dog and cat ectoparasites
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
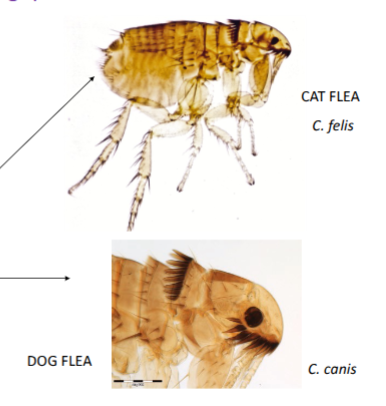
flea species
fleas are insects - 6 legs, distinct body regions
adult fleas suck blood
wild animals - all rodents, carnivores, birds, domestic small and companion animals
not ususally a problem for livestock
>95% of flea species are ectoparasitic on mammals
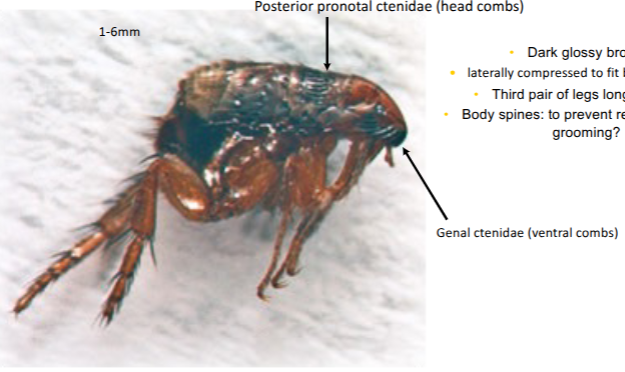
general morphology of flea
dark glossy brown
laterally compressed to fit between hairs
3rd pair legs longer, stout
body spines to prevent removal during grooming
resilin in back legs is compressed to release
peak acceleration = 100G
clearing and preserving specimens to see characteristics
place flea in 10% potassium hydroxide
water
dehydrate in alcohol series to 100%
xylene to clear
DPX or similar to mount on glass slide
nice clear prep for ID
veterinary importance of fleas
most common cause of skin problems in cats
intense irritation, anaemia
FAD - flea allergic dermatitis of dogs and cats
skin reactions and dermatitis in people
transmission of tapeworm - dipylidium canium, bacteria - bartonella cat scratch disease
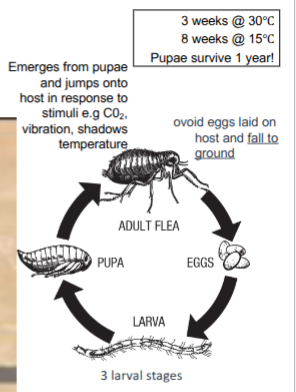
generalised life cycle of fleas
95% life cycle is hidden in environment
adult flea survives 21days on host, takes multiple blood meals, several times per day, female begins laying eggs 36h later, later on average, depositing 20-30 eggs per day
diagnosis of fleas
presence of fleas
pruritis
presence of flea dirt
comb hair and put debris on wet paper towl
flea dirst appears red
larvae actively move away from light
maggot like, distinct brown head
13 segments, posterior bristles
susceptible to desiccation
looping movement
can move several meters

diagnosis of FAD
clinical signs = alopecia, excessive grooming, skin damage
hypersensitivty to allergens in flea saliva
one flea can trigger response
secondary infections possible
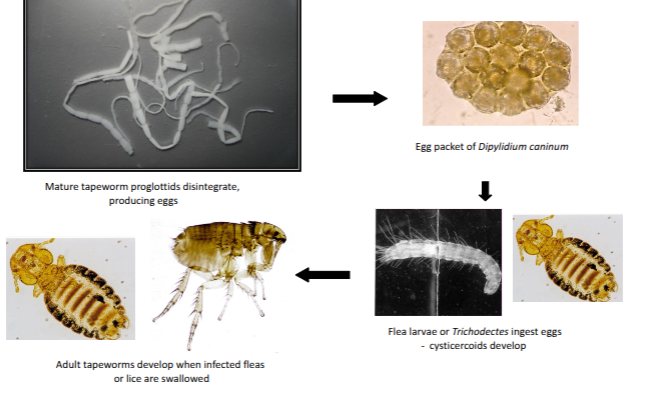
transmission of dipylidium canium
mature tapeworms proglottis disintegrate, producing eggs
eggs packet of dipylidium caninum
flea larvae or trichodectes ingest eggs - cysticercoids develop
adult tapeworms develop when infected fleas or lice are swallowed
segments are mobile - can emerge from anus and crawl onto coat, releasing egg packets onto coat where fleas and lice ingest them
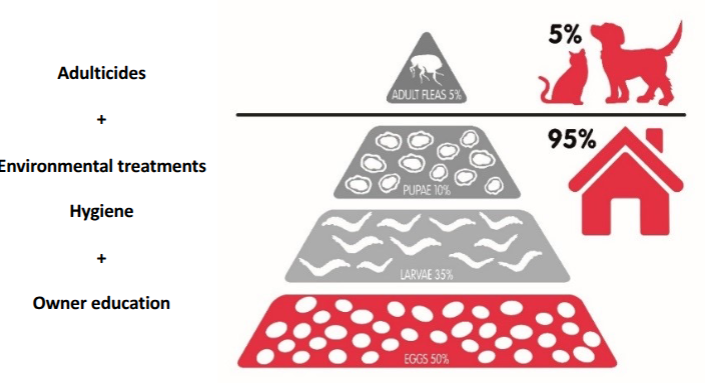
flea control
adulticides
isoxazolines
phenylopyrazole, fipronil spot-on or spray
neonicotinoid, imidacloprid spot-on
other - nitenpyram tablets, flumethrin/imidacloprid collars
enviromental treatments
kills eggs and larvae - insect growth regulators - chitin synthetase inhibitors - inhibits egg hatch and proper moulting, juvenile hormone analogues - prevents moulting/pupation e.g methropene
kills larvae and adults - insecticides - synthetic pyrethroids e.g permethrin - toxic to cats, low efficacy, present in some flea sprays
owner education
if only adulticide or enviromental treatments used then owners will still see fleas on their pet
if both adulticide and enviromental treatments are used but used inconsistently or just once, then reinfestation will occure by adults emerging from pupae
combined approach targeting fleas on host and enviroment needed for 2-4 months minimium to control fleas in infested houses
continuous coverage needed - owner compliance of paramount importance
other hygiene measures - vaccuming and washing bedding to kills eggs/ larvae/ pupae
mites
mites and ticks don’t have distinct body regions like insects. 8 legs in adults
burrowing and non-burrowing - both can cause mange
burrowing mites
3 genera, 5 species
sarcoptes scabei
notoedres cati
demodex spp
sarcoptes scabei - sarcoptic mange/ scabies
1 species - host adapted forms
transmitted during physical contact
highly contagious
causes mange in dogs, foxes, pigs, camelids
causes severe mange of livestock in warmer countries but rare uk
sarcoptes scabei - morphology
round flattened with rounded head
stumpy front legs
dorsal surface has folds of cuticle giving rise to thumb print pattern and is covered scales and prominent spines
sarcoptes scabei - life cycle
each tunnel contains a single female mite - 3 eggs per day, hatch larvae within tunnels after 3-4 days
larvae exit tunnels and successive moulting to eight-legged protonymph, tritonymph and adults in pockets on skin
egg to adult in 14 days
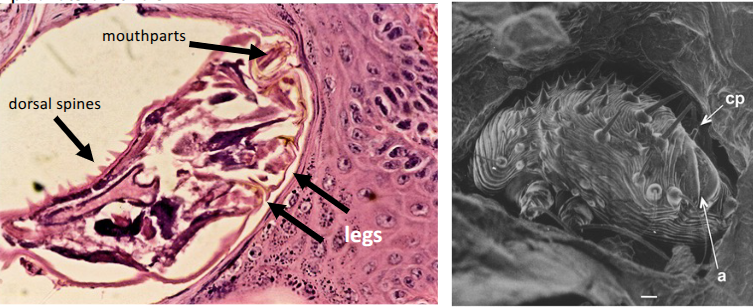
sarcoptic mange
intensely pruritic, papular lesions, hair loss and crusting
mange can spread - most severe forms of condition are more often seen on head - periocular skin, pinnal margins - neck elbows and hocks
hypersensitivity
wildlife - highly pathoegenic in foxes, hedgehogs possible wildlife resevoir of infection for pets
human form - humans - human scabies - distinct and highly contagious, debilitating
sarcoptes scabei - diagnosis
itchy dog
superficial and broad skin scrapings
dermatitis in household
ELISA
rarely seen in cats
in skin scrapings look for evidence of all life cycle stages
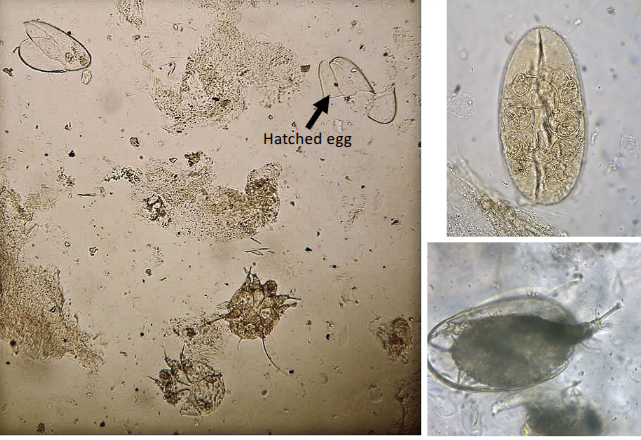
sarcoptes scabei control
macrocyclic lactones: selamectin, moxidectin spot ons
isoxazolines - fluralaner tablets
amitraz washes
contra-indications - ivermectin not recommended due to CNS signs in collies
notes = treat all in contact with dog
treat all grooming instruments and bedding
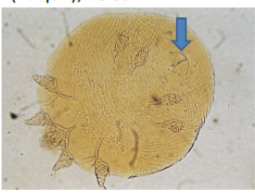
notoedres spp
found on face, head and ears of cat and occasionally other small animals
morphology - like sarcoptes in shape, prominent dorsal striations in form of concentric rings. no scales and spines. very small. dorsal anus(arrow)
life cycle similar to S. scabei
rare but severe notoedric mange can be fatal
transient human dermatitis
treatment - macrocyclic lactone spot on
demodex spp - demodicosis/ demodectic mange
many species, host specific - highly evolved to occupy hair follicles, feed on dead skin
dermdex canis - dogs
dermodex cati and demodex gatoi - cats
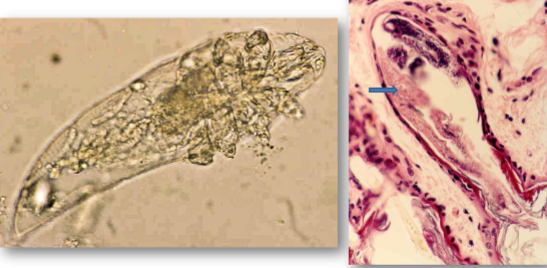
life cycle of demodex spp
demodex spp normally commensal
life cycle takes 18-24 days to complete
demodex spp are unable to survive away from hosts body
in dogs transmission is via mammary skin while suckling
demodex spp affect all animals, humans too, very host specific
common dermatological condition of dogs
very rare in cats
demodex spp significance
when health is compromised
scaling and alopecia, papules and pustles
face, shoulder, neck and limbs
dogs - 2 clinically distinct forms, classified in various ways. can be adult or juvenille in onset. complex pathoegenesis. thickened skin, pustles, crusts
localised - mainly young dogs - lesions may spontaneously resolve
generalised - severe disease complicated by secondary bacterial infection
diagosis = deep skin scrapings, trichograms
treatment = can be difficult
macrocyclic lactones
isoxazoline
amitrax washes
non-burrowing mites
3 genera
otodecetes cynotis
cheyletiella spp
trombicula autumnalis
otodectes cynotis
deep in ear, feeding on debris near ear drum
life cycle - transmission is direct by ear contact. life cycle ~ 3 weeks
clinical signs
in cats often a brownish wacy exudate with crusting
causes intense itching with head shaking
secondary bacterial infection can result in purulent otitis externa - dark brown exudate. 50-80% of such cases associated with otodectes cynotis
treatment
isoxazolines
various drops
imidacloprid, selamectin spot ons
treat all in-contact dogs and cats in household
cheyletiella spp
commensal of dogs, cats and rabbits
common cause of mild scaling dermatosis
mites seen among debris against dark background
diagnosis - mite shape, palpal claws. eggs also in superficial scrapings
zoonotic - mites will transfer to humans causing papules on arms and abdomen
cheyletiellosis
lesions typically occur dorsally on rump and shoulders
common in rabbits
in dogs infestations possibly more prevelant in boxers and cocker spaniels
control = no licensed products, fipronil, ivermectin
trombicula spp
trombicula autumnalis in europe. only larvae are parasitic, peak abundance in autumn
significance - puritis, erythema, papules, crusting, self-trauma. possibly associated with seasonal canine illness
diagnosis - difficult - mites often not seen
treatment - fipronil shown to be effective
lice
order = phthiraptera
obligatory parasites of birds or mammals
2 sub-orders = mallophaga and anoplura
mallophaga contain the biting/chewing lice
anoplura contain suckling lice
3 species = trichodectes canis, linognathus stetosus, felicola subrostrata
dogs - trichodectes canis - biting/chewing louse
small, yellow 1-2mm
dark markings on abdomen
claws for gripping hairs
life cycle - same as for bovicola spp
can survive off host for 7 days
T. canis - pathology
harmful for puppies and old or neglected dogs
clinical signs
head, neck and tail attached to base of hairs
intense itching, scratching, biting at these sites feeding on scales and debris
matted coat, inflammation and excoriation
alopecia and bacterial involvement
dog may appear nervous
vector for tapeworm dipylidium caninum
transmission of dipylidium caninum
dogs - linognathus stetosus - suckling louse
clinical signs - skin lesions such as excoriation, miliary dermetitis or urticaria-like lesions and even necrtotic skin lesions have been described. may cause anaemia in heavy infestation
diagnosis - head and neck areas. louse morphology. long eared dog breeds such as spaniel, basset and afghan hounds are particularly susceptible
cats - felicola subrostrata - biting/ chewing louse
relatively rare
clinically signs
face, back and pinnae
dull ruffled coat
scaling, crusts and alopecia
distinctive triangular head
cat and dog louse control
neonicotinoid - imidacloprid spot on
fipronil spray/spot on
sarolaner/ selamectin spot on
tick classification
class = arachnida
subclass = acari
order = ixodia
family = ixodidae = hard ticks
family = argasidae = soft ticks
how important are hard ticks
transmit pathogens - vector capacity similar to mosquitos
production losses due to tick-borne diseases in ruminants in developing countries
TBD in companion animals
dogs as resevoir hodtd for TBDs
all tick-borne diseases are zoonoses and/or clinically important in domestic animals
many emerging tick-borne diseases
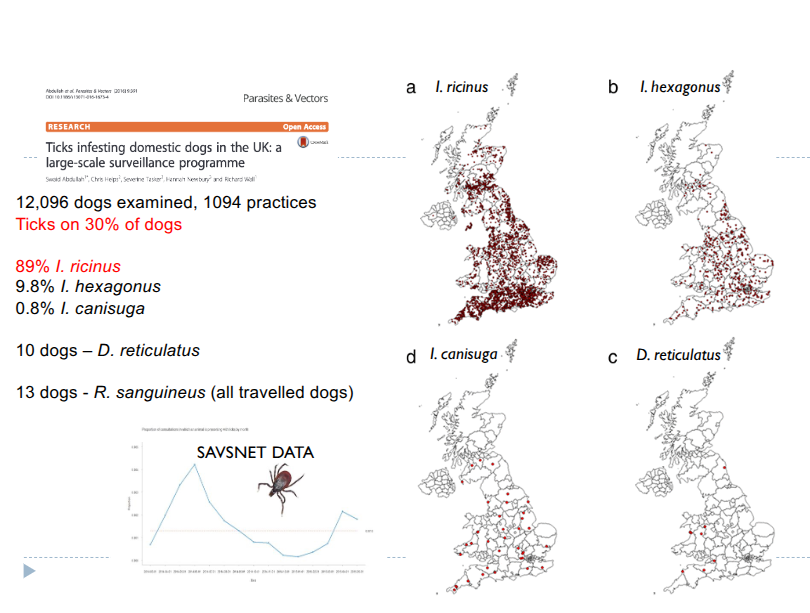
ticks in UK
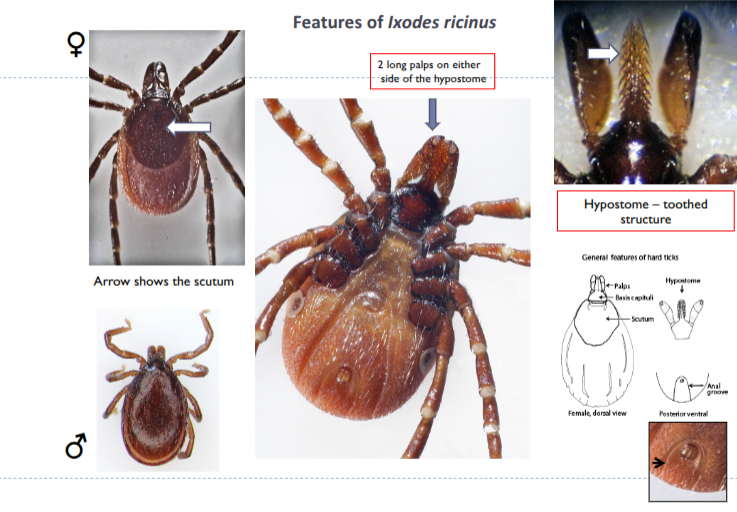
Ixodes ricinus
I. hexagonus
dermacentor reticulatus
ticks in europe
Ixodes ricinus
I. hexagonus
dermacentor reticulatus
rhipicephalus sanguineus
D. reticulatus
features of ixodes ricinus
ticks start to quest in spring
take refuge in undergrowth on hot days
2 main peaks in activity - spring and autumn
feed on wide host range - birds, small mammals, deer, sheep, cattle, dogs, humans
habitat - wooded area, upland pastures, scrub, sometimes urban gardens
most abundant - transmit lyme disease, louping ill, red water, anaplasma, rickettsias
3 host life cycles = 3 yrs in uk
blood feeding
female ticks can increase in weight >100-fold following engorgement and mating

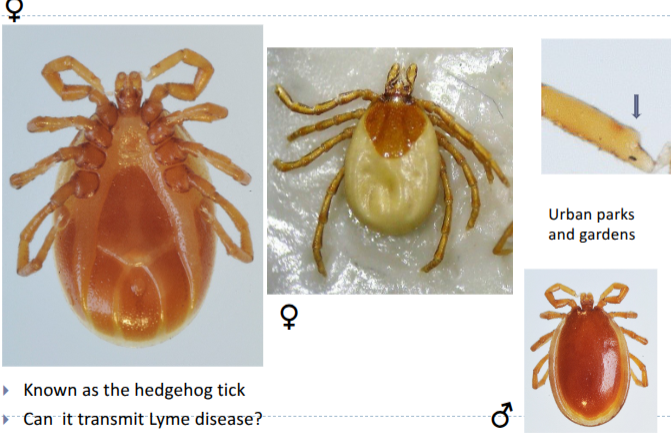
ixodes hexagonus
known as hedgehog tick
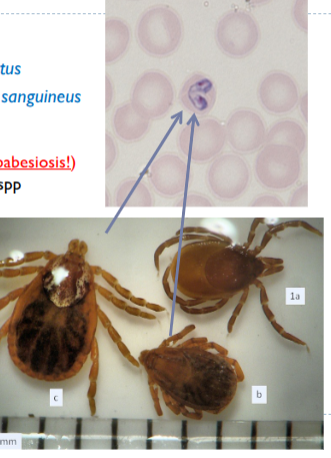
rhipicephalus sanguineus
known as brown dog tick
highly adapted to feeding on dogs
transmits canine babesiosis and ehrlichiosis
has lateral projections on false head
adapted to living in dog accomodation
prefers ears, interdigital spaces, axilla
females drop off at night - thousands eggs deposited in crevices, cracks in dog kennel
huge number infect single dog but most are in environment
can infest uk homes
mainly southern europe

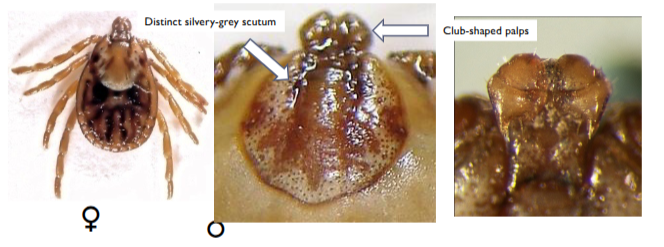
dermacentor reticulatus
meadow tick
in europe transmits canine babesiosis
likes cool wet climates - extend northwards in europe - new populations in germany and southern uk
distinct silvery-grey scutum
club shaped palps
babesia of dogs and their vectors
babesia spp
b.canis = dermacentor reticulatus
b.canis(vogeli) = rhipicephalus sanguineus
Ia = I ricinus - not a vector of canine babesiosis
Ib = R. sangineus
Ic = dermacentor spp
distrubution in uk
drivers of range expansion of ticks
changes in climate throughout europe
vegetation increases support feeding hosts - roe deer to new habitats
new woodland habitat for deer and small animals
impact of connectivity and urban green corridors
tick control
dogs
permethrin and imidacloprid spot-on
impregnated collar
dogs/cats
imidacloprid(not effective against ticks by itself) and flumethrin collar
fipronil spot on
fluralaner
in place for travelling dogs
isoxazolines and ticks
latest products with very quick kill and can prevent pathgen transmission
claim = fluralaner prevents transmission of canine babesiosis and borrelia for 12 weeks
no product 100% effective
non prevent all TBDs
inspect and remove ticks asap