applied kinesiology chapter 5
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Shoulder joint is attached to _____ skeleton via the _______ at SC joint
axial; clavicle
Scapula movement usually occurs with movement of ________
humerus
Wide range of motion of the shoulder joint in many different planes requires a significant amount of _____
laxity
Common to have instability problems: Rotator cuff ___________, and subluxations & __________
impingement; dislocations
The price of mobility is reduced _______
stability
The more mobile a joint is, the ____ stable it is & the more stable it is, the less _______
less; mobile
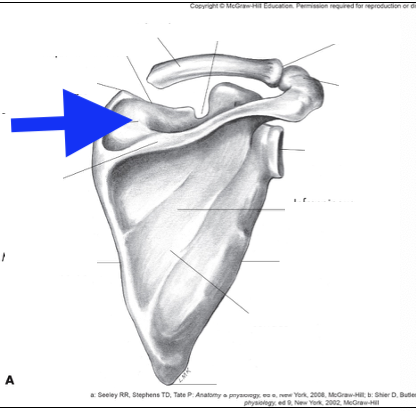
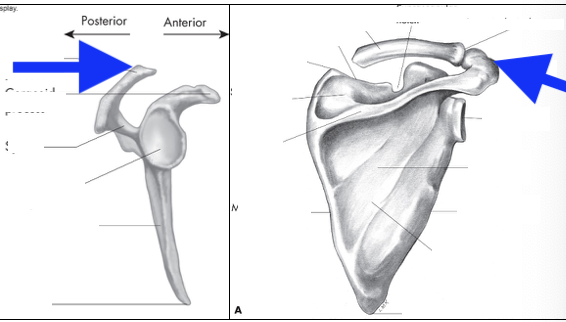
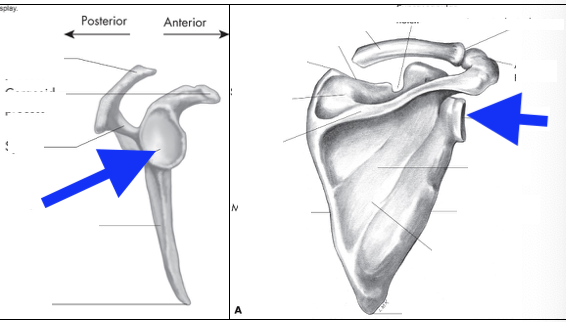
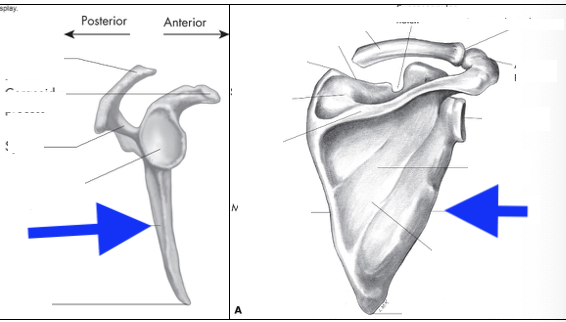
supraspinous fossa
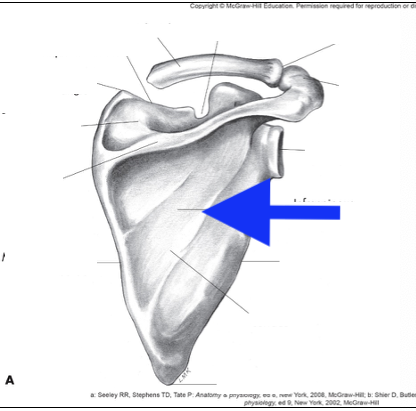
infraspinous fossa
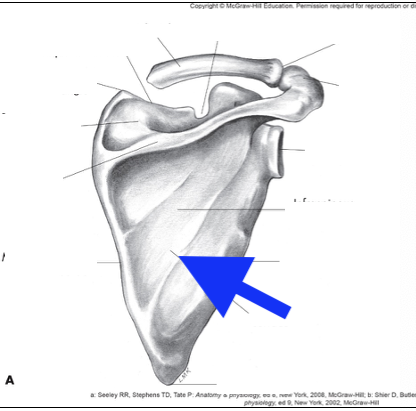
subscapular fossa
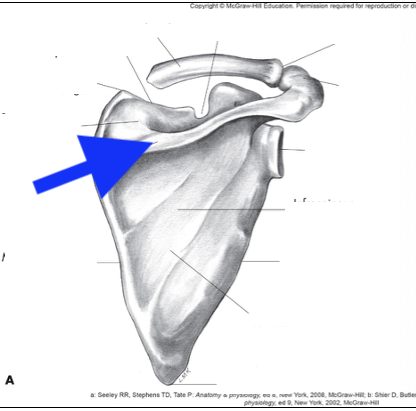
spine of scapula
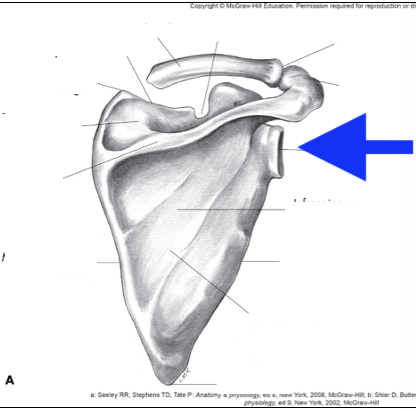
glenoid fossa
coracoid process
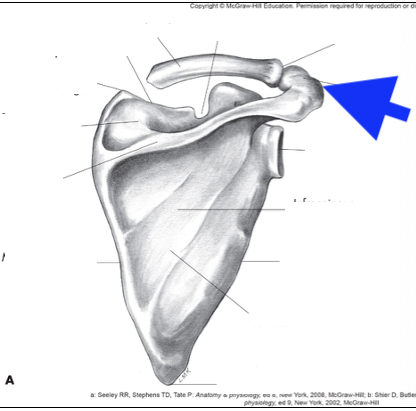
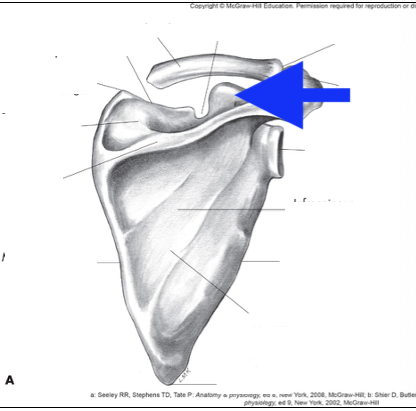
acromian process
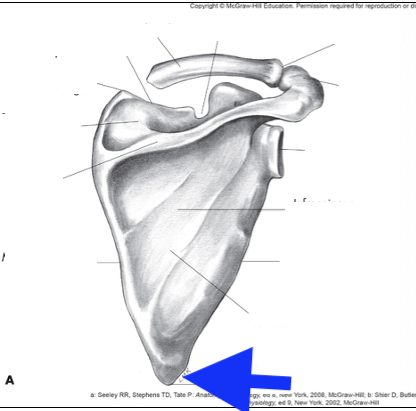
inferior angle
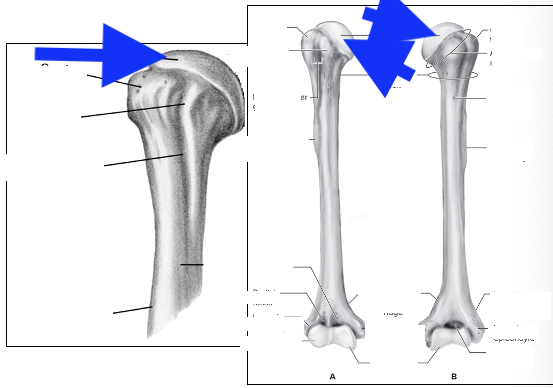
head
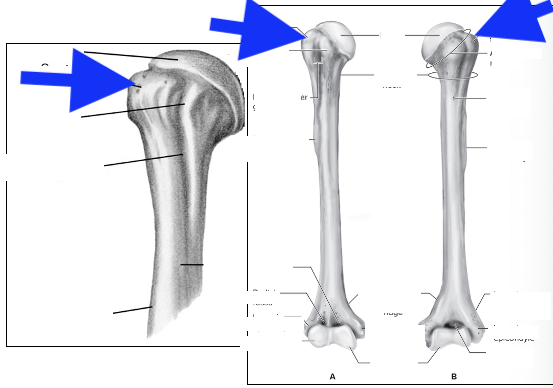
greater tubercle
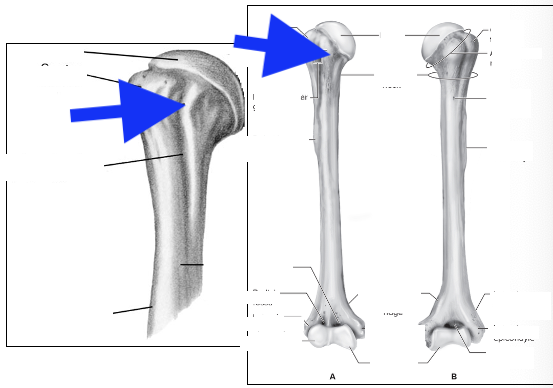
lesser tubericle
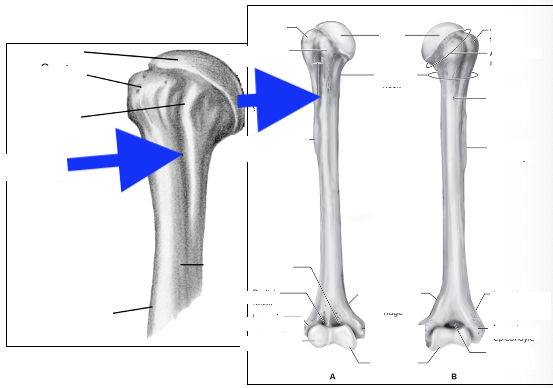
intertubercle groove
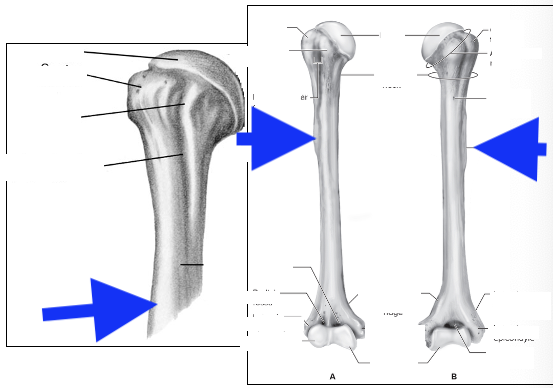
deltoid tuberosity
acromian process
glenoid fossa
lateral border
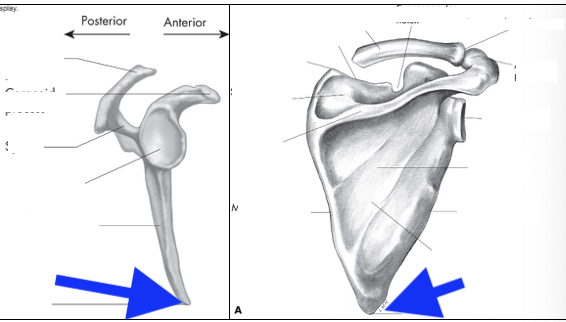
inferior angle
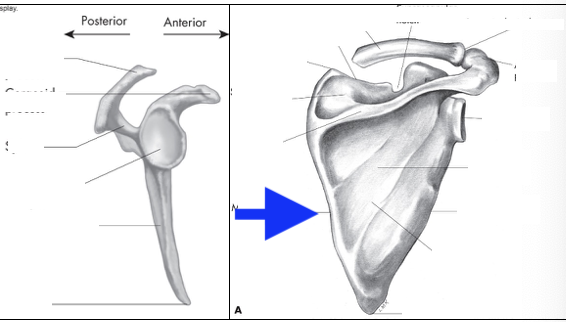
medial border
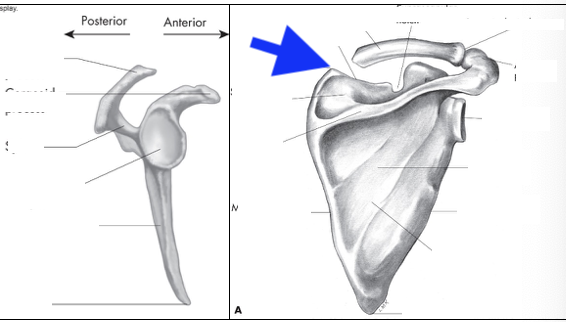
superior angle
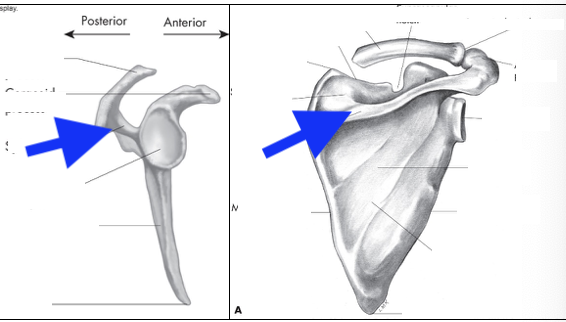
spine of scapula
glenoid labrum slightly enhances stability by deepening the _______ _____
glenoid fossa
glenoid labrum supports the _____ of the humerus
head
glenoid labrum can be compared to a _________
washer
glenoid labrum injured with sudden _________ movements and with ______
overhead; trauma
Glenohumeral ligaments provide _______, especially __________ and __________
stability; anteriorly; inferiorly
Ligaments in the glenohumeral joint are quite ___ until extreme ranges of _______ reached due to wide range of motion involved
lax; motion
in the glenohumeral joint, ________ is sacrificed to gain ________
stability; mobility
in the glenohumeral joint, determining exact range of each movement is ________ due to accompanying shoulder girdle ________
difficult; movement
glenohumeral joint is frequently injured due to __________ design
anatomical
the glenohumeral joint lacks _________ & _________ in muscles
strength; endurance
___________ are common in the glenohumeral joint
dislocations
the rotator cuff is frequently ________
injured
difference in internal rotation range of motion between an individual’s throwing & nonthrowing shoulders
GIRD
overhead athletes with a GIRD of greater than 20% had a ______ risk of injury
higher
Superior Labral tear from Anterior to Posterior
SLAP tear
the Deltoid, Coracobrachialis, and Teres major are examples of what?
intrinsic glenohumeral muscles
intrinsic glenohumeral muscles originate on ______ & _______
scapula; clavicle
the rotator cuff group are examples of what?
intrinsic glenohumeral muscles
latissimus dorsi and pectoralis major are examples of what?
extrinsic glenohumeral muscles
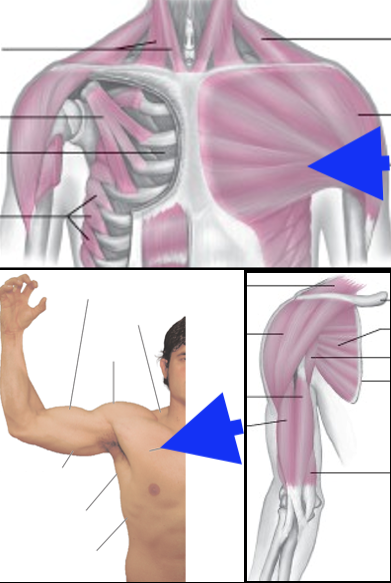
pectoralis major
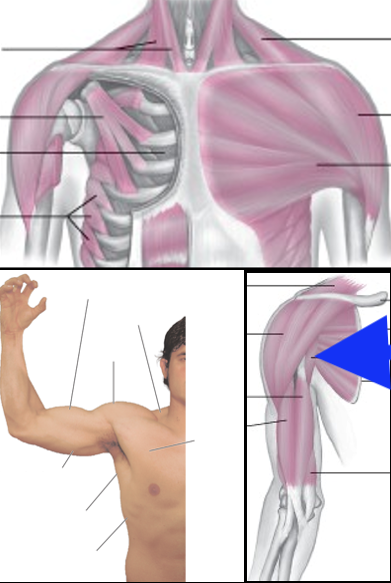
coracobrachialis
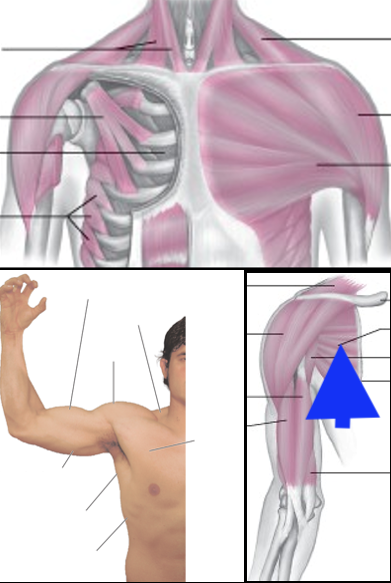
subscapularis
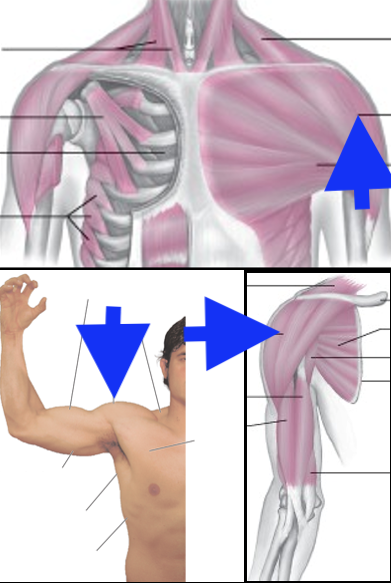
deltoid
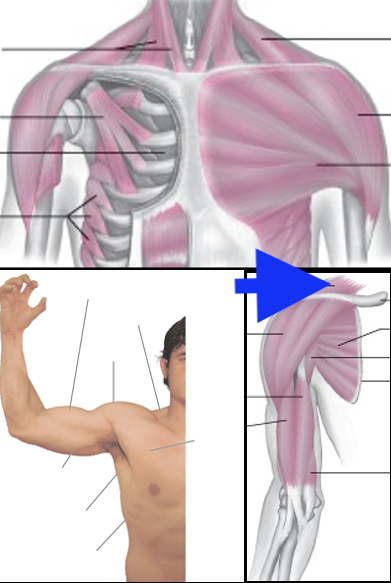
supraspinatus
deltoid
supraspinatus
latissimus dorsi
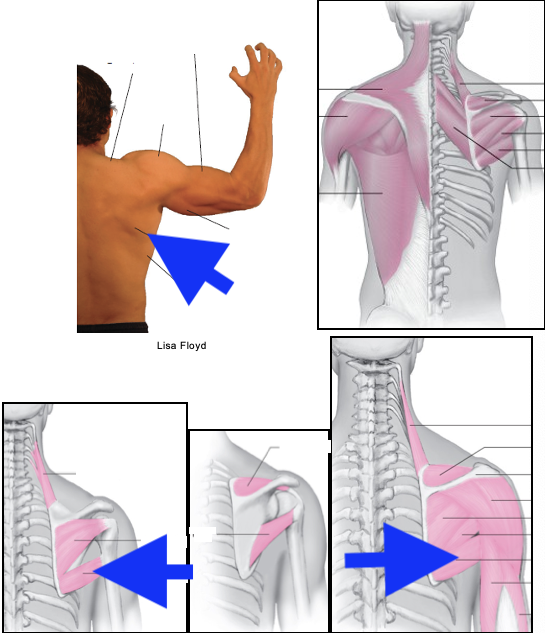
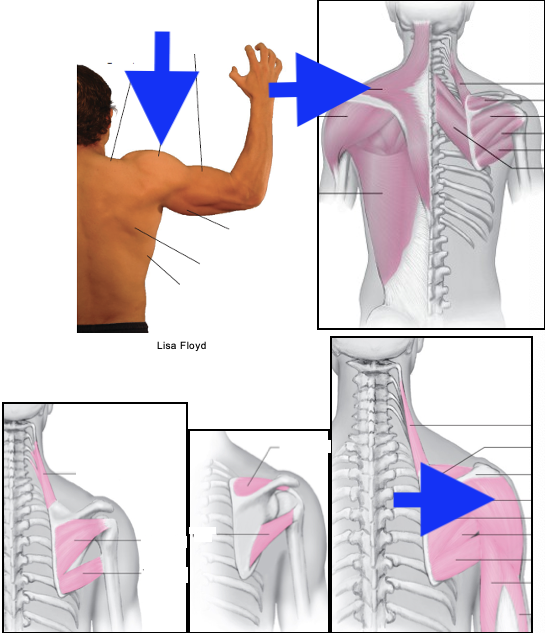
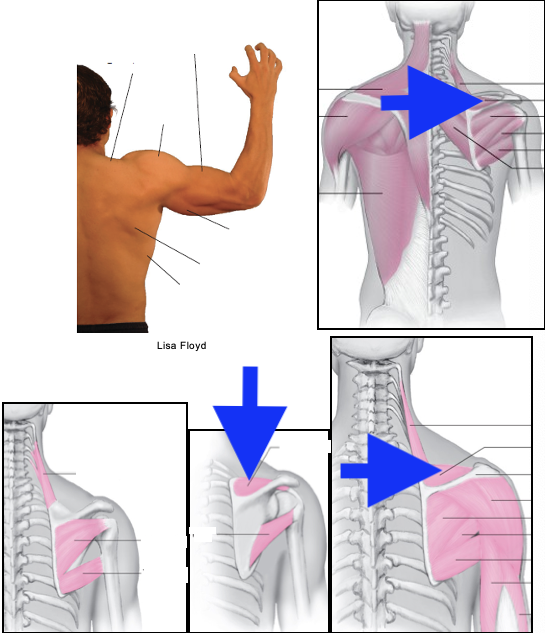
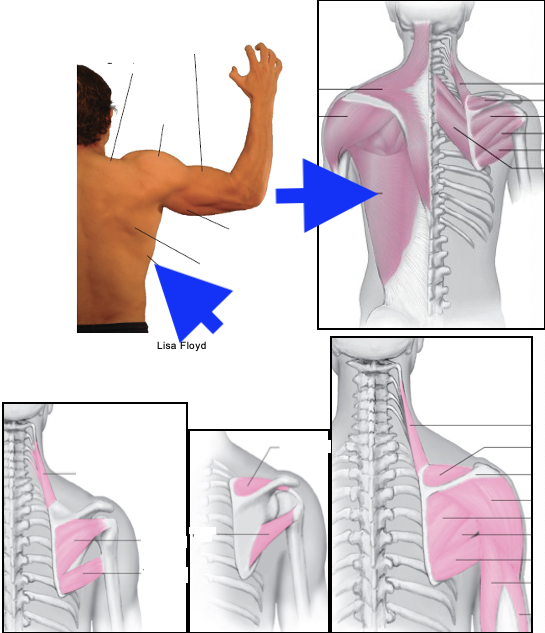
teres major
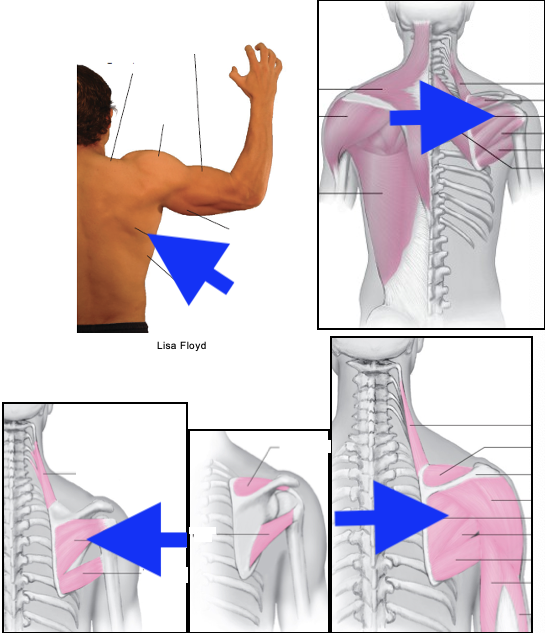
infraspinatus
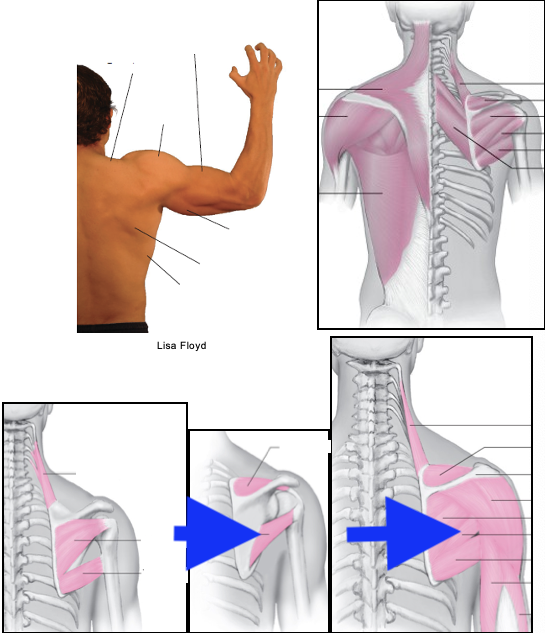
teres minor
All shoulder joint muscles are innervated from the _________ plexus
brachial
rotator cuff muscles
supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor and subscapularis
acronym for rotator cuff muscles
SITS
muscle that attaches to greater tubercle from above (Abduct)
supraspinatus
muscle that attaches to greater tubercle posteriorly (Ext. Rot.)
infraspinatus
muscle that attaches to greater tubercle posteriorly (Ext. Rot.)
teres minor
muscle that attaches to lesser tubercle anterior (Int. Rot.)
subscapularis
muscle that crosses shoulder, elbow, and radioulnar joint
biceps brachii
biceps brachii is weaker in shoulder ________
flexion
muscle that crosses shoulder and elbow joints; agonist for shoulder extension
triceps brachii