BF
1/208
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
209 Terms
what fluids are studied
cerebrospinal (brain + spine)
synovial (surrounds joints)
serous
what does serous fluid consist of
pleural (chest cavity and lungs)
peritoneal (fluid between abdomen and organs)
pericardial (around heart)
routine analysis of BF
gross examination
total cell count
differential count
microbiologic examination
chemical analysis
cytology examination
function CSF
cushion
waste collection
nutrient circulation
lubrication
regulate volume of intracranial pressure
chemical environment
where does CSF circulate between
pia and arcahnoid layer
what processes if CSF involved in
active secretion
transport
ultrafiltration from plasma
csf three membranes and meanings
dura matter = outer
arachnoid = middle
pia = inner
normal CSF volume in adults
90-150 mL
normal CSF volume neonate
10-60 mL
turnover of CSF per day and hour
500-600 mL/day
20 mL/hour
what is increased CSF called
hydrocephalus
when does hydrocephalus occur
circulation is blocked or reabsorption is impaired
how is CSF collected , and where
how much can be safely removed
lumbar puncture
L3 and L4 lumbar space
L4 and L5 for neonates
10-20 mL of fluid
what would you record for CSF collection
total volume of the tap in all tubes
how many tubes of CSF is collected, where do they go
3
chemistry
micro
hematology
w
what would a 4th tube of CSF be used for
observation of a pellicle
when is CSF stable
within an hour , no clots
do you refrigerate CSF
NO
what does it mean when CSF exhibits xanthochromia
contains bilirubin
what is xanthochromia
yellow discoloration
what is cell count performed on
hemacytometer
what can CSf indicate
infection of meninges
subarachnoid hemorrhage
CNS malignancies
demyelinating disorders
example of menginges infection
bacterial meningitis
example of CNS malignancy
acute leukemia
example of demyelinating disorder
multiple sclerosis
what does CSF lab analysis involve
gross examination
microscopic examination
chemical analysis
whats involved in CSF gross examination
color, clarity, clotting ← bleed or poorly drawn
whats involved in CSF microscopic examination
RBC, WBC counts, differentials
what is involved in CSF chemical analysis
glucose and protein
what do you do to distinguish a traumatic tap from an intracranial hemorrhage
observe clearing from tube to tube
what indicates a traumatic puncture
first tube contains blood , but remaining are clear
what does it mean for CSF if all tubes are uniformly bloody
subarachnoid hemorrhage present
what does it mean if CSF (supernatant?) is clear
traumatic tap
blood at bottom
what does it mean if CSF (supernatant?)is yellow or pink- what does each color mean
hemorrhage
yellow = bilirubin broken down, OLD BLOOD
pink = fresh NEW blood
what does it mean if CSF after centrifugation is clear
bacteria
what should you observe for in CSF after centrifugation
xanthochromia
what does subarachnoid hemorrhage sample look like in 1-4 hours , what does it contain
pale pink ← oxyhemoglobin
erythrocyte
neutrophils
lymphocytes
what does subarachnoid hemorrhage sample look like in 12 hours , what does it contain
yellow xanthochromia (bilirubin)
peaks 2-4 weeks
macrophages englufed with RBCs OR stored iron (hemosiderin)
1-8 weeks siderophages
should CSF clot? why?
no, CSF does not contain fibrinogen
characteristics of traumatic tap
blood decreasing amounts
clot formation
colorless supernatant
negative D dimer
characteristics of subarachnoid hemorrhage
blood is in equal amounts
does not clot
xanthrochromic
positive D dimer
hemosiderin
what is normal for CSF gross examination
CSf should be clear
what is normal cell count for CSF
adult 0-5 uL
neonate 0-30 uL
what is CSF normal differential
lymphocytes and monocytes normal
lymph 60%, mono 30%, poly 2%
what is CSF normal chemical examination
glucose : 50-80 mg/dL
protein 15-45 mg/dL
where is cell counts performed
chamber with undiluted fluid
equation for cell count
(#of cells counted ) x (dilution)
__________________________________
(#of squares counted) x (volume of 1 sq)
when is protein count in CSF higher
neonates have higher count that adults
after the age of 40 it increases as well
what does increased CSF protein indicate
traumatic tap
increased permeability of blood CSF barrier
infections
subarachnoid hemorrhage
increased synthesis of IgG, neurosyphilis, MS
what do CSF glucose values need to be compared to
serum glucose values
what is the normal adult CSF glucose levels
60-70% of plasma levels
what is an increased CSF glucose related to
plasma elevations w
what is a decreased CSF glucose value related to
impaired glucose transport
increased glycolytic activity
increased glucose utilization by bacteria
what in CSF aids in diagnosing and managing meningitis
CSF lactacte
what are the causes of an incease in CSF lactate levels, and what are their values
bacteria : <35 mg/dL
viral 25 mg/dL
w
what can CSF lactate also be used to monitor
head injuries , tissue destruction
what is pleocytosis
increased amount of WBCs in body fluid
type of WBC correlates with condition or disorder
what do neutrophils indicate
bacterial infection
what do lymphs indicate
viral
Guillain Barre (own immune system attacks nerves)
what do plasmacytes indicate
multiple sclerosis
what do eosinophils indicate
allergic reactions
rare
example: shunt
what do monocytes/macrophages indicate
phagocytized
what can b seen in CSF
WBC, RBC
ependymal
macrophage
malignant cells
what do WBCs indicate in CSF
inflammatory or infectious process in CNS
meningitis → increase in WBC
what do RBCs indicate in CSF
subarachnoid hemorrhage
intracranial bleeding
what produces CSF into brain ventricles
the choroid plexus
what do germinal matrix cells have to do with CSF
give rise to various cell types in CNS
what do macrophages indicate in CSF
inflammatory response or immune reaction in CNS
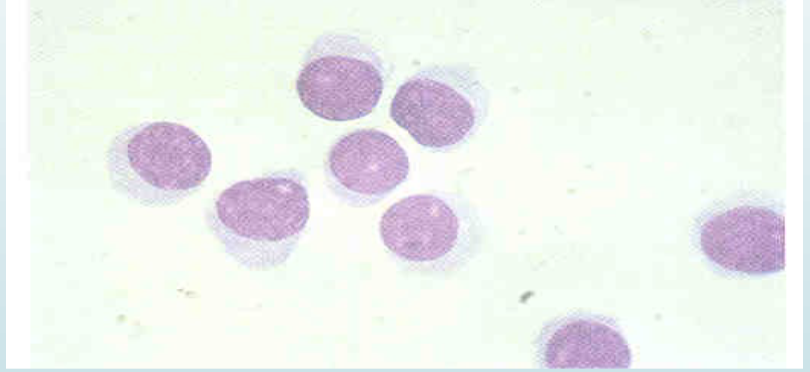
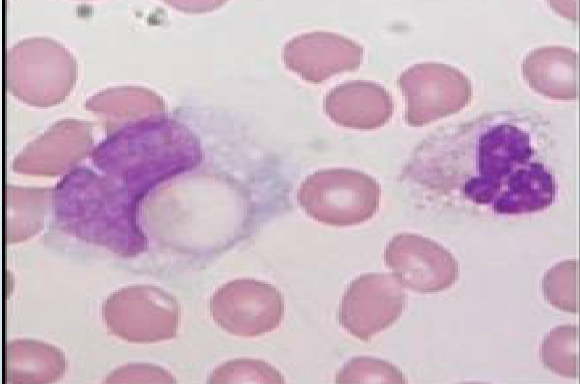
what is this cell
lymphocyte
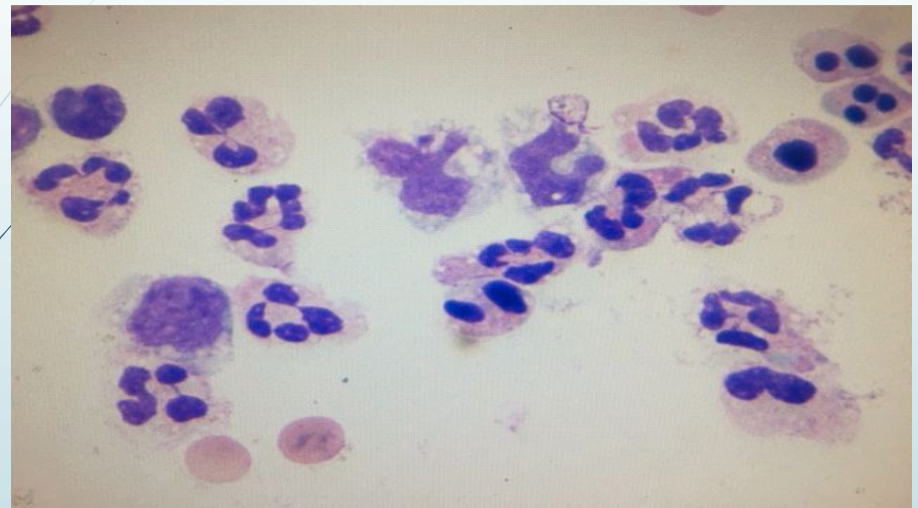
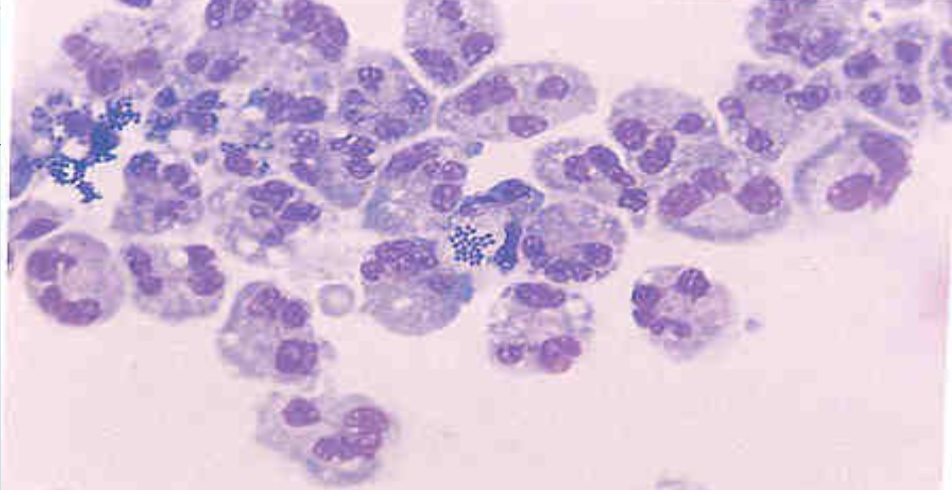
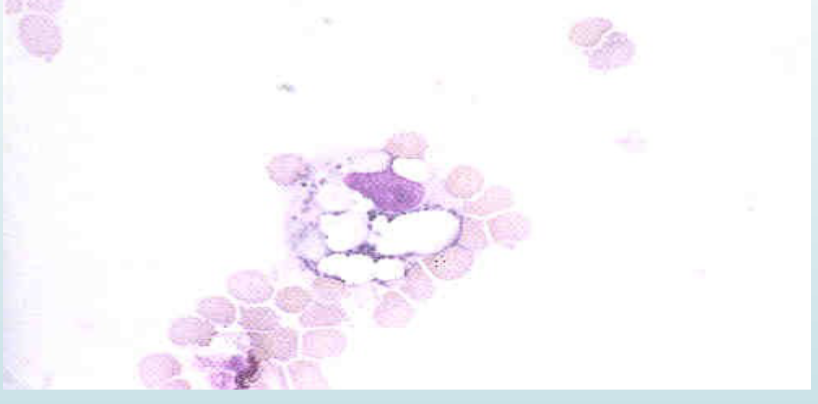
what is seen in the picture
segs, monos, and nRBCs
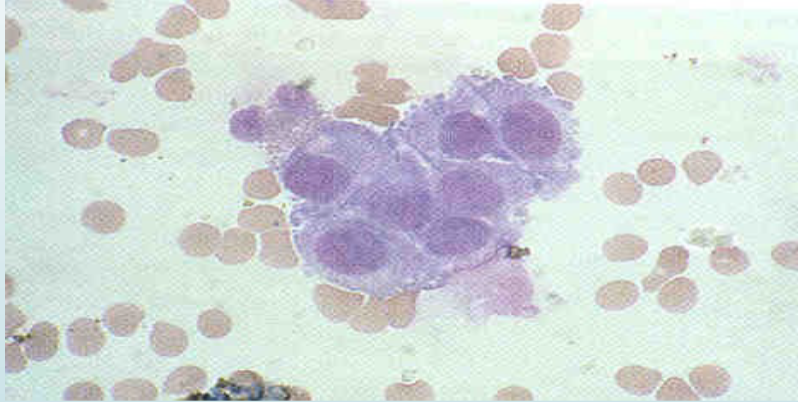
what is pictured
the choroid plexus
eccentric nucleus
lining cells
waxy cytoplasm
clustered together
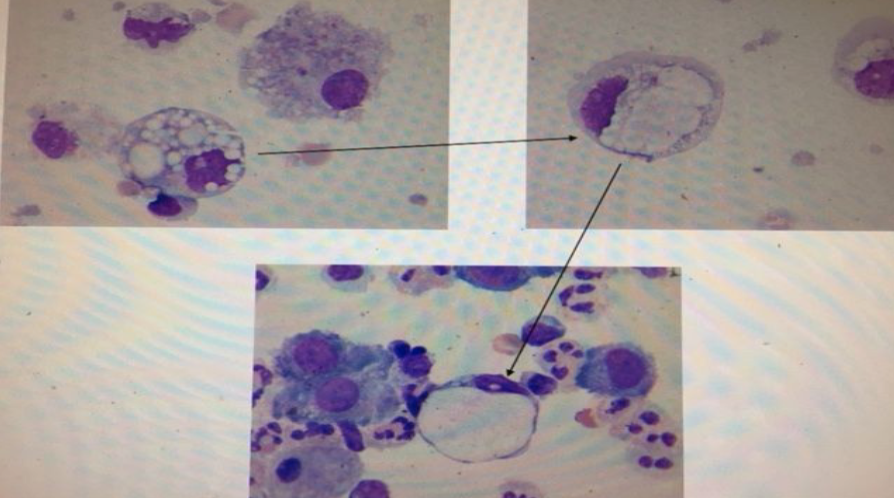
signet ring
monocyte phagocytizing vacuole
what is pictured
subarachnoid hemorrhage
what are WBC levels / findings in Bacterial Meningitis
>50k WBC/uL
90% neutrophils
INC protein
DEC glucose
what can cause bacterial meningitis
H influenzae
S pneumonia
N meningitis
GBS
what is seen in viral meningitis
mild - severe leukocytosis
predomiately lymphs → large and reactive
what causes viral meningitis
enteroviruses
what are the types of acute leukemia
lymphoblastic
myeloblastic
what causes fungal meningitis
cryptococcus neoformans (india ink)
low or normal glucose
elevated protein
what is seen with intracranial shunts for hydrocephalus
increased monocytes
iINC macrophages
INC eos
where are malignant cells more common
lung
breast
GI
neutrophils with bacteria
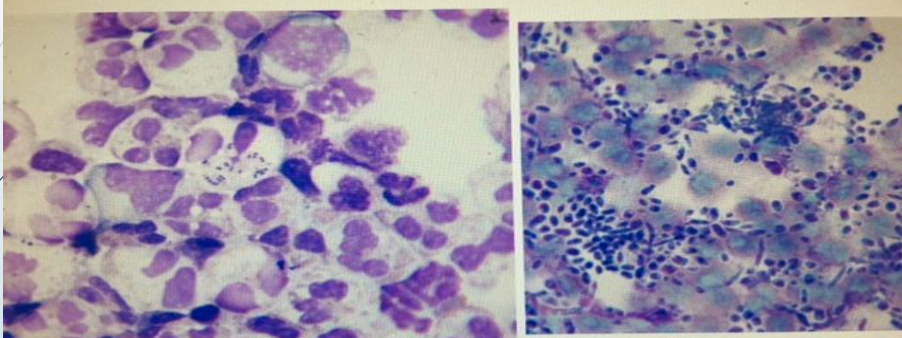
bacteria and yeast
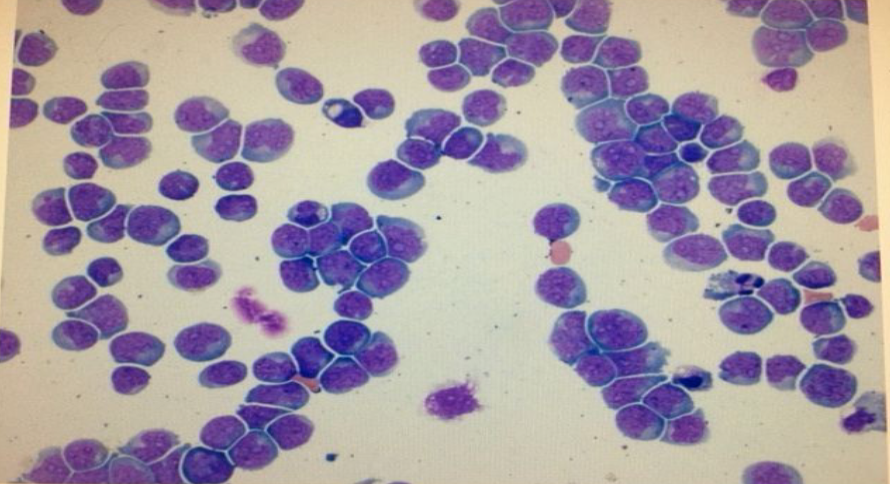
acute leukemia
intracranial hemorrhage
what is synovial fluid? where is it found
supplied nutrients to cartilage
lubricant to surface joints
removes debris
found in joint cavities
what is general normal chemical composition of synovial fluid like? why
same as plasma
it is ultra-filtrate of plasma
what are some properties of synovial fluid
straw color
viscous
essential to proper lubrication
hyaluronic acid
hyaluronate = mucopolysaccharide for viscosity
what is the normal volume for synovial fluid,where is it found
1-4 mL
knee, hip, elbow
what does a large amount of synovial fluid volume mean
disease process
what are normal WBC value for synovial fluid ? what composes that
<200 uL
lymphs are majority (mononuclear)
<25% neutrophils
what is normal for synovial fluid in terms of RBCs and crystals
there should be none seen
how is synovial fluid collected? how many tubes?
arthrocentesis with a heparinized needle
three tubes
should there be clots in synovial fluid? why?
NO
does not contain fibrinogen
what should the patient do before synovial fluid collection
fasting for 6 hours
what are the tubes used for in synovial fluid
1: sterile for micro
2: heparin/EDTA for microscopy
3: plain tube for clot formation, gross examination, chemical examination
what is preferred for the 2nd tube in synovial fluid
heparin
what is involved in routine examination of synovial fluid
physical appearance
cell count
differential
crystal exam
chemical
physical appearance for synovial fluid
color viscosity, clarity
cell count for synovial
RBC and WBC