Biology B10: The human nervous system
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
What do enzymes and cells need in order to work properly?
V stable conditions
Can’t work well if conditions around them change too much
Homeostasis
The regulation of the internal conditions of a cell / organism to maintain optimum conditions for function in response to internal + external changes
What does homeostasis do?
Maintains optimal conditions for enzyme action + cell functions
What does homeostasis consist of?
Automatic control systems that ensure internal body conditions stay as constant as possible
In the human body, what internal conditions does homeostasis control?
Body temperature
The water content of the body
Blood glucose concentration
What do automatic control systems in humans involve?
Nervous responses in nervous system
Chemical responses in hormone system
What do all automatic control systems need to function?
Receptor cells
Coordination centres
Effectors
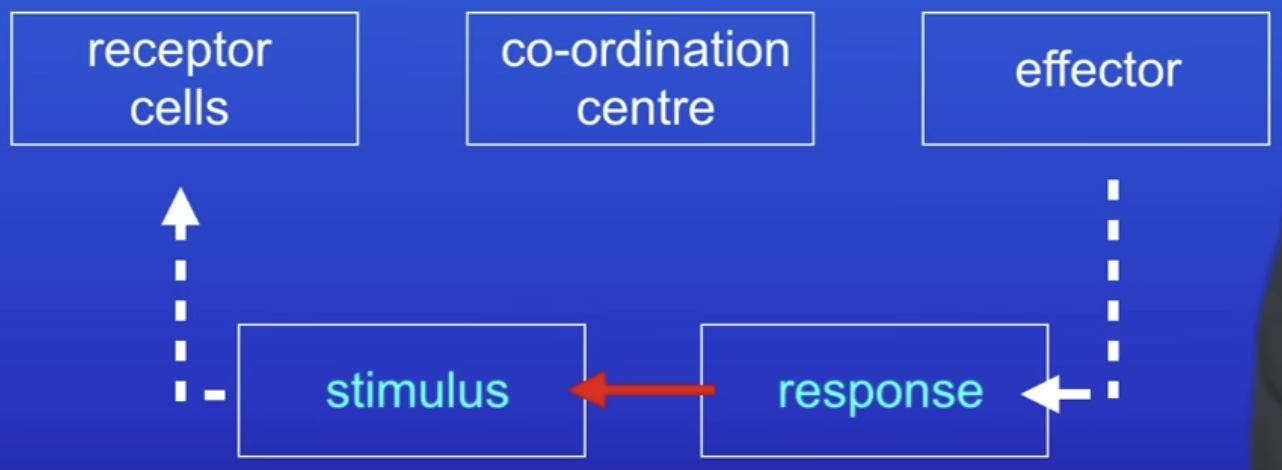
Receptors cells
Detect changes in the environment (stimuli)
Pass info to coordination centre
Environment
Refers to the bodies
Internal conditions (eg blood glucose concentration)
External conditions (eg temp of skin)
Coordination centres
Receives + processes info from receptor cells
Sends instructions to the effector
* Spinal cord
* Pancreas
Effectors
Muscles or glands
Bring about responses to stimulus that restore body conditions to optimum levels
* Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
What makes up the central nervous system (CNS)?
The brain
Spinal cord
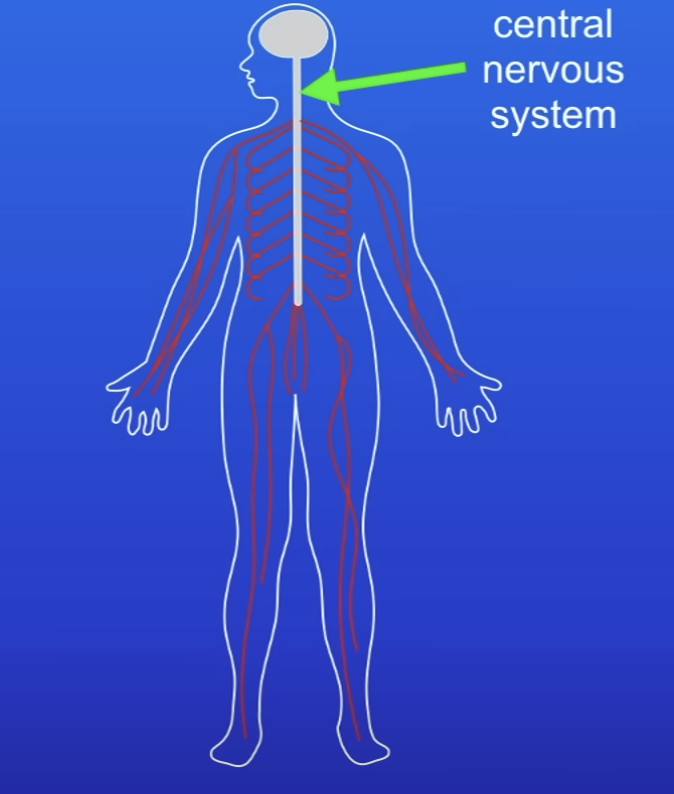
Role of nervous system
Enables humans to react to surroundings + coordinate behaviour
Done thru reflec arc
* Electrical signals that pass along neurones
How does our nervous system work?
Receptors detect stimulus
Sends EI down neurones to the CNS
CNS = coordination centre
CNS sends EI down the motor neurones to effectors
Effectors bring about a response
Eg muscles contract or glands secrete hormones
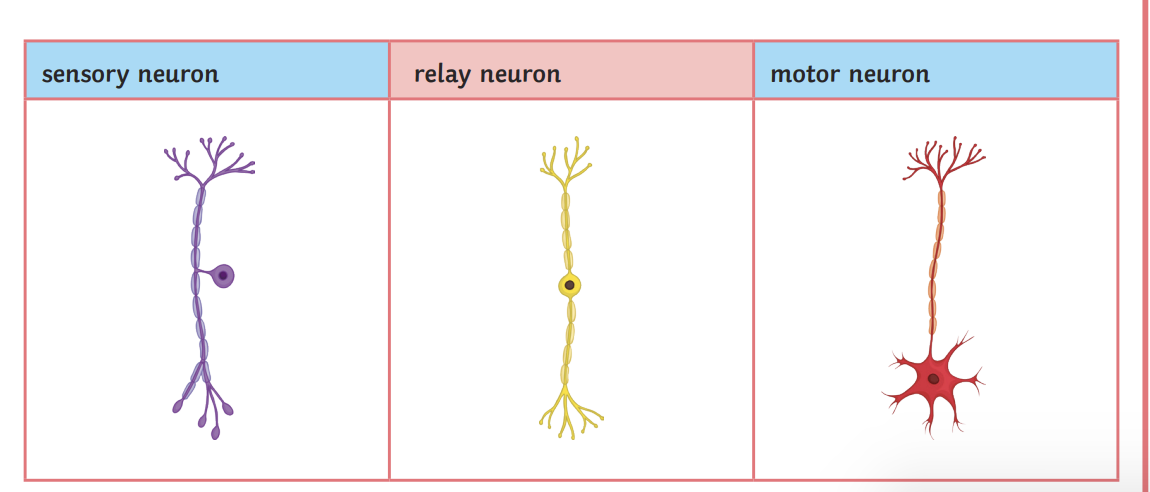
Sensory neurones
Nerve cells that carry impulses from sense organs to CNS
* To make effectors respond
* Glands: secretes hormones
What makes reflexes automatic and rapid?
No decision making by conscious part of the brain
Since reflexes are automatic and rapid how does it help us?
Protect us from danger
So minimise damage to the body
Why are reflexes important?
Protect us from danger
They take care of basic body functions
Eg breathing
What types of neurones do reflexes involve?
Sensory neurones
Motor neurones
Relay neurones
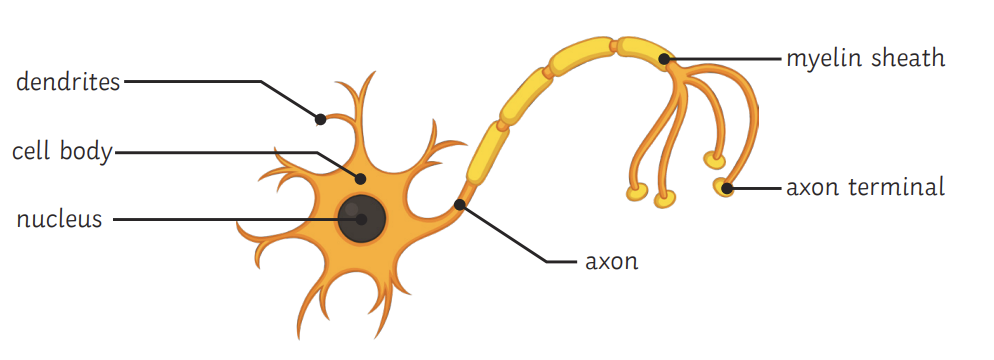
Nerve cell labelled
Axon = Long, EI travel along
Axon surrounded by myelin sheath (fatty cells)
Insulates EI
Dendrites = branched endings, connect neurons tog
Relay neurones
Connect a sensory + motor neurone
In CNS
1. Stimulus
2. Receptor
3. Sensory neurone
4. Relay neurone
5. Motor neurone
6. Effector
7. Response
Synapses
Junction, gap where the ends of two neurons meet
Ensures EI travel only in 1 direction
In the reflex arc, where are synapses found?
Between
Sensory + relay neurones
Relay + motor neurones
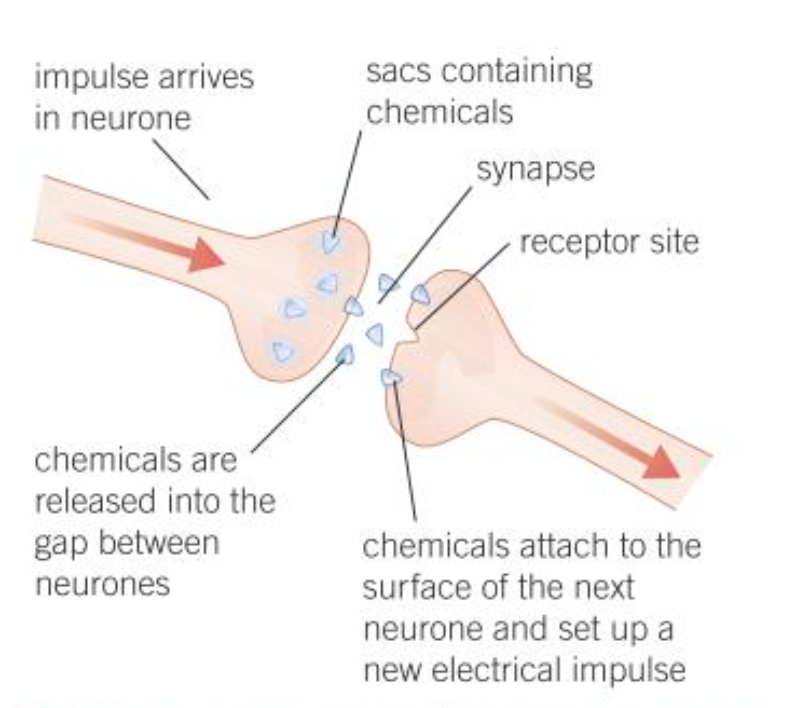
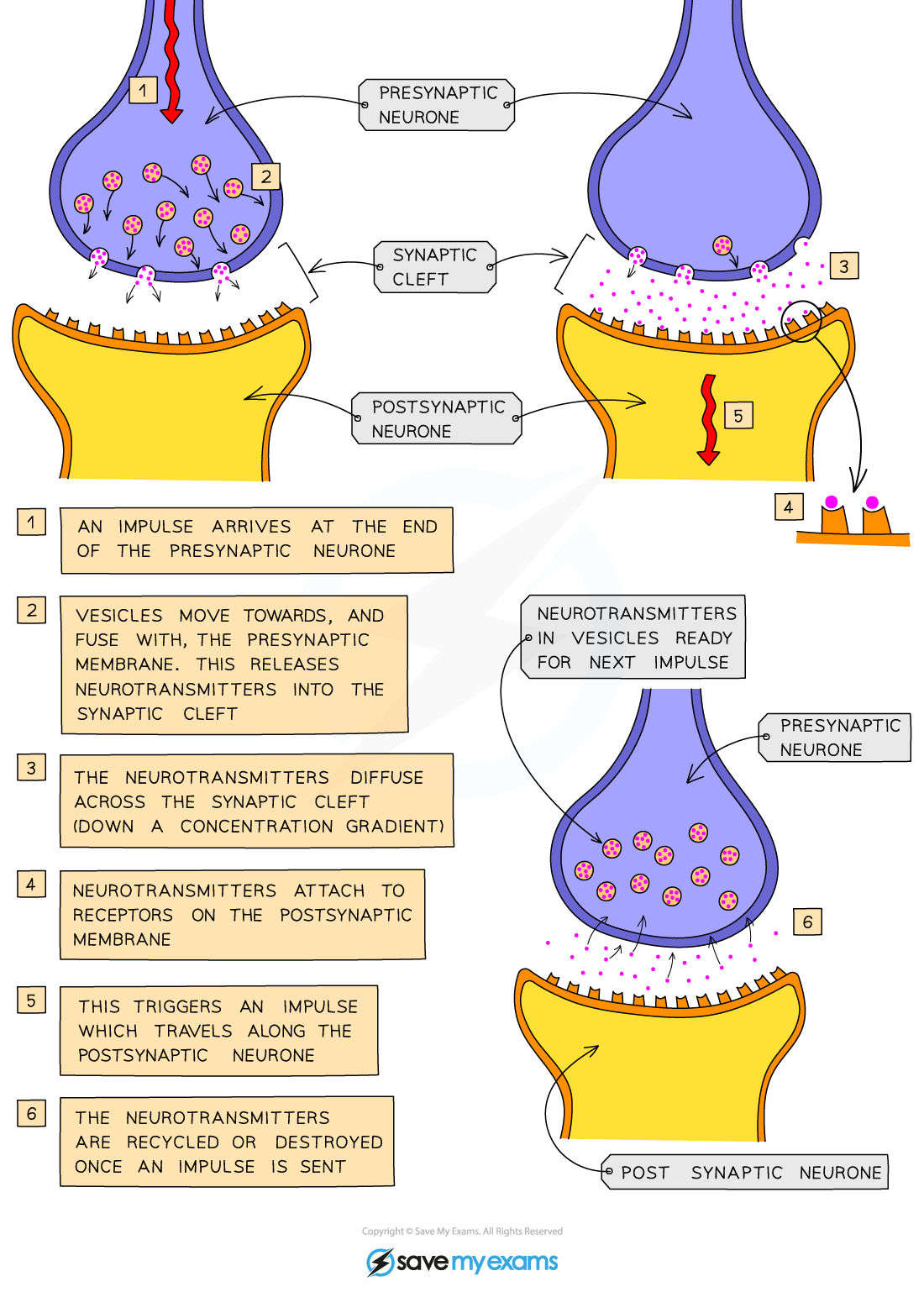
How do synapses work?
EI arrives at the end of the axon on the neuron
Chemicals released from vesicles
Diffuse across synaptic gap
Chemicals attatch to surface of next neurone + set up new EI
Which is the only place in the nervous system where drugs can affect the nervous system and why?
Synapses
Only part of the NS where messages are chemical, not electrical
How do neurotransmitter chemicals cross the synapse?
Diffusion
Down a CG
Passive process
What can the frequent use of drugs lead to?
Overstimulation of neurons → loss of function
Brain
Controls complex behaviours eg language
Made up of interconnected neurons
Organ part of the CNS
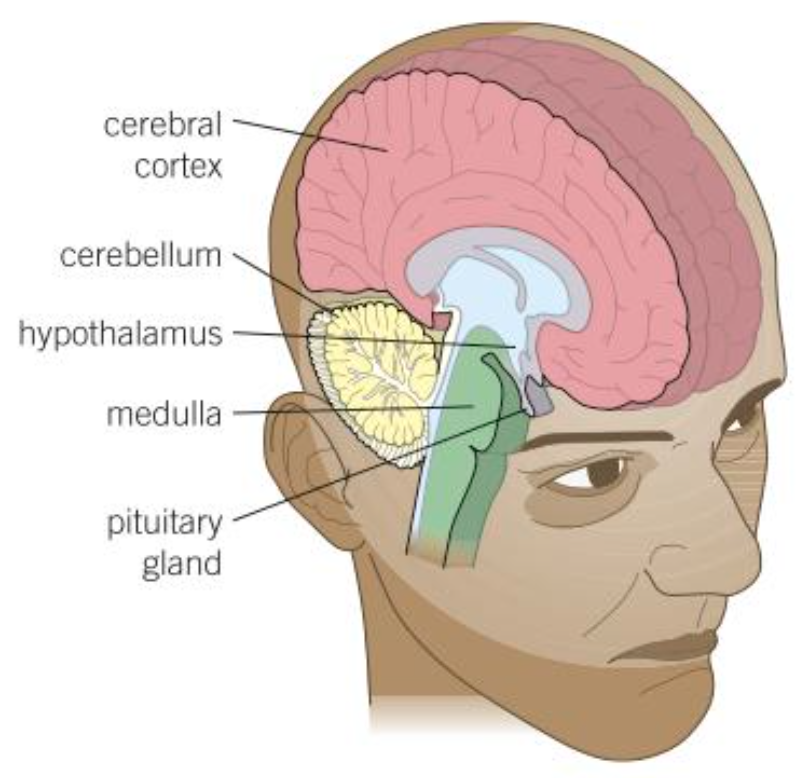
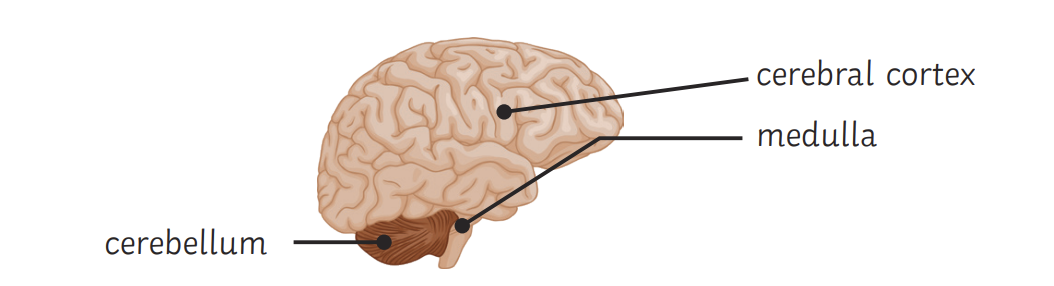
Cerebral cortex
Highly folded, outer layer of the brain
Controls consciousness, memory + language
Cerebellum
Controls balance + coordinates movements
Medulla
Controls unconscious activities
Heart + breathing rate
Pituitary gland
Produces different hormones
Why is the understanding of the brain limited?
V complex
Diff regions can’t be studied in isolation
Why is studying the brain difficult + difficult to treat brain damage/diseases?
Protected by skull → tricky to access
Structures in brain are v complex
So difficult to work out which parts of the brain carry out specific functions
Delicate + easy to damage
Why can brain surgery be performed on conscious patients?
No sensory nerve endings in the brain
Benefits of procedures carried out on the brain and nervous system
Improving quality of someone’s life
Risks of procedures carried out on the brain and nervous system
More permanent damage
As we don’t fully understand how brain + NS work
Eye
Sense organ
Contains receptors sensitive to light intensity + colour of light
* It refracts light rays as it enters the eye and focuses it onto the retina
Iris
Colored part of the eye
Controls size of the pupil (+ so how much light reaches the retina)
Made of muscles that contract or relax to change the size
Lens
Transparent lens
Starts focusing of light rays onto the retina
* Contains receptor cells for light
What do the receptor cells in the retina allow us to detect?
Light intensity
Light colour
Purpose of the eye?
To receive light + focus it onto the retina at the back of the eye
How does the eye detect light?
Light rays pass thru the cornea → pupil in the centre of the iris → lens
Lens focuses LR onto the retina (back of eye)
Receptor cells in retina send the EI down the optic nerve to the brain
When brain receives these messages + interprets them as a visual image
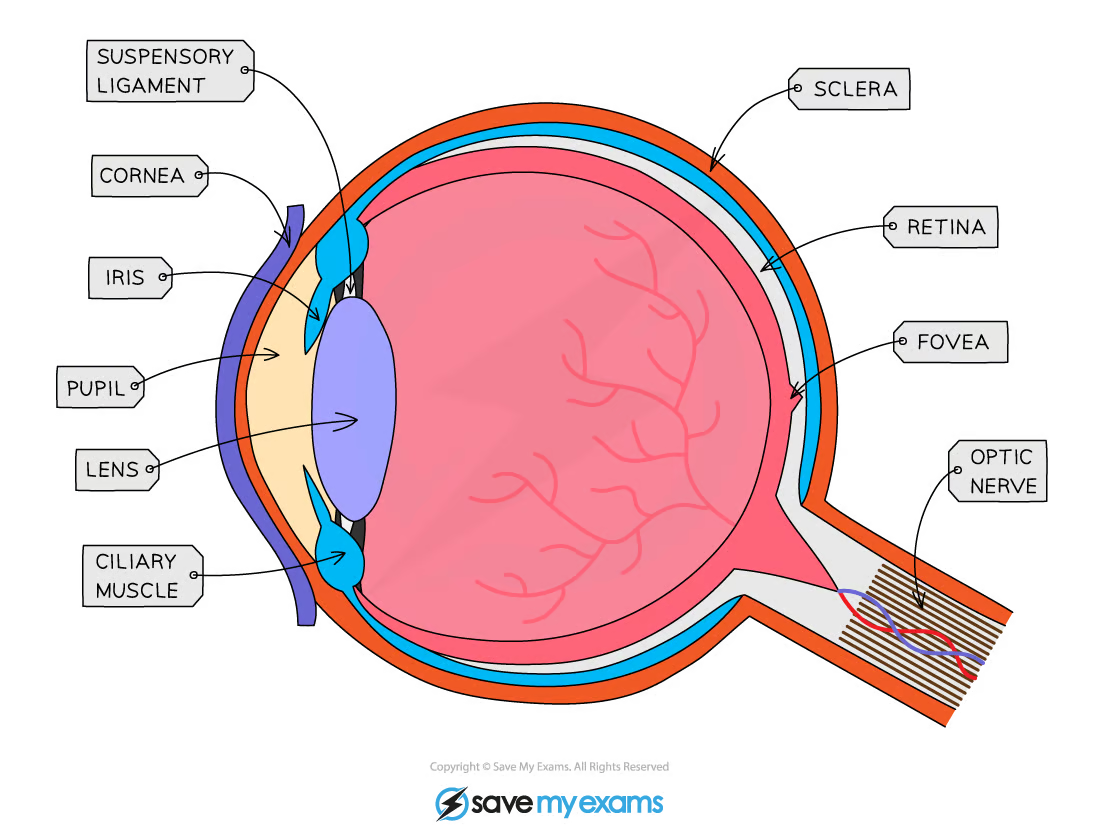
* Tough outer structure that protects the eye
Optic nerve
Sensory neurone that carries impulses betw the eye + the brain
How do the ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments work with the lens?
Allow us to focus on distant or near objects
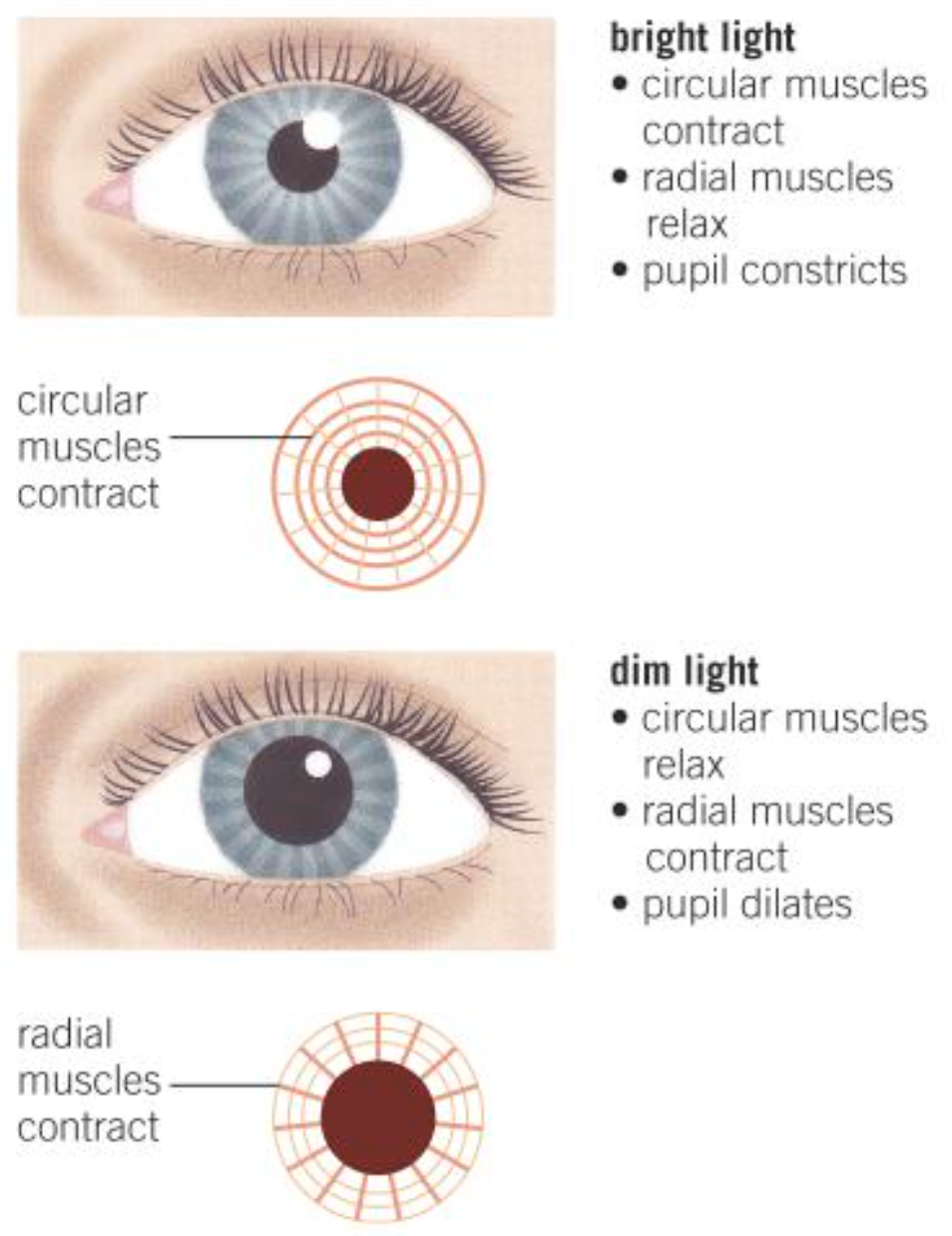
What two groups of muscle is the pupil reflex controlled by?
Radial muscle
Circular muscles
Blind spot
Point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye that has no retina
But the brain fills in the gap
How does focusing light differ in the cornea and the lens?
Cornea: fixed focus
Lens: allows us to focus on near and distant objects (shape of lens can change)
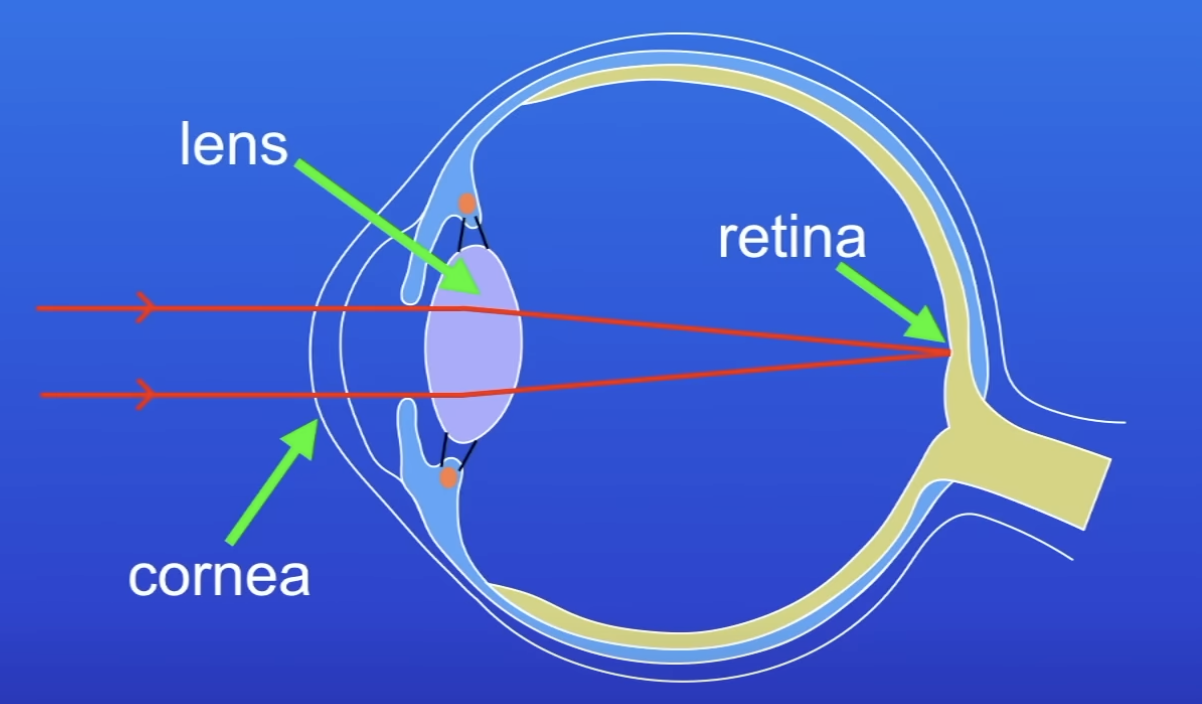
How does light from distant and near objects need to be focused and why?
Distant: small amount
Light from distant objects travels in almost parallel rays
Near: a large amount
Light from near objects spreads out v strongly
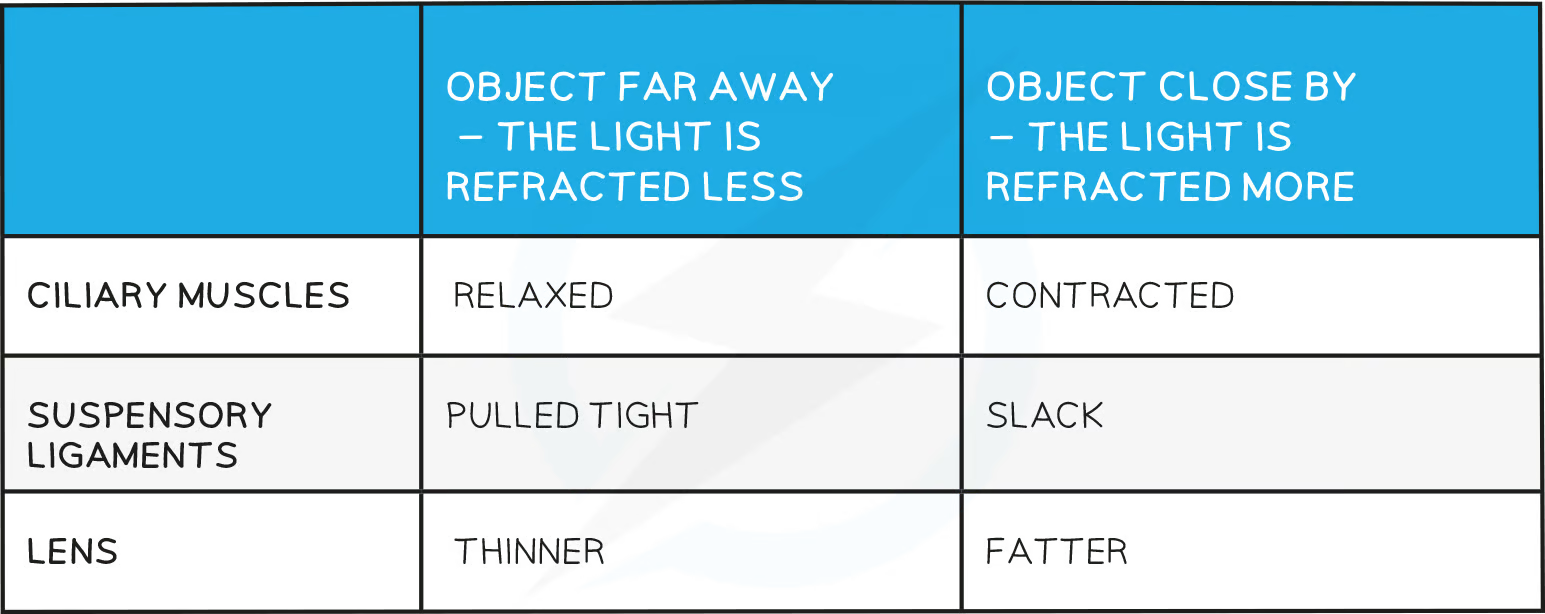
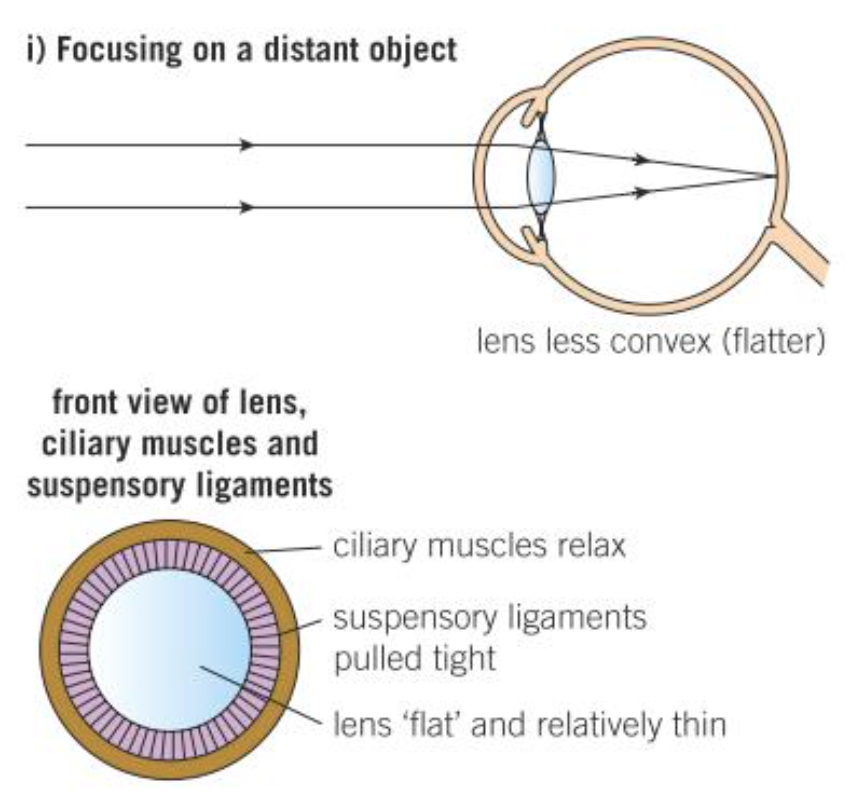
How do we focus on distant objects?
Ciliary muscle relaxes
So suspensory ligaments pulled tight
Lens pulled thin
So LR only slightly refracted
LR will be focused on a point on the retina
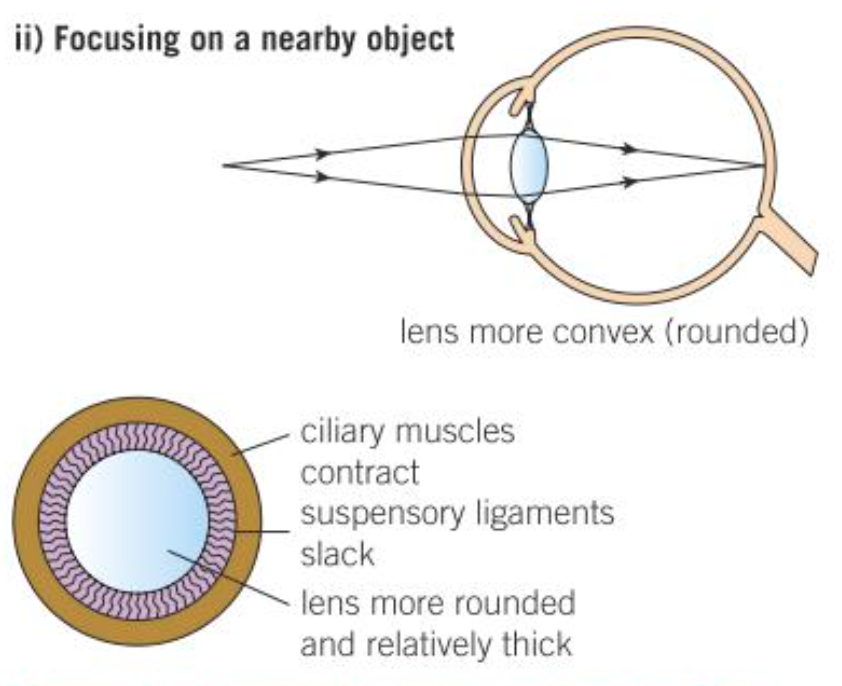
How do we focus on near objects?
Ciliary muscle contracts
So the suspensory ligaments loosen
Lens is thicker
It refracts the LR more strongly
The LR will be focused on a point in the retina
Hyperopia
Long-sightedness
Can focus on distant objects
Can’t focus on nearby objects
* Can focus on near objects
* Can’t focus on distant objects
How is an image formed?
Upside down
But the brain interprets it the right way up
General causes of eye defects
Light rays don’t focus correctly on the retina
So they are short or long-sighted
Image on retina = out of focus
What is the brain made of?
Billions of interconnected neurones
What does the brain have?
Diff regions that carry out diff functions