6.1: Market Failures and the Role of the Government
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts related to market failures and the role of the government in economics.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is a market failure?
A situation in which the free-market system fails to satisfy society's wants as private markets do not efficiently bring about the allocation of resources.
What are the four types of market failures?
Public Goods
Externalities
Monopolies
Unequal distribution of income
What characterizes a public good?
Public goods are non-exclusionary and shared in consumption.
What is the Free-Rider Problem?
A situation where individuals benefit from resources without paying for them.
Why must the government provide public goods?
The free market cannot profitably provide them due to the Free-Rider Problem.
What does non-exclusionary mean in the context of public goods?
People cannot be excluded from enjoying the benefits, even if they do not pay.
What does shared consumption mean in regards to public goods?
One person's use of a good does not diminish another person's ability to use it.
What happens if left to the free market concerning public goods?
Essential services would be under-produced.
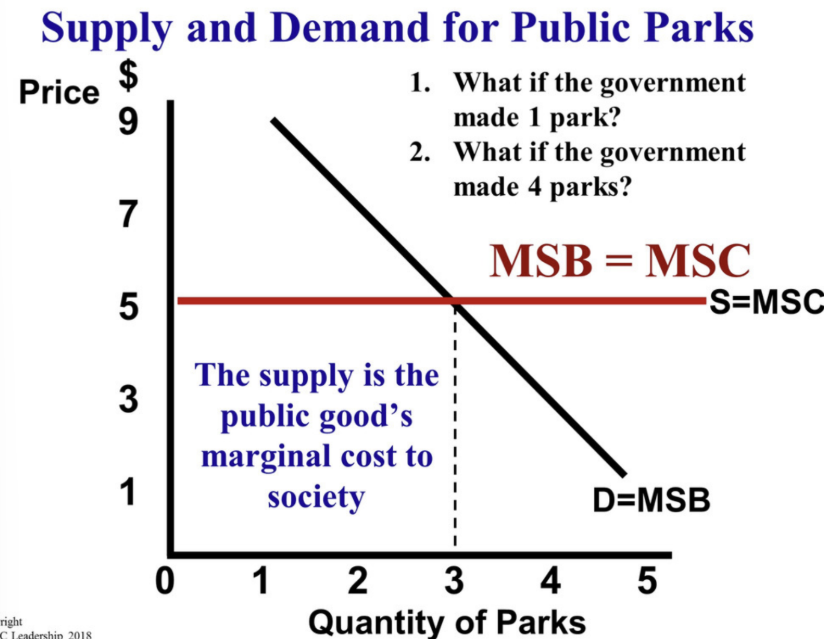
How does the government determine the quantity of public goods?
They utilize supply (marginal social cost) and demand (marginal social benefit) and produce where MSB = MSC.
What is the Marginal Social Benefit of a public good?
Its usefulness to society, determined by citizens' willingness to pay.
The government provides public goods until…
Marginal Social Benefit equals Marginal Social Cost (MSB = MSC)
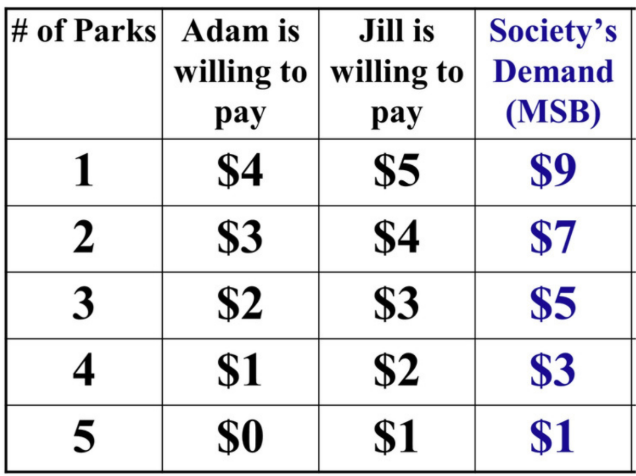
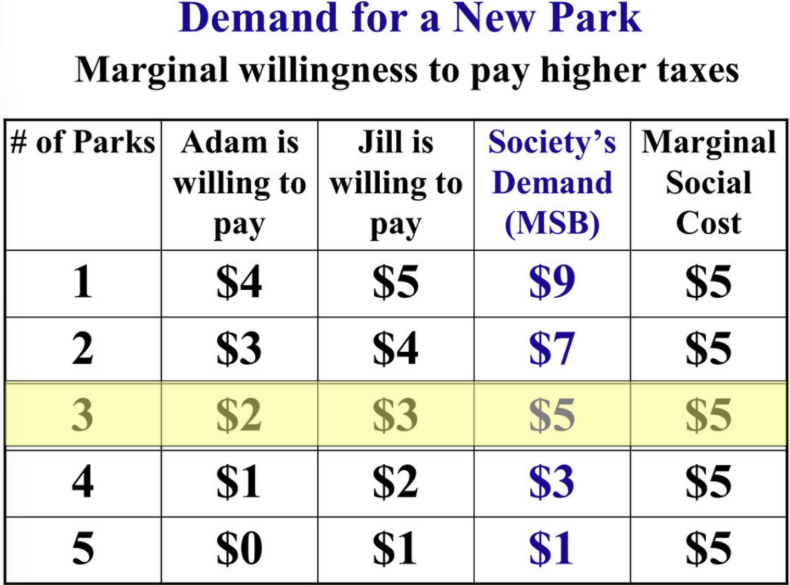
What is the social demand/society’s demand for a public good?
The combined willingness to pay from all members of society.
What is an externality?
A side effect or consequence of an industrial activity that affects other parties without being reflected in the costs.
What is the public sector?
The part of the economy that is controlled by the government and provides public services and goods.
What is the private sector?
The part of the economy that is run by individuals and businesses, providing goods and services for profit.