Section 4 Test MCQ
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
The level of output in the long run is known as
Potential Output
The blank curve shows the negative relationship between the aggregate price level and the quantity of aggregate output demanded in the economy.
Aggregate Demand
Transfer payments are payments which
governments make to households when government receives a good or service
As a recessionary gap is eliminated through self-correcting adjustment, the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium real output
Decreases, increases
in the basic equation of national income accounting, the government directly conta and influences
G:C and I
Fiscal policy involves
deliberate changes in taxation and/or guvernment spending
The current level of real GOP lies below potential GDP. An appropriate fiscal policy would be to which will shift the curve to the
increase government purchases, AD: right
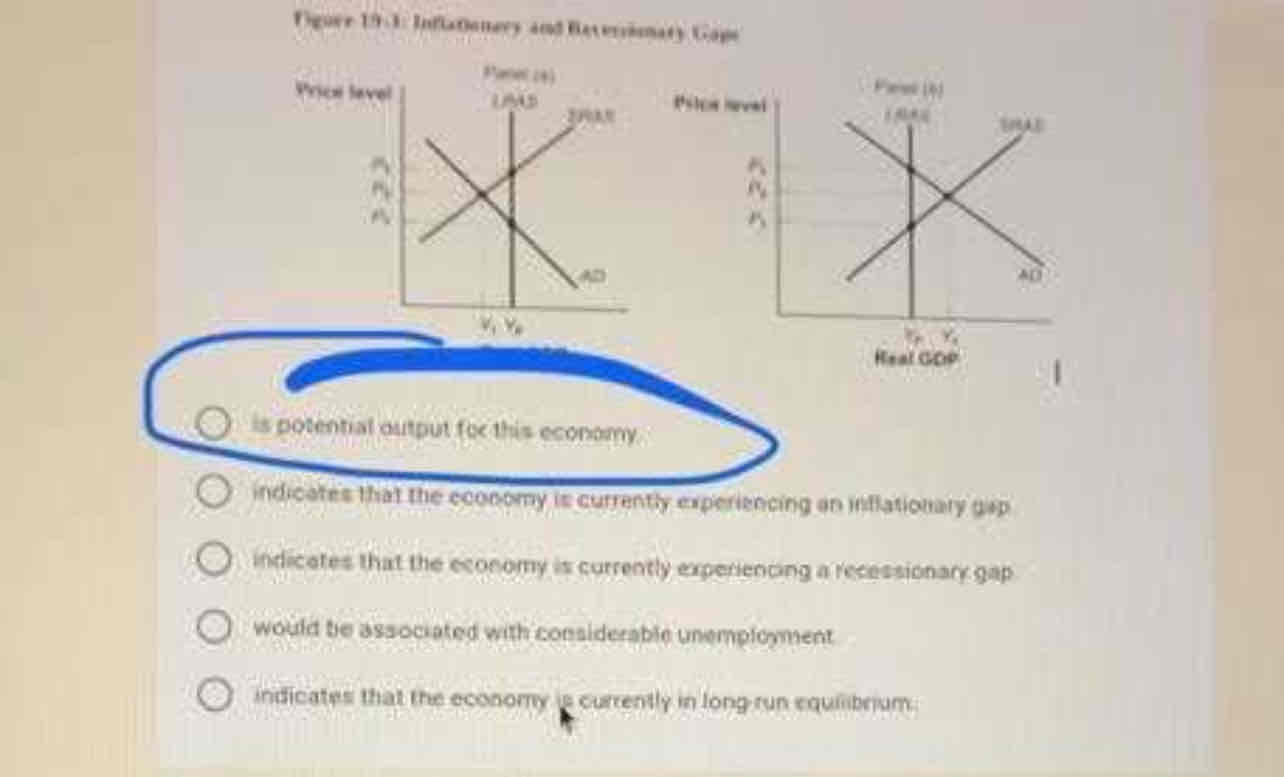
Is potential output for this economy
The long run in macroeconomics analysis is a period
In which nominal wages and other prices are flexible
The multiplier is equal to
1/(1-MPC)
The short run aggregate supply curve is positively sloped because
wages are sticky or don't readily adjust to changes in economic conditions in the short run
The multiplier process
is limited with the total change in real GDP dependent upon the size of the marginal propensity to consume
When the aggregate price level rises, this will, other things equal
result in a decrease in the quantity of aggregate output demanded
Suppose that a financial crisis decreases investment spending by $100 billion and the marginal propensity to consume is 0.80. Assuming no taxes and no trade, by how much will real GDP change
$500 billion decrease
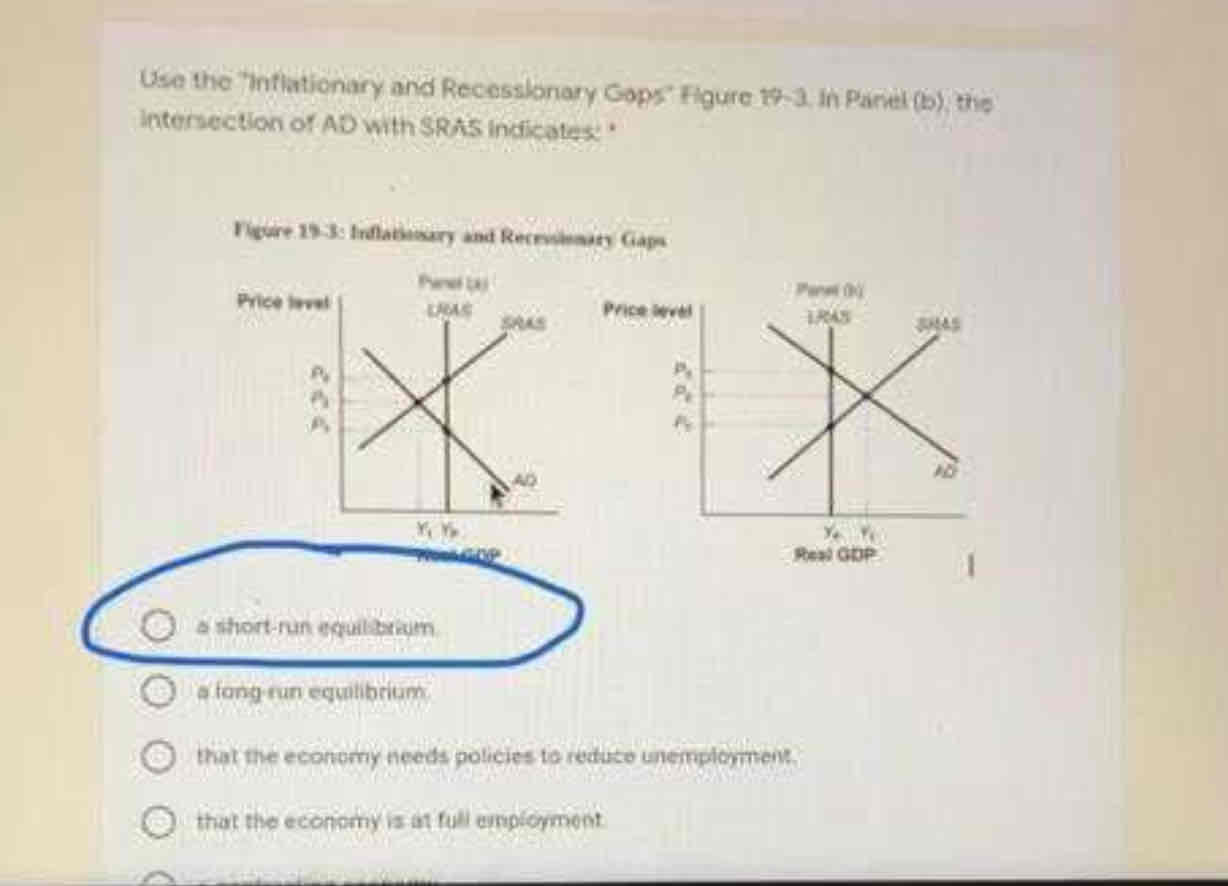
A short run equilibrium
Changes in short-run aggregate supply can be caused by changes in
Wages
When the economy is on the short-run aggregate supply curve and to the left of the long-run aggregate supply curve, actual aggregate output will eventually equal potential output as:
nominal wages fall and the sport run aggregate supply curve shifts to the right.
An example of an automatic stabilizer that works when the economy contracts is:
a rise in government transfers, as more people receive unemployment insurance benefits
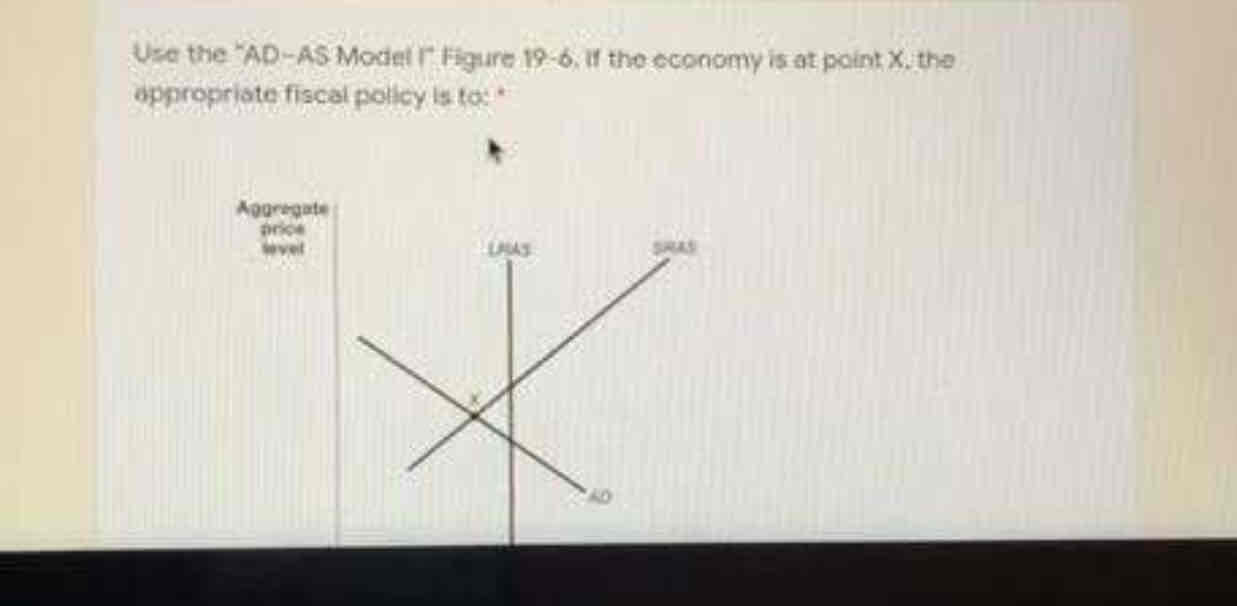
Decrease taxes and increase government spending
The consumption function will shift up if
households expect an incresse in the mininum wage in the future
If the marginal propensity to consume is 0.5, Individual autonomous consumption is $10,000, and disposable income is $40.000, then individual consumption spending is
$30,000
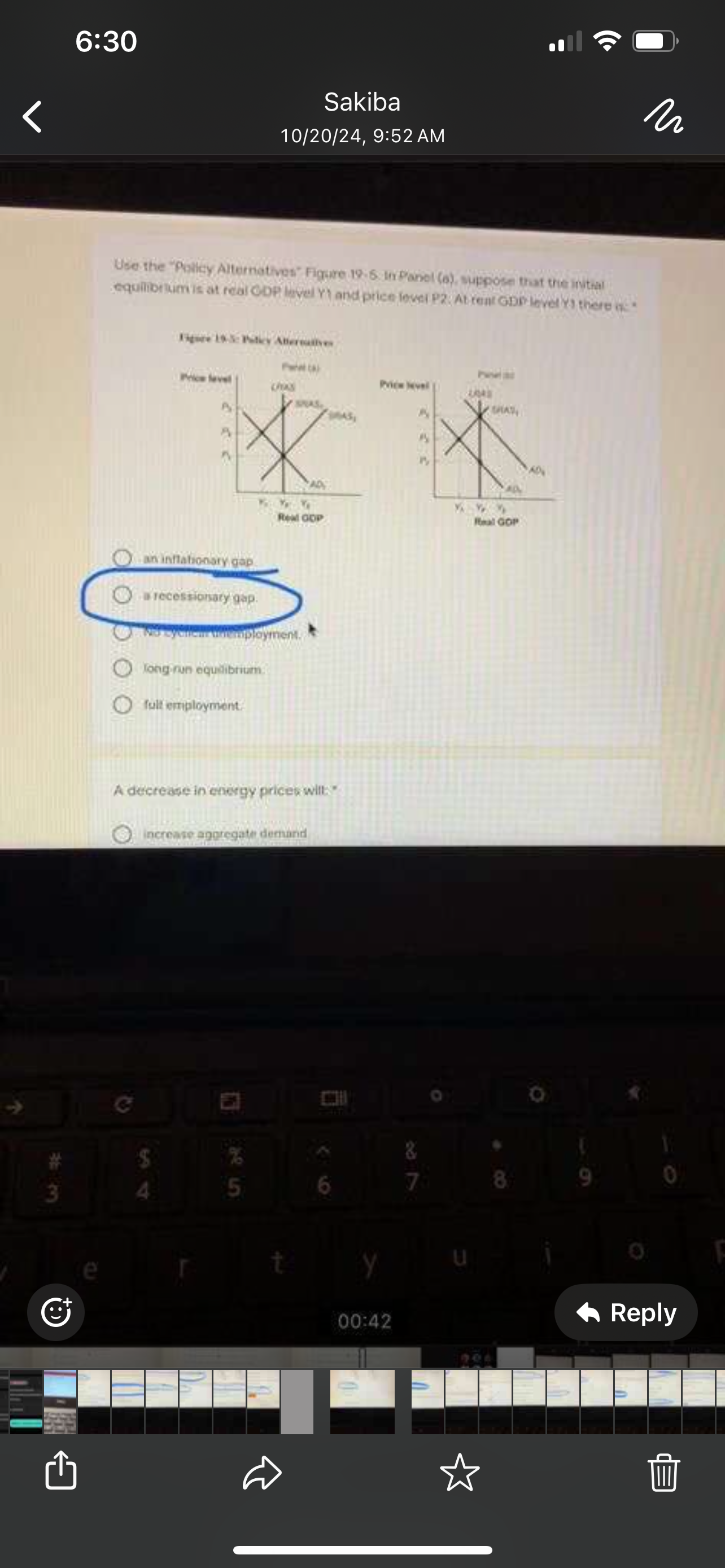
A recessionary gap
Stagflation may result from
A increase in the price of imported oil
A increase in the short aggregate supply curve may be caused by
A increase in productivity
Aggregate demand will increase if
The public becomes more optimistic about future income
Suppose the economy is experiencing a recessionary gap. To roove equilibrium aggregate output closer to the lever of potential output, the best fiscal policy option is to
Decrease taxes
A increase in the aggregate price level will increase
the quantity of aggregate output supplied in the short run
A autonomous increase in aggregate spending
Increases GDP by more than that amount
An example of an automatic stabilizer is
Tax reciepts rising when GDP rises
Other things being equal, expectations of lower disposable income in the future would and shift the consumption function
decrease autonomous consumption down
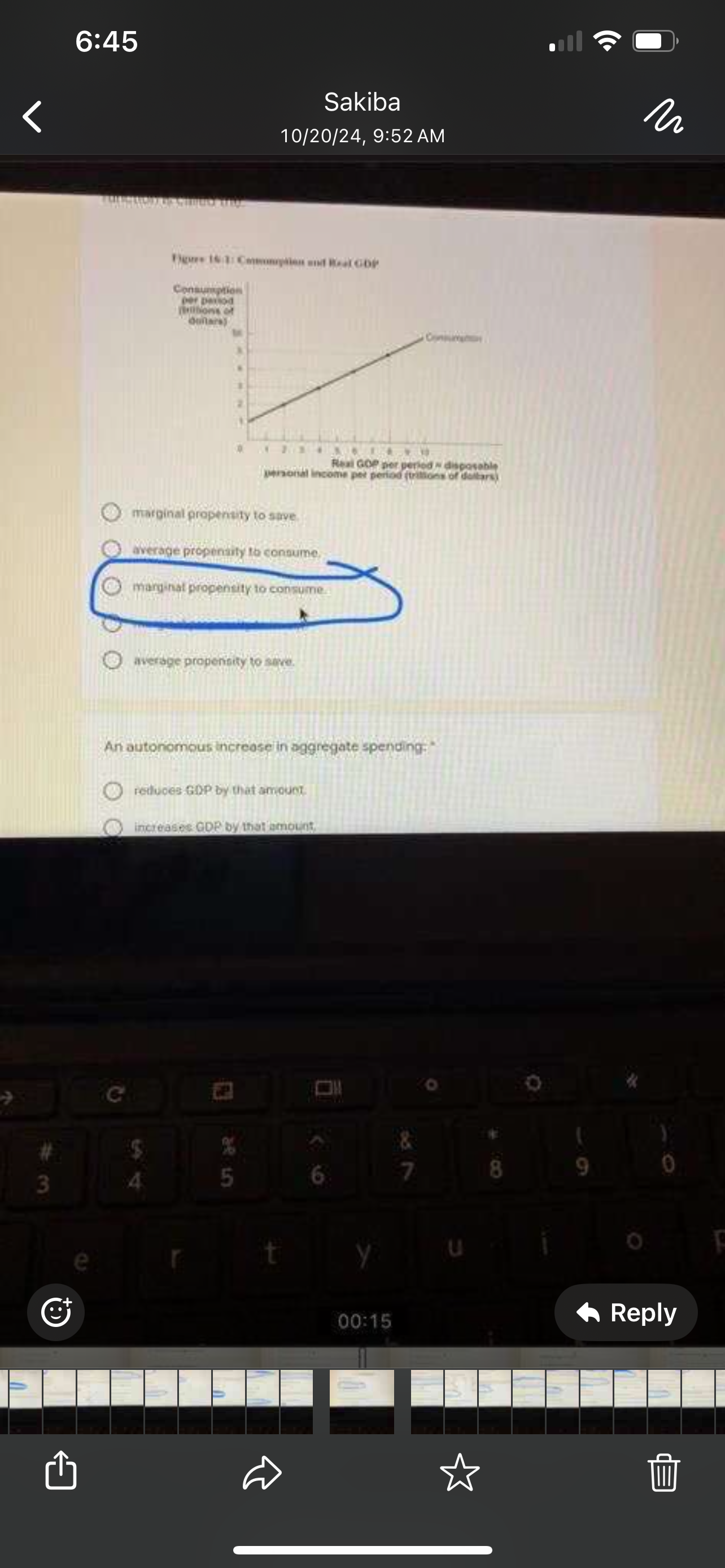
Use the "Consumption and Real GDP Figure 16-1. The slope of the consumption function is called the
Marginal propensity to consume
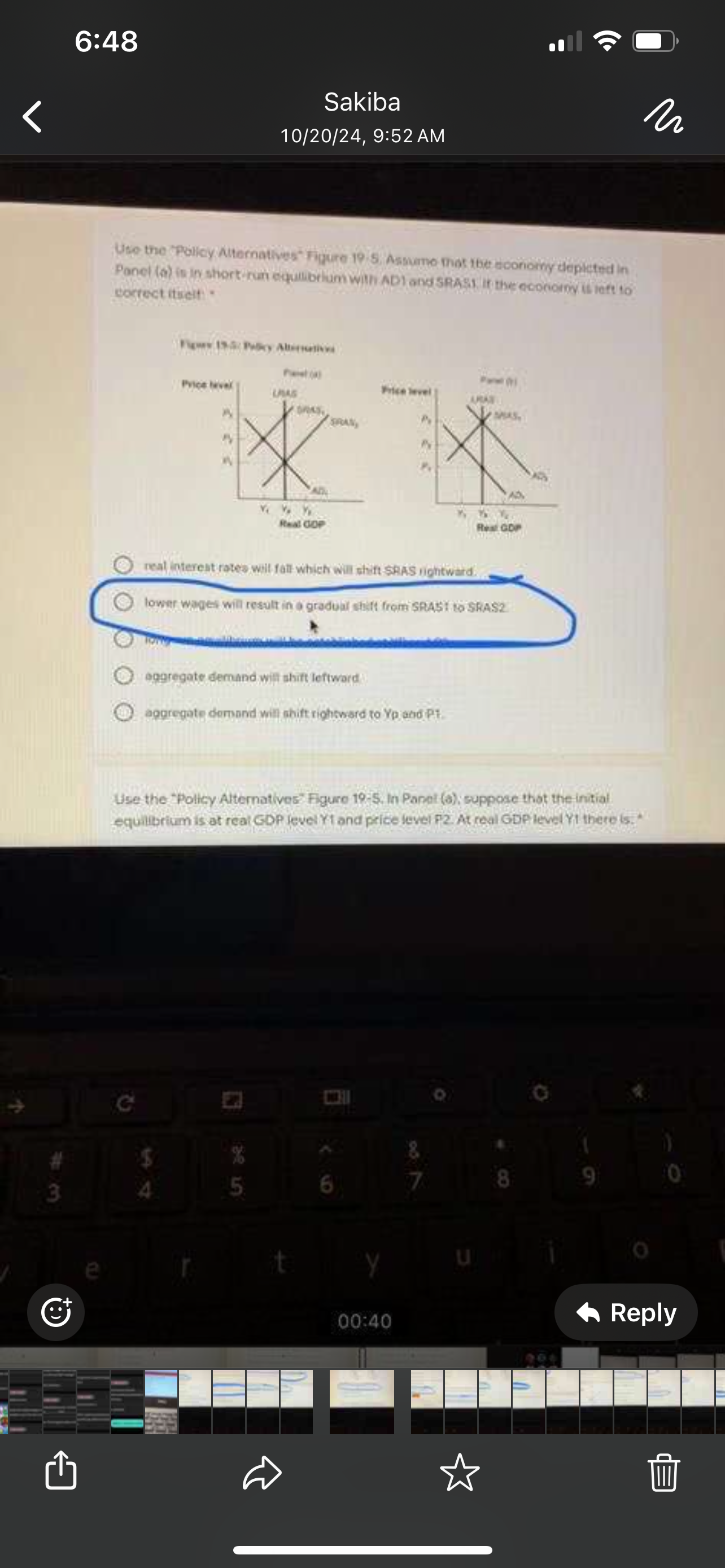
Use the "Policy Alternatives" Figure 19-5. Assume that the economy depicted in Panel (a) is in short-run equilibrium with AD1 and SRAST if the economy is left to correct itselt
lower wages will result in a gradual shift from SRAST1 to SRASZ2
According to the wealth effect, when the price level decreases, the purchasing power of assets
Increases and consumer spending increases
An economy is currently in the midst of a recession. An example of a government policy aimed at moving the economy back to potential GDP is:
an increase in goverment spending on enfrastructure improvements
An inflationary gap occurs when
Actual output exceeds potential output
Actual investment spending is equal to
the sum of planned investment spending and unplanned investment spending
A decrease in energy prices will
Increase short-run aggregate supply