Taxonomic Evidence: strcutural and Biochemcial characters. Floral Morphology and pollination
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What are the reproductive structures of angiosperms called?
Flowers, which is a modified shoot bearing specialized appendages (modified leaves)
What are modified shoot called?
Receptacle
What is the floral stalk referred to?
The Pedicel
How are flower usually born in?
Axil of a more or less modified leaf known or a bract
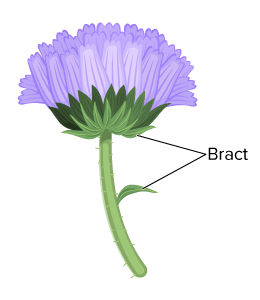
What is a bract?
Smaller leaf like structures
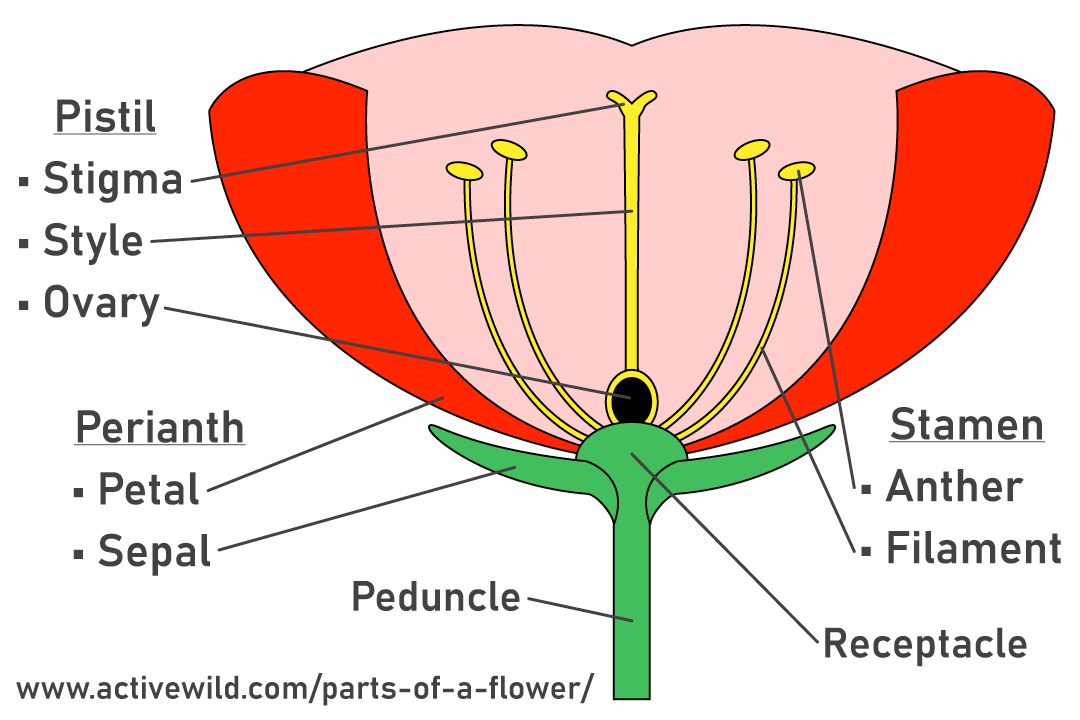
What are the three major parts of a flower?
Perianth (outer protective/ or colorful structures), Androecium (pollen producing) and the gynoecium (ovule-producing)
What are flowers that have all three major parts?
Complete
What is the difference between and perfect and imperfect flower?
If flower is bisexual (perfect)
Or if either is lacking is unisexual (imperfect)
What qualifies a species to be monoecious?
Both staminate and carpellate flowers are borne on a single ind
What qualifies a species to be dioecious?
The stameninte and carpellate flowers are borne are borne on separate individual plants.
What is a whorl and the 4 whorls of a flower?
circle of plant parts; a circular arrangement of three or more similar anatomical parts.
Calyx
Corolla
Androecium
Gynoecium

What are tepals?
The Perianth parts that are undifferentiated, Calayx and Corolla look the same
What is the outer whorl composed of, and what is it collectively known as?
Sepals, collectively called the Calyx
What is the inner whorl composed of and collectively known as?
Petals, collectively called the corolla
How can you tell the difference between sepals and petals?
The sepals are green and provide protection for the developing flower and petals are colored and showing used to attract pollinators
What does the androecium comprise of?
All the stamens which are differentiated into anther and filament.
How many pollen grains do anthers contain?
4 pollen sacs which a re connected by teh connective.
What are all the carpels composed of?
The gynoecium, this is the site of pollination and fertilization in the flower.
Stigma, collects and facilitates the germination of pollen
Style, a usually slender region specialization for pollen tube growth
Ovary: enlarged basal portion that surround and protects the ovules
What does it mean when a flower has actinomorphic/ radial symmetry?
The parts are arranged so that two or more planes bisecting the flower through the center will produce symmetrical halves
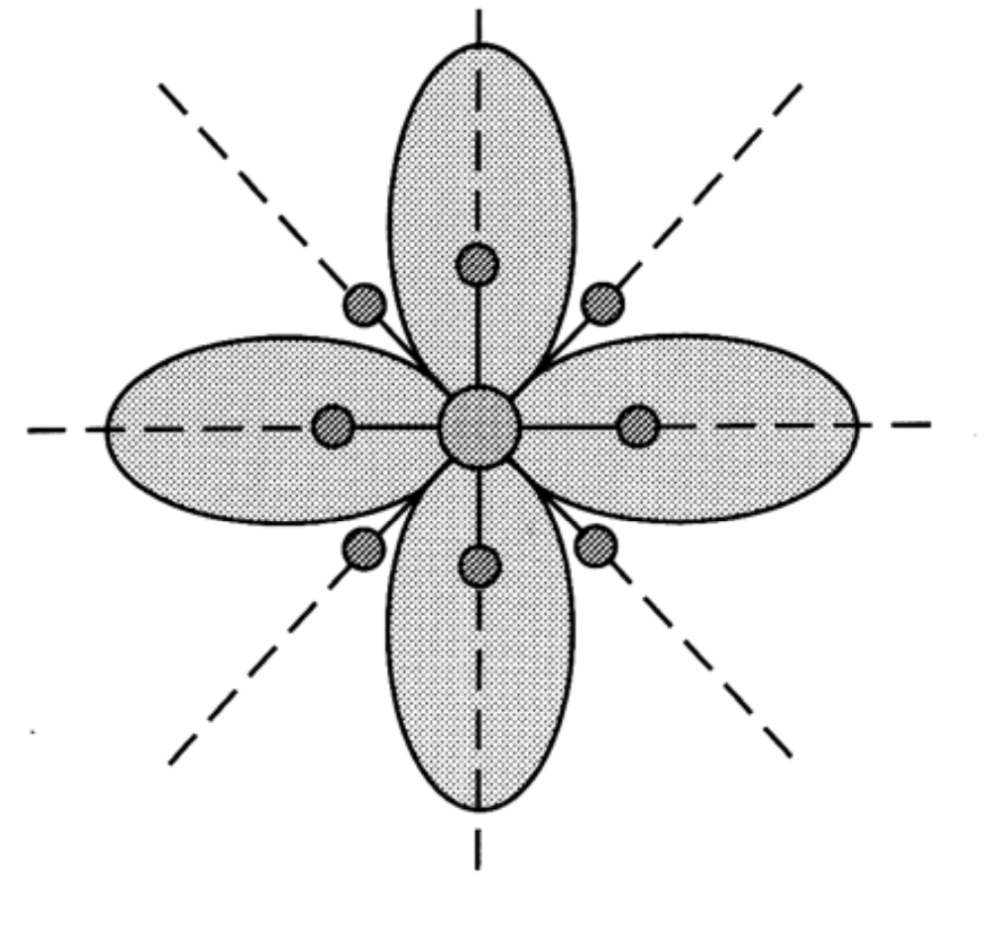
What does it mean when flower parts have bilateral symmetry also known as zygomorphic.
The parts of the flower are arranged so that they can be divided into symmetrical halves only on one plane
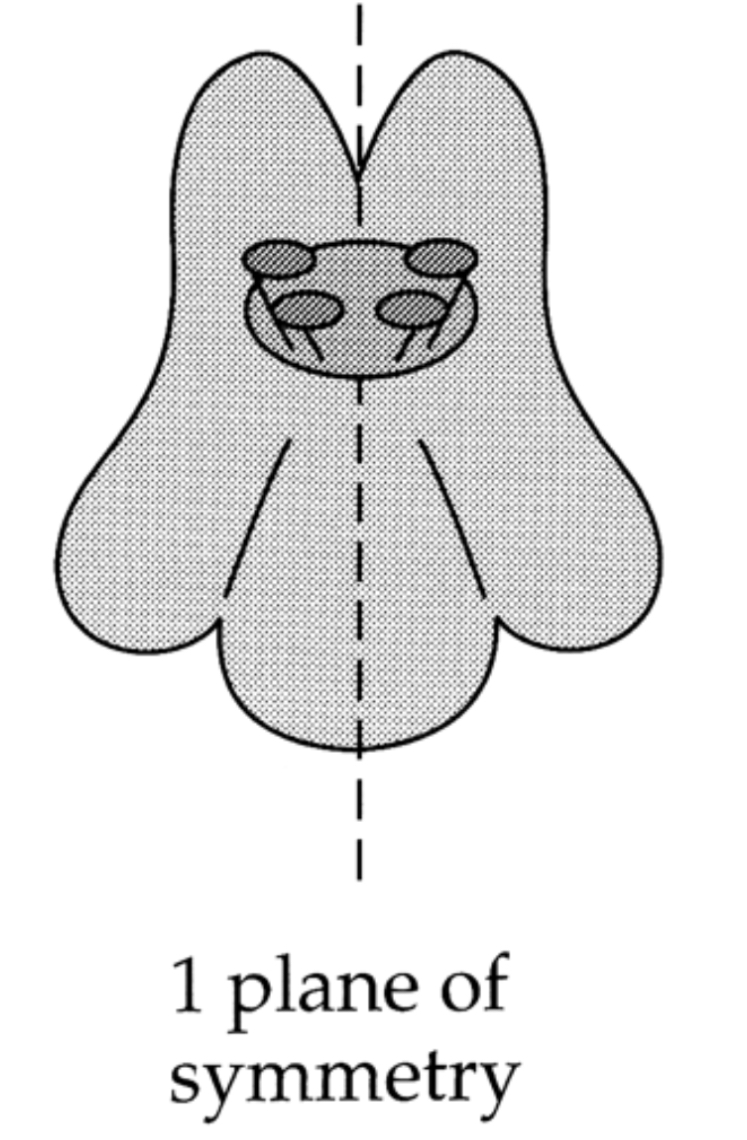
What are a few flower that have no plane of symmetry known as what type of symmetry?
Asymmetrical
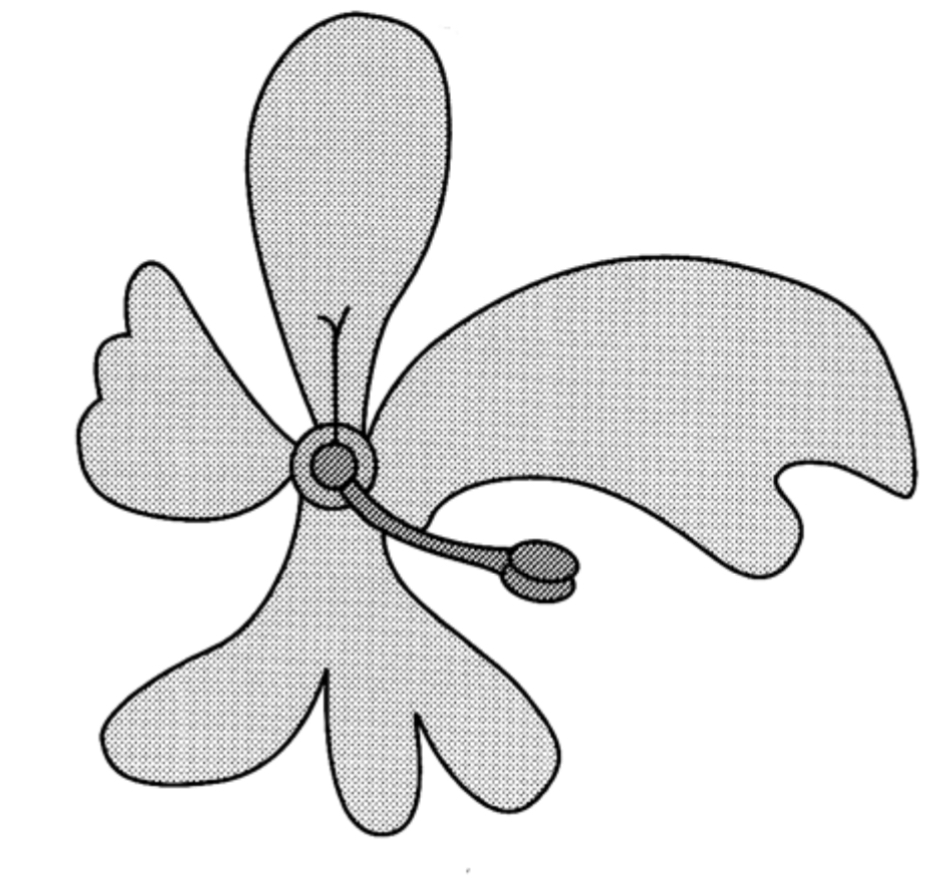
What is the fusion of like parts called?
Connation
What is the fusion of unlike parts?
Adnation
What is apocarpus?
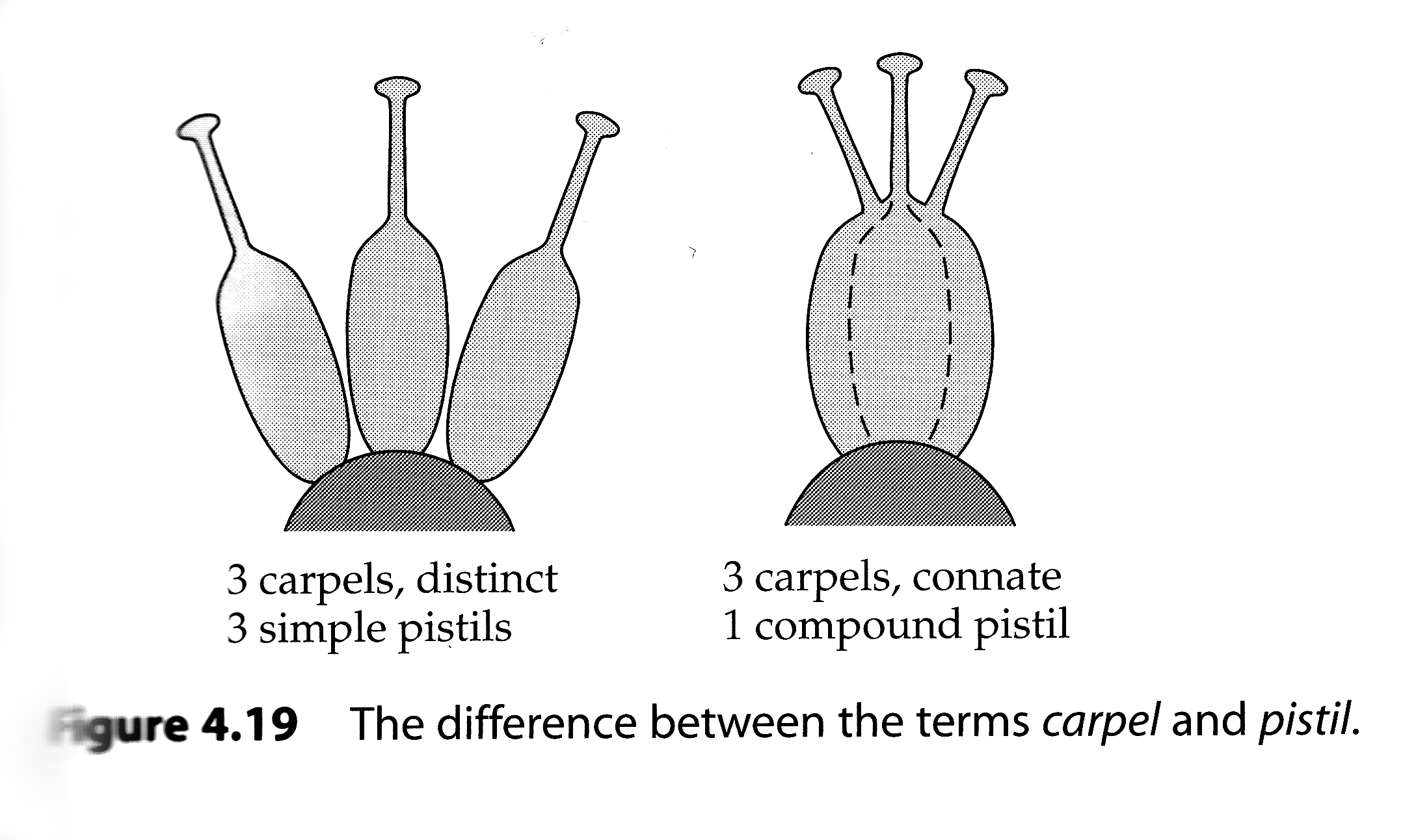
How does the Pistil differ form Carpels?
Carpels are the basic unit of the gynoecium, can be distinct or connate. If they are distinct, then the term pistil is equivalent in meaning to the term carpel. If connate, the terms aren’t equal bc each carpel constitutes only one unit within a pistil→ compound
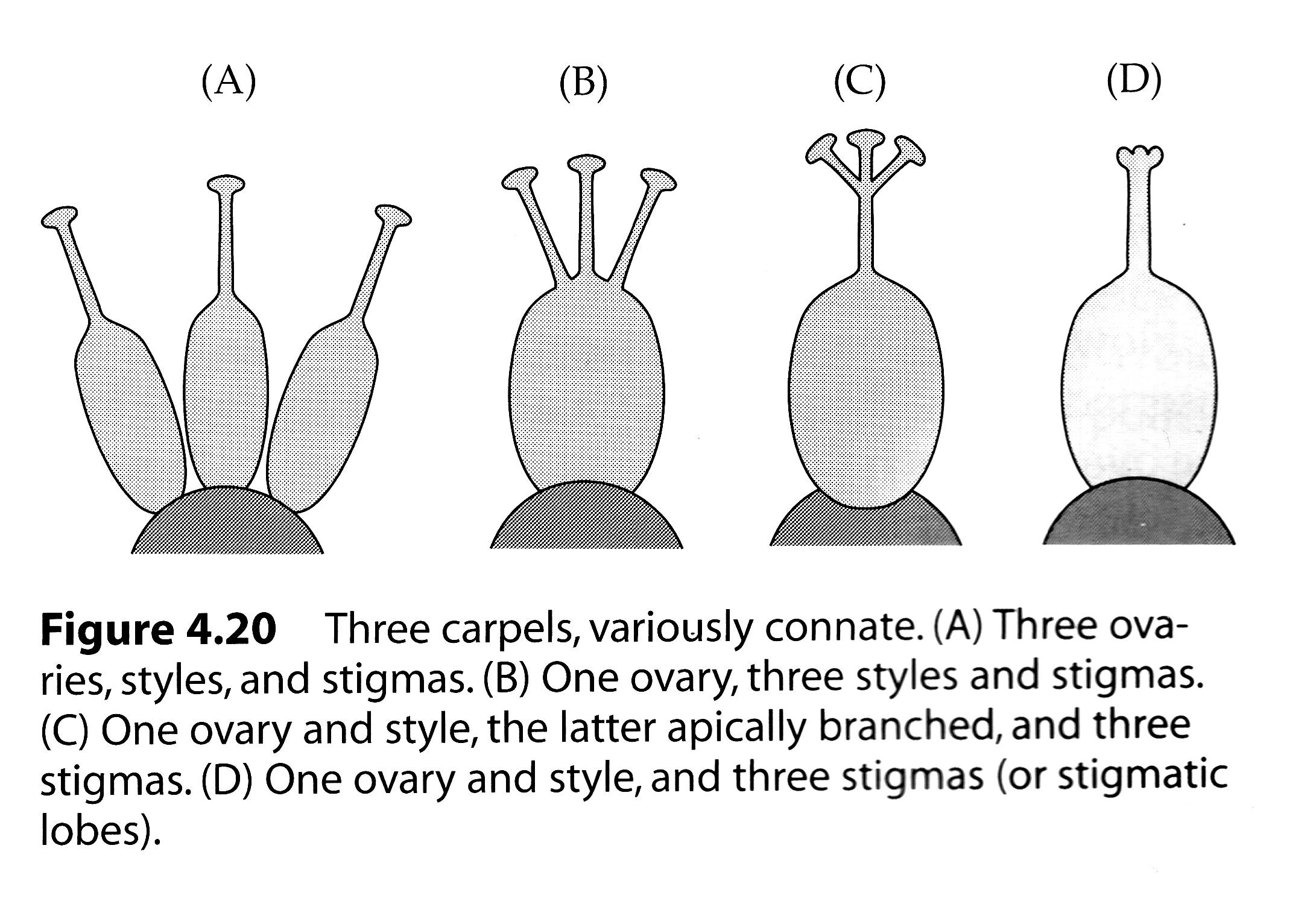
What is some ways to figure out the number of parts in extreme connation?
Count fused carpels by number of styles, stigmas or stigma lobes,
Placentation
Also most flowers are based on a particular numerical plan- patterns of 3, 4 ,5 or various multiples
What are the three major insertion types?
Hypogynous, perigynous and epigynous
Flowers that care called hypogynous mean with?
Means in which the Perianth and androecium are inserted below the gynoecium
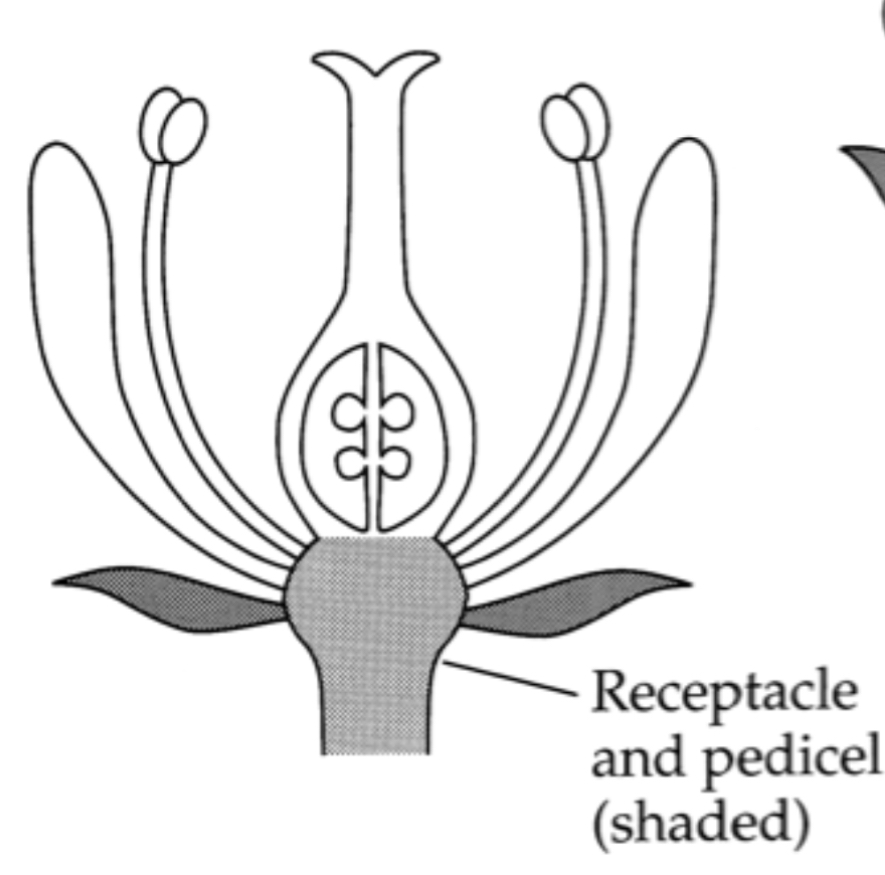
What are the ovary Said to be when the plant is hypogynous?
Superior
What does it mean when a ovary is said to be Epigynous?
Occurs when the Perianth and Stamens appear to be attached to the upper part of the ovary due to the fusion of thy hypanthium
If a flower said to be epigynous what is the ovary structure?
Inferior
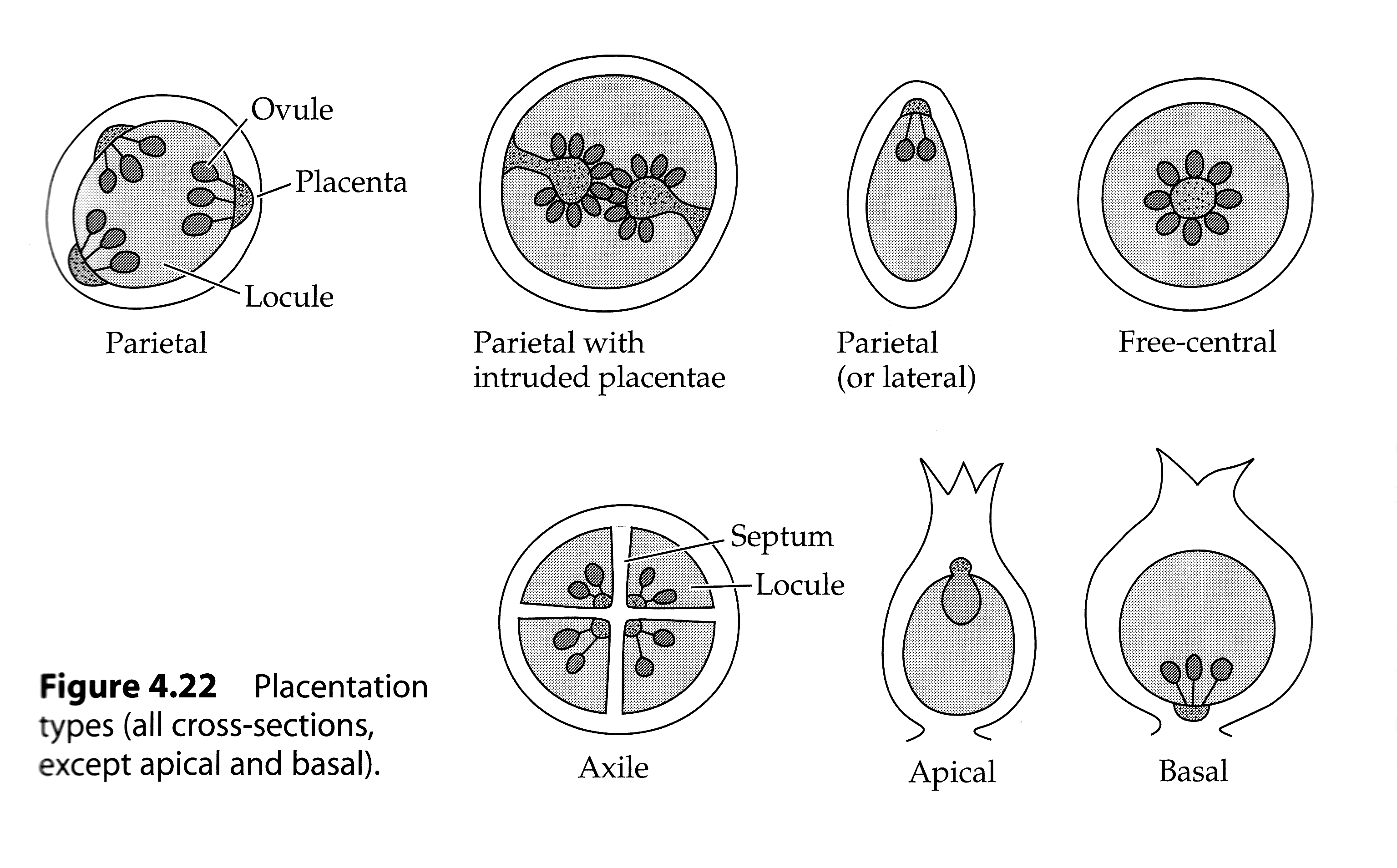
What is the wall separating adjacent locules called?
Septum (or septa)
What are the major Placentation types
Parietal, free control, axile, apical and basal
What does basifixed mean?
Referring to structure such as anther, that is attached to its base.
What does Didynamous mean?
Having two long and two Short stamens
What is a stameninode?
A sterile Stamen
What does it mean when a plant is tetradynamous?
Having 4 long and two short stamens
What is process of pollination
The sperm of seed plants are package in pollen grainS
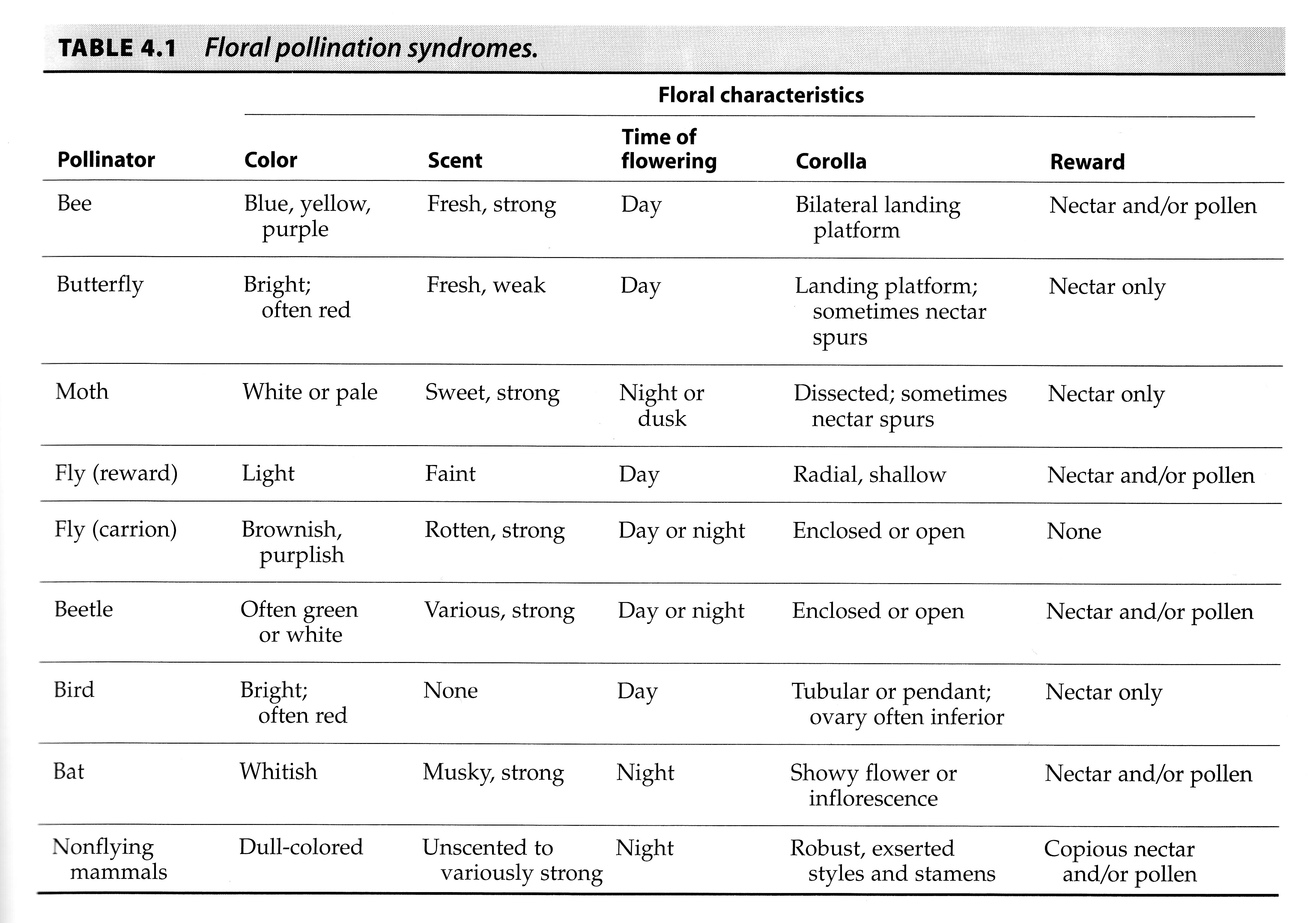
What are the three pollination syndromes?
Wind
Water
Animal
How can you tell if a flower is wind pollinated?
By the production of a large amount of pollen that is readily transported by wind currents and by efficient means of trapping airborne pollen.
Are small and lack much of a corolla, including grasses, sedges, oak and beeches
What is animal pollination?
More efficient transporters of pollen than wind, they can be found where there is little wind. They promote cross pollination.
Floral Pollination syndromes
Pollination
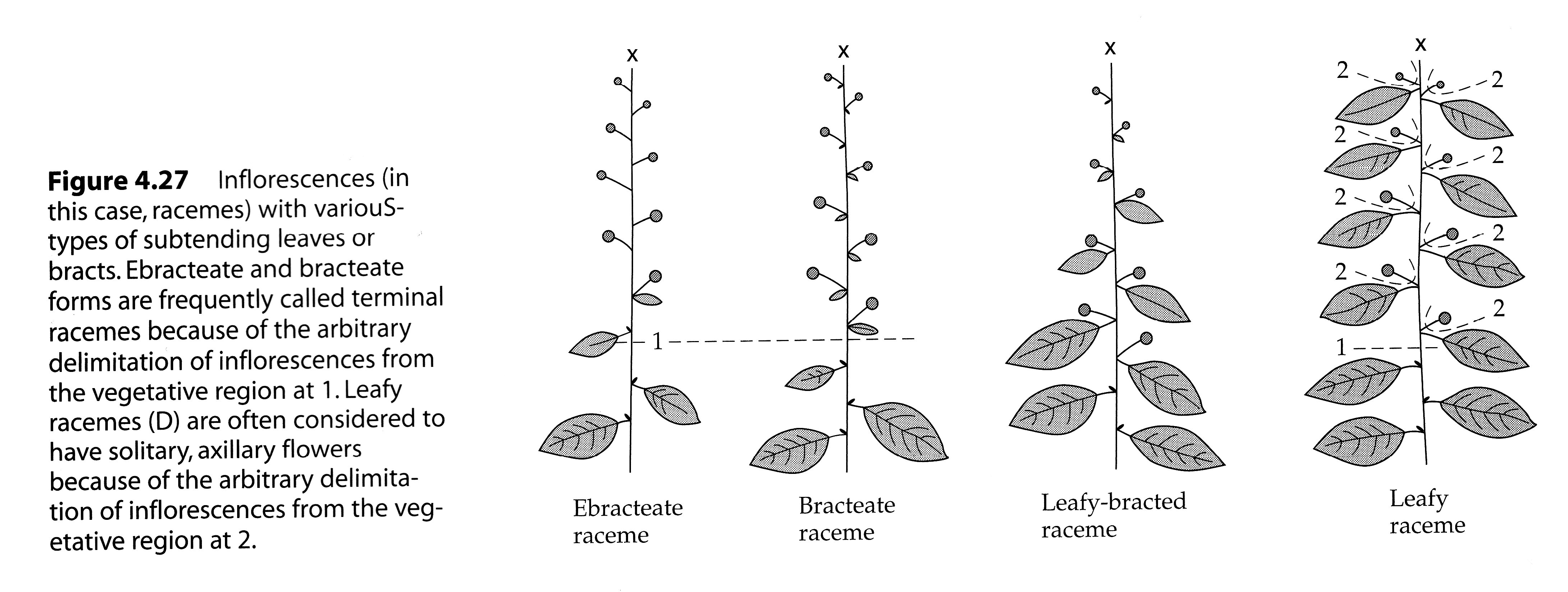
What is the definition of an inflorescence?
As the shoot system which serves for the formation of flower of flowers and which is modified according. The arrangement of flowers on plant
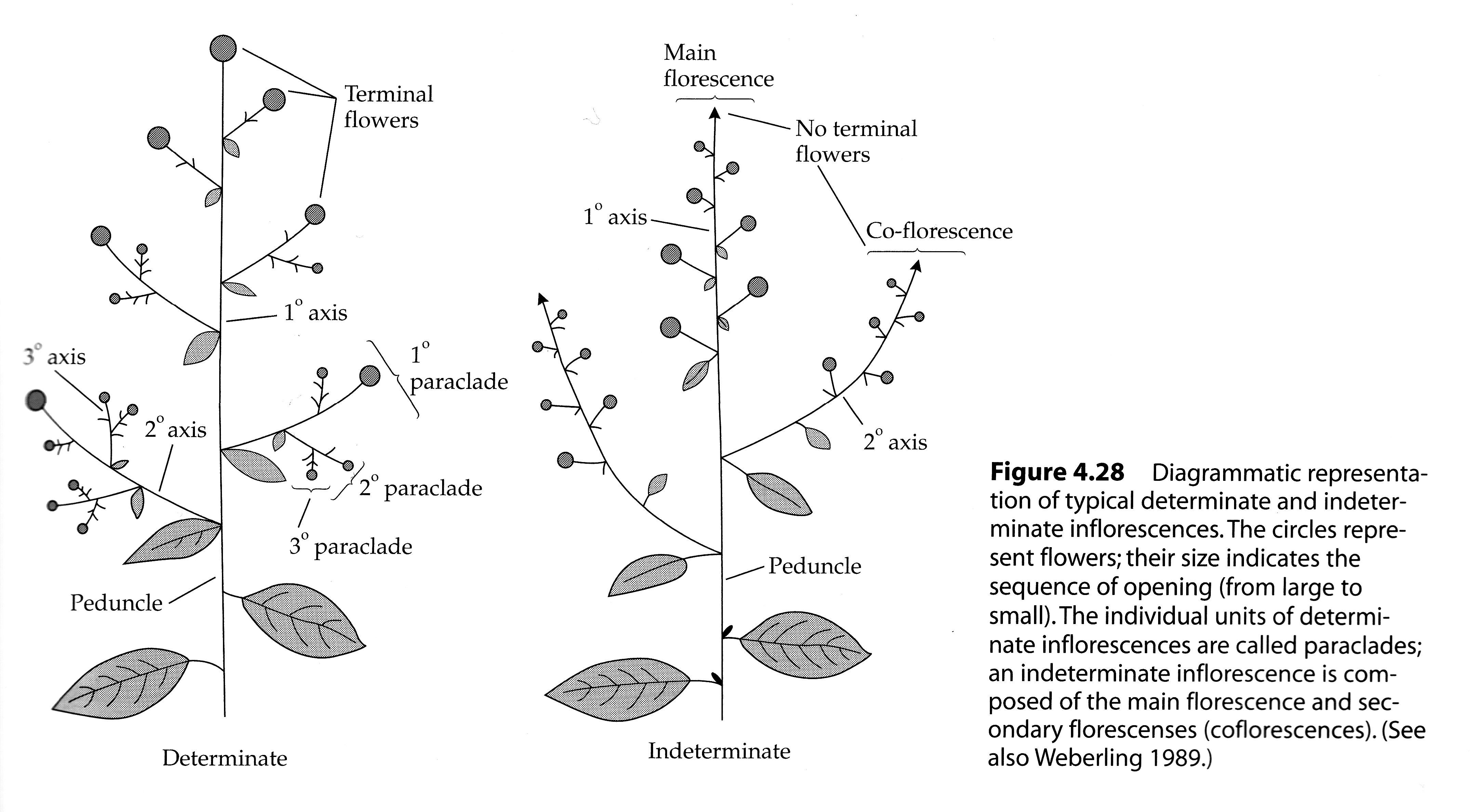
What are the two inflorescence types that occur in angiosperms?
Determinate (main axis ends in a flower )and Indeterminate (growing produces only lateral flowers
What is a fruit?
Is a mature ovary along with fused accessory structure (hypanthium or Perianth parts)
Simple fruits are divided into two categories, what are they
Those formed from a single carpel or several fused carpels
Those that develop from several separate carpel of a single gynoecium (aggregate)
What is the formation of a multiple fruit?
Product of the gynoecia of several closely clustered flowers