ID Organic Structures
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
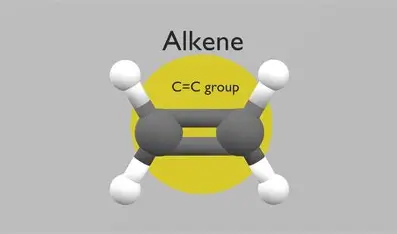
Alkene
carbon carbon double bond
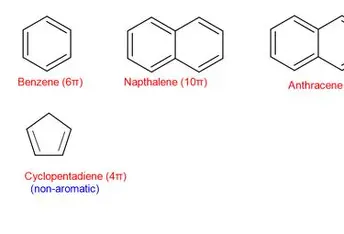
Arene (aromatic ring)
six-membered ring in which all atoms are forming “double” bonds with their neighboring atoms – all six atoms
equally share the six electrons that form the
double bonds; nonpolar
Alcohol
structurally related to water, but one
hydrogen has been replaced by carbon.
Polar like water, and can participate in
hydrogen bonding as both proton donor
and acceptor
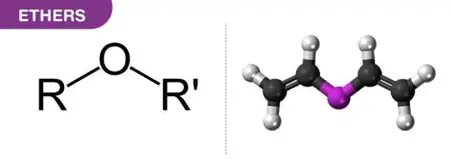
ether
structurally related to water, but BOTH
hydrogens have been replaced by carbon.
Much less polar than water and can
participate in hydrogen bonding only as
proton acceptor
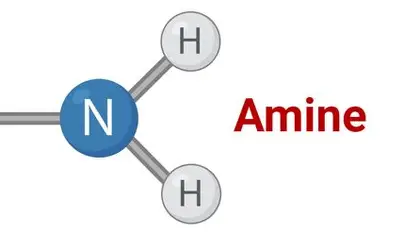
Amine
structurally related to ammonia (NH 3 )
but one or more hydrogens have been
replaced by carbon. Polar like ammonia, and
can participate in hydrogen bonding as both
proton donor (if it has N–H) and acceptor
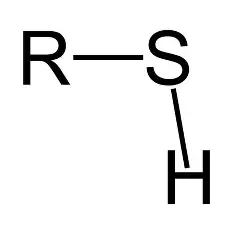
Thiol
structurally related to alcohols, but
oxygen has been replaced by sulfur. Can be
oxidized to disulfide (–S–S–). NONPOLAR,
and it CANNOT participate in hydrogen
bonding