Ornithology Exam 1
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Characteristics of Birds
Bipedal
Feathers
Beak
Gizzard
Endothermic
Pygostyle and Uncinate processes
Lay eggs
Evolution
Change in alleles freqs in population over time
Natural Selection
Mechanism of evolution
Avg survival/repro of individuals of different phenotypes
Adaptive Radiation
One taxa diverging into different species due to varying niches
Ex. Finches on Galapagos
Convergent Evolution
Similar adaptations that have evolved in distantly related organisms due to similar environments
Ex. Toucans and Hornbills
6 main biogeographical areas
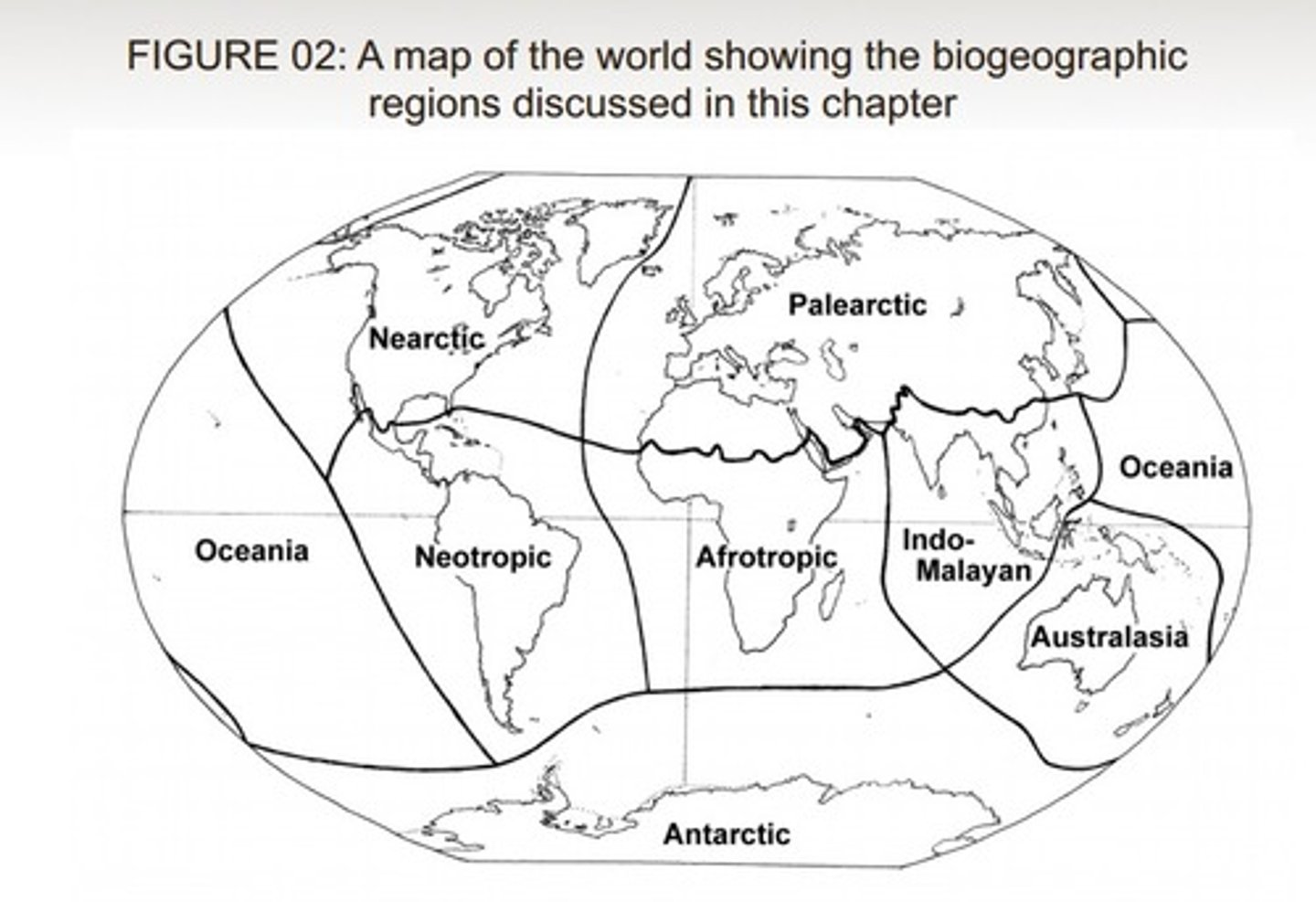
Avifauna
Regional assemblages of bird species
Differences and similarities between Archaeopteryx and modern birds
Similarities: Furcula and veined feathers
Differences: Long tail, multiple digits, no keeled sternum, and TEETH
Confuciusornis
First birds with true beak and a pygostyle
Enantiornithines
Sister to true birds; lacked uncinate processes and had teeth
Ornithothoraces
True birds
Has feathers, pygostyle
Fused hand bones and pneumatic bones
Furcula and uncinate processes
Keeled sternum
Why did birds evolve feathers?
For temperature regulation
First 4 times flight was evolved?
First, BUGS
Second, Pterosaurs
Third, dinosaurs => now BIRDS
Finally, mammals => BATS
Theories of flight
Arboreal: Glide to flight
Cursorial: Small dinos w/ elongated wings were better at jumping and catching prey => flight
Wing-assisted incline running: Wing strokes came from flapping to climb trees
What are feathers?
Unique to theropods and made of beta-keratin
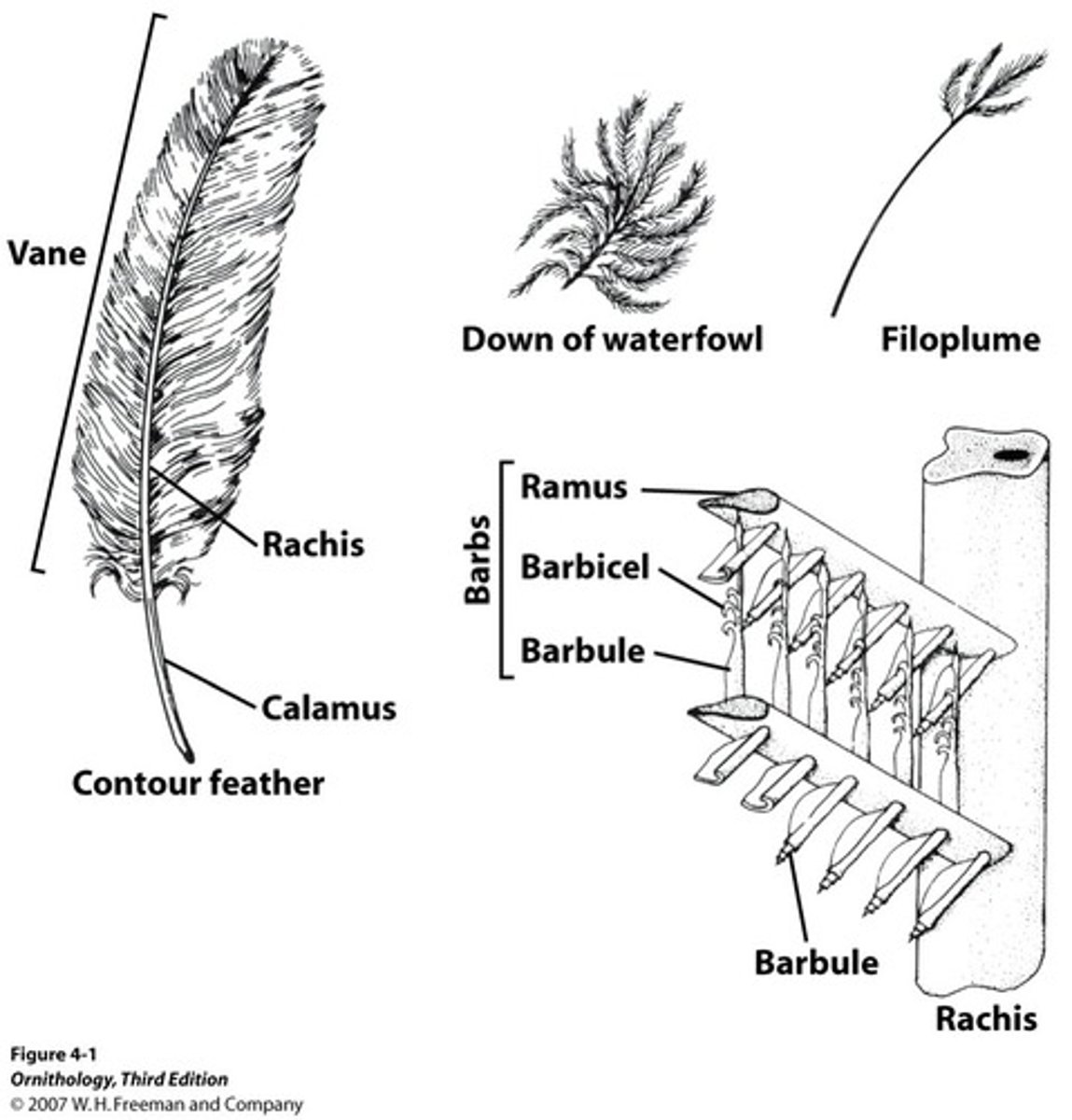
Different parts of a feather
Importance of feathers
Insulation
Waterproofing
Sexual selection
Flight
What are contour feathers?
Vaned feathers that cover entire body of birds
Fluffy/downy plumulaceous base
Creates smooth surface over body
What are flight feathers?
Feathers used for flight
Remiges (wing feathers) attach to hand bones and ulna; generates LIFT
Rectrices (tail feathers) attach to pygostyle; FLIGHT CONTROL
What are down feathers used for?
Trap and keep warm air next to bird body.
What are bristiles?
Consist of only rachis and basal barbs; found on head
Help feel and trap insects (sensory)
What are filoplumes?
fine hairlike feather with few short barbs at the tip, used for sensory and detech adjacent veined feathers
8-12 on each flight feather
How do feathers develop?
Bulb => barb and barbule develop => Rachis fusion => sheath degenerates => sheath falls off
How do birds care for their feathers?
Preening
Allopreening
Use oil from uropygial gland
What is molting?
Replacement of feathers, typically once a year (twice a year for birds with alternative plumage)
Molting begin at middle most feathers until whole wing/tail is complete
When do birds molt?
Resident species molt at anytime
Short distance migrators molt prior to migration
Long distance migrators begin molting prior but complete at destination
What are the 4 major classes of pigments
Melanins
Carotenoids
Psittacofulvins
Porphyrins
What subgroups make up melanins?
Eumelanin which covers black and grays; increase structural integrity
Pheomelanin which covers reds, browns, rufous, and buff tans
Seen in all birds!
What are carotenoids?
Red and yellow pigments
Acquired through diet => honest signal of health/fitness
What are psittacofulvins?
Responsible for the coloration on ONLY parrots
NOT due to diet
What are porphyrins?
Pigment containing metal
Fluorescent under UV light
NOT due to diet
What are structural colors?
Colors that come from interaction b/w light and nanostructure on feathers
Blues, most greens, and iridescence
What is constructive/destructive interference?
When the light waves bounces in-phase, it is constructive and colors are seen
When light waves bounce out-phase, it is destructive and no colors are seen
What is iridescence?
Change in hue with angle of observation
Due to melanin granules in feather barbs
What are the 4 major components of flight?
Take-off
Maneuvering
Stabilizing
Landing
What are the 4 major forces acting on flight?
Gravity
Lift
Drag
Thrust
What is the Bernoulli effect?
States that air must travel further OVER the wing than under it, which causes reduction in air pressure
Seen in consistent flight
What is the angle of attack?
The angle at which birds use to take-off
What is the purpose of the alula?
Maintain lift at lower speeds, similar to slats on an airplane
What are the two main forms of flight?
Soaring and gliding
What are the two main forms of soaring?
Thermal soaring, often used by hawks and vultures
Dynamic soaring, often used by seabirds
What is flapping flight?
When bird actively adds thrust to flight
Forward thrust created on downstroke of wing
Often seen in small birds
What is hummingbird flight?
Lift generated on upstroke and downstroke of wing
Creates hovering movement
How are gliding and bounding flight different from each other?
In gliding, wings are open; In bounding, wings are folded
Flap gliding is efficient at slower speeds; Flap bounding is efficient at higher speeds
What is formation flying?
When birds fly in formation to conserve energy (50%) by using the rising vertex of the bird in front of them
What are the muscles for flight?
Pecturalis, used in downstroke of flight (Large and directly attached to humerus)
Supracorracoideus, used in upstroke of flight (Smaller and indirectly attached to humerus)
Flight adaptation evolution from oldest to newest
Asymmetrical wings
Pygostyle
Keeled sternum
Uncinate processes
What metrics are used to categorize wings?
Wing loading: Mass of bird / wing area
Wing aspect ratio: Length of wing / width of wing
What are broad wings better for?
Slower air speeds and reducing INDUCED drag
Which bird is an example of one with broad wings?
Eagles
What are sleek wings better for?
High air speeds and reducing PROFILE drag
Which bird is an example of one with sleek wings?
Hawks