Female Reproductive Anatomy - Duct System
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
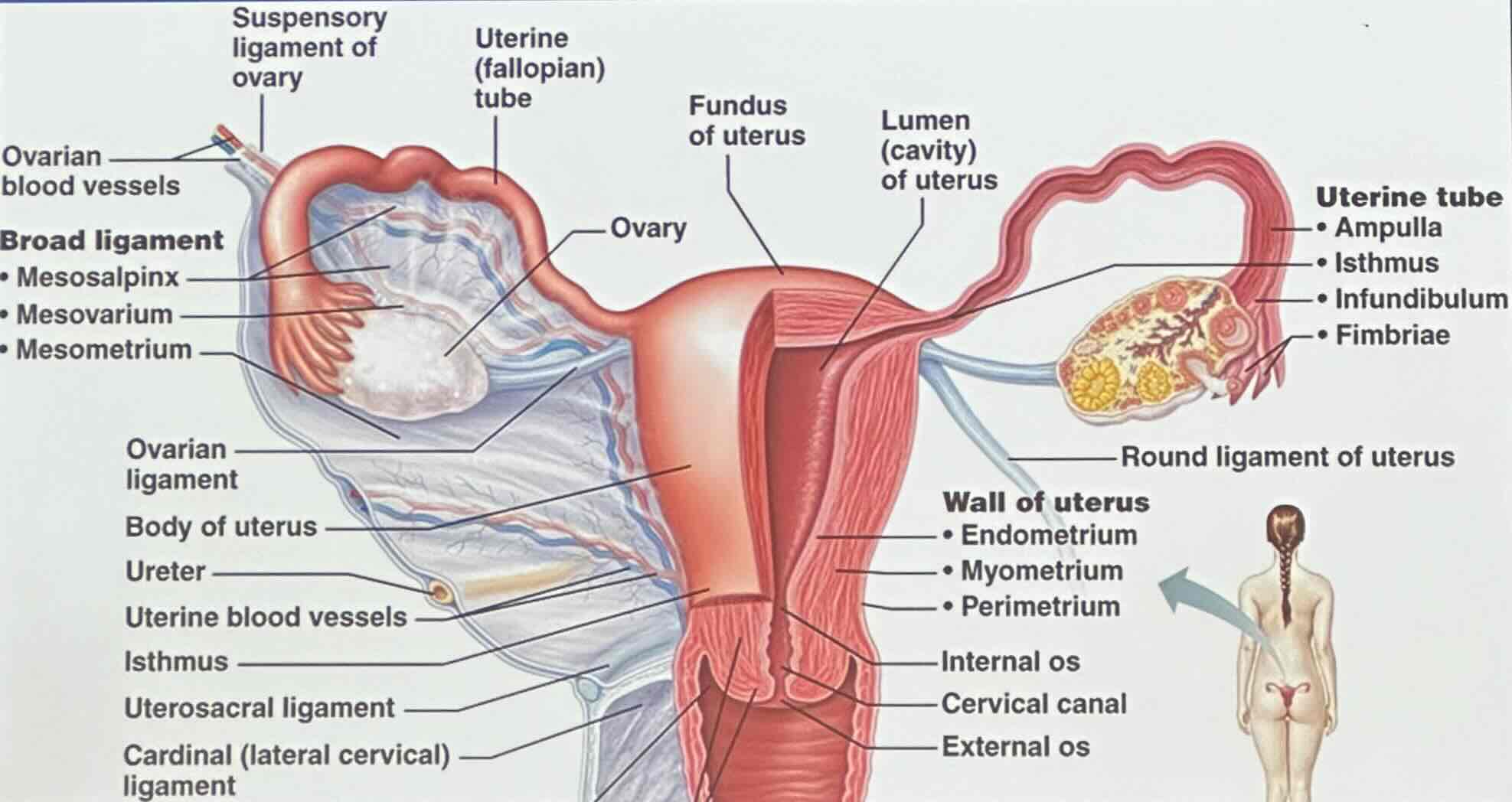
What does the uterine tubes consist of?
the uterine tubes consist of oviducts and the fallopian tubes
Are the uterine tubes connected to the ovaries?
NO, the uterine tubes are not connected to the ovaries
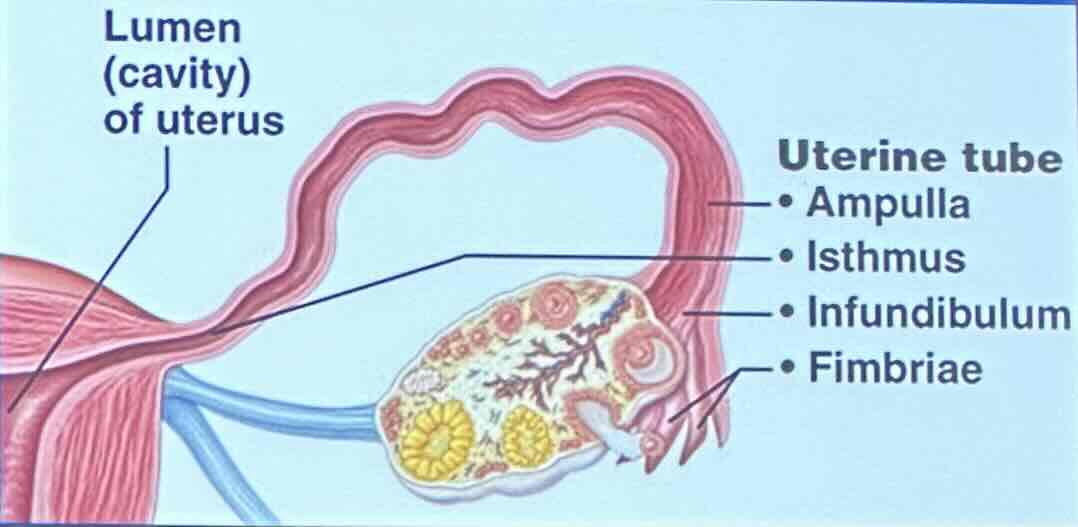
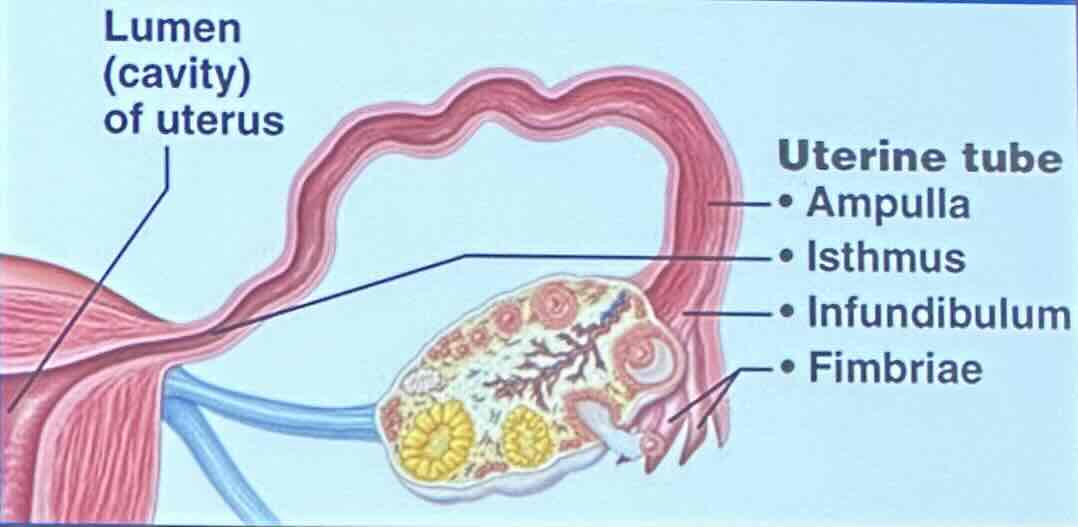
Uterine Tubes: Infundibulum
the infundibulum is a funnel-shaped region that bears ciliated fimbriae
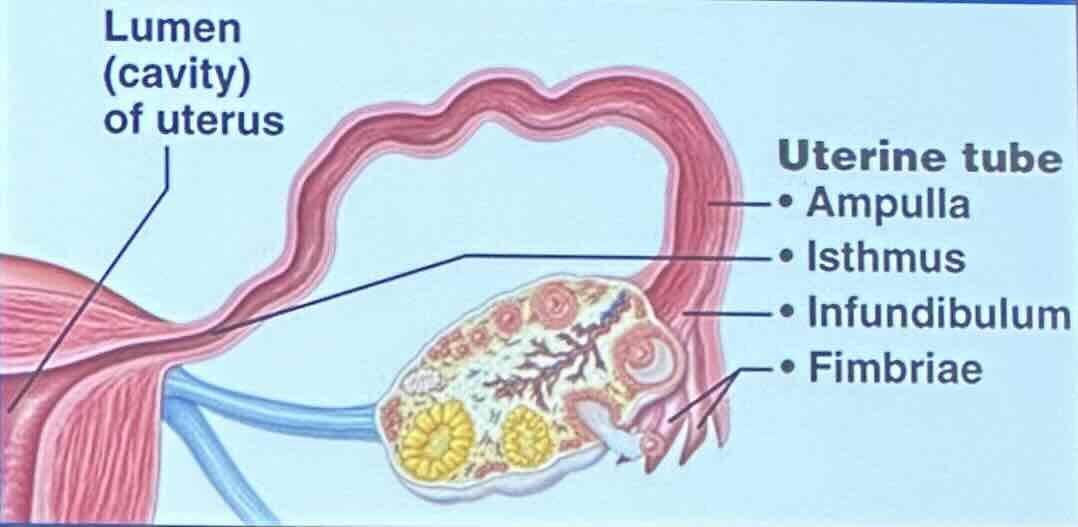
Uterine Tubes: Infundibulum - What does the ciliated fimbriae in the infundibulum do?
the ciliated fimbriae help make sure materials go through the fallopian tube during ovulation
Uterine Tubes: Infundibulum - What does the infundibulum recieve?
the infundibulum receives ovulated oocyte
Uterine Tubes: Ampulla
the ampulla is widened region
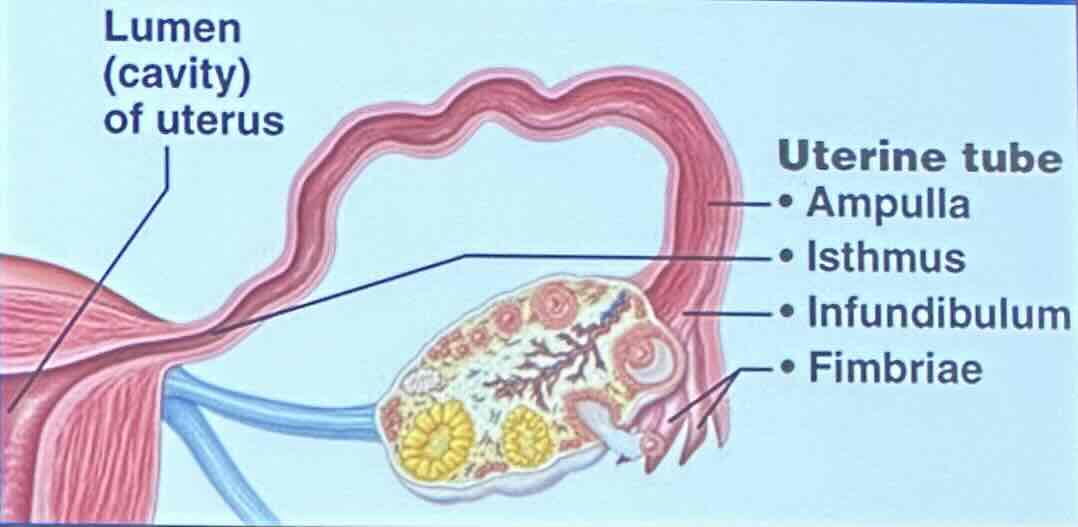
Uterine Tubes: Ampulla - What is the ampulla the usual site of?
the ampulla is the usual site of fertilzation
Uterine Tubes: Isthmus
the isthmus is a constricted region attached to the uterus
What does the walls of the uterine tubes contain?
the wall of the uterine tubes contains smooth muscle
What is the mucosa of the uterine tubes?
the mucosa of the uterine tube is highly folded with 2 types of cells:
ciliated cells
nonciliated cells
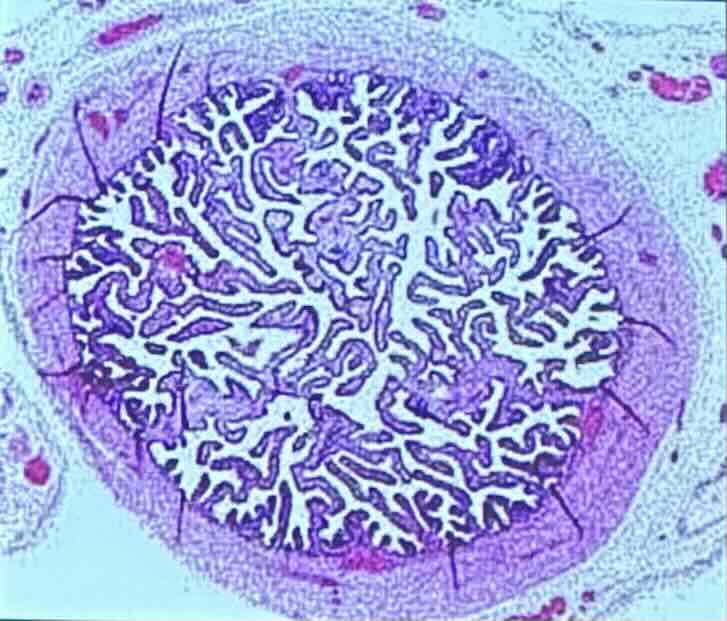
Mucosa of Uterine Tubes: Ciliated cells
ciliated cells help transport ovulated oocyte towards the uterus
Mucosa of Uterine Tubes: Nonciliated cells
nonciliated cells have microvilli that promote nourishing secretion
What is a ectopic pregnancy?
an ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy that can’t be carried to full term because the fertalized egg grows outside of the uterus
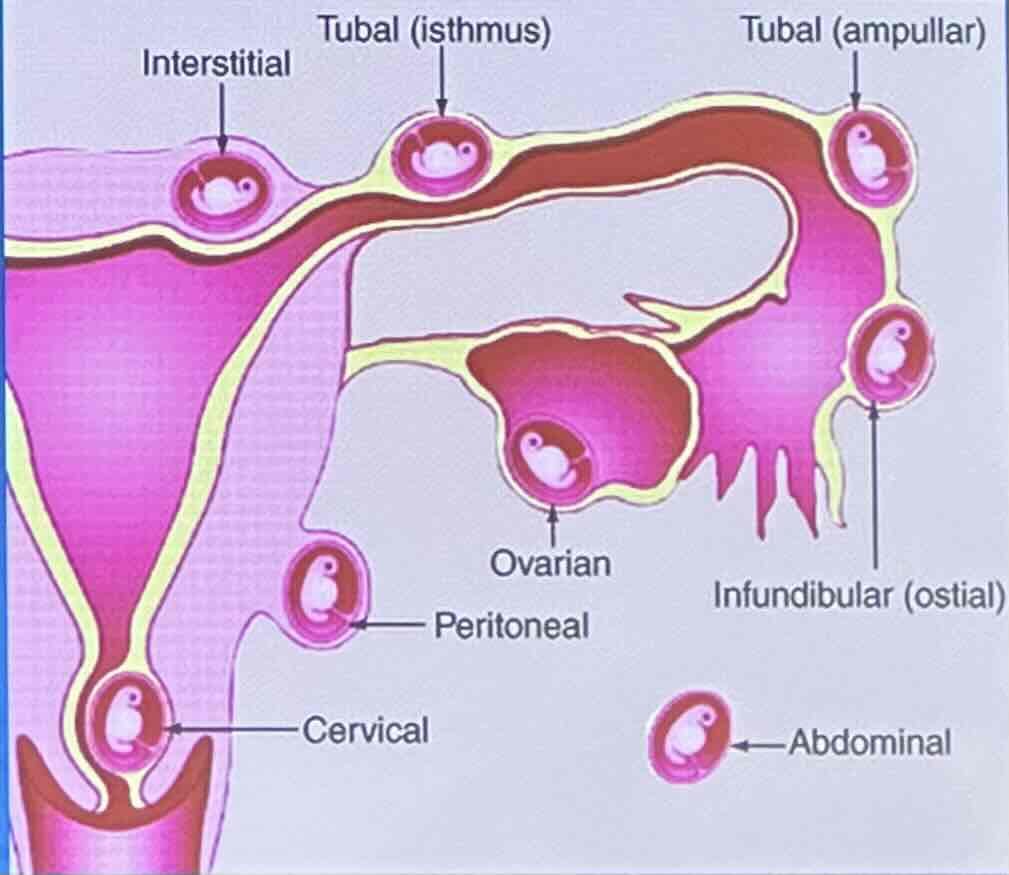
Where do fertilized eggs usually grow during ectopic pregnancy?
During an ectopic pregnancy, fertlized eggs are usually in the ovioduct
What is PID?
PID stands for pelvic inflammatory disease; an infection of the female reproductive organs
What is a hysterectomy?
a hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus and cervix; supracervical hysterectomy removes only the uterus not the cervix
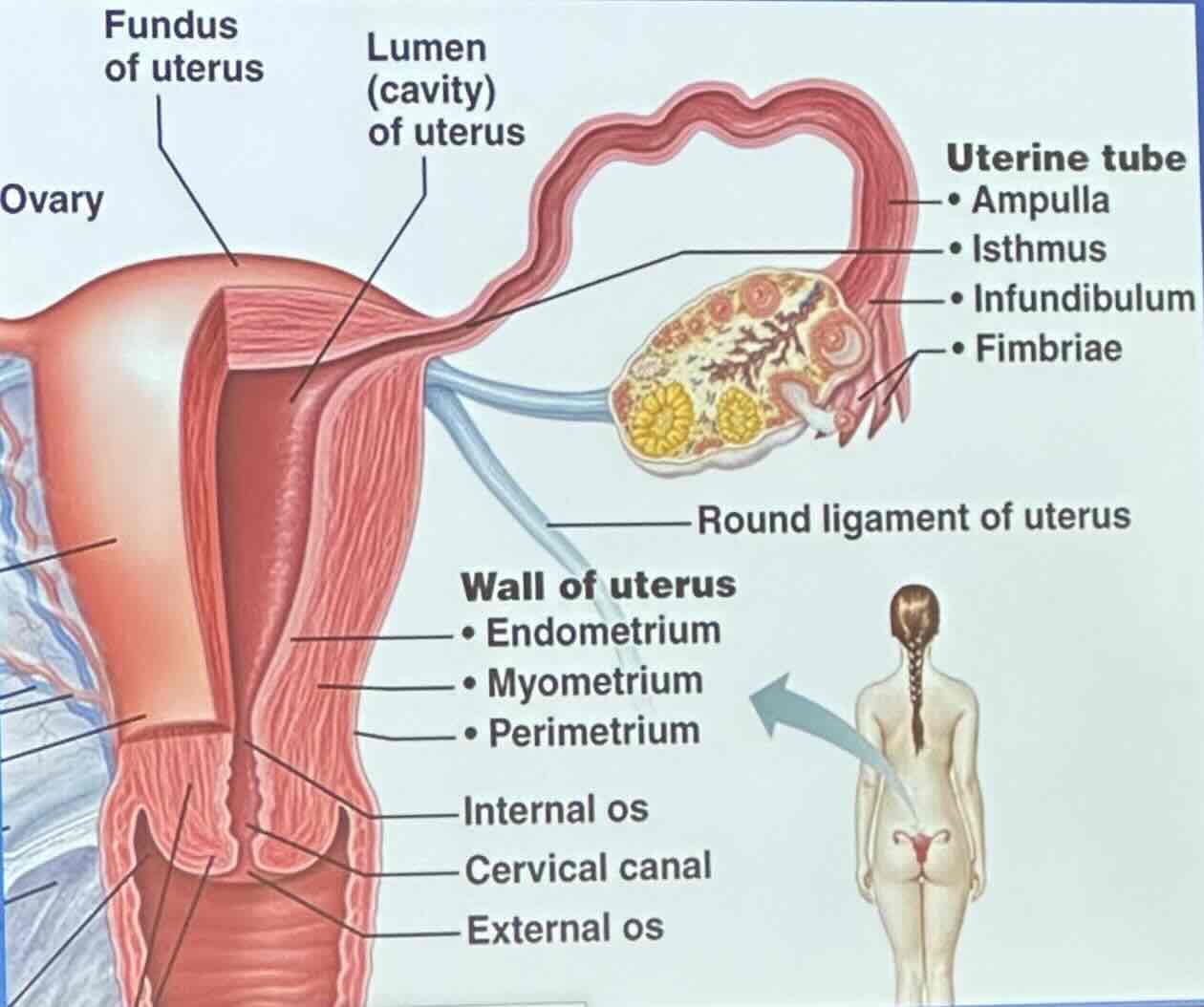
What is the uterus also known as?
the uterus is known as the womb
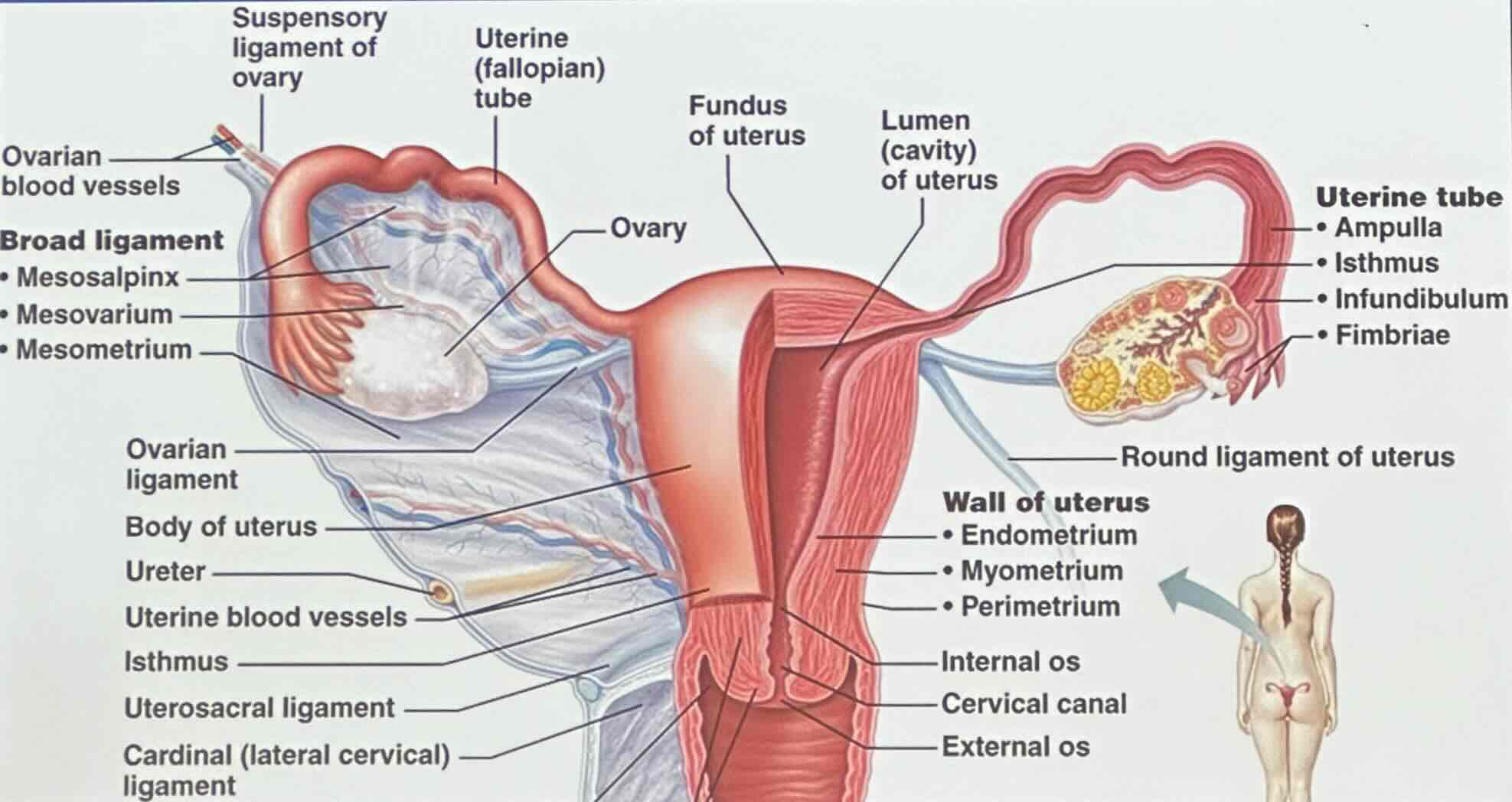
What does uterus (womb) receives and nourish?
the uterus receives and nourish developing embryo
What does the uterus (womb) consist of?
the uterus consists of the fundus, body, and cervix (containing cervical glands)
What is a pap smear?
a pap smear is when a doctor scrap cells from the surface of the cervix mucosa to test for abnormal cells
What is a prolapsed uterus?
a prolapsed uterus occurs when the muscles and tissues of a female’s pelvis weaken
Uterus: What does the wall of the uterus consist of?
perimetrium
myometrium
endometrium
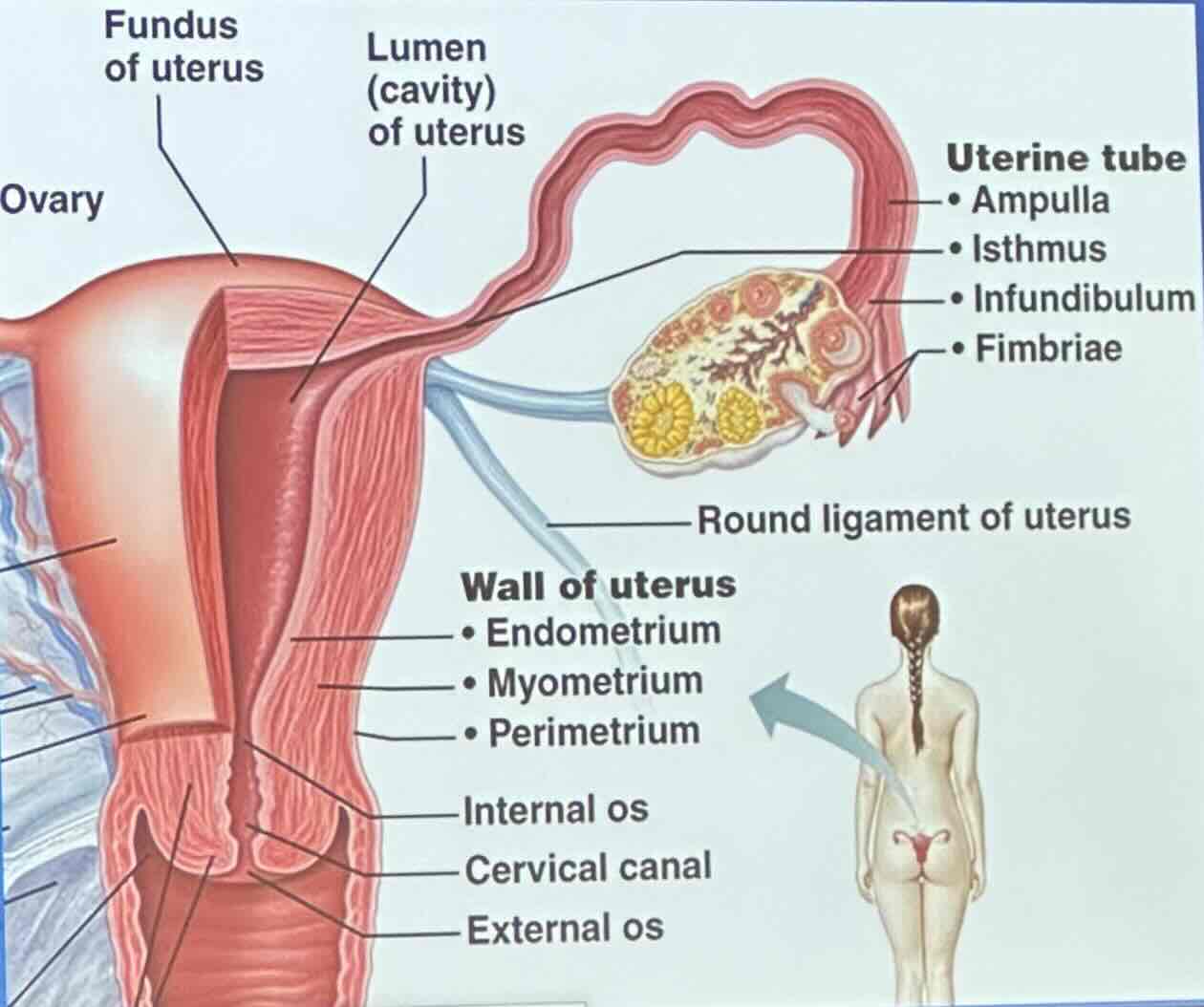
Uterus: Perimetrium
visceral peritoneum
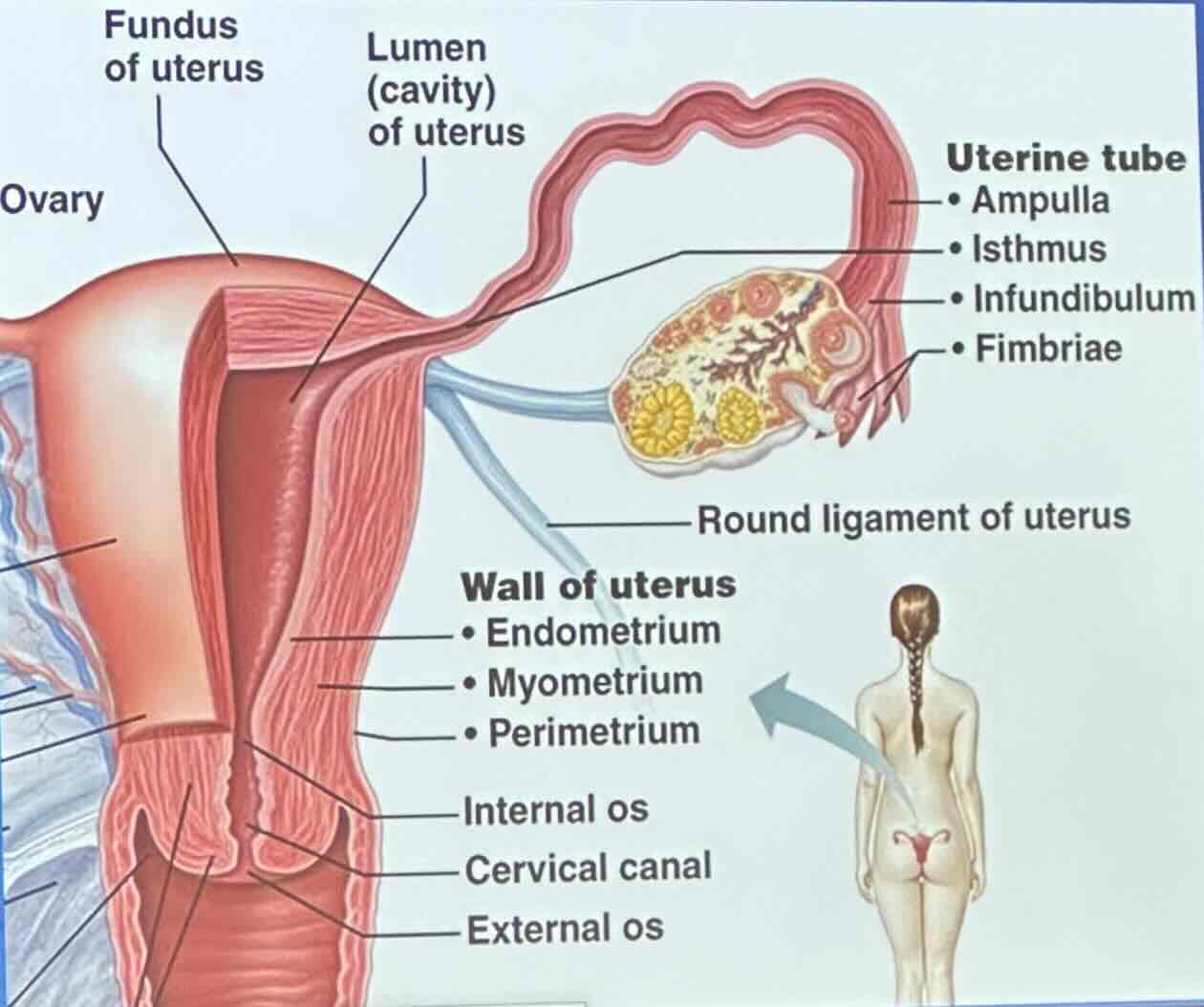
Uterus: Myometrium
bundles of smooth muscle
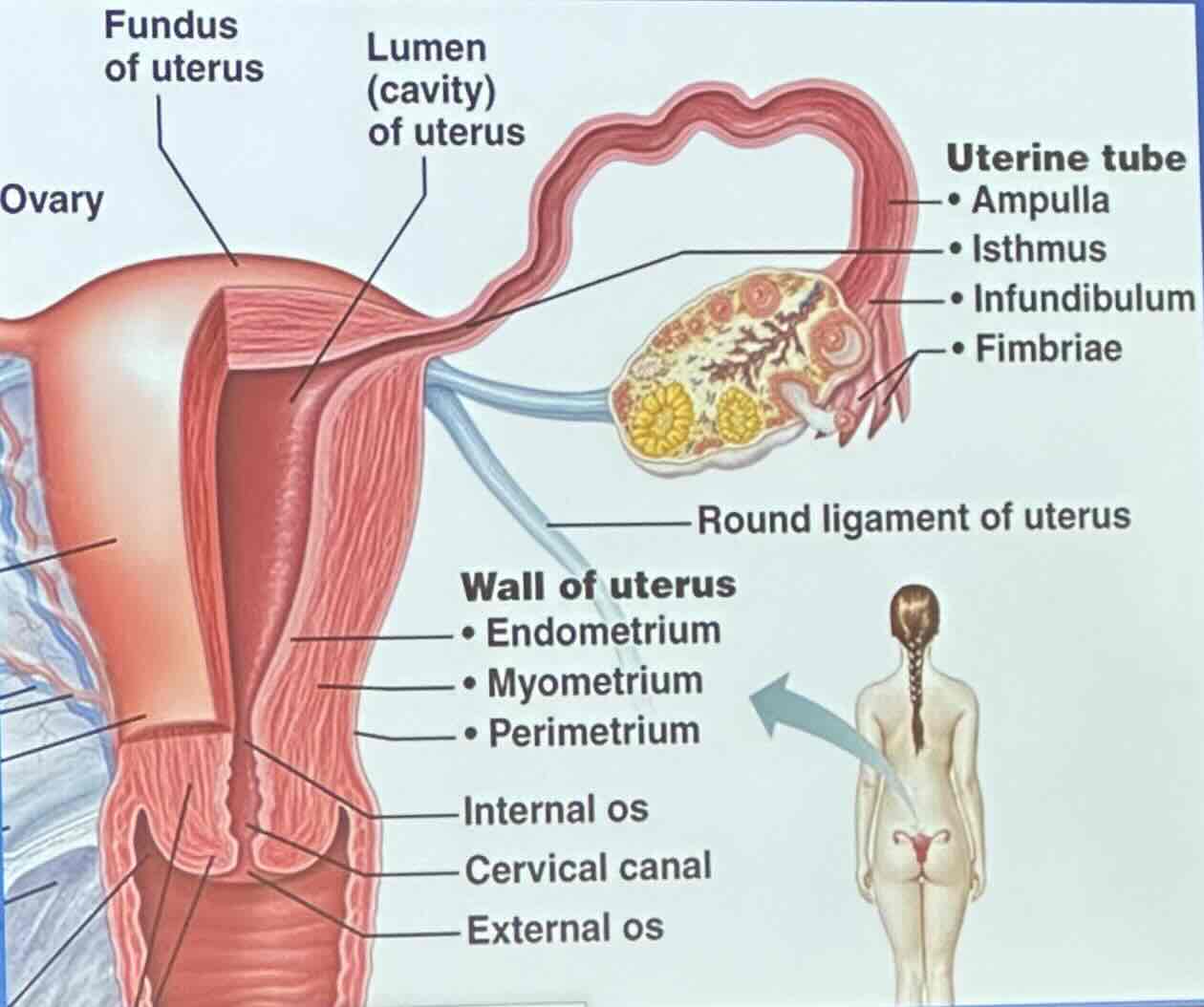
Uterus: Endometrium
innermost; receives implanted embryo if fertilization occurs
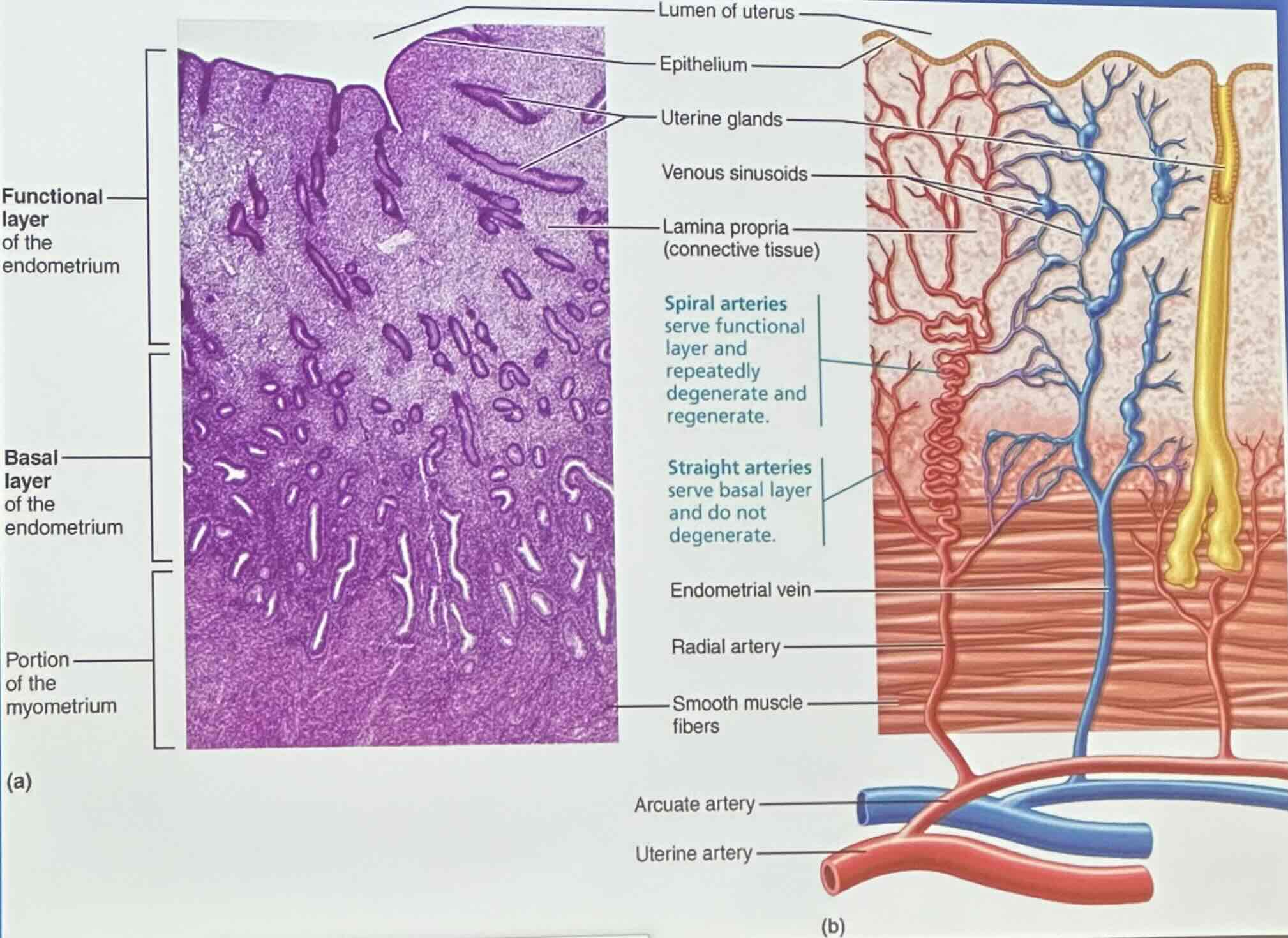
Endometrium Structure & Blood Supply: Functional layer of the endometrium
stratum functionalis shed during menstruations
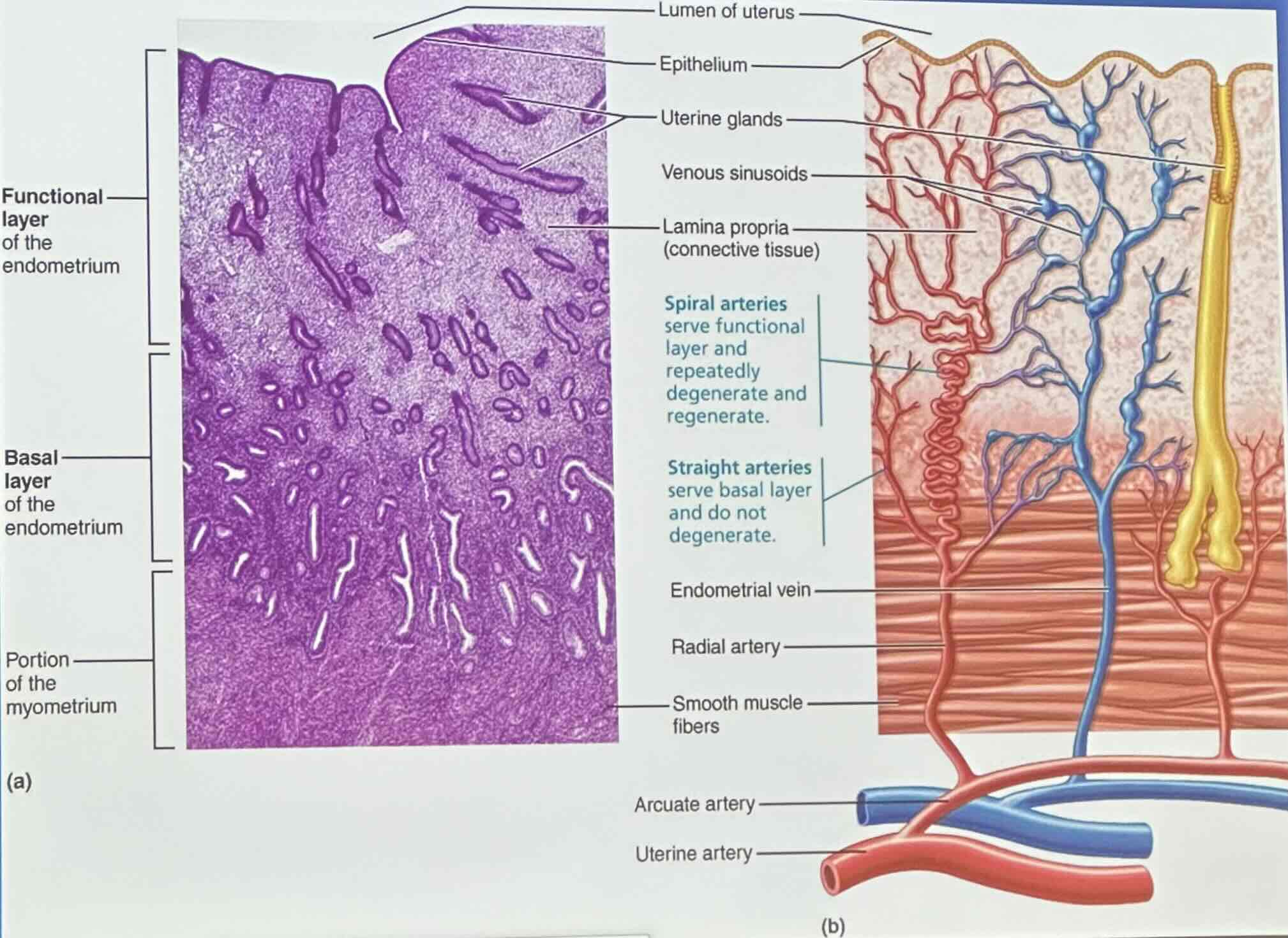
Endometrium Structure & Blood Supply: Basal layer of the endometrium
stratum basalis forms a new functional layer after menstruation ends
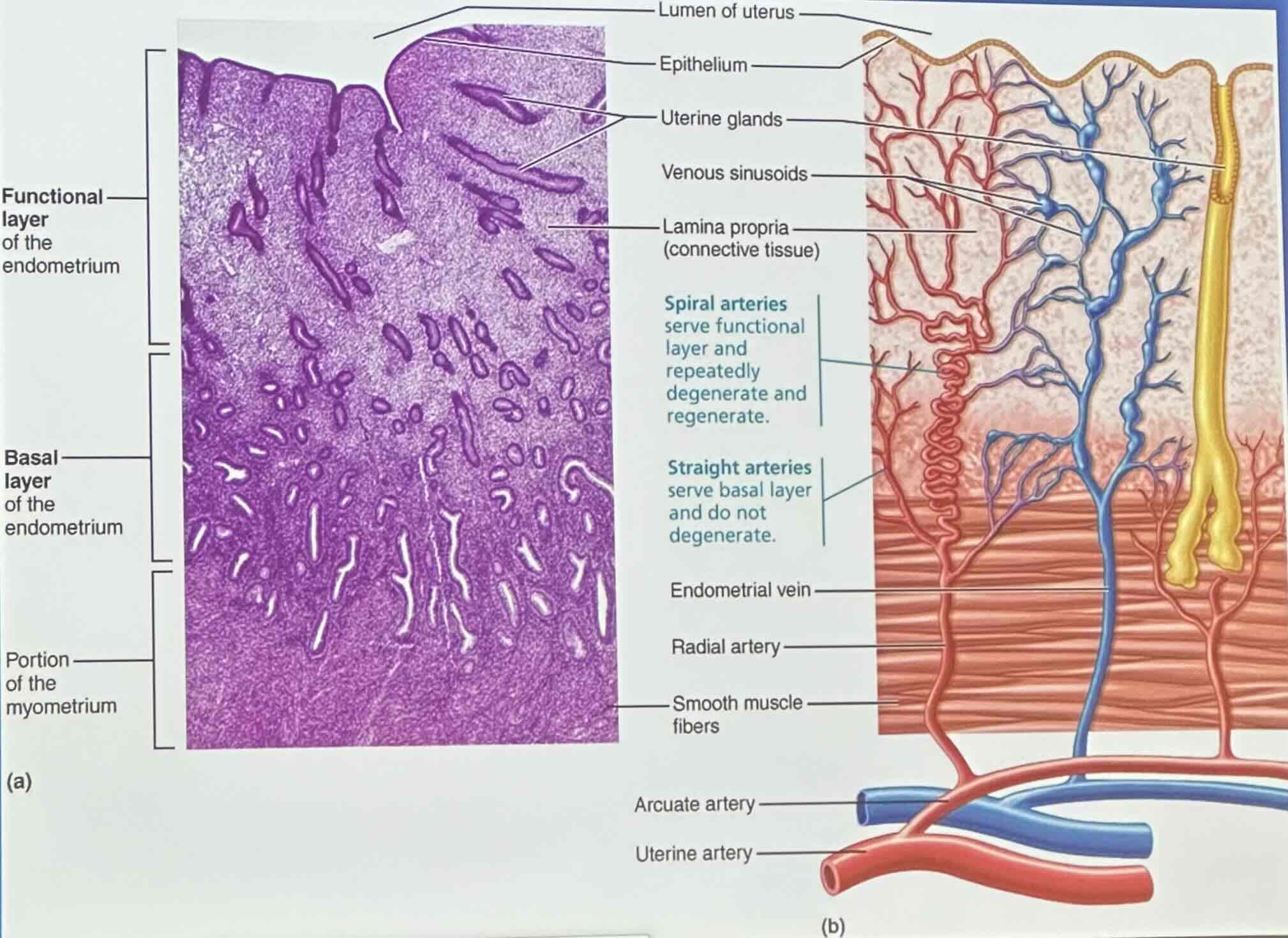
Endometrium Structure & Blood Supply: Spiral arteries
spiral arteries serve functional layer and repeatedly degenerate and regenerate
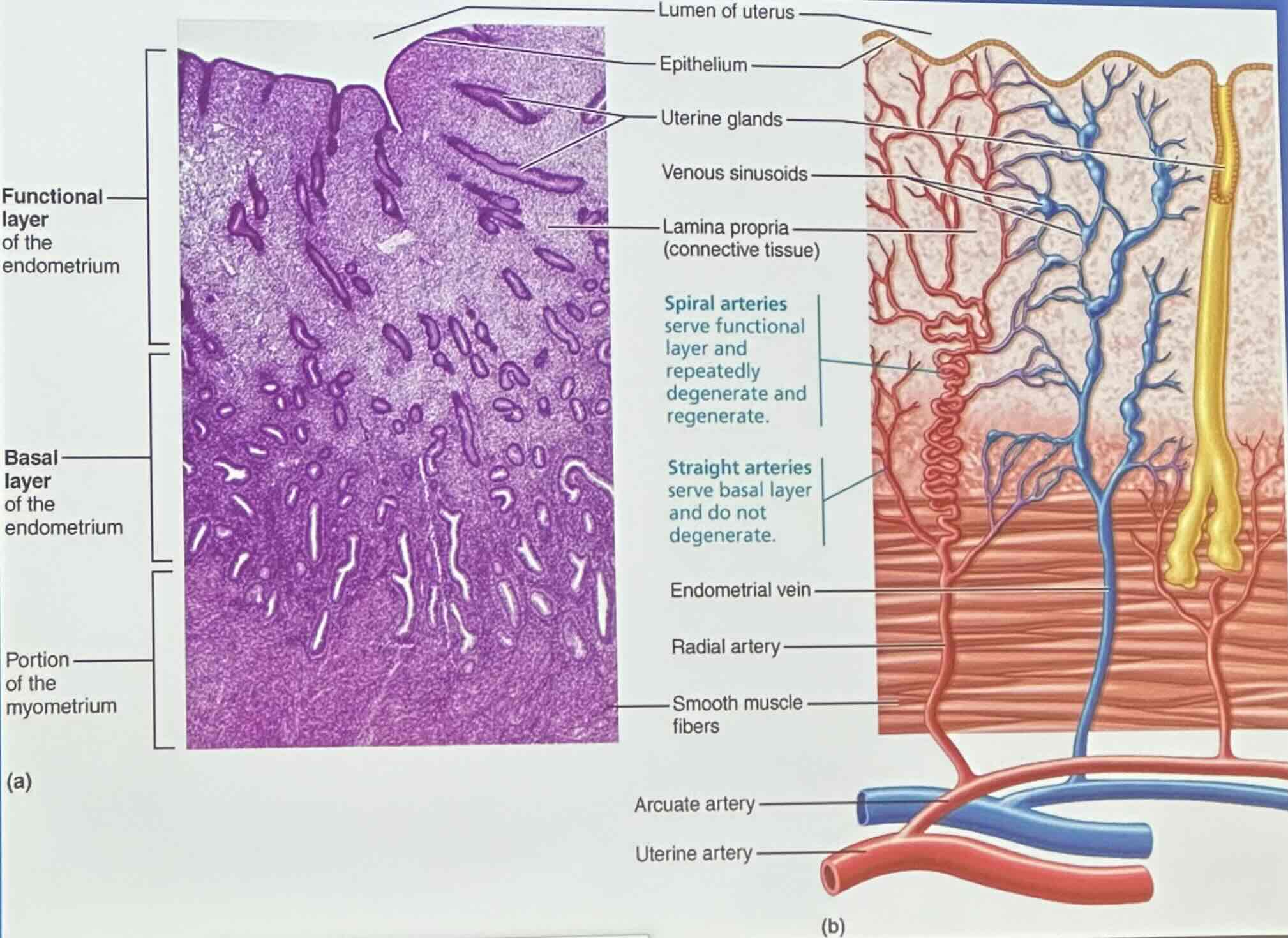
Endometrium Structure & Blood Supply: Straight arteries
straight arteries serve basal layer and do not degenerate
What is the male organ of copulation (sexual intercourse)?
penis
What is the female organ of copulation (sexual intercourse)?
vagina
Where is the vagina located?
the vagina is sandwiched between the urinary bladder and rectum
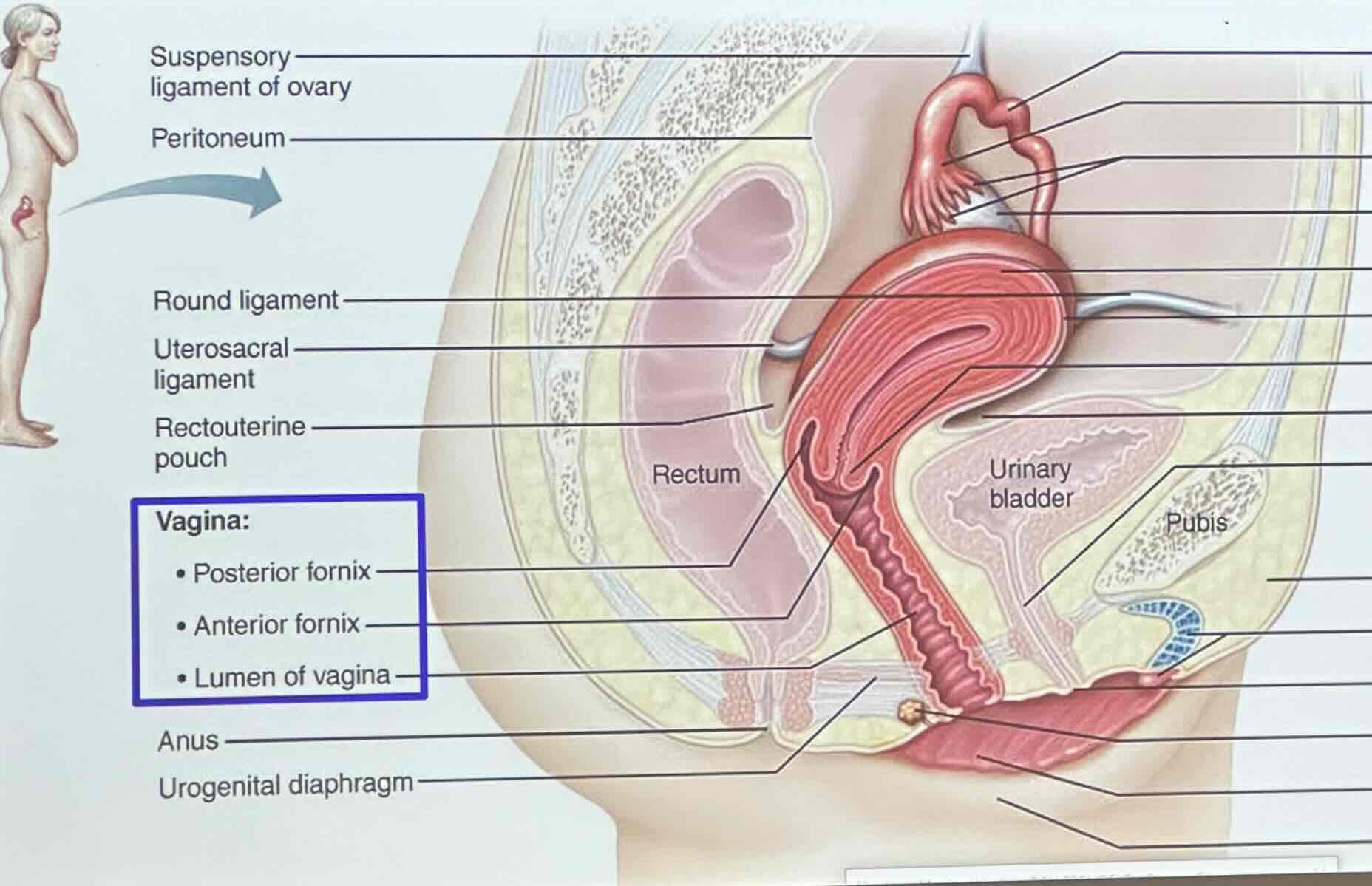
What is the vagina a passageway for?
the vagina is a passageway for menstrual flow and the delivery of an infant
What is the orientation of the vagina?
the vagina usually tilts forward (anteverted), but may be retroverted
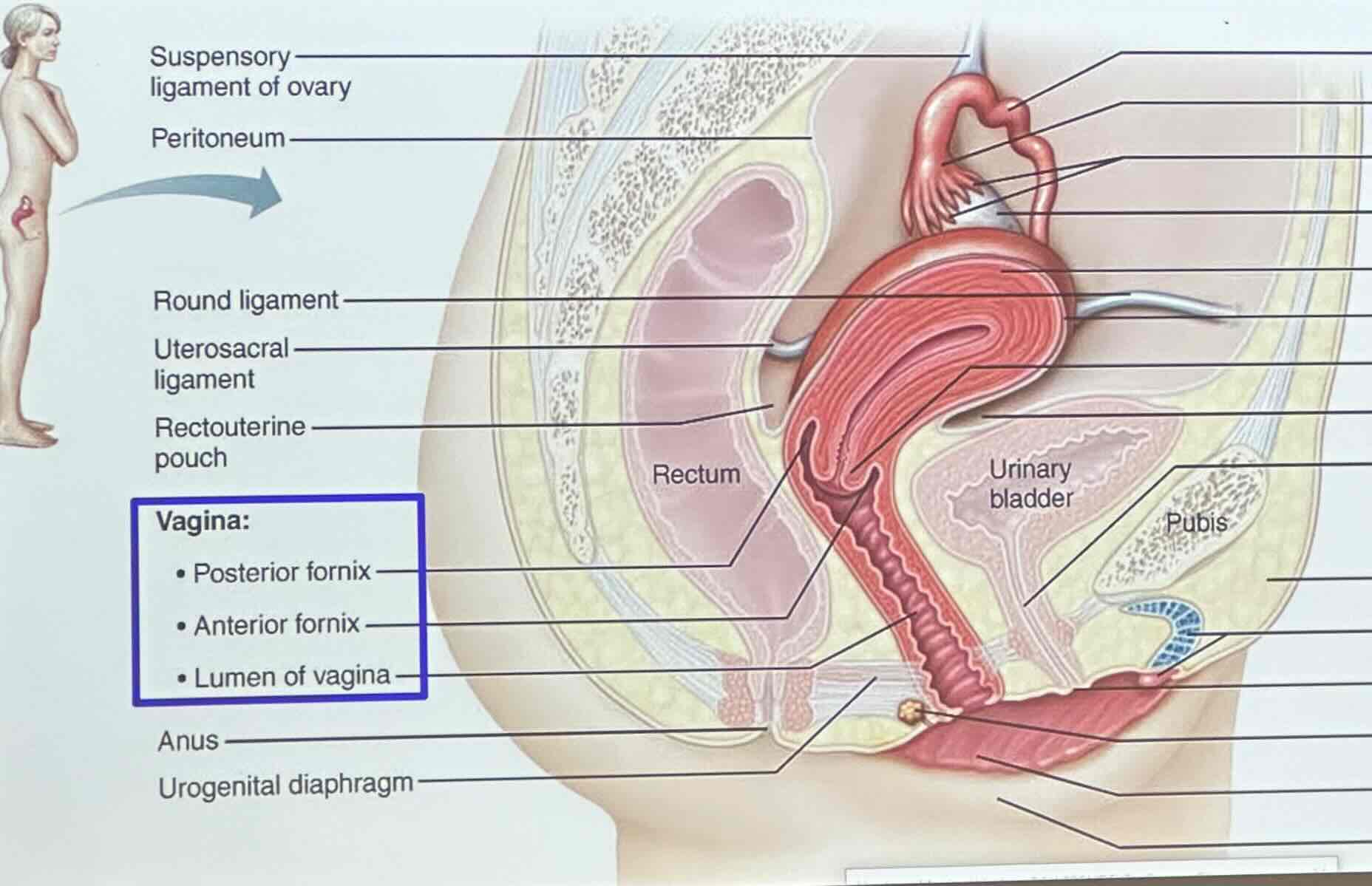
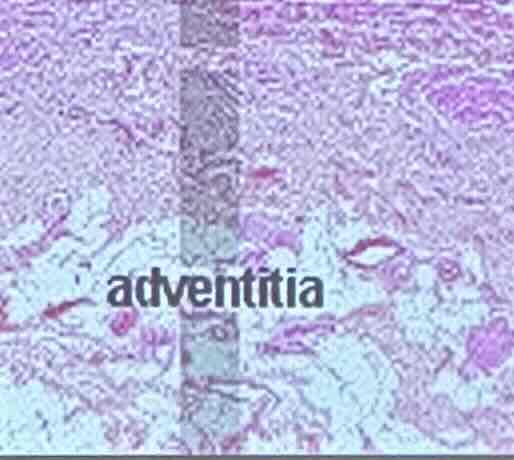
What does the wall of the vagina consist of?
adventitia
muscularis
mucosa
Vagina: Adventitia
fibrostatic outer layer

Vagina: Muscularis
smooth muscle
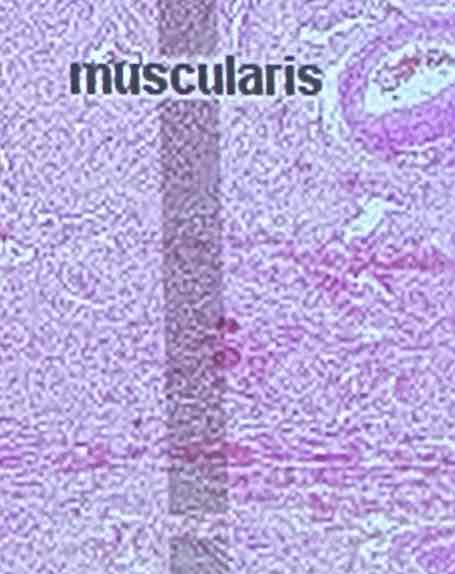
Vagina: Mucosa
innermost; stratified squamous epithelium with rugae
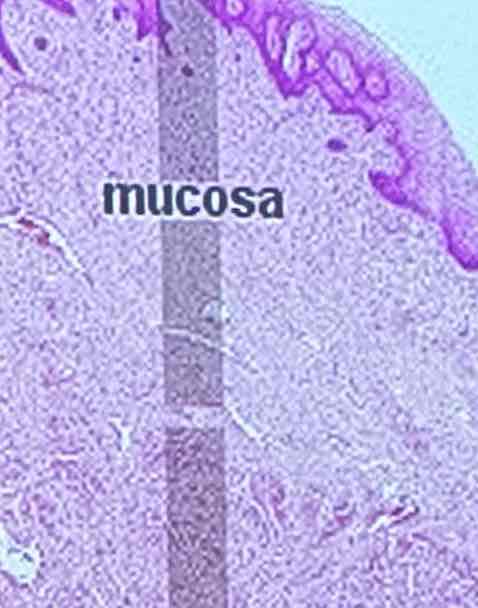
Vagina: What is the vagina lubricated by?
the vagina is lubricated by cervical mucous glands and mucosal fluid from the vaginal epithelium
Vagina: What type of environment is the vagina (in adults)?
the vagina has an acidic environment
Vagina: What type of environment is the vagina (in adolescents)?
the vagina has an alkaline environment
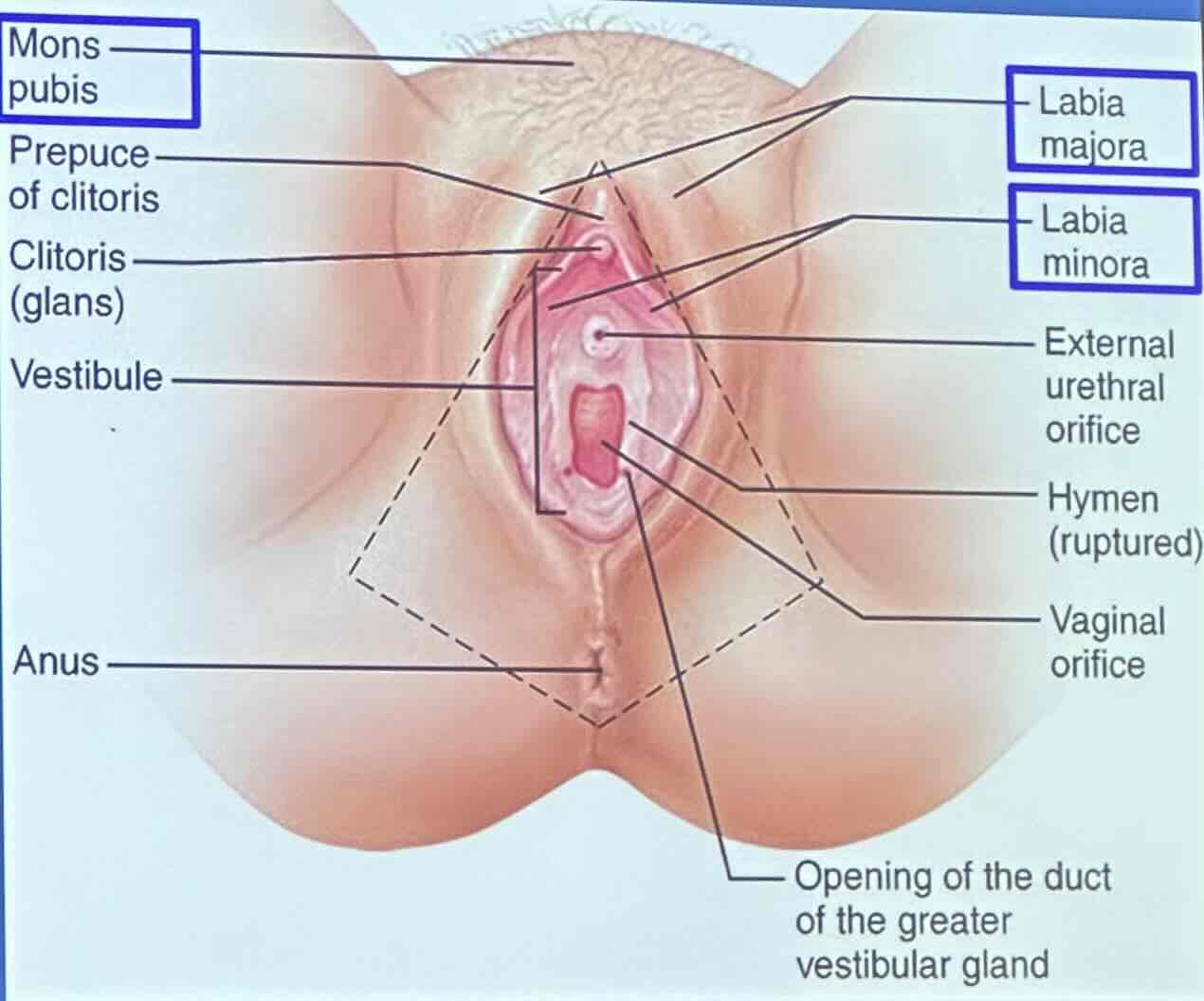
What is the hymen?
the hymen is a piece of tissue covering or surrounding part of your vaginal opening, range form thin to thick; not only sex tears/breaks it, it could be broken by sports, tampons, etc.