test 1 (blood, heart, blood vessels)
1/204
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
205 Terms
functions of the circulatory system
-transport: O₂, CO₂, nutrients, wastes, hormones, and stem cells
-protection: inflammation, limit spread of infection, destroy microorganisms and cancer cells, neutralize toxins, and initiate clotting
-regulation: fluid balance, stabilizes pH of ECF, and temp control
plasma
-matrix of blood (45-50% of BV)
-clear, light yellow fluid
formed elements
-blood cells and cell fragments
-red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
granulocytes
-neurtophils, eosinophils, basophils
-leave in 8 hours and live 5 days longer
agranulocytes
lymphocytes & monocytes
albumins
-smallest and most abundant
-contribute to viscosity and osmolarity
-influence blood pressure, flow, and fluid balance (regulates fluid volume)
globulins
-antibodies
-provide immune system functions
-alpha, beta, and gamma
fibrinogen
precursor of fibrin threads that help form blood clots
nitrogenous compounds
-free amino acids from dietary protein or tissue breakdown
-urea
-toxic end products of catabolism
-normally removed by the kidneys
viscosity
resistance of a fluid to flow, resulting from the cohesion of its particles
osmolarity of blood
-the total molarity of those dissolved particles that can’t pass through the blood vessel wall
-if too high, blood absorbs too much water, increasing BP
-if too low, too much water stays in tissue, BP drops, and edema occurs
-optimum level is achieved by the body’s regulation of sodium ions, proteins, and RBCs
hemopoiesis
production of blood, especially its formed elements
hemopoietic tissues
-yolk sac produces stem cells for first blood cells
-liver stops producing blood cells at birth
-spleen remains involved with lymphocyte production, more for storage
-mostly made in bone marrow
colony-forming unit
specialized stem cells only producing one class of formed element of blood
myeloid hemopoiesis
blood formation in the bone marrow
lymphoid hemopoiesis
blood formation in the lymphatic organs (beyond infancy this only involves lymphocytes)
erythrocyte functions
-carry oxygen from lungs to cell tissues
-pick up CO₂ from tissues and bring to lungs
erythrocyte features
-lack mitochondria; anaerobic fermentation to produce ATP
-lack of nucleus and DNA; no protein synthesis or mitosis
carbonic anhydrase (CAH) in cytoplasm
-produces carbonic acid from CO₂ & water
-important role is gas transport and pH balance
hemoglobin features
-adult has 2 alpha and 2 beta chains
-fetal contains 2 alpha and 2 gamma chains
-4 heme groups
heme groups
nonprotein moiety that binds O₂ to ferrous iron (Fe) at its center
hematocrit
-packed cell volume
-percentage of whole blood volume composed of RBCs
erythrocyte production
-average lifespans=about 120 days
-development takes 3-5 days
-first committed cell= erythrocyte colony-forming unit that has receptors for erythropoietin (EPO) from kidneys
-erythroblasts multiply and synthesize hemoglobin
liver apoferritin
-binds to create ferritin for storage of Fe
-reduction of free iron reduces bacterial growth in blood plasma
negative feedback control (erythrocytes)
-drop in RBC count causes hypoxemia detected by kidney
-kidney production of erythropoietin stimulates bone marrow
-RBC count increases in 3-4 days
stimuli for increasing erythropoiesis
-low levels O₂ (hypoxemia)
-high altitude
-increase in exercise
-loss of lung tissue in emphysema
erythrocyte death & disposal
-RBCs rupture (hemolysis) in narrow channels of spleen and liver
-macrophages in spleen; digest membrane bits; separate heme from globin
-globins hydrolyzed into amino acids
-iron removed from heme
-heme pigment converted to biliverdin (green); biliverdin converted to bilirubin (yellow); released into blood plasma (kidneys- yellow urine); liver removes bilirubin and secretes into bile; concentrated in gallbladder, released into small intestine, bacteria create urobilinogen (brown)
polycythemia
excess of RBCs
primary polycythemia (polycythemia vera)
-cancer of erythropoietic cell line in red bone marrow
-RBC count as high as 11 million RBCs/µL; hematocrit 80%
secondary polycythemia
-from dehydration, emphysema, high altitude, or physical conditioning
-RBC count up to 8 million RBCs/µL
dangers of polycythemia
-increased blood volume, pressure, viscosity
-can lead to embolism, stroke, or heart failure
causes of anemia
-inadequate erythropoiesis or hemoglobin synthesis
-kidney failure and insufficient erythropoietin
-iron deficiency
pernicious anemia
autoimmune attack of stomach tissue leads to inadequate vitamin B₁₂ absorption
hypoplastic anemia
slowing of erythropoiesis
aplastic anemia
complete cessation of erythropoiesis
hemorrhagic anemia
from bleeding
hemolytic anemia
from RBC destruction
anemia consequences
-tissue hypoxia and necrosis (patient is lethargic; shortness of breath upon exertion; life-threatening necrosis of brain , heart, or kidney)
-blood osmolarity is reduced, producing tissue edema
-blood viscosity is low (heart races and pressure drops; cardiac failure may ensue)
antigens
-complex molecules on surface of cell membrane that activate an immune response
-genetically unique to the individual
-used to distinguish self from foreign matter
-foreign antigens generate an immune response
-A, B, Rh (D)
agglutinogens
antigens on the surface of the RBC that are the basis for blood typing
antibodies
-proteins (gamma globulins) secreted by plasma cells
-part of immune response to foreign matter
-bind to antigen and mark them for destruction
-forms antigen-antibody complexes
agglutinins
-antibodies in the plasma that bring about transfusion mismatch
-anti-A, anti-B, & anti-Rh
clumping (agglutination)
-antibody molecule binding to antigens
-causes clumping of RBCs
universal donor
-type O-
-lack RBC antigens
-donor’s plasma may have both antibodies against recipient’s RBCs (anti-A, anti-B, anti-Rh)
universal recipient
-type AB+
-lacks plasma antibodies; no anti-A, anti-B, or anti-Rh
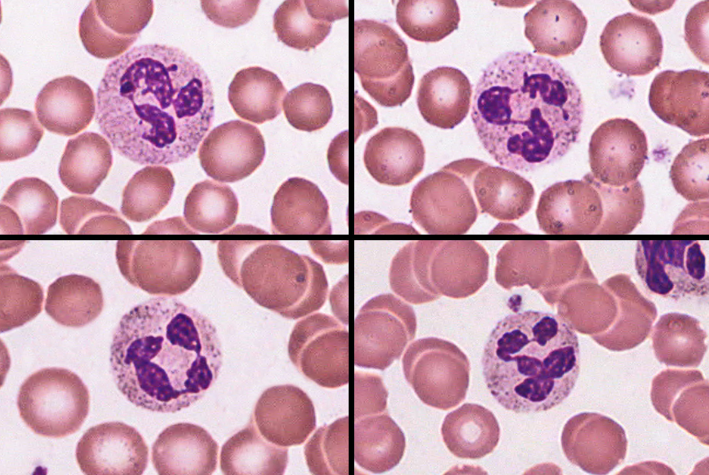
neutrophil
-60-70%
-barely visible granules in cytoplasm; 3-5 lobed nucleus
-aggressively antibacterial
eosinophil
-2-4%
-large rosy-orange granules; bilobed nucleus
-increased numbers in parasitic infections, collagen diseases, allergies, diseases of spleen and CNS
-release enzymes to destroy large parasites
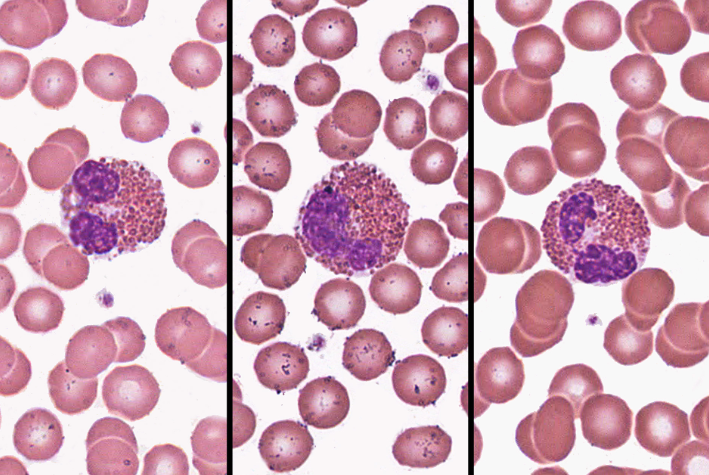
basophil
-less than 1%
-large abundant, violet granules (obscure S-shaped nucleus)
-increased numbers in chickenpox, sinusitis, diabetes
-secrete histamine & heparin
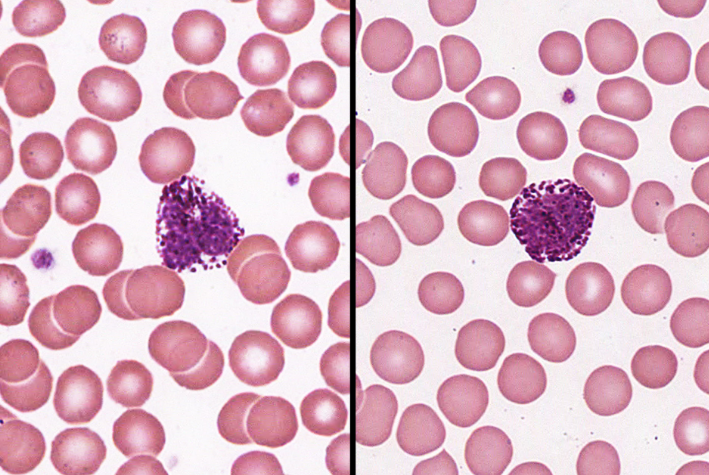
lymphocyte
-25-33%
-variable amounts of bluish cytoplasm (scanty to abundant); ovoid/round, uniform dark violet nucleus
-increased number in diverse infections and immune responses
-destroy human cells (cancer, foreign, and virally infected cells)
-secrete antibodies and provide immune memory
-provide long-term immunity (decades), being continuously recycled from blood to tissue fluid to lymph and back to the blood
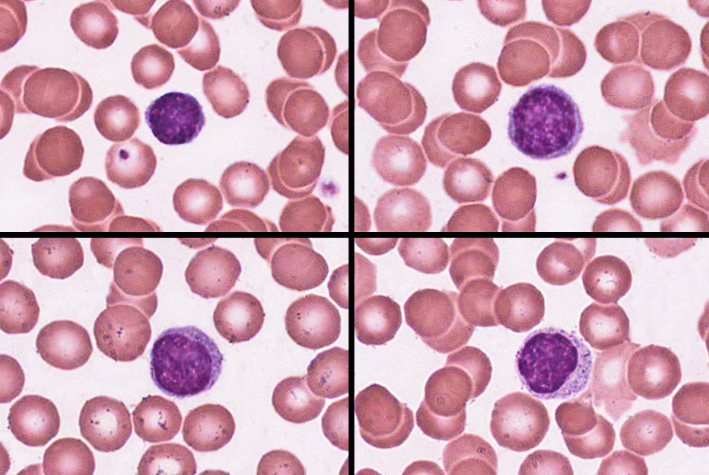
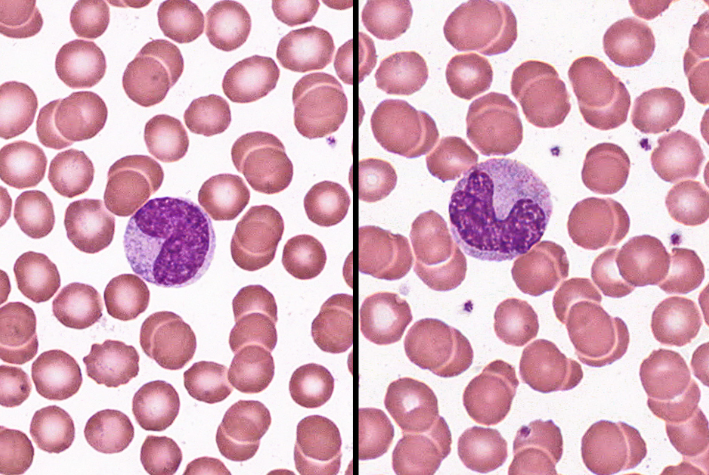
monocyte
-3-8%
-usually largest WBC; ovoid, kidney, or horseshoe-shaped nucleus
-increased numbers in viral infections and inflammation
-leave in 20 hours, transform into macrophages, and live for several years
histamine
-vasodilator
-speeds flow of blood to an injured area
heparin
-anticoagulant
-promotes the mobility of other WBCs in the area
-from basophils and mast cells
-interferes with formation of prothrombin activator
leukopoiesis
production of white blood cells
hemopoietic stem cells (HSCs) differentiate into
-myeloblasts: form neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
-monoblasts: form monocytes
-lymphoblasts: form lymphocytes
hemostasis
-the cessation of bleeding
-stopping potentially fatal leaks
hemostatic mechanisms
-vascular spasm
-platelet plug formation
-blood clotting (coagulation)
platelets (thrombocytes)
-small fragments of megakaryocyte cells
-contain a complex internal structure and an open canalicular system
platelet functions
-secrete vasoconstrictors that help reduce blood loss
-stick together to form platelet plugs to seal small breaks
-secrete procoagulants or clotting factors to promote clotting
-initiate formation of clot-dissolving enzyme
-chemically attract neutrophils and monocytes to site of inflammation
-phagocytize and destroy bacteria
-secrete growth factors that stimulate mitosis to repair blood vessels
thrombopoiesis
stem cells (that develop receptors for thrombopoietin) become megakaryoblasts
megakaryoblasts
-repeatedly replicate DNA without diving
-form gigantic cells called megakaryocytes with a multilobed nucleus
megakaryocytes
-live in bone marrow adjacent to blood sinusoids
-long tendrils of cytoplasm (proplatelets) protrude into the blood sinusoids, blood flow splits off fragments called platelets
vascular spasm
-prompt constriction of a broken vessel
-most immediate protection against blood loss
vascular spasm causes
-pain receptors, some directly innervate blood vessels to constrict
-smooth muscle injury
-platelets release serotonin (vasoconstrictor)
vascular spasm effects
-prompt constriction of a broken vessel
-pain receptors (short duration)
-smooth muscle injury (longer duration)
-provides time for other 2 clotting pathways
platelet plug formation
-intact vessels have a smooth endothelium coated with prostacyclin (a platelet repellent)
-broken vessels exposes collagen
-platelet pseudopods stick to damaged vessel and other platelets
-pseudopods contract—draw together a platelet plug
-platelets degranulate releasing a variety of substance (serotonin, ADP, etc.)
-positive feedback loop
coagulation (clotting)
-last and most effective defense against bleeding
-conversion of plasma protein fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin threads to form frame work of clot
-procoagulants (clotting factors)—usually produced by the liver; are present in plasma
-activate one factor and it will activate the next to form a reaction cascade
extrinsic pathway
-factors released by damaged tissues begin cascade
-2 proteins
-initiated by release of tissue thromboplastin (factor III) from damaged tissue
-cascade to factor VII, V, and X (fewer steps)
intrinsic pathway
-factors found in blood begin cascade (platelet degranulation)
-4 proteins
-initiated by platelets releasing Hageman factor (factor XII)
-cascade to factor XI to IX to VIII to X
completion of coagulation
-activation of factor X (leads to production of prothrombin activator)
-prothrombin activator (converts prothrombin to thrombin)
-thrombin (converts fibrinogen into fibrin monomers; monomers covalently bind to form fibrin polymer; factor XIII cross links fibrin polymer strands)
-positive feedback (thrombin speeds up formation of prothrombin activator)
fibrinolysis
-dissolution of a clot
-factor XII speeds up formation of kallikrein enzyme
-kallikrein converts plasminogen into plasmin, a fibrin-dissolving enzyme that breaks up the clot
platelet repulsion
platelets do not adhere to prostacyclin-coated endothelium
thrombin dilution
-by rapidly flowing blood
-heart slowing in shock can result in clot formation
antithrombin
-from liver
-deactivates thrombin before it can act on fibrinogen
hemophilia
-family of hereditary diseases characterized by deficiencies of one factor or another
-Sex-linked recessive (on X chromosome)
-Hemophilia A missing factor VIII (83% of cases)
-Hemophilia B missing factor IX (15% of cases)
-Hemophilia C missing factor XI (autosomal)
hemophilia A
-physical exertion causes bleeding and excruciating pain
-transfusion of plasma or purified clotting factors
-factor VIII produced by transgenic bacteria
hematomas
masses of clotted blood in the tissues
thrombosis
abnormal clotting in unbroken vessel
Thrombus
-clot (stationary)
-most likely to occur in leg veins of inactive people
pulmonary embolism
clot may break free, travel from veins to lungs
embolus
anything that can travel in the blood and block blood vessels (moving)
vitamin K
-is required for formation of clotting factors
-coumarin, warfarin (coumadin)
aspirin
-suppresses thromboxane A₂
-other anticoagulants discovered in animal research
-medicinal leeches used since 1884 (hirudin)
-snake venom from vipers (arvin)
streptokinase
-enzyme made by streptococci bacteria
-used to dissolve clots in coronary vessels
-digests almost any protein
tissue plasminogen activator (TPA)
works faster, is more specific, and now made by transgenic bacteria
hementin
produced by giant Amazon leech
pericardium
-double-walled sac that encloses the heart
-allows heart to beat w/o friction, provides room to expand, yet resists excessive expansion
parietal pericardium
-superficial fibrous layer of connective tissue
-deep, thin serous layer
visceral pericardium (epicardium)
-serous membrane covering heart
-adipose in thick layer in some places
-coronary blood vessels travel through this layer
pericarditis
painful inflammation of the membranes
endocardium
-smooth inner lining of heart and blood vessels
-covers the valve surfaces and is continuous with endothelium of blood vessels
fibrous skeleton of the heart
-framework of collagenous and elastic fibers
-provides structural support and attachment for cardiac muscle and anchor for valve tissue
-electrical insulation between atria and ventricles; important in timing and coordination of contractile activity
atrioventricular sulcus
separates atria and ventricles
interventricular sulcus
-overlies the interventricular septum that divides the right ventricle from the left
-contain coronary arteries
pectinate muscles
internal ridges of myocardium in right atrium and both auricles
trabeculae carneae
-internal ridges in both ventricles
-may prevent ventricle walls from sticking together after contraction
ventricles relax
-pressure drops inside the ventricles
-semilunar valves close as blood attempts to back up into the ventricles from the vessels
-AV valves open
-blood flows from atria to ventricles
ventricles contract
-AV valves close as blood attempts to back up into the atria
-pressure rises inside of the ventricles
-semilunar valves open and blood flows into great vessels
angina pectoris
-chest pain from partial obstruction of coronary blood flow
-pain caused by ischemia of cardiac muscle
-obstruction partially blocks blood flow
-myocardium shifts to anaerobic fermentation, producing lactate and thus stimulating pain
myocardial infarction (MI)
-sudden death of a patch of myocardium resulting from long-term obstruction of coronary circulation
-responsible for about 27% of all deaths in the U.S.
mechanical junctions
tightly join cardiomyocytes