Chapter 18: Cell Death
Cell Death
Cell death is a natural process that plays a crucial role in various biological phenomena, including development, tissue homeostasis, and immune responses.
There are two major forms of cell death: apoptosis and necrosis.
Apoptosis
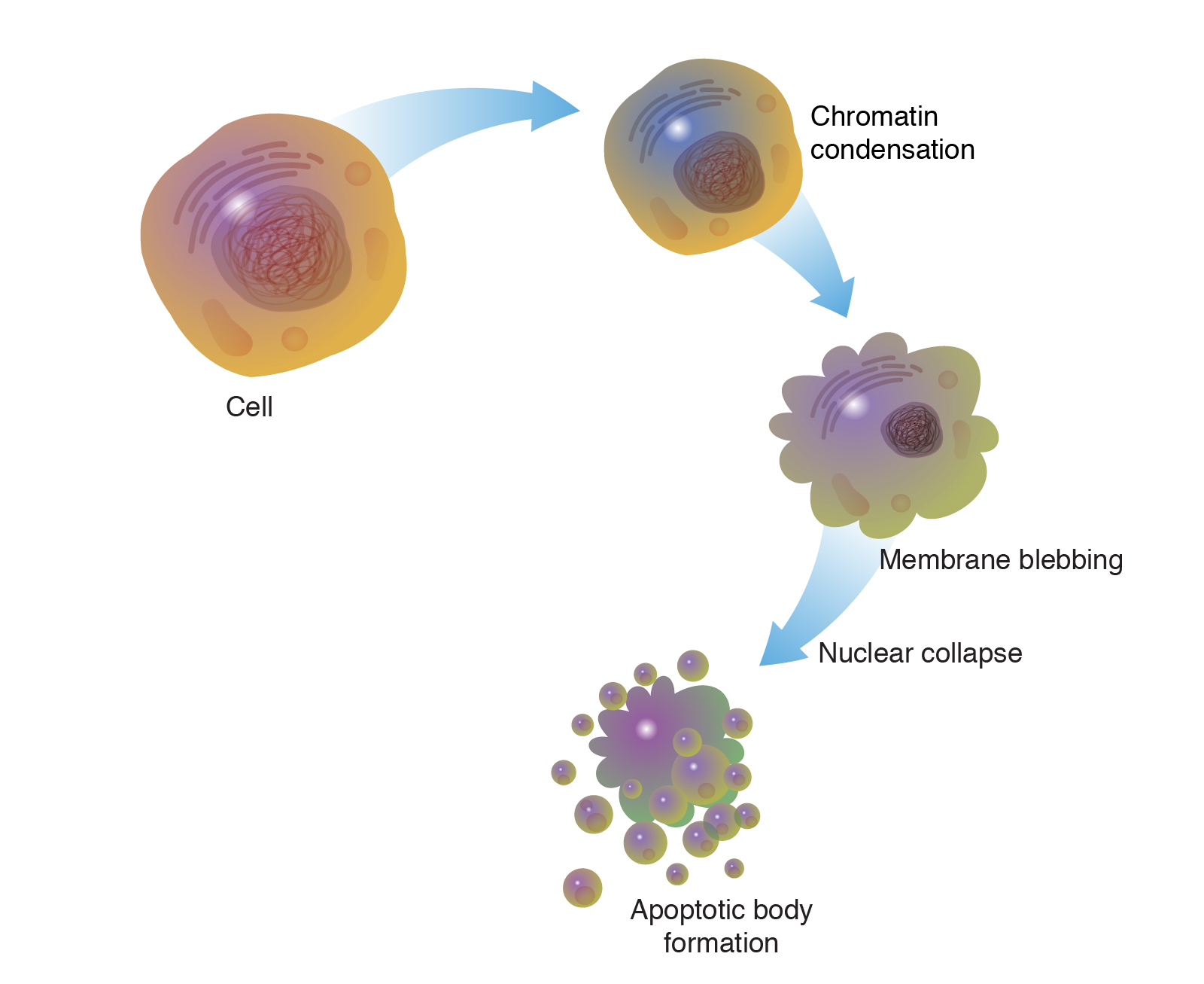
Apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, is a tightly regulated process involved in the normal development and maintenance of tissues. It is characterized by cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and the formation of apoptotic bodies.
Apoptosis serves important functions such as eliminating damaged, infected, or unwanted cells, shaping organs during development, and maintaining tissue balance.
Necrosis
- Necrosis is a type of cell death resulting from acute cellular injury or trauma. It involves cell swelling, organelle damage, membrane rupture, and the release of cellular contents into the surrounding environment.
- Necrosis is generally considered an uncontrolled and inflammatory form of cell death, often associated with pathological conditions or severe cellular stress.
- In addition to apoptosis and necrosis, there are other forms of regulated cell death, including autophagy-dependent cell death (autophagic cell death) and programmed necrosis (necroptosis).
- The balance between cell survival and cell death is tightly regulated by various signaling pathways and molecular mechanisms.
Overview on Apoptosis
- Apoptosis is a highly regulated form of programmed cell death that plays a crucial role in various biological processes.
- It is involved in tissue development, maintenance of tissue homeostasis, immune response, and elimination of damaged, infected, or unwanted cells.
Mechanisms and Signaling Pathways:
- Apoptosis can be triggered by extrinsic or intrinsic pathways, often involving a complex interplay of signaling molecules.
- The extrinsic pathway is initiated by the binding of extracellular death ligands, such as Fas ligand or TNF-alpha, to their respective death receptors on the cell surface.
- The intrinsic pathway, also known as the mitochondrial pathway, is regulated by the balance of pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 protein family.
- In response to cellular stress or damage, pro-apoptotic proteins like Bax and Bak promote mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization, leading to the release of cytochrome c and other apoptotic factors from the mitochondria.
- Cytochrome c forms a complex with Apaf-1, activating caspase-9 and subsequently initiating a caspase cascade that ultimately leads to cell death.
Caspases and Execution of Apoptosis:
- Caspases are a family of proteases that play a central role in apoptosis execution.
- Initiator caspases, such as caspase-8 or caspase-9, are activated through the extrinsic or intrinsic pathways, respectively.
- Activated initiator caspases then cleave and activate effector caspases, such as caspase-3 and caspase-7, which dismantle cellular components and initiate cell death.
- Caspases cleave various cellular substrates, including structural proteins, DNA repair enzymes, and inhibitors of cell survival pathways, leading to characteristic morphological and biochemical changes in apoptotic cells.
Morphological and Biochemical Changes:
- Apoptosis is characterized by distinct morphological changes, including cell shrinkage, membrane blebbing, chromatin condensation, and fragmentation into apoptotic bodies.
- The cell membrane remains intact during early stages of apoptosis, preventing the release of cellular contents and minimizing inflammation.
- Apoptotic bodies are subsequently engulfed and cleared by neighboring cells or phagocytes, preventing the release of potentially harmful cellular contents.
Regulation and Anti-Apoptotic Mechanisms:
- Several cellular mechanisms tightly regulate apoptosis to maintain tissue homeostasis and prevent excessive cell death.
- Anti-apoptotic proteins, such as Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL, inhibit pro-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family, preserving cell survival and blocking mitochondrial apoptosis.
- Various signaling pathways, including growth factor signaling and survival pathways like PI3K/Akt, can promote cell survival by inhibiting pro-apoptotic factors or activating anti-apoptotic mechanisms.
Dysregulation of Apoptosis and Disease:
- Dysregulation of apoptosis is implicated in various diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, autoimmune diseases, and developmental abnormalities.
- Defective apoptosis can lead to uncontrolled cell proliferation, resistance to cell death, or aberrant cell clearance, contributing to disease progression.
- Understanding the molecular mechanisms of apoptosis dysregulation provides potential targets for therapeutic interventions.
Apoptosis Research and Therapeutic Applications:
- Apoptosis research continues to advance, uncovering new components and regulatory mechanisms.
- Therapeutic strategies targeting apoptosis aim to induce cell death in cancer cells or promote cell survival in conditions like neurodegeneration.
- Cancer treatments often involve inducing apoptosis in tumor cells, either through chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted therapies that activate pro-apoptotic.