Bio 2 Unit 1 Microscopy
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
problem with fluorescence
How do you distinguish excitation light that is reflected or scattered from the sample from light that is absorbed and emitted?
How to tell what is signal and what is noise?
noise
amorphous high level background fuzz
propagation
control the ______ of light through the optical train with barrier and beam-splitting mirrors
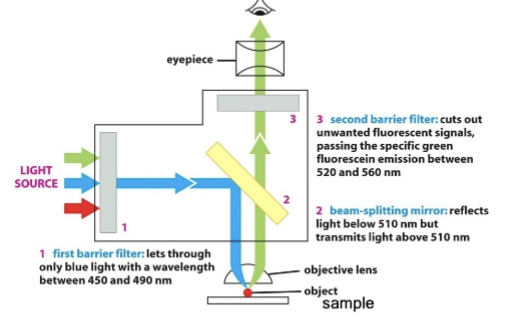
barrier filter
use this to only allow precise wavelengths of light for excitation (#1)
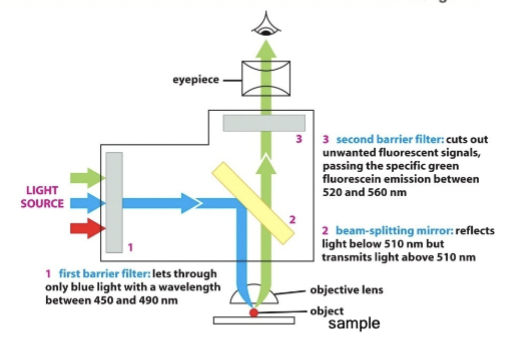
beam-splitting filter
place this in the optical train that reflects excitation but passes emission wavelengths (#2)
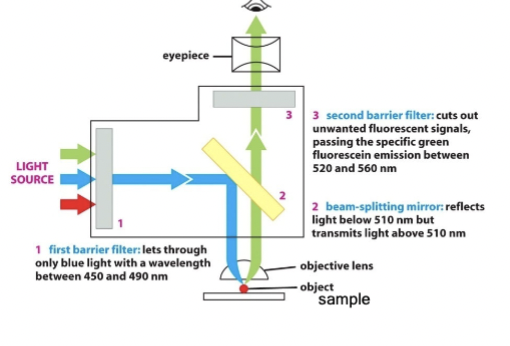
block unwanted
place an additional barrier filter (#3) to _____________ wavelengths (because #1 and #2 are not perfect)
advantages of fluorescence microscopy
can follow live-events within cells via fluorescent proteins, and can “interrogate” local environment non-intrusively via biosensors
problems with fluorescence microscopy
all planes of light are combined into one. can resolve sub-cellular structures (~250 nm) but not protein level structures (~1 nm). phototoxicity
sea of fluorescence
excitation light re-enters objective from all layers of sample
total internal reflection microscopy
alternative to fluorescence microscopy; Use critical-angle excitation to illuminate only the thin section adjacent to the coverslip. Cannot "see" beyond ~ 125 nm
confocal microscopy
alternative to fluorescence microscopy; Use pinholes to remove out of plane fluorescence, but reduces the signal levels
super-resolution light microscopy
alternative to fluorescence microscopy; a variety of new techniques that overcome resolution limits by controlling the waveform or "structure" of incident light or by counting individual emitted photons.
electron microscopy
Alternative to fluorescence microscopy; Use higher energy optics using electrons not photons. Provides higher resolution, but must use harsh fixation and complex post-fixation techniques (dead tissues).
atomic force microscopy
alternative to fluorescence microscopy; physiological microenvironment, but must "touch" samples.
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
A fluorescence microscope that could collect information from a single "optical-slice", ignoring all other light. Patented in 1961 by Marvin Minsky to study the neuronal basis of cognition
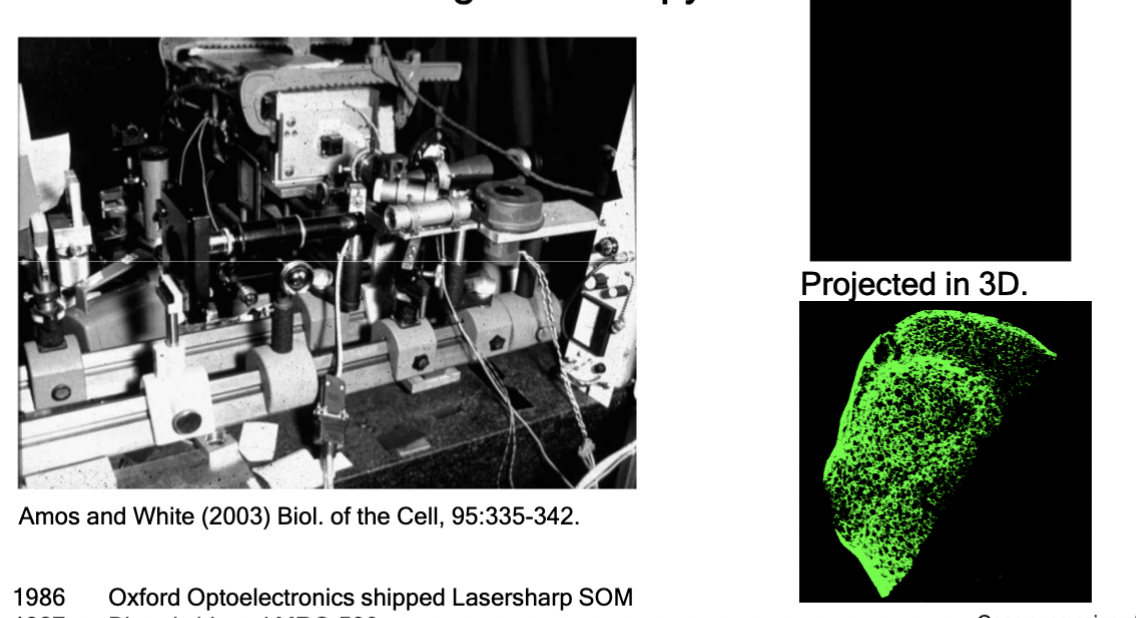
required advancements for confocal microscopy
high power light source, e.g. lasers
high sensitivity detectors, e.g. photomultiplier tubes (PMTs)
high speed scanning and de-scanning, e.g. computers
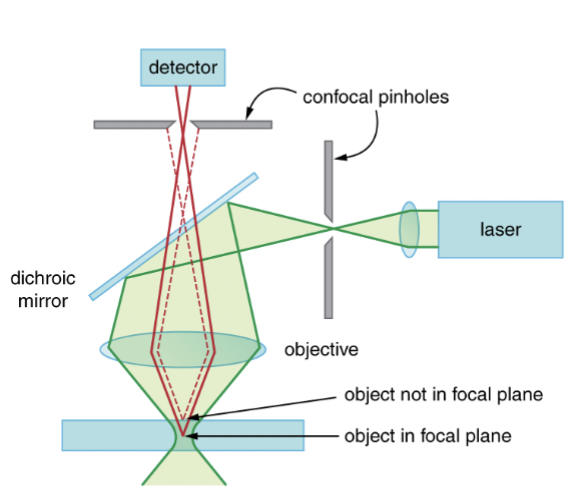
How a Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope Works
A laser (light source) is focused on a single point in the sample.
The pinhole only lets light through to the detector that comes from a single focal plane in the sample.
Light from other focal planes are blocked (definition of confocal).
The laser "focus" is swept across the sample volume, X/Y, and Z. ("laser scanning")
A computer processes the stream of data from the detector and assembles "optical" sections.
Fluorescence filters are required but not shown here
phototoxicity
problem with confocal laser scanning microscopy: Intense laser light can disrupt cellular function
photobleaching
problem with confocal laser scanning microscopy: Laser can heat the sample, denature proteins, generate free-radicals, bleach fluorophore, etc
spinning disk
alternative to confocal laser scanning microscopy; Single point of scanned laser illumination is replaced by ____________ with many pinholes, and PMT replaced by CCD camera.
Benefits: not as phototoxic and very fast
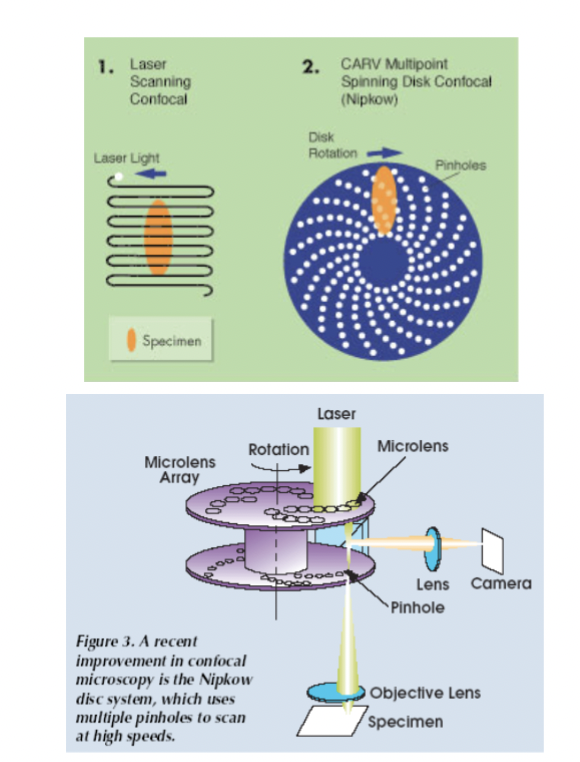
problems with spinning disk
low intensity, cannot adjust pinhole, cross-talk between light incident through one hole and emitting through another. Thick fluorescent samples lead to the problem "Sea of Fluorescence". Optical limits to resolution, etc
fixing low intensity and optical limits
Vastly improved sample preparation: great new FPs such as mNeonGreen, iRFP, improvements in reagents to clear samples such as RIMS, CLARITY, and 3DISCO
New light microscopes including light sheet, structured illumination (SIM), PALM, STORM, etc.
new light microscopes
10 nm resolution with light microscope - look at where each photon comes from in the sample and project the structure
reporters, biosensors, optogenetics
FP probes to measure and control cellular processes; can help fix optical limits to resolution
new modalities
electron microscopy, optical tomography (OCT, whole animal), atomic force microscopy, micro–computed tomography
lenses
light passed through the objective onto the sample
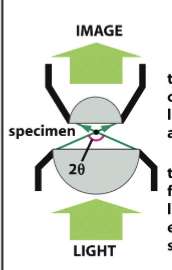
objective lens
collects a cone of light rays to create an image
condenser lens
focuses a cone of light rays onto each point of the specimen
resolving power
of the microscope, depends on the width of the cone of illumination and therefore on both the condenser and objective lens. Calculated via this formula: 0.61λ/nsinθ
wavelength is emission

numerical aperature
nsinθ in the equation above; a function of the lens’ light collecting ability. For dry lens, this cannot be more than 1, but for oil-immersion lenses, it can be as high as 1.4. The higher this is, the greater the resolution and the brighter the image. However, this advantage is obtained at the expense of very short working distances and a very small depth of field.
resolution
defined as the minimum distance (e.g. nm or μm) between two objects where you can still tell they are two objects. Changes with the objective and the emission wavelength of the fluorophore.
iris
controls how much light enters the eye
lens
focuses light to the retina (back of eye)
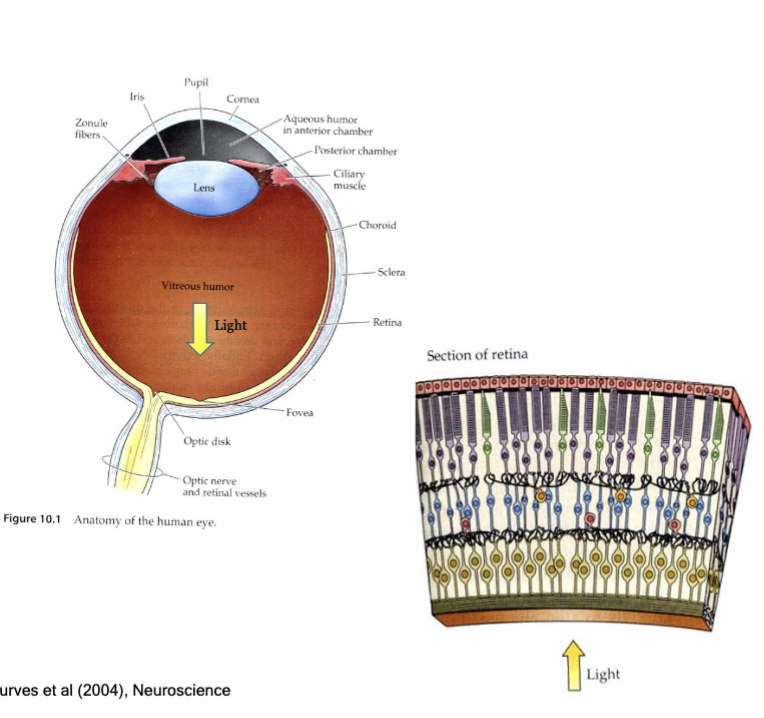
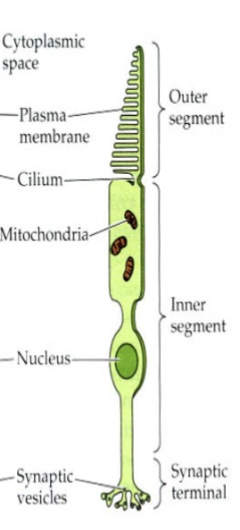
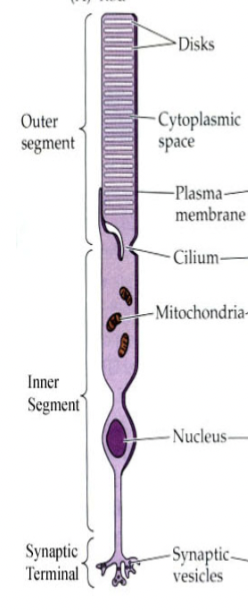
Photoreceptor cells
in the retina, they detect light. They also convert light energy into action potentials, which are then processed into an image.
fovea
light sensing cells are differentially spaced in the retina around this.
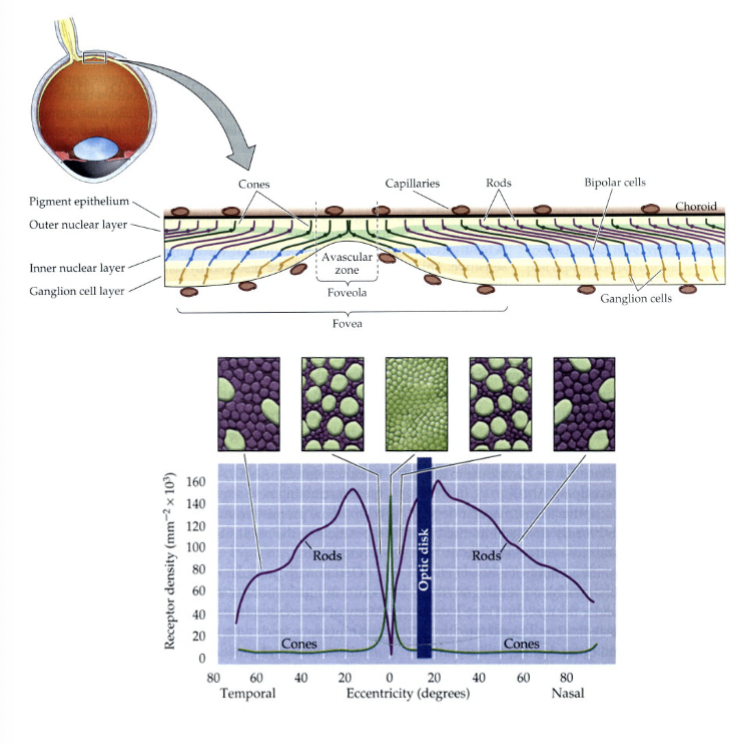
cones
color sensing ______ densely populated the area around the fovea. In bright light the iris is narrowed light and focused on the fovea
Light vision
rods
low-light sensing ______ are distributed much more broadly. In the dark your irises dilate and distribute light more broadly over the retina
Intensity
cones definition
color-sensing photoreceptor cells but are useless in low-light conditions. Three different types sense different colors.
rods definition
highly sensitive photoreceptor cells but “saturate” in even moderate light conditions (stop working)
evolved
Rods and cones are ______ to function in our environment allowing us to function from mid-day to mid-night.
strengths of human vision
Very high dynamic range (from -3 to +8 Luminance without saturating).
High sensitivity within visual spectrum.
Remarkable dual-function detector.
Spatial and temporal processing combines image formation with scene segmentation and identification.
weaknesses of human vision
Non-quantitative, nonlinear response to different intensity and wavelengths.
Limited to visual spectrum, no infrared, ultraviolet, x-ray, radiowave ...
Variation from person to person.
Processing includes questionable coding making us susceptible to optical illusions, blind spots, etc.
Limited magnification and resolution.
quantitative microscopy
Modern Microscopy uses Sensitive Detectors that translate the intensity of light into images that can be "seen" and measured; collecting digital images

images
can be collected from Photomultiplier Tubes (PMTs), CCD cameras, CMOS cameras
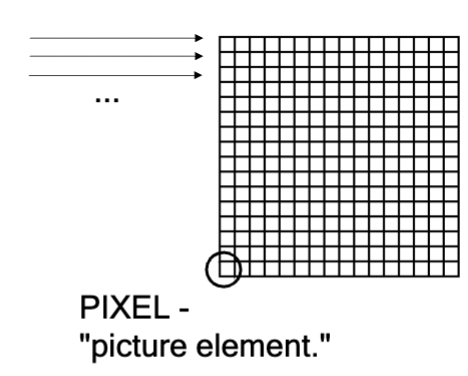
CCD and CMOS cameras
capture images in RASTER format into individual PIXELS; each pixel has associated intensity, can have multiple wavelengths
characteristics of human vision
not quantitative, large dynamic range, hard to saturate
characteristics of digital images
numbers - consistent, low dynamic range, easily saturated, separable into distinct channels.
digital raster images
can be further segmented into “objects” (ie region of interest)
optical illusions
take advantage of optical design of the eye as well as visual persistence and other post-processing visual algorithms
information found in images
intensity, relative intensity, localization; morphometric - position, size, and shape; kinematics and dynamics - movement and rates of change
data analysis pipeline
question → collect images → process images to enhance contrast → measure feature → answer → present
Can fail at any step.
Working backwards: 1. Changing LUTS, 2. filters - smoothing, sharpening, 3. re-orienting image - translation, rotation, warping, 4. Re-sampling - interpolating
FIJI
FIJI Is Just ImageJ; software tool for handling images
arrays
images are just _______ of numbers
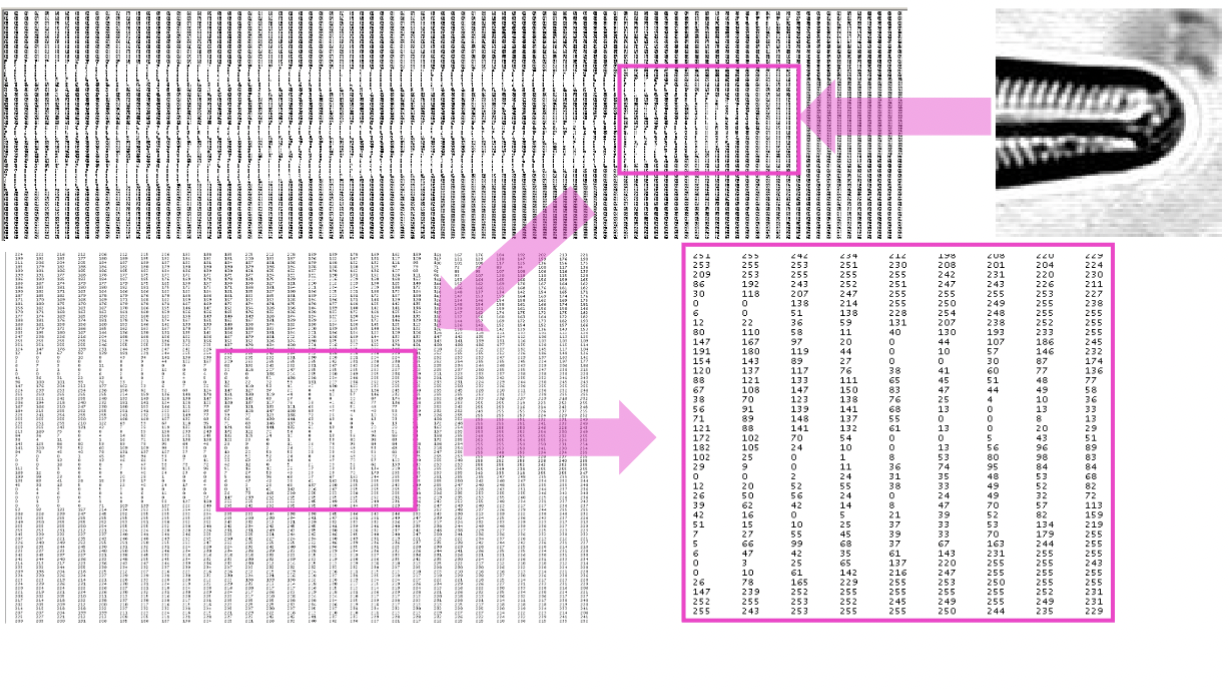
pixels
2D digital images are in Raster format composed of many individual ________ (picture-elements); the smallest picture element within a raster image. Each has a numerical value associated with it which can be used to describe a color
image pixel dimensions
in microscopy, these are set during acquisition by the physical width and height of a camera sensor size, or by determining the scan dimensions for raster scanning confocal systems
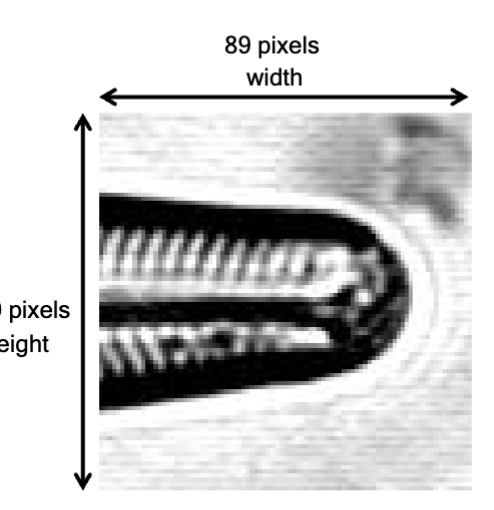
image bit depth
For all digital images, this determines the minimal and maximum numerical value for each pixel. Values are calculated from 0 to 2(bit_depth) - 1. Determined at the time you capture the image.
8-bit
0 (dark) to 255 (light)
28 - 1 = 255
12-bit
0 (dark) to 4095 (light)
212 - 1 = 4095
16-bit
0 (dark) to 65535 (light)
216 - 1 = 65535
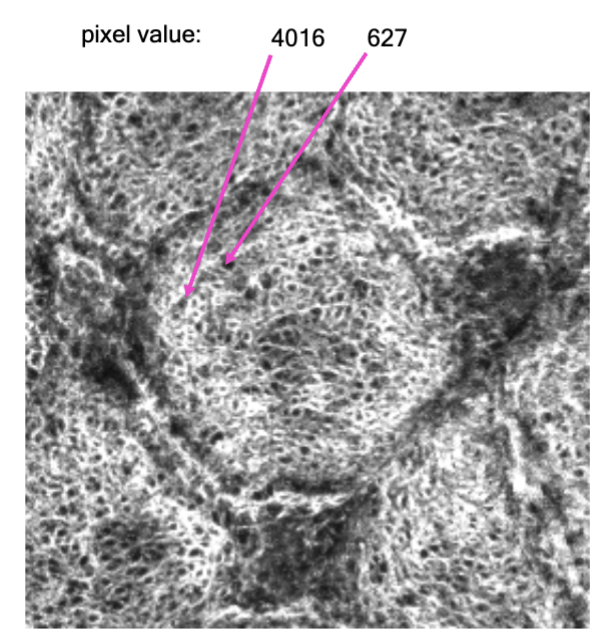
32-bit
real numbers ('single float') & fractions! Note: We can calculate and store real number images but these are NOT captured directly by a camera.
8-bit memory
on the camera chip, pixels in the image store values from 0 to 255.
If you "add" two image arrays and store in an 8-bit image, they can only hold values between 0 and 255
saturated
Camera sensors can be _________ producing pixels that contain the maximum value for their bit depth. The intensity of the pixel is above what can be stored
integer storage
Mathematical manipulations of 8-bit pixels are limited by 8-bit positive…
255
Values that are larger than 8-bit positive integers, i.e. > 255, are set to…
0
Values that are smaller the 8-bit positive integers, i.e. < 0, are set to….
pixel depth
pixels can shown integers or real numbers, and the ranges are limited by this of the image (ex 0 to 255)
image processing and image analysis
To get the most value out of your images, you need to understand how they are formed and the kinds of information they contain. These are fundamental tools in bioengineering.
digital images
just arrays of numbers. The size of the array and the value range of each entry is limited by the hardware used to collect and store the data (bit depth). The dynamic range is determined by the bit-depth
histogram of an image
tells you how much information it contains, e.g. signal to noise. Consider the effect of changing Brightness and Contrast.
channels
Microscope images can have multiple ________ (3-, 4-, 5-D arrays). The processing and the colors mapped to these can change how the images appears
imaging ethics
With the ease of manipulation there are many opportunities for mis-application of image processing and image analysis for fraud. Some rules to follow:
Be transparent about your manipulation. Provide details about the manipulations and how they are applied equally to experimental and control images.
Do not choose "Best" images for publications but rather the most "Representative" that you used.
Do not manipulate regions of a single image or fabricate images.
Journals will want your "raw images" and image processing/analysis tools to publish with your data.
You must be willing to provide anyone with your raw data. This ensures "reproducibility."
Journals employ "forsensic image analysis" software to detect potential fraud and will reject or publicly withdraw your paper from publication.
Look-up Tables (LUTs)
The colors chosen to represent intensity values can be arbitrarily selected (e.g. grey scale to green scale...). These relate the numerical value of a pixel to a color on the display, and changing one of these of an image does not change the pixel values.
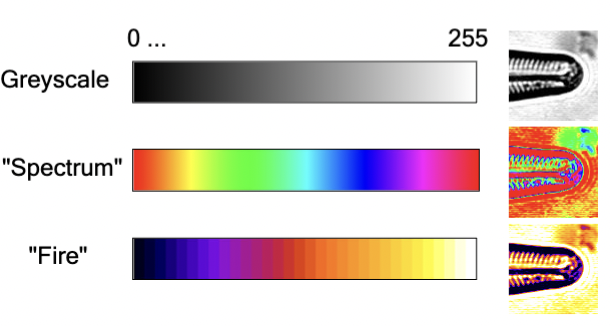
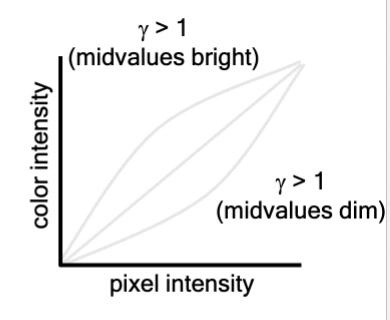
gamma-LUT
LUTs can be “non-linear,” altering the function that relates the pixel value to a level of grey or other color. Each intensity is a function of pixel intensity raised to the gamma power
color channels
multiple can be represented as color images; these represented by another LUT is often called a false-color or pseudo-color image
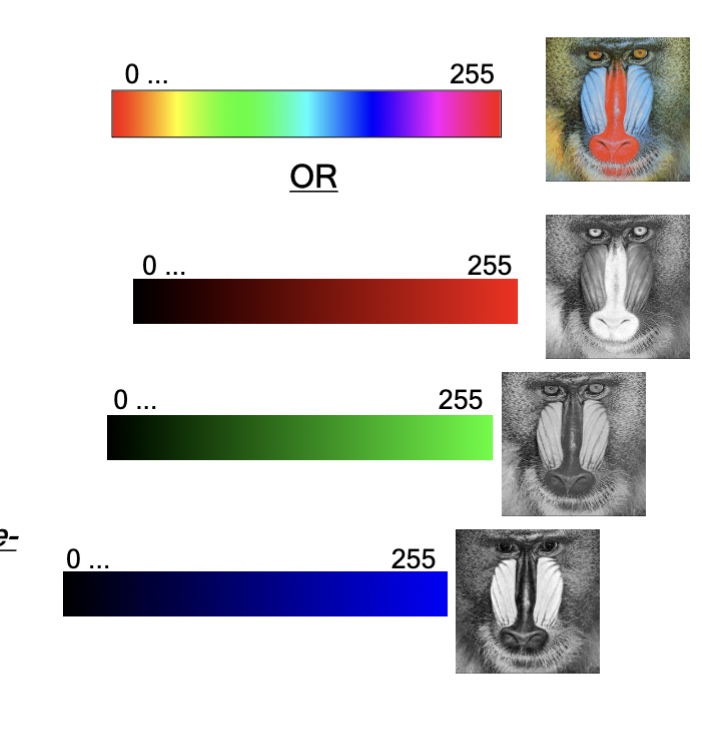
colors
can be represented in one LUT or by 3 or 4 independent greyscale channels (eg. 3 or 4 independent LUTs), each representing a primary color
Red-Green-Blue (RGB), Cyan-Magenta-Yellow-Black (CMYK)
image processing
involves application of mathematical operations on the image.
image analysis
involves using the values in the pixels, often to extract spatial or temporal information from an image or images.
histogram
Graphical display of frequency data, can explain how changes in image LUTs (brightness and contrast) work. A graphical display of frequency data.
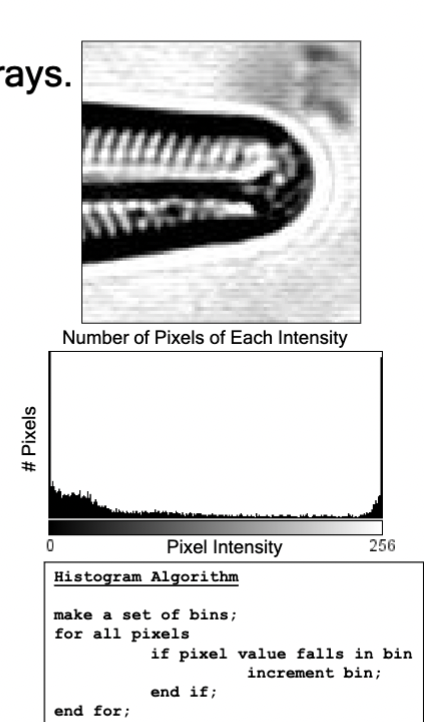
brightness and contrast (B&C)
For a given image, the bit depth may be larger than the actual dynamic range of the data in the image. These kinds of histogram adjustments restrict the visible dynamic range to improve and alter the visual image display.
Image> Adjust> Brightness/Contrast
• Min set to slightly above image background.
• Max set to slightly above average pixel value
Setting the Brightness and Contrast through Histogram Adjustment
type of image processing where you are directly changing values in the arrays. Increasing "Brightness" or "Contrast" changes the pixel values and can be seen in changes to the image and its histogram. (also "levels" in photoshop)
brightness adjustments
add or subtract values to change visual brightness of the image. This is an example of adding value to the pixel values from the og image (brighter)
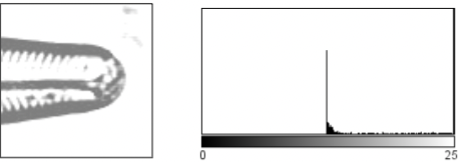
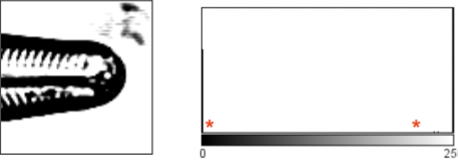
contrast adjustments
change the histogram spread to display the full dynamic range, or a limited range. This is an example of taking part of the OG histogram (between *s ) and spread it out
killer application of FIJI
ROI manager (region of interest) - every variety of structure of the image can be saved. Don’t have to change the image values in imageJ all the time
optical filters
alter the light that passes through them
fluorescence filters
pass only certain wavelengths of light
polarizing filters
pass only certain orientations of light
neutral density filters
reduce the intensity of light
image processing filters
numerical operations that takes one image as input and create a new second image; smooth, sharpen, edge enhancement, etc.
smooth
filters that reduce noise
sharpen
filters that increase local contrast
edge enhancement
filters that increase the contrast at object boundaries
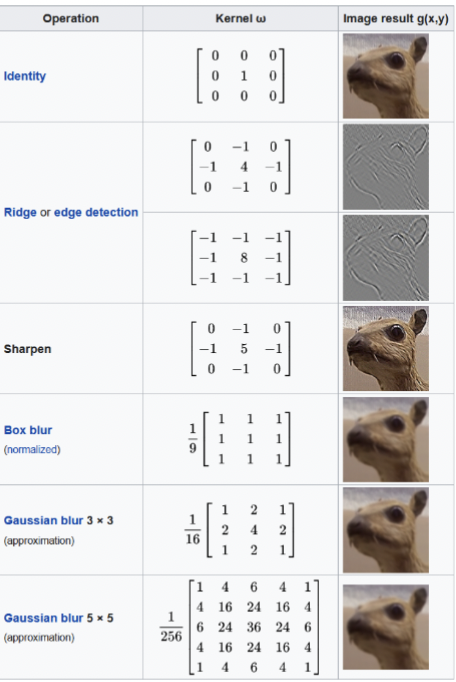
kernel
An array of pixels is filtered by convolution with this . The contents of this dictate the effect of the filter. Filters alter pixel numerical values and can change the total intensity, or even the histogram
regions of interest (ROIs)
digitally stored Vector Structures in ImageJ/FIJI. They are stored internally as sets of coordinates of XYZ or XYZT positions. You can store anything you select as one of these including polygons, hand-drawn lines, segmented structures, points, links, parts of the image selected by intensity thresholds, ...
Can be used to Measure associated intensities and geometrical morphology, and can be used to construct new ones and can be assembled into groups to generate 'categories' of objects. For instance in the next demo we collect a set of nuclei
measuring ROIs
You can select a range of features to measure using the Analyze->Set Measurements dialog. You can then measure those features with Analyze → Measure.
Measurements are recorded to a Results Table that can be exported for further analysis with Excel, Matlab, Python, Prism, etc
segmentation
using intensity values to identify regions or objects within an image.
Simple _________can be performed by thresholding the image.
Image → Adjust → Threshold
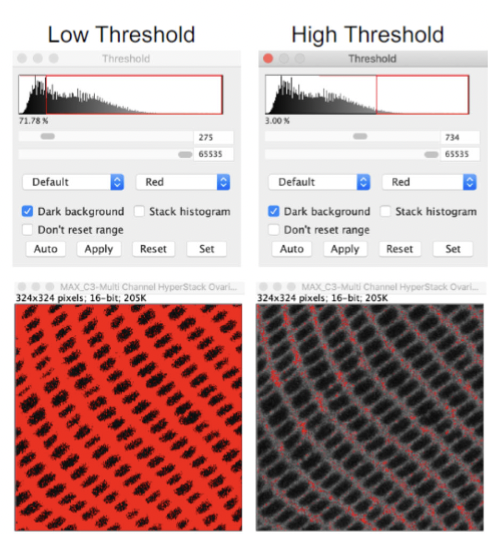
thresholding
setting the minimum and maximum pixel values to be included or excluded from a resultant image.
mask
Thresholding creates a "_____" where values not within the threshold limts. A ______ image has a color within the defined limits and another color representing pixels outside the limits
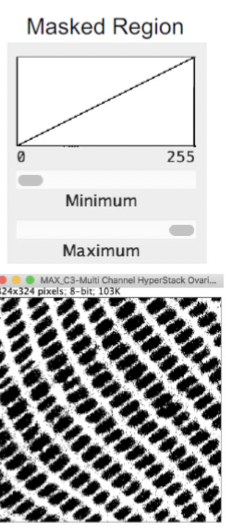
binary mask
a mask can be converted into a _______ where values inside the limits are set to 1 and values are set to 0 outside the limits
single images
XY
stacks
XYZ → composed of multiple images, or Slices, in an XY plane at regular positions along the Z axis