Inflation and Deflation (deflation)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Deflation
Sustained decrease in average price level.
Demand-side deflation
Fall in aggregate demand shifts AD curve left.
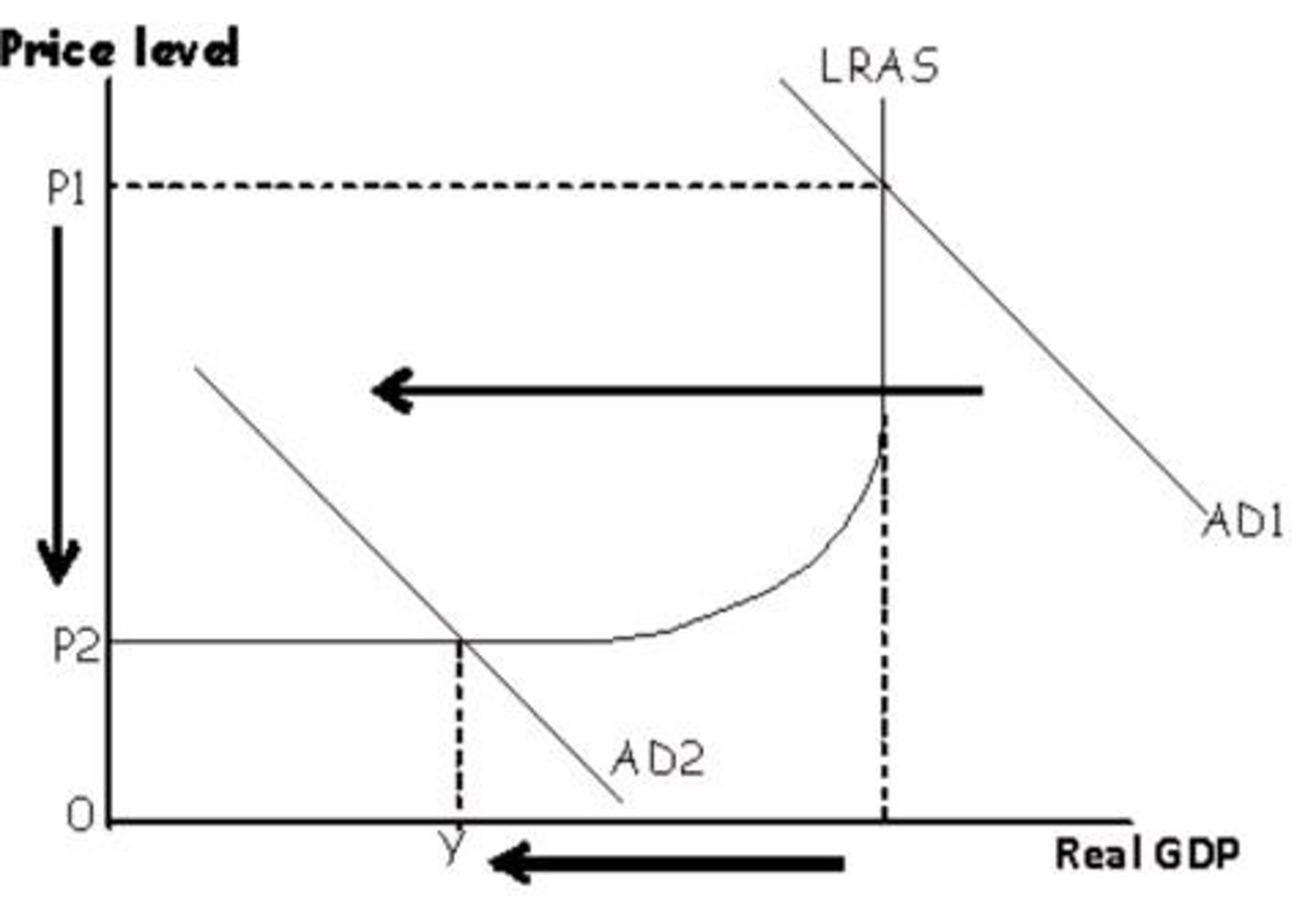
Supply-side deflation
Increase in economic capacity shifts LRAS right.
Bad deflation
Caused by falling aggregate demand, often recessionary.
Good deflation
Caused by increased production capacity, beneficial.
Disinflation
Decrease in inflation rate, not prices.
Sticky wages
Resistance to nominal wage cuts by workers.
Real balance effect
Lower prices increase consumption and AD.
Real value of debt
Debt worth more during deflationary periods.
Real interest rates
Interest rates adjusted for inflation; can be positive.
Real wage unemployment
Unemployment caused by rising real wages.
Deflationary spiral
Cycle where deflation causes further deflation.
Consumer spending
Decreases during deflation due to delayed purchases.
Economic growth
Often slows during periods of deflation.
Nominal wage cuts
Actual reduction in workers' money wages.
Aggregate demand (AD)
Total demand for goods and services in economy.
Long-run aggregate supply (LRAS)
Total output an economy can produce sustainably.
Short-run aggregate supply (SRAS)
Total output firms produce at current prices.
Price level
Average level of prices in an economy.
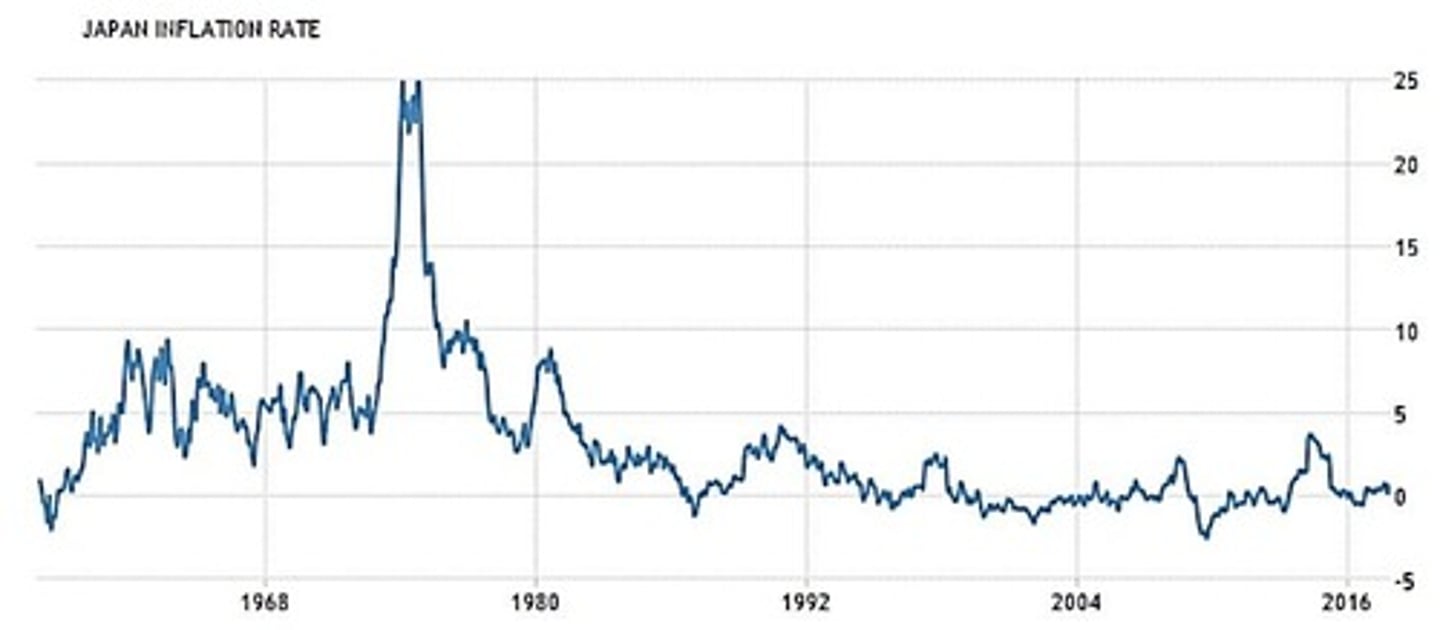
Japan's deflationary experience
Prolonged deflation in Japan during 1995-2014.
OPEC
Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries; influences oil prices.
Luxury goods
Non-essential items often delayed during deflation.
Debt repayments
Higher percentage of income during deflation.
Consumer expectations
Beliefs about future price movements affecting spending.
Deflationary Spiral
A cycle of falling prices and wages.
Real Interest Rate
Nominal interest rate adjusted for inflation.
Aggregate Demand
Total demand for goods and services in economy.
Deflationary Expectations
Belief prices will fall in the near future.
Right Kind of Deflation
Deflation from efficiency and lower production costs.
Long-Run Aggregate Supply (LRAS)
Represents total output at full employment.
International Competitiveness
Ability to sell goods competitively abroad.
Real Value of Savings
Purchasing power of savings increases during deflation.
Deferred Spending
Postponing purchases due to expected price drops.
Expansionary Fiscal Policy
Increased government spending and reduced taxes.
Quantitative Easing (QE)
Central Bank buys bonds to increase money supply.
Liquidity Trap
Monetary policy ineffective at zero interest rates.
Helicopter Drop
Directly distributing money to consumers.
Announcement Effects
Public declarations influencing economic expectations.
Devaluation
Reducing currency value to boost exports.
Positive Multiplier Effect
Increased spending leads to further economic growth.
Consumer Spending
Expenditure by households on goods and services.
Price Level
Average of current prices across the entire spectrum.
Exchange Rate Changes
Fluctuations in currency value affecting trade.
Purchasing Power
Amount of goods/services one unit of currency buys.
Supply Side Deflation
Deflation resulting from increased production efficiency.
Economic Agents
Individuals or entities making economic decisions.
Real Incomes
Income adjusted for inflation, reflecting purchasing power.
Short Periods of Deflation
Temporary deflation without severe economic impact.
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
Responsiveness of demand to price changes.
Consumer Confidence
Optimism regarding future economic conditions.