Chapter-7_Carbohydrates
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
Sialic acid
A complex monosaccharide that is found on the surface of normal cells and some cancer cells; serves as a marker for cell identity.
Carbohydrates
The most abundant class of bioorganic molecules, constituting about 75% by mass of dry plant materials.
Cellulose
A structural carbohydrate in plants that serves as a building material for plant cell walls.
Starch
A storage carbohydrate in plants that provides energy reserves.
Glycogen
A storage form of glucose in animals, highly branched and used for short-term energy reserves.
Monosaccharide
A simple carbohydrate that contains a single polyhydroxy aldehyde or polyhydroxy ketone unit.
Disaccharide
A carbohydrate that consists of two monosaccharide units linked together.
Oligosaccharide
A carbohydrate that contains 3 to 10 monosaccharide units covalently bonded.
Polysaccharide
A polymeric carbohydrate containing many monosaccharide units linked together.
Chirality
The geometric property of a molecule having non-superimposable mirror images.
Aldose
A monosaccharide that contains an aldehyde functional group.
Ketose
A monosaccharide that contains a ketone functional group.
Reducing sugar
A sugar that can act as a reducing agent because it can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid.
Glycoside
An acetal formed from a cyclic monosaccharide by replacement of the hemiacetal carbon -OH group with an -OR group.
Hyaluronic acid
An acidic polysaccharide that serves as a lubricant in joints and has jelly-like consistency.
Heparin
A small highly sulfated polysaccharide that acts as a blood anticoagulant.
Glycolipid
A lipid molecule that has one or more carbohydrate units covalently bonded, involved in cell recognition.
Glycoprotein
A protein molecule that has one or more carbohydrate units covalently bonded; plays a role in cell recognition.
Trioses
are monosaccharides that contain three carbon atoms.
Tetroses
are monosaccharides that contain four carbon atoms.
Pentoses
are monosaccharides that contain five carbon atoms.
Hexoses
monosaccharides that contain six carbon atoms.
Heptoses
are monosaccharides that contain seven carbon atoms.
Sucrose
is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose linked by an α-1,2-glycosidic bond.
Lactose
is a disaccharide composed of glucose and galactose linked by a β-1,4-glycosidic bond.
Maltose
is a disaccharide composed of two glucose units linked by an α-1,4-glycosidic bond.
Oligosaccharides
are carbohydrates composed of 3 to 10 monosaccharide units.
Homopolysaccharides, Heteropolysaccharides
____________ consist of one type of monosaccharide, while consist _______________of multiple types.
Homopolysaccharides
Examples include starch, glycogen, and cellulose.
Heteropolysaccharides
Examples include hyaluronic acid and heparin.
Cellulose
provides structural support to plant cell walls.
Starch
is composed of amylose and amylopectin, which are polymers of glucose.
Glycogen
serves as a short-term energy reserve in animal cells.
Glycoproteins
facilitate cell recognition and signaling.
Reducing Sugars
can participate in redox reactions due to their ability to be oxidized.
Disaccharide
is composed of two monosaccharides linked by a glycosidic bond.
Polysaccharides
are made up of multiple monosaccharide units linked together.
Starch, Cellulose
__________ is a storage carbohydrate, while _________ provides structural integrity.
Enantiomers
are pairs of molecules that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other, often related to chirality.
Optical Activity
refers to the ability of chiral compounds to rotate the plane of polarized light.
Racemic Mixture
is a 1:1 mixture of two enantiomers of a chiral molecule.
Oxidation, Reduction
Monosaccharides can undergo __________, __________, and glycosylation reactions.
hydrolysis
Disaccharides can undergo ___________ to yield monosaccharides and can participate in glycosidic bond formation.
cellular signaling
Oligosaccharides can participate in hydrolysis and can be involved in __________ and recognition.
monosaccharides
Polysaccharides generally undergo hydrolysis to release __________ and can also be involved in modifications.
Chirality
can significantly influence the interactions and functions of biochemical
N-acetylneuraminic acid
IUPAC name of sialic acid
Carbohydrates
constitute 75% by mass of dry plant materials
2/3 carbohydrates by mass
average human diet for carbohydrate intake
4 kilocalories of energy
how much energy does each burned gram of carbohydrates release
CnH2nOn
general formula for carbohydrates
molecular size
carbohydrates are classified based on…
Monosaccharides
cannot be broken down into smaller substances by hydrolysis reaction
stereoisomers
same molecular formula and same bonding patterns but differ in the arrangement of atoms in space
chiral carbon
a carbon atom that has 4 different groups bonded to it
nonsuperimposable mirror images
are images where not all of the points coincide when the mirror images are laid upon each other
superimposable mirror images
are images which all of its points coincide
Constitutional Isomers
are isomers that have different connectivity
Skeletal Isomers
isomers with different carbon atom arrangements
Positional Isomers
have different locations of functional groups
Functional Isomers
are isomers that have different functional groups
Diastreoisomers
stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other
Dextrorotatory compound, clockwise
is a chiral compound that rotates the plane-polarized light in a ________ direction
Levorotatory compound, counterclockwise
is a chiral compound that rotates the plane-polarized light in a ___________ direction
20
The response of the body to the D isomer of the hormone is__ times greater than its response to the L isomer of the hormone
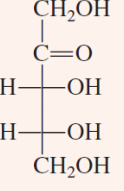
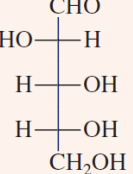
D-Glyceraldehyde and Dihydroxyacetone
two trioses that are important intermediates in the process of glycolysis
Glycolysis
series of reactions that converts 2 glucose molecules to 2 molecules of pyruvate
D-Glucose
found in high amounts in ripe fruits; blood sugar; also known as dextrose
D-Galactose
brain sugar; synthesized from glucose in the body for the production of lactose
D-Fructose
also known as levulose and fruit sugar; sweetest-tasting of all sugars; dietary sugar
D-Ribose
Component of ribonucleic acids (RNAs) and energy-rich compounds such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
two cyclic structures
monosaccharides containing five or more carbon atoms, such open-chain structures are actually in equilibrium with….
Oxidation
reaction that will convert primary alcohol to aldehyde to carboxylic acid
Reduction
reaction that will convert aldehyde to primary alcohol
Aldonic Acid
Tollens and Benedict’s solutions, oxidize the aldehyde end of an aldose to give an
brick-red precipitate
Benedict’s solution gives a ___________ with reduced sugars; indicates a positive result
Strong oxidizing agents, dicarboxylic acids
can oxidize both ends of a monosaccharide at the same time (the carbonyl group and the terminal primary alcohol group) to produce a _________
Aldaric
Such polyhydroxy dicarboxylic acids are known as
primary alcohol; alduronic acid
biochemical systems enzymes can oxidize the ________ end of an aldose such as glucose, without oxidation of the aldehyde group, to produce an________
Hydrogen
The carbonyl group present in a monosaccharide (either an aldose or a ketose) can be reduced to a hydroxyl group, using ______ as the reducing agent.
Alditols
polyhydroxy alcohols
Glycoside
is an acetal formed from a cyclic monosaccharide by replacement of the hemiacetal carbon -OH group with an -OR group
Phosphoric Acids
Phosphate esters, formed from _________ and various monosaccharides, are commonly encountered in biochemical systems
Oxygen Bridge
Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharides joined through an “______________.”
Glycosidic Linkage
is the bond between two monosaccharide
Malt
germinated barley that has been baked and ground
Maltose
produced whenever the polysaccharide starch breaks down
Maltase
the enzyme that breaks the glucose–glucose α(1→4) linkage present in maltose, is found both in the human body and in yeast
Cellubiose
an intermediate in the hydrolysis of the polysaccharide cellulose
Lactose
major sugar found in milk
Scandinavians and Northern Europeans
Lactose intolerance is lowest among _______ and ______
North America, Southeast Asia, Africans, and Greek
Lactose Intolerance is highest among ______, _____, ______, ______
60%
percentage of majority in which are lactose intolerant
Lactic Acid
Bacterial fermentation of the lactose further along the intestinal tract produces
Sucrose
common table sugar; is the most abundant of all disaccharides and occurs throughout the plant kingdom.
Invert Sugar
When sucrose is cooked with acid-containing foods such as fruits or berries, partial hydrolysis takes place, forming some ______
Honeybees, invertase
______ and many other insects possess the enzyme ____-_