SCIN Biology Unit (SHORT DEFINITIONS ONLY)
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biology unit terms and definitions for investigative science, this set contains only shorter answer questions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Xylem
dead, hollow, long thin tubes which allow water to move up the stem from the roots to the leaves. They have specially thickened cell walls which hold the plant up.
Capillary action
adhesion and cohesion of water molecules.
Phloem
living, long tube like cells which carry glucose down the stem from the leaves to the roots. Small holes in the ends of the cells allow the continuous flow of glucose between cells.
Cambium cells
where cell division, mitosis, occurs in the stem of plants, making more xylem and phloem cells
Vascular bundles
consists of xylem, phloem, and cambium
Osmosis
the movement of water from high concentration to low concentration through a semipermeable membrane
Turgid
when plant cells are stiff and full of water, holding up the plant upright.
Flaccid
when plant cells are dehydrated and the plant wilts
Hypertonic solution
a solution with a high concentration of solute dissolved in water
Hypotonic solution
a solution with a low concentration of solute dissolved in water
Isotonic solution
a solution with the same solute concentration inside and outside the cell
Transpiration
the evaporation of water from the surface of leaves
Transpiration pull
the pull of water up the xylem of the plant when water evaporates from the leaves
Waxy cuticle
a waxy layer preventing evaporative water loss
Epidermis
protects palisade mesophyll, helps to prevent water loss, single transparent layer permits light to pass into the leaf
Palisade mesophyll
tightly packed layer of cells with large amounts of chlorophyll for absorbing sunlight, main site of photosynthesis.
Spongy mesophyll
irregular in shape and loosely packed, fewer chlorophyll and large air spaces for exchange of CO2 and O2 gases between leaf palisade layer and environment.
Stomata
Small holes in lower surface controlling gas exchange and rate of transpiration
Guard cells
Swells or shrinks with water by osmosis to control the opening or closing of Stomata
Turgor pressure
water pressure
Conditions for photosynthesis
sunlight and chlorophyll
Site for photosynthesis
chloroplast
Purpose of photosynthesis
to make food from sunlight
Airspaces
speeds up the rate of diffusion
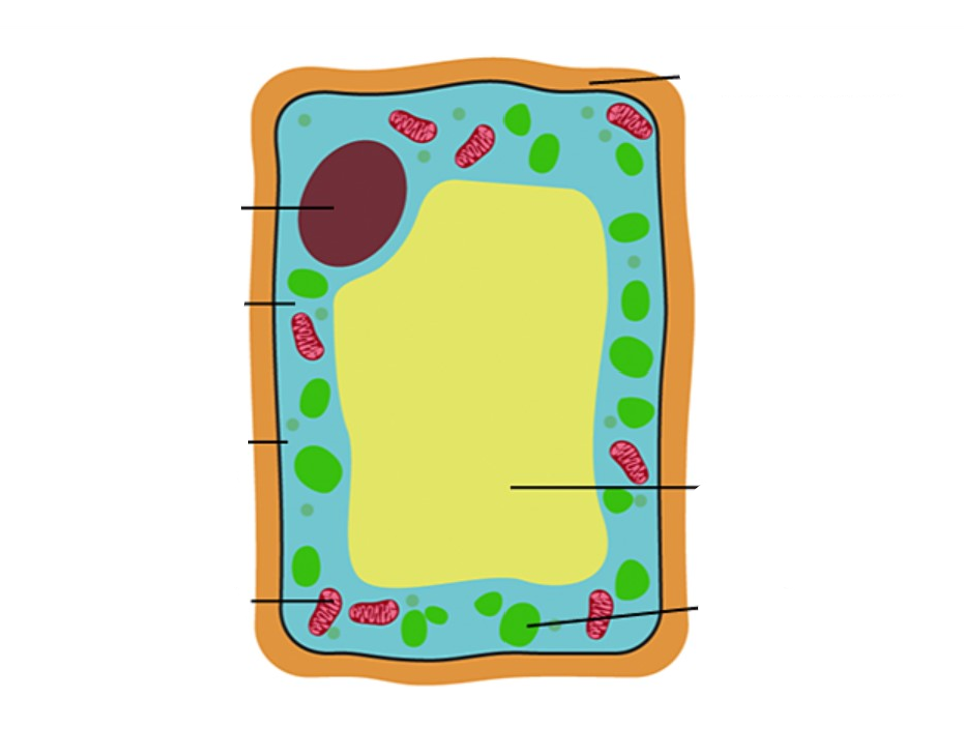
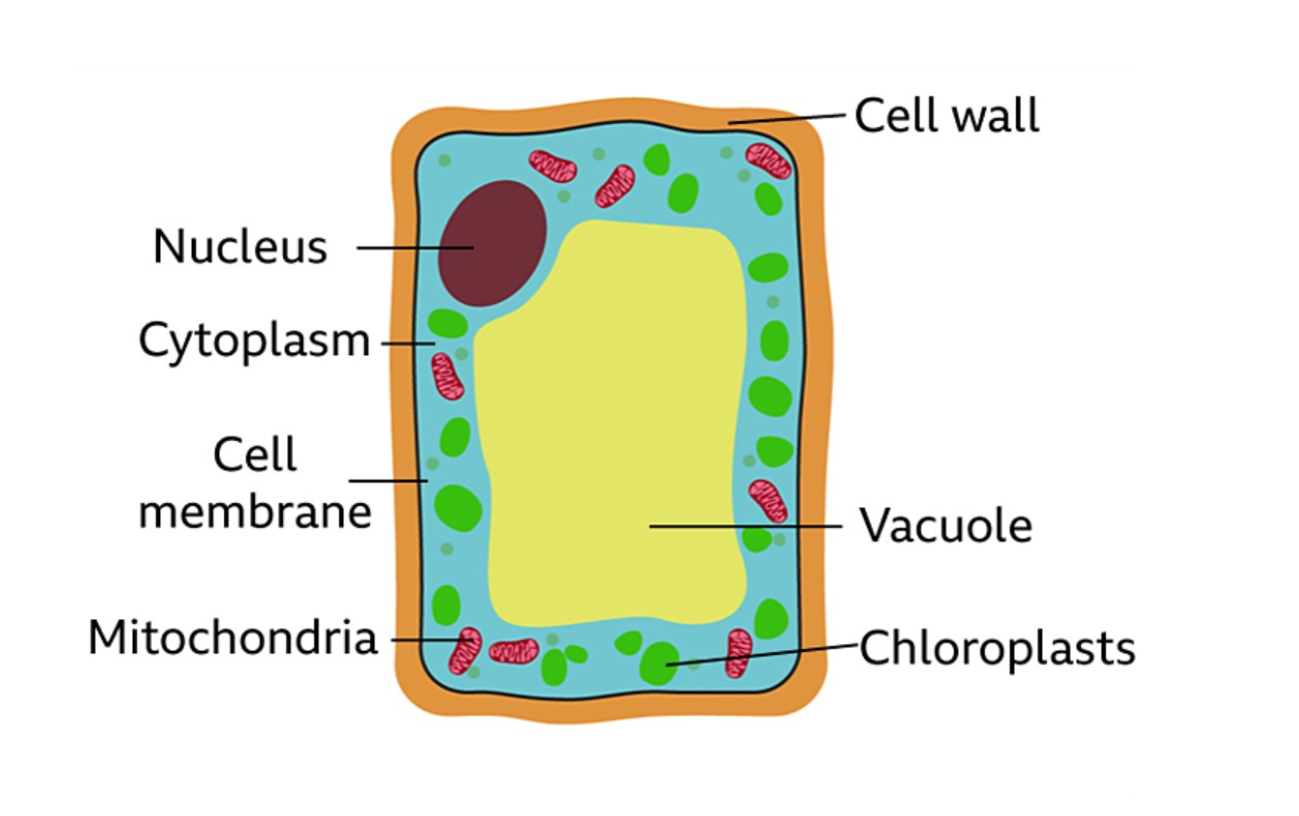
Labelling parts of the cell (from top to down, left side then right side)
Nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria, cell wall, vacuole, chloroplasts
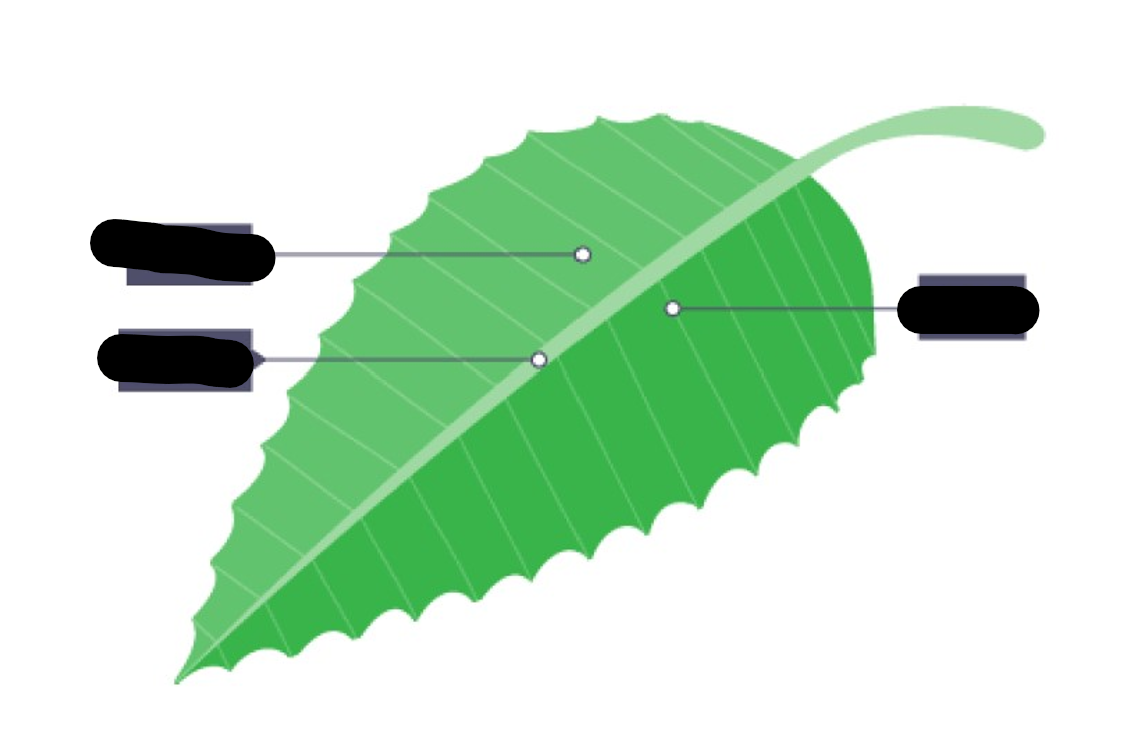
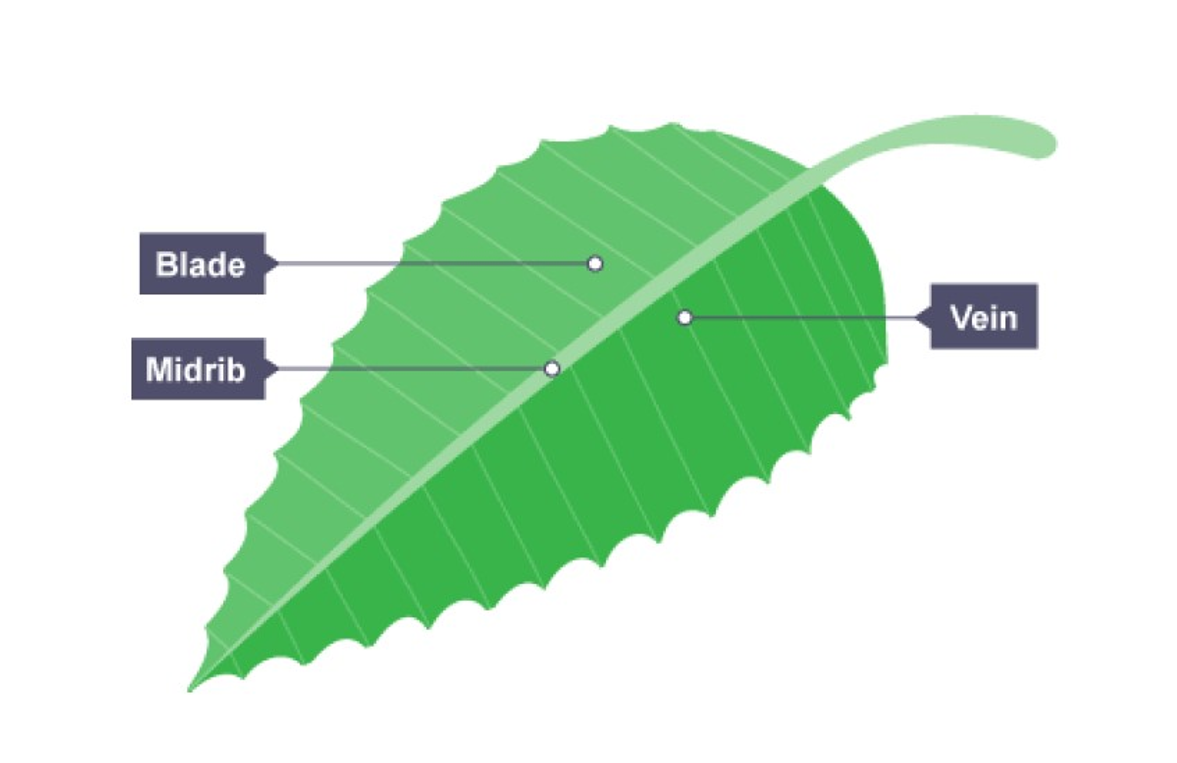
Labelling parts of the leaf (from top to down, left side then right side)
Blade, midrib, vein
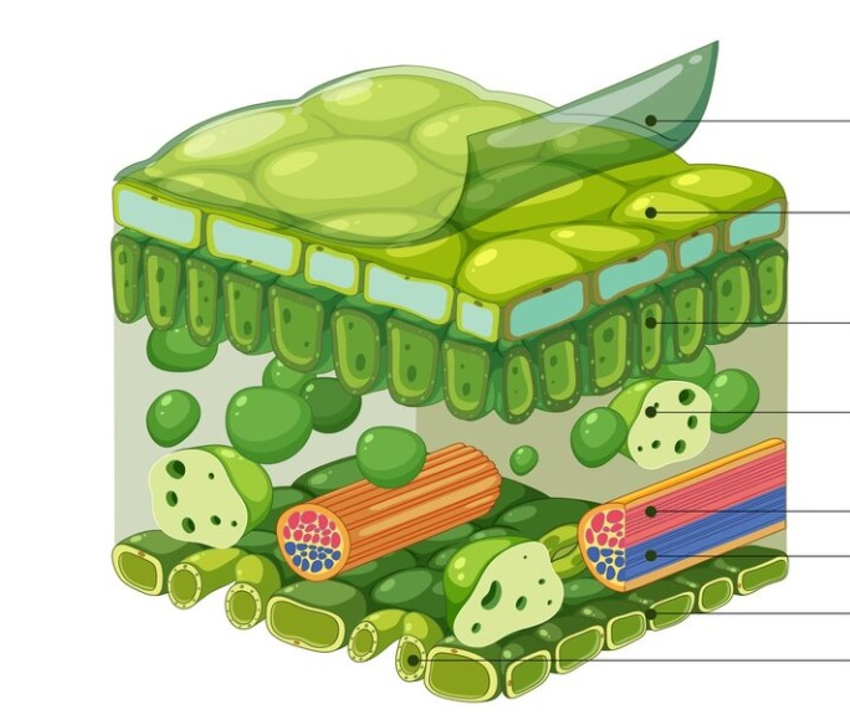
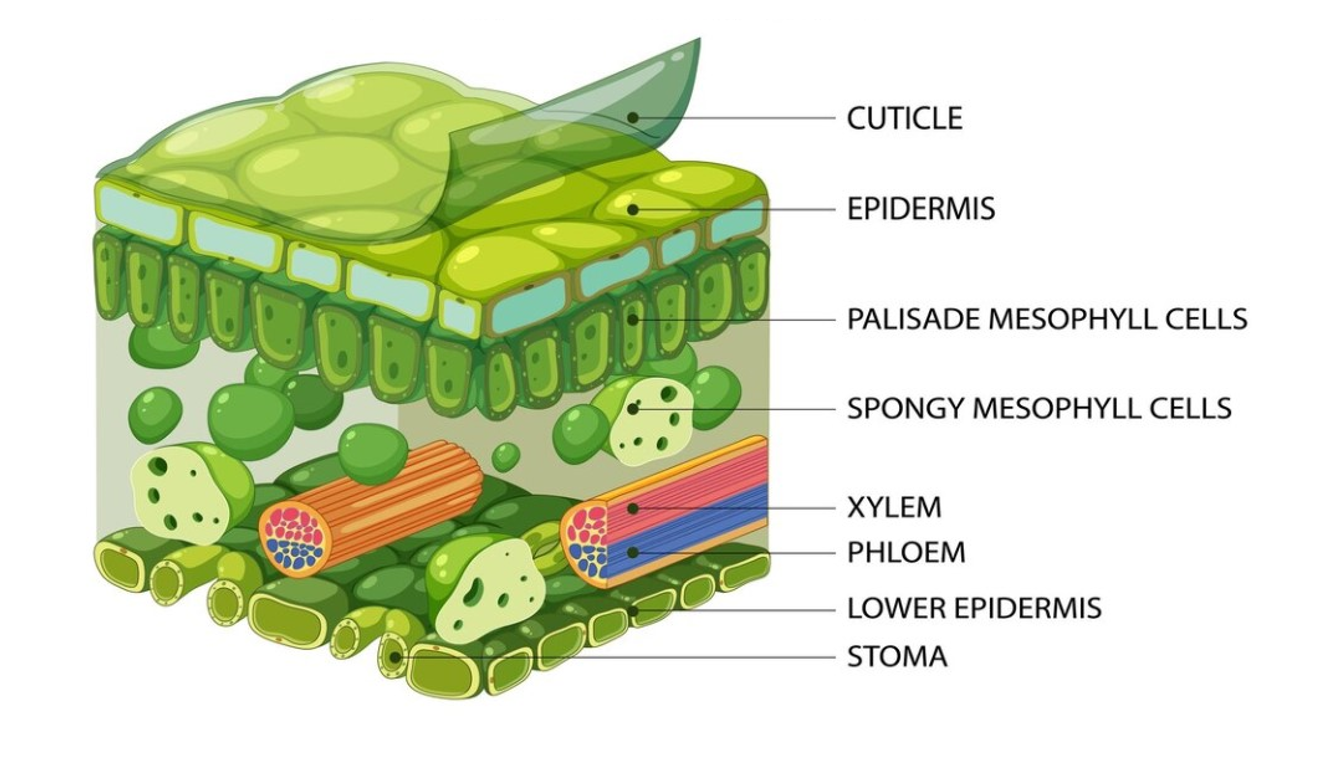
Labelling cross section of the leaf (top to bottom)
Waxy cuticle, upper epidermis, palisade mesophyll cells, spongy mesophyll cells, xylem, phloem, lower epidermis, stoma
Factors that increase the rate of transpiration
high wind, high light intensity, high temperature, low humidity
Meristematic tissue
The tissue in plants where cell division takes place
Primary growth
the elongation of the plant, the plant growing taller
Name the 2 processes that occur in primary growth
- cell division/mitosis in the zone of cell division (meristem) 2. cell elongation in the zone of cell elongation
Secondary growth
the increase in diameter/thickness of roots/stems/branches
Where does secondary growth occur?
cambium
Cambium
made up of meristematic cells that are undifferentiated, found between the xylem and phloem in vascular bundles
Meristematic cells
cells that undergo mitosis
First stage of secondary growth in the stem
Cambium in vascular bundles grows completely around the stem to form a ring and the cambium thickens
Primary xylem and phloem
another term for old phloem and xylem
Why do trees form rings?
In summer the xylem cells grow larger than in winter, forming rings of larger, lighter wood, and smaller, darker wood
Why is secondary growth important to the development of the plant?
1.thickening of the stem can support a larger and taller canopy, capturing more light for the plant 2. more xylem and phloem is created, therefore more sugar and water can be transported to the increased amount of plant tissue.
Functions of the root
Anchor the plant into the soil, absorb water and minerals, store food in the form of starch
Parts of the root
Root cap, meristematic tissue (zone of cell division), zone of elongation, zone of differentiation, root hairs
Root cap
produces a layer of slime that coats the surface of the root and lubricates it as it pushes through the soil
Zone of elongation
the cells get longer
Zone of cell differentiation
the cells start to become specialised for a specific function
Root hairs
increase the surface area available to absorb more water and minerals from soil
Tropism
a growth response of a plant towards or away from a stimulus coming from one direction
Types of tropisms
photo, geo, hydro, chemo, thermo, thigmo
Phototropism
light
Geotropism
gravity
Hydrotropism
water
Chemotropism
chemical
Thermotropism
heat
Thigmotropism
touch
Where is auxin produced?
in the shoot tip (apical meristem) of the shoots, ie the zone of cell division and the meristematic tissue. Auxin travels down into the zone of elongation
What does auxin promote?
promotes the elongation of cells in the zone of elongation, therefore increasing upwards growth
Where does auxin migrate to?
in shoots, auxin migrates to the dark side of the zone of cell division then flows down into the dark side of the zone of elongation
Where does auxin accumulate?
auxin accumulates in the lower side of the stem or root due to gravity
High auxin concentration in stems
causes cell elongation to occur
High auxin concentration in roots
inhibits cell elongation
Auxin in the root cap was originally produced…
in the youngest leaves and transported to the root via the phloem