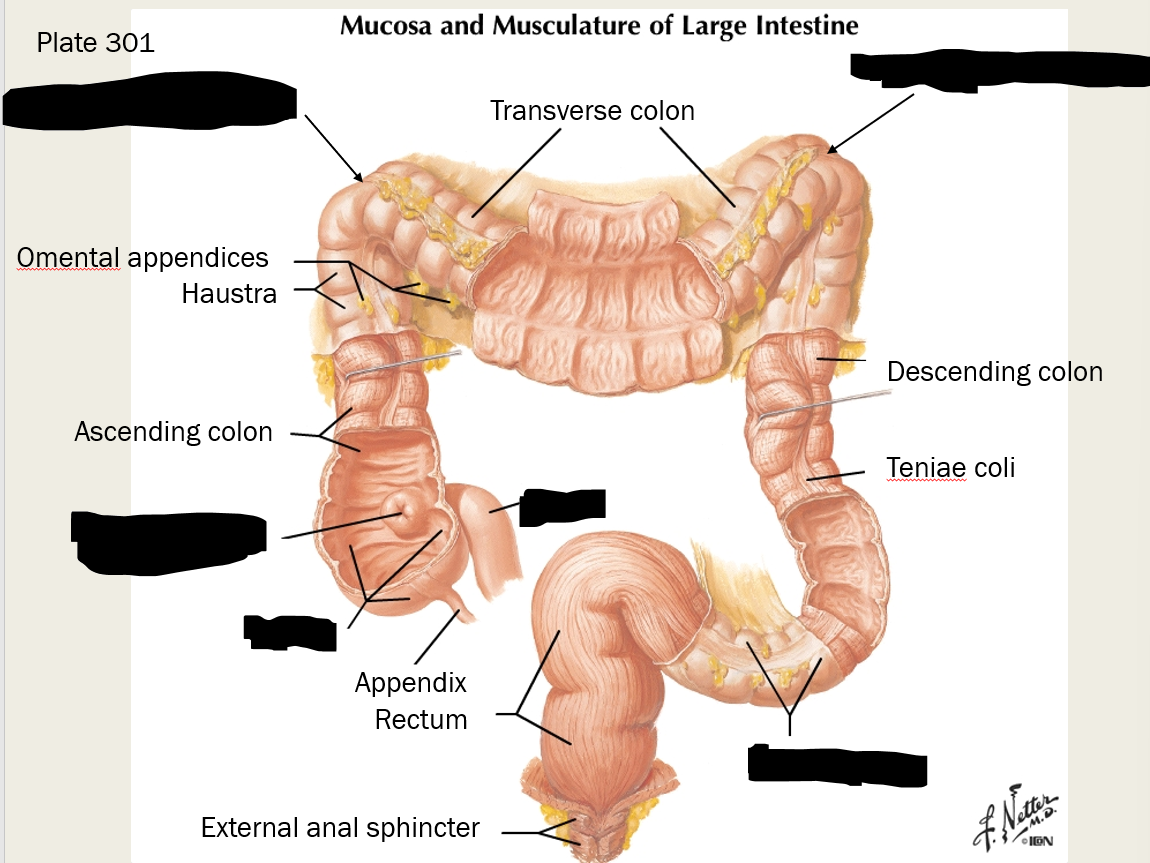
label these structures
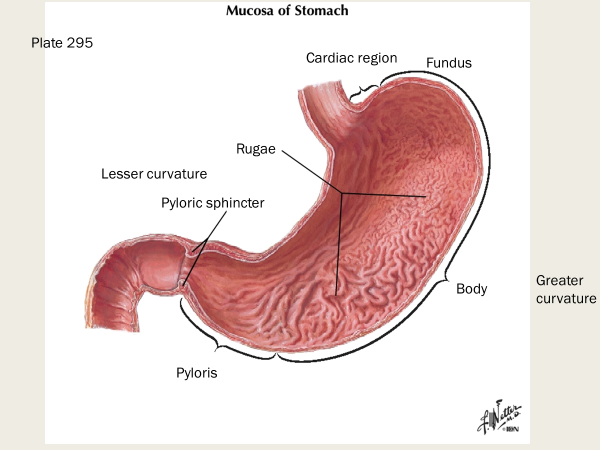
T or F - pyloric stenosis is more common in AMAB than AFAB
true; affects about 1:150 male infants vs only 1:750 female infants
what are the three sections of the small intestine, where most digestion occurs?
duodenum, jejunum, ileum
what is the region of alkaline hydrolysis, absorption, and transport
small intestine
label
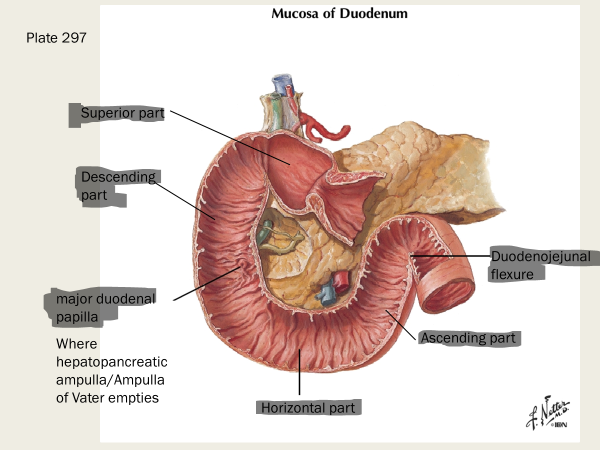
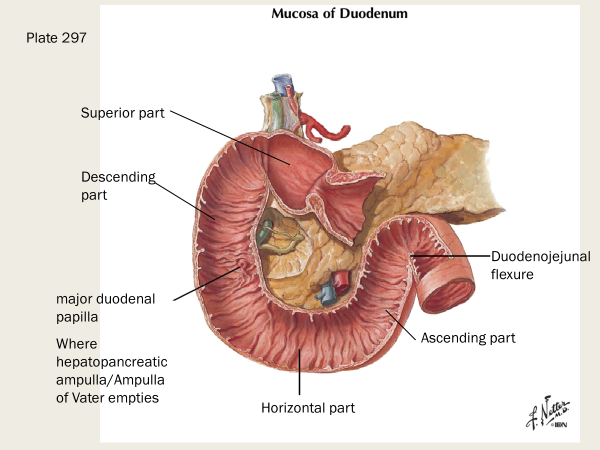
the sigmoid colon is a ____peritoneal organ
sigmoid colon is intra-peritoneal
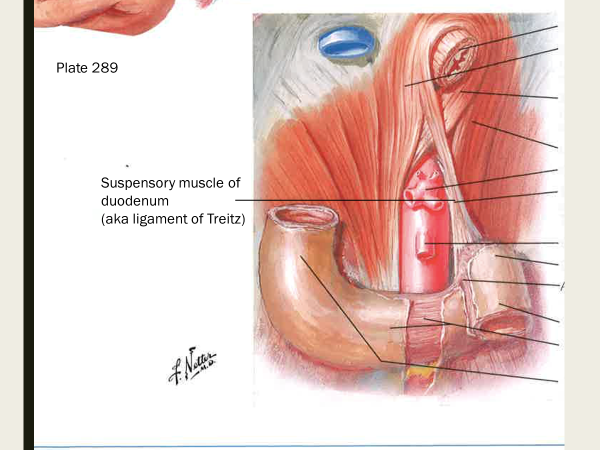
what does the suspensory muscle of the duodenum do? (AKA ligament of Treitz)
supports boundary of duodenum into jejunum; it’s a skeletal m from diaphragm and fibromuscular band of smooth m from duodenum
a band of tissue in the abdomen that anchors the duodenum and helps move food through the gastrointestinal tract
what is the vascular supply for the jejunum?
long straight aa (vasa recta), and single tier of arcades (branches of superior mesenteric artery)
the jejunum makes up ___% of the intraperitoneal section of small intestine
~40%
the ileum makes up about __% of the intraperitoneal section of the small intestine
~60%
describe the vascular supply for the ileum.
several tiers of arcades, short straight aa
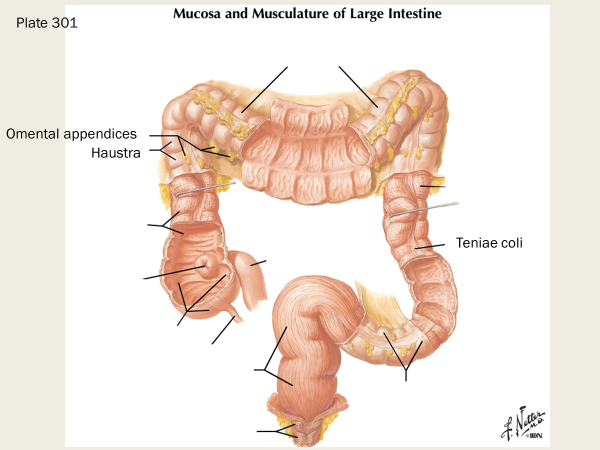
haustrum
the haustra of the colon (singular haustrum) are the small pouches caused by sacculation, which give the colon its segmented appearance
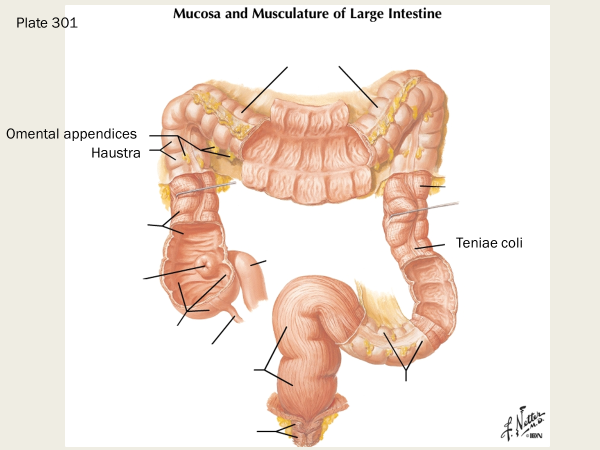
omental appendices
small, fat-filled pouches of the peritoneum that are attached to the large intestine
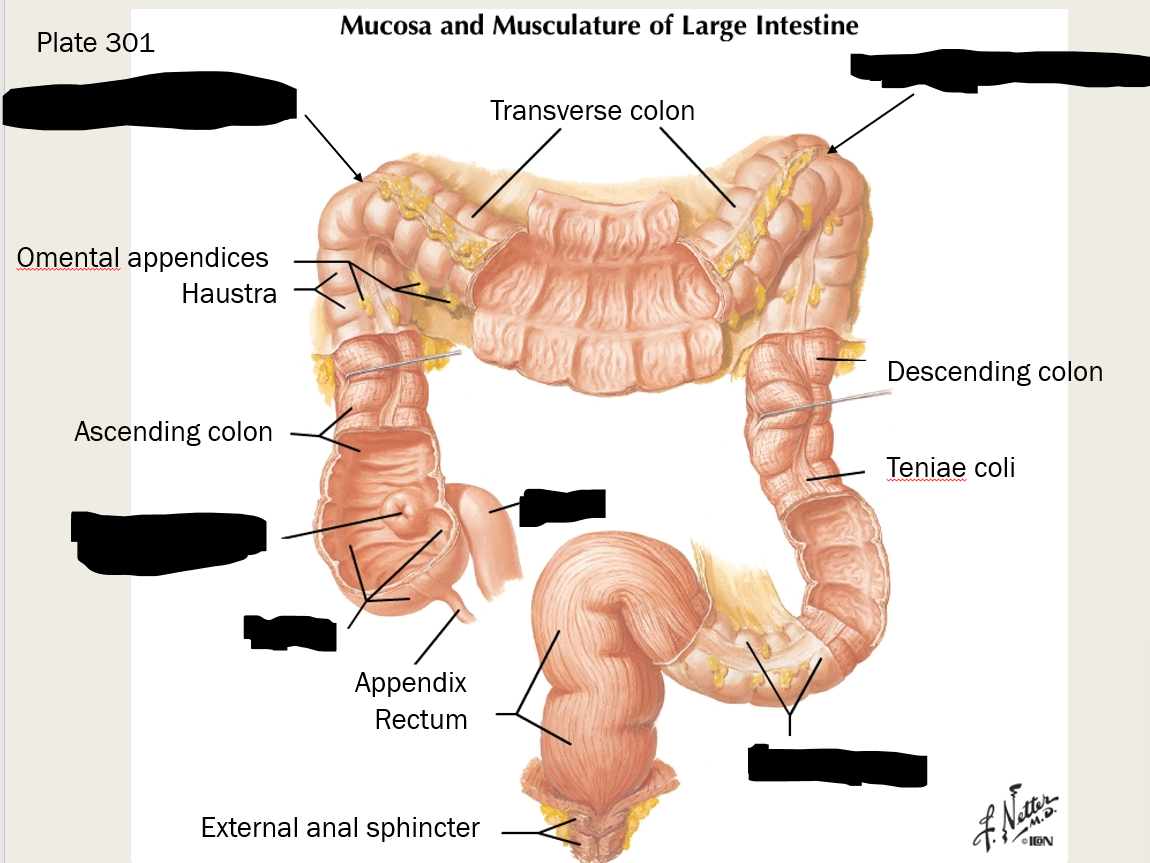
label these structures
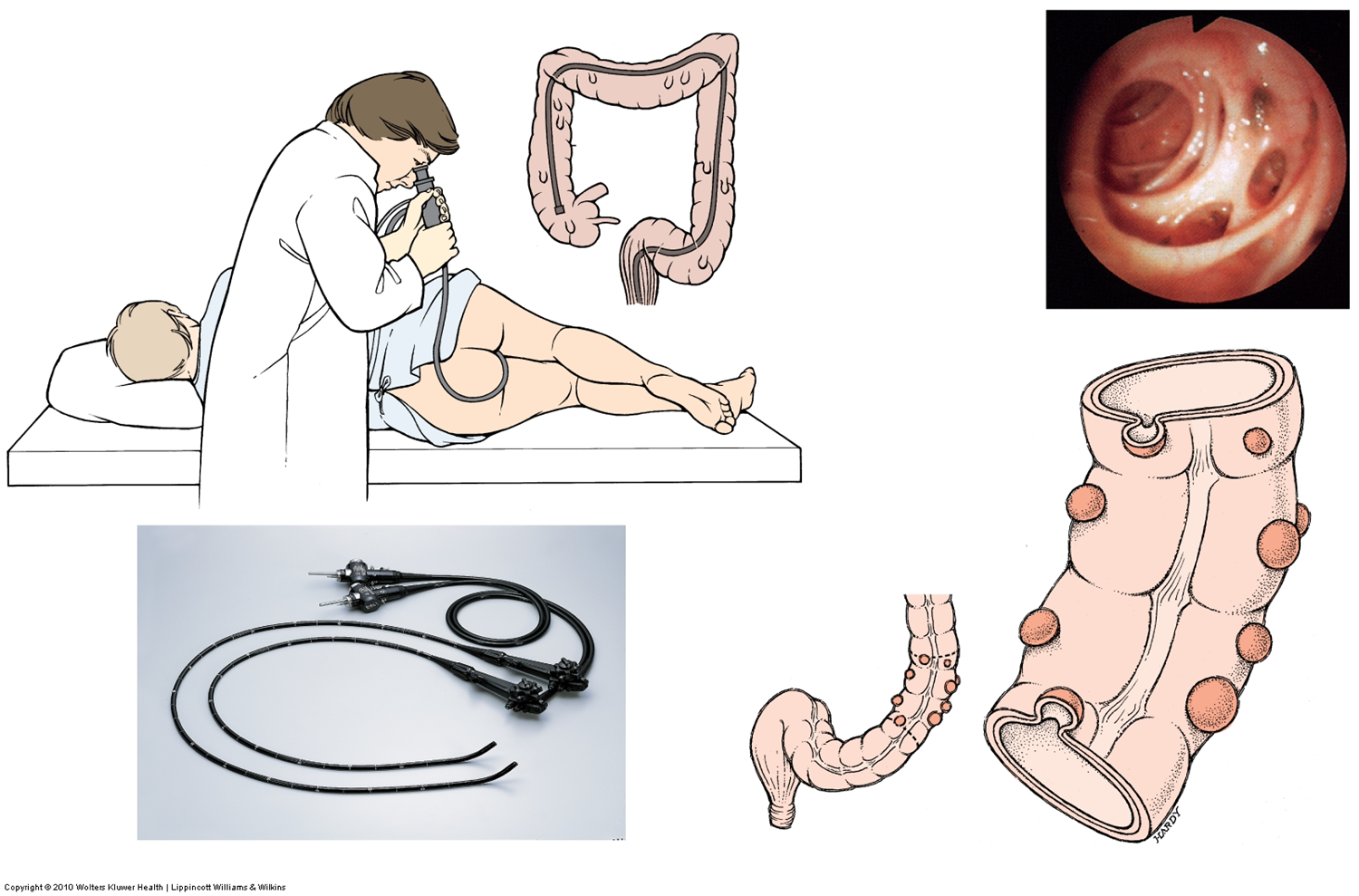
what are diverticula?
envaginations/out-pocketings of mucosa of colon; subject to infection and rupture
diverticulosis
disorder with development of diverticula