Final Exam - Lecture Notes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/197
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
198 Terms
1
New cards
macroevolution
What does this diagram depict
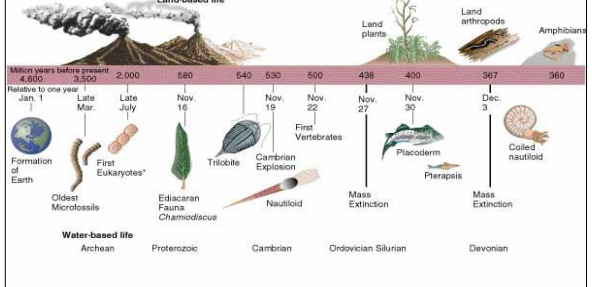
2
New cards
microevolution
These examples show what type of evolution
* some bird species evolving larger beaks to eat from backayard bird feeders
* Lizards are growing longer limbs and stickier toes for climbing buildings
* Fish and pets are developing resistance to human pollutants and posionsmi
* some bird species evolving larger beaks to eat from backayard bird feeders
* Lizards are growing longer limbs and stickier toes for climbing buildings
* Fish and pets are developing resistance to human pollutants and posionsmi
3
New cards
phenotype
* an individuals observable characteristics e.g height , eye colour
* also physiology, behavior etc. colour blindness, lactose intolerance
* also physiology, behavior etc. colour blindness, lactose intolerance
4
New cards
genotype
an individual’s genetic make up
* can be described from all of an indvidual’s genetic material, or from a subset
* can be described from all of an indvidual’s genetic material, or from a subset
5
New cards
Locus
location of a particular gene is called a
6
New cards
allele
a version of a particular gene is called a
7
New cards
a locus is a location of a particular gene (gene ID) and an allele is a version of a particular gene (A or a)
What is the difference between a locus and an allele
8
New cards
Genotype (subset) = aa or Aa ( one genotype per individual) and an allele = a or A ( two alleles per locus per individual)
Compare Genotype vs. locus. vs allele
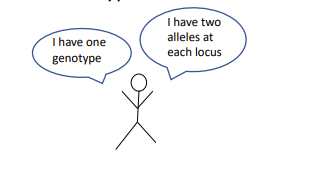
9
New cards
Germ-line mutations
what mutations occur in reproductive cells (vs. somatic mutations)
10
New cards
Recombination
the mixing and matching during meiosis. shuffles mutations to produce new sequences
11
New cards
neutral, deleterious and advantageous
What three things can mutations be?
12
New cards
neutral
* mutations that has no effect (doesn’t change encoded protein, or occurs in noncoding DNA)
\
\
13
New cards
deleterious
mutations that are harmful (in protein-coding gene regions)
14
New cards
advantageous
mutations that create an improved chance of survival or reproduction - RARE!! (and depends on environment)
15
New cards
substitution
what type of mutation is this
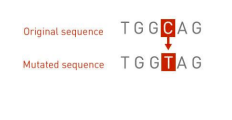
16
New cards
insertion
what type of mutation is this?

17
New cards
deletion
what type of mutation is this?

18
New cards
Natural Selection
results in adaptations ( thanks to darwin?)
19
New cards
Fitness
measured as reproductive success ( often also influenced by longevity)
20
New cards
no
Did Darwin know anything about genetics?
21
New cards
Mendel
who worked with peas rediscovered in 1900
\
* (also led to confusion re genetic variation wrt discrete traits (green vs yellow)
\
* (also led to confusion re genetic variation wrt discrete traits (green vs yellow)
22
New cards
Fisher
who recognized that many traits are controlled by multiple genes?
23
New cards
modern evolutionary synthesis
The contributions of Darwin+ Mendel + Fisher and other created our current understanding of evolution called the
24
New cards
Positive selection
selection that increases the frequency of an advantageous trait
25
New cards
Frequency
how common is an allele in a population ( 50 % = _____ of 0.5)
26
New cards
increase
overtime selection _____ (increases or decreases) the frequency of an advantageous allele within a population
27
New cards
dominant allele
***An allele that expresses its phenotypic effect even when heterozygous with a recessive allele***;
28
New cards
recessive allele
A type of allele that when present on its own will not affect the individual.
29
New cards
negative selection
selective removal of alleles that are deleterious
30
New cards
balancing selection
selection that maintains two or more alleles (different phenotypes)
* e.g heterozygote advantage
* e.g heterozygote advantage
31
New cards
stabilizing selection
a type of natural selection in which genetic diversity decreases as the population stabilizes on a particular trait value
\
* Instead of favoring individuals with extreme phenotypes, it favors the intermediate variants.
\
* Instead of favoring individuals with extreme phenotypes, it favors the intermediate variants.
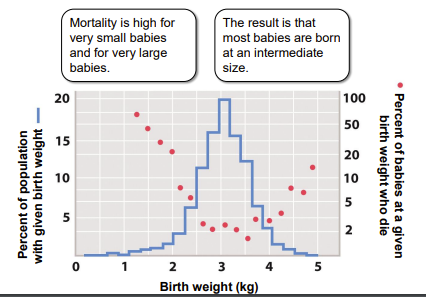
32
New cards
directional selection
* occurs when individuals with traits on one side of the mean in their population survive better or reproduce more than those on the other.
* shifts the population mean
* shifts the population mean
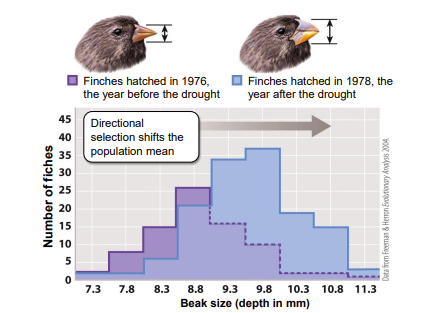
33
New cards
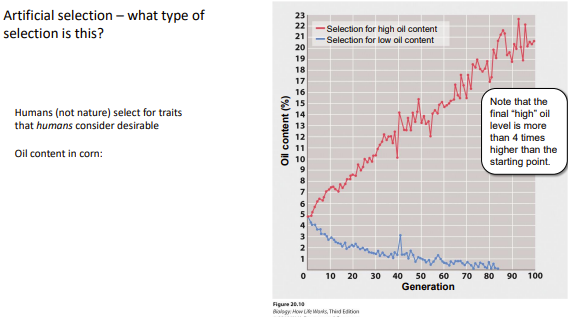
artificial selection
an evolutionary process in which humans consciously select for or against particular features in organisms
34
New cards
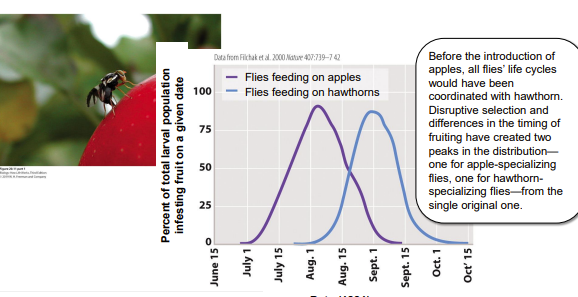
disruptive selection
A form of natural selection in which extreme values for a trait are favored over intermediate values, causing subpopulations of a single species within the same habitat to develop different adaptations.
35
New cards
Intrasexual selection
interactions between individuals of one sex
36
New cards
intersexual selection
interactions between males and females
37
New cards
Genetic drift
random evolutionary change
* result of chance events - non-random nothing to do with adaptation
* result of chance events - non-random nothing to do with adaptation
38
New cards
evolution
What does genetic drift lead to
39
New cards
population bottlenecks
reduce genetic diversity
* when population recovers it doesn’t magically reclaim diversity
* genetic drift continues to eliminate alleles when population remain small
* when population recovers it doesn’t magically reclaim diversity
* genetic drift continues to eliminate alleles when population remain small
40
New cards
m = neutral mutation
what does m equal
* note its fate is influenced by chance events\\
* neither adaptive or delterious
* note its fate is influenced by chance events\\
* neither adaptive or delterious
41
New cards
fixation
the only remaining allele ( 100% or frequency of 1.0)
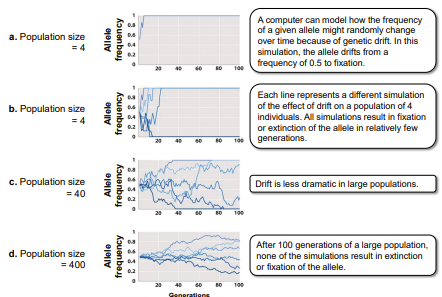
42
New cards
small,large
Genetic drift can be very important in __ opulations __and much less important in__ ____ populations
43
New cards
reduces
Migration _____ ( increase or reduces ) genetic variation between populations
44
New cards
Migration makes populations -______ ( more or less ) similar to one another
45
New cards
1) in conservation genetics isolated populations are a concern - without gene flow, they lose genetic diversity from genetic drift, and small population become inbred
2) if maladapted individuals migrate to a new area, they will be selected against- although weakly maladapted individuals can impact new populations
2) if maladapted individuals migrate to a new area, they will be selected against- although weakly maladapted individuals can impact new populations
List two reasons why gene flow can be important source of genetic variation
46
New cards
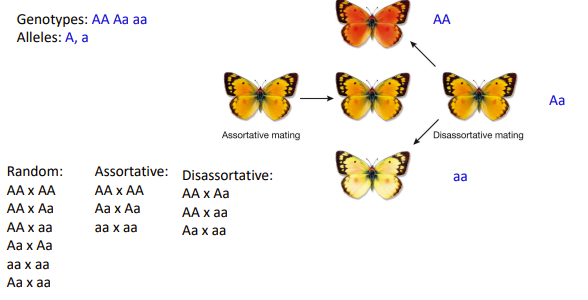
allele
Non random mating alters genotype frequencies without affects ____ frequencies
47
New cards
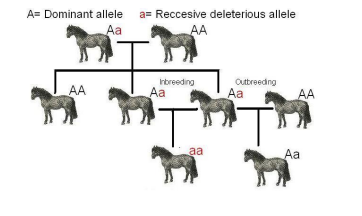
Inbreeding
a form assortative mating
48
New cards
homozygosity
mating between relative can lead to increased ________
* can leads to inbreeding depression because inbred offspring are more likely to have two copies of a deleterious recessive allele
* can leads to inbreeding depression because inbred offspring are more likely to have two copies of a deleterious recessive allele
49
New cards
molecular evolution
\
New mutations arise - over time
* Fixation following drift or selection
* Elimination following drift or selection
* Maintained at intermediate frequencies (balancing selection)
\
\
different mutation become fixed in different population
New mutations arise - over time
* Fixation following drift or selection
* Elimination following drift or selection
* Maintained at intermediate frequencies (balancing selection)
\
\
different mutation become fixed in different population
50
New cards
Time since most recent common ancestor
the amount of time that two species have been isolated from each other
51
New cards
different
species that have been isolated from each other for a long time should have ______ genetic differences from each other compared to species that have been isolated from each other for a short time
52
New cards
Molecular clock
the number of genetic differences among species can give clues about how much time has passed since they diverged froma common ancestor
\
* can vary a lot and have to be calibrated for different genes and different taxa
\
* can vary a lot and have to be calibrated for different genes and different taxa
53
New cards
chordata
a phylum of the animal kingdom comprising all animals that have, at some stage in their life, a notochord ( a hollow dorsal nerve cord), pharyngeal slits and a muscular tail extending past the anus
\
* includes subphyla Cephalochordata, Urochordata, Vertebrate (vetebrates)
\
* includes subphyla Cephalochordata, Urochordata, Vertebrate (vetebrates)
54
New cards
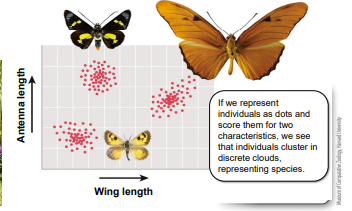
species
real biological entities
* often look different from one another
* nothing static
* often look different from one another
* nothing static
55
New cards
Biological Species Concept
* Groups of actually or potentially interbreeding populations that are reproductively isolated from other groups
56
New cards
morphospecies concept
concept that says if it walks like a duck , its a duck
\
( Note there are cryptic species that look very simillar)
\
( Note there are cryptic species that look very simillar)
57
New cards
asexual species
Biological species concept can not define what type of species?
58
New cards
ecological species concept (ESC)
different species have different niches
* resources and habitats
* resources and habitats
59
New cards
phylogenetic species concept (PSC)
\
all members of a species descended from a common ancestor
* long ago all life on earth had a common ancestor
( very recently: not all famliy members have the same most recent common ancestor)
\
all members of a species descended from a common ancestor
* long ago all life on earth had a common ancestor
( very recently: not all famliy members have the same most recent common ancestor)
\
60
New cards
prezygotic and postzygotic
What two things make up reproductive isolation?
61
New cards
pre-zygotic
eggs arent fertilized
could be
* behavioral isolation
* temporal isolation (flowering time in plants)
* gametic isolation (fertilization attempts fail - abalone proteins on sperm surface need to interact with eggs)
* mechanical incompatibility (genitals don’t fit - Drosophilia example)
* ecological isolation ( lady buys: henoseplachna yastomiia dn H. niponica feed and mate on different host plants)
could be
* behavioral isolation
* temporal isolation (flowering time in plants)
* gametic isolation (fertilization attempts fail - abalone proteins on sperm surface need to interact with eggs)
* mechanical incompatibility (genitals don’t fit - Drosophilia example)
* ecological isolation ( lady buys: henoseplachna yastomiia dn H. niponica feed and mate on different host plants)
62
New cards
post zygotic
eggs are fertilized
* usually because of genetic incompatibility
* usually because of genetic incompatibility
63
New cards
behavioral isolation
when species are reproductively isolated from others due to differences in behavior.
64
New cards
temporal isolation
when two or more species reproduce at different times.
65
New cards
gametic isolation
a type of prezygotic barrier where the gametes (egg and sperm) come into contact, but no fertilization takes place.
66
New cards
mechanical incompatibility
a physical incompatibility between reproductive organs of two organisms.
67
New cards
ecological isolation
form of reproductive isolation, wherein habitat preferences of species lowers the probability of mating.
68
New cards
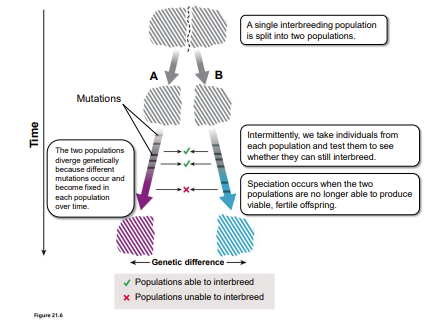
reproductive isolation
When two population separate from each other, their genetic similarity decreases over time and eventually leads to ______
69
New cards
allopatric speciation
\-different place
* speciation isn’t instant - intermediate stage sometimes recognized as subspecies
* speciation isn’t instant - intermediate stage sometimes recognized as subspecies
70
New cards
dispersal and vicariance
One population can divide in to the following
71
New cards
dispersal
migration of taxa into different geographic areas across preexisting geographical barriers such as mountain chain.
72
New cards
vicariance
separation of taxonomic groups due to the appearance of new geographic barriers such as oceans, mountains,
73
New cards
peripatric speciation
a peripheral place
* a small population is isolated or near the edge of a larger populatin
* population is smaller
* th environment may be different in ____ population
* a small population is isolated or near the edge of a larger populatin
* population is smaller
* th environment may be different in ____ population
74
New cards
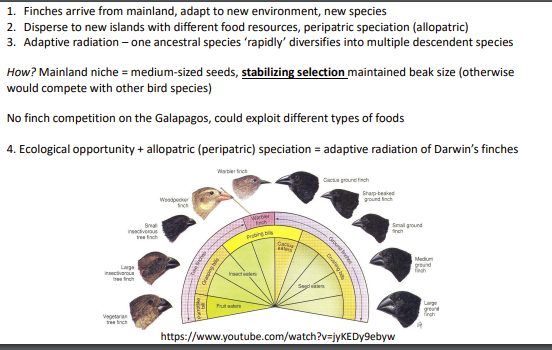
adaptive radiation of Darwin Finches
ecological opportunity + allopatric (peripatric ) speciation =
75
New cards
co- speciation
speciation in one taxon leads to speciation to another
ex.
parasite that has one host species
host species undergoes speciation and become two
parasite population now also split into two will eventually also speciate without gene flow
ex.
parasite that has one host species
host species undergoes speciation and become two
parasite population now also split into two will eventually also speciate without gene flow
76
New cards
sympatric speciation
* happens in the same place
* speciation in the same geographic place
* gene flow can prevent speciation by sharin alleles between groups
* Natural selection
* speciation in the same geographic place
* gene flow can prevent speciation by sharin alleles between groups
* Natural selection
77
New cards
instantaneous
speciation can be ____ in plants
\
* hybrids may retain two complete sets of parental chromosomes e.g diploid parents (two sets of chromosomes ) and tetraploid hybrids (four sets of chromosomes)
\
* hybrids may retain two complete sets of parental chromosomes e.g diploid parents (two sets of chromosomes ) and tetraploid hybrids (four sets of chromosomes)
78
New cards
viable and fertile
Hybrids can be ___ __and__ ___, and if they can not interbreed with parents (reproductive barrier ) = new species
79
New cards
allopolypoids
( allo= different, poly= mutiple, ploid = fold)
* results from hybridization between two different species
* results from hybridization between two different species
80
New cards
Autopolyploids
( auto- self)
* breeding between members of the same species in which meiosis fails , gamete is not haploid
* breeding between members of the same species in which meiosis fails , gamete is not haploid
81
New cards
Darwin
the idea of descent with modification (aka evolution) - common ancestor comes from
82
New cards
1) nested pattern of similarities among species on present-day earth
2) Historical pattern of evolution recorded by fossils
2) Historical pattern of evolution recorded by fossils
What two patterns help us understand how 10 million species evolved in - 3.5 billion years
83
New cards
phylogeny
shows the history of descent with branching ( multiple descendants over time)
84
New cards
phylogenetic trees
provide hypotheses of evolutionary relationships (taxonomy classifies organisms)
\
( note why a hypotheses, they provide the best explanation or the relatedness among organisms based on existing data)
\
( note why a hypotheses, they provide the best explanation or the relatedness among organisms based on existing data)
85
New cards
closest relatives
species are considered to be _____ if they share a common ancestor not shared by any other species/group = sister groups
86
New cards
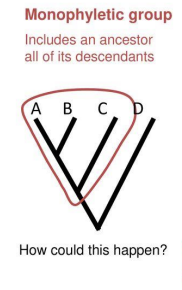
monophyletic group:
a common ancestor plus all its descendants
87
New cards
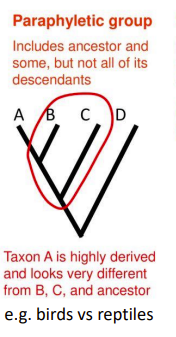
paraphyletic group
includes some but not all, of the descendants of a common ancestor
88
New cards
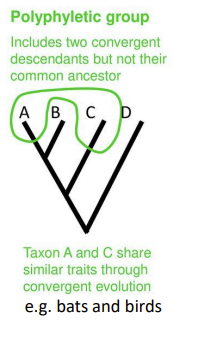
polyphyletic group
does not include the last common ancestor of all members (convergent evolution)
89
New cards
1) inherited from a common ancestor ( common ancestry) = homologous traits)
2) Independently evolved in two different lineages
2) Independently evolved in two different lineages
What are the two reasons why taxa have characters in common
90
New cards
synapomorphy
a shared, derived trait
91
New cards
outgroup
comparator that is closely related, but less so than the members of the group are to one another (represents ancestral traits_
92
New cards
parsimony
the simplest tree (fewest number of evolutionary changes ) is favored
93
New cards
distance based tree
based tree assumes constant rate of evolutionary change
94
New cards
the fossil record
* evidence that supports phylogenetic hypothesis
* show that groups which branch from early nodes in phylogenies appear early in the geologic record- and allow us to infer time since divergence (molecular clock calibration)
* Provide a record of extinct species
* Link species to the environment ( e.g metorite = huge changes dinosaur extinction)
\
* show that groups which branch from early nodes in phylogenies appear early in the geologic record- and allow us to infer time since divergence (molecular clock calibration)
* Provide a record of extinct species
* Link species to the environment ( e.g metorite = huge changes dinosaur extinction)
\
95
New cards
* organisms muse be buried in order to be fossilized
* marine life more likely to be fossilized than terrestrial
* marine life more likely to be fossilized than terrestrial
Why is the fossil record incomplete
96
New cards
Hard parts of the organisms
Which parts of the organism are more likely to be preserved as fossils?
\
( clams vs, nematode worms, pollen vs flowers, diatoms vs amoebas)
\
( clams vs, nematode worms, pollen vs flowers, diatoms vs amoebas)
97
New cards
trace fossils
insight into behavior and anatomy, e.g feeding trails of snails and trilobites
98
New cards
molecular fossils
ancient DNA from 100,000 year old neanderthal bones are an example of
99
New cards
preserved
Occasionally whole organism with delicate parts including flowers, seaweeds, mushrooms , embryos are _______
100
New cards
geological time scale
The fossil record produced ______ showing major events in the hisotry of life on earth