Unit 2 Population & Migration
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
1
New cards
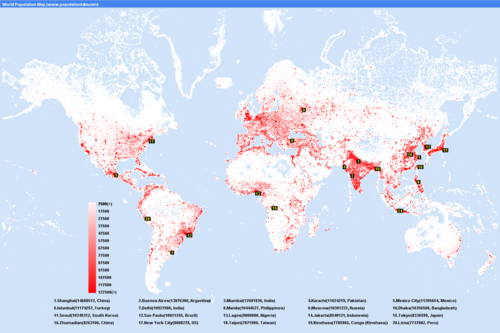
Population Distribution
Physical factors: climate (mid-latitude regions 60-degree North or South of the equator), landforms (mountain, desert, etc. have lower population), water (drinking, for farming, transportation)
Human Factors: Culture, Economics, Government, Transportation, Industry, Time of day
Human Factors: Culture, Economics, Government, Transportation, Industry, Time of day
2
New cards
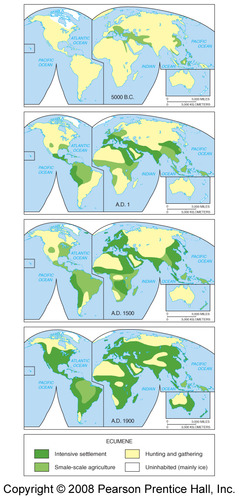
Ecumene
The portion of Earth's surface occupied by permanent human settlement.
Has changed over time
Population clusters: South Asia, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Europe
Has changed over time
Population clusters: South Asia, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Europe
3
New cards
Population Density
A measurement of the number of people per given unit of land
4
New cards
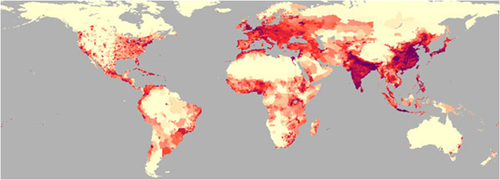
Arithmetic Densterm-0ity
The total number of people divided by the total land area.
Says little about where people actually live or distributed in space
Says little about where people actually live or distributed in space
5
New cards
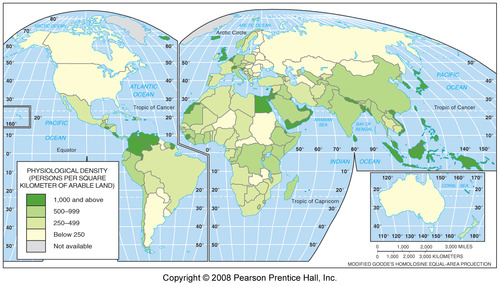
Physiological Density
total population divided by arable land (farmable land)
Can help show Carrying capacity of a country
Can help show Carrying capacity of a country
6
New cards
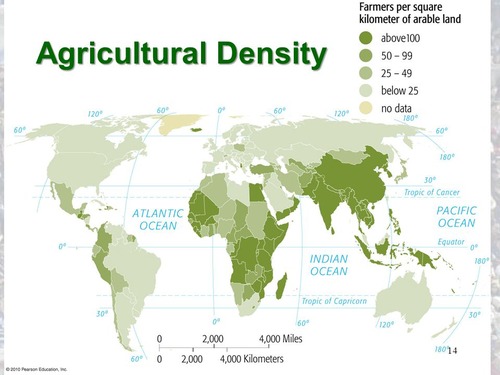
Agricultural Density
number of farmers divided by arable land
can help determine LDC vs MDC.....MDC will have less farmers because of industrialization of farming techniques
can help determine LDC vs MDC.....MDC will have less farmers because of industrialization of farming techniques
7
New cards
Carrying Capacity
the largest population that an environment can support at any given time
8
New cards
Overpopulation
The number of people in an area exceeds the capacity of the environment to support life at a decent standard of living.
9
New cards
cohort
group unified by a specific common characteristic
10
New cards
Sex Ratio
The number of males per 100 females in the population.
11
New cards
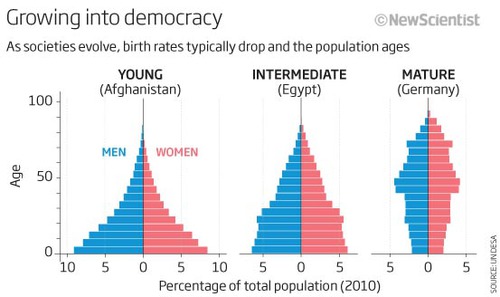
Population Pyramid
A bar graph representing the distribution of population by age and sex.
12
New cards
demographics
the characteristics of a population with respect to age, race, gender etc
13
New cards
Life Expectancy
The average number of years an individual can be expected to live, given current social, economic, and medical conditions. Life expectancy at birth is the average number of years a newborn infant can expect to live.
14
New cards
Natural Increase Rate (NIR)
The percentage growth of a population in a year
crude birth rate minus the crude death rate.
crude birth rate minus the crude death rate.
15
New cards
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
16
New cards
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
The total number of deaths in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
17
New cards
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
The average number of children a woman will have throughout her childbearing years.
# lower in MDC and higher in LDC
# lower in MDC and higher in LDC
18
New cards
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
The total number of deaths in a year among infants under 1 year old for every 1,000 live births in a society.
19
New cards
Demographic Balancing Equation
Total Population Change = Births - Deaths + Immigrants - Emigrants
20
New cards
Doubling Time
The number of years needed to double a population, assuming a constant rate of natural increase.
Rule of 70
70 divided by % NIR = how long it will take the population to double
Rule of 70
70 divided by % NIR = how long it will take the population to double
21
New cards
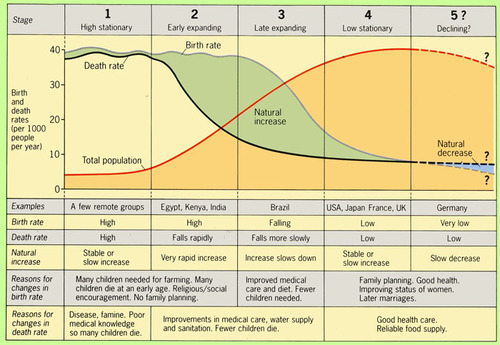
Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
Shows population change as countries modernize. The process of change in a society's population from a condition of high crude birth and death rates and low rate of natural increase to a condition of low crude birth and death rates, low rate of natural increase, and a higher total population.
5 stages of population change that countries pass through as they modernize
5 stages of population change that countries pass through as they modernize
22
New cards
Epidemiological Transition Model (ETM)
distinctive causes of death in each stage of the demographic transition
1. Pestilence & Famine
2. Receding Pandemics
3. Degenerative & Human Created Diseases
4. Delayed Degenerative Diseases
5. Reemerging Infectious & Parasitic Diseases
1. Pestilence & Famine
2. Receding Pandemics
3. Degenerative & Human Created Diseases
4. Delayed Degenerative Diseases
5. Reemerging Infectious & Parasitic Diseases
23
New cards
Thomas Malthus
Eighteenth-century English intellectual who warned that population growth threatened future generations because, in his view, population growth would always outstrip increases in agricultural production. (population can outgrow food supply)
result will be war, famine, disease. (natural checks to population growth)
result will be war, famine, disease. (natural checks to population growth)
24
New cards
Neo-Malthus
People who adapted Malthus basic ideas to modern conditions
Argue the global overpopulation is a threat & will lead to depletion of nonrenewable resources, increased pollution, food shortages, as well as social/political/economic/environmental catastrophe
Argue the global overpopulation is a threat & will lead to depletion of nonrenewable resources, increased pollution, food shortages, as well as social/political/economic/environmental catastrophe
25
New cards
Esther Boserup
Argues against Malthus
Population change drives the intensity of agricultural production - people will find ways to increase the production of food by increasing workforce, machinery, fertilizers, etc.
It is not about production but rather distribution of food
Population change drives the intensity of agricultural production - people will find ways to increase the production of food by increasing workforce, machinery, fertilizers, etc.
It is not about production but rather distribution of food
26
New cards
Pronatalist Policies
government policies that encourage child birth to promote population growth
incentives: tax breaks, free child care, family discounts on government services, longer maternity/paternity leave,
Can be seen in countries in stage 5 of DTM
Ex: Italy, Japan, Germany, Singapore, Denmark
incentives: tax breaks, free child care, family discounts on government services, longer maternity/paternity leave,
Can be seen in countries in stage 5 of DTM
Ex: Italy, Japan, Germany, Singapore, Denmark
27
New cards
Antinatalist Policies
government policies that discourage child birth to decrease population growth
Incentives: Government sponsored/access to contraceptives, abortions, sterilization, or family planning clinics, higher taxes/fines for having multiple kids, access to low cost healthcare for smaller families,
Can be seen in countries in stage 2 or 3 of DTM
Ex: China, India, Nigeria
Incentives: Government sponsored/access to contraceptives, abortions, sterilization, or family planning clinics, higher taxes/fines for having multiple kids, access to low cost healthcare for smaller families,
Can be seen in countries in stage 2 or 3 of DTM
Ex: China, India, Nigeria
28
New cards
Contraceptives
used to prevent pregnancy: birth control, condoms etc
29
New cards
Dependency Ratio
The number of people under age 15 and over age 65 compared to the number of people active in the labor force
30
New cards
Medical Revolution
Medical technology invented in Europe and North America that is diffused to the poorer countries of Latin America, Asia, and Africa. Improved medical practices have eliminated many of the traditional causes of death in poorer countries and enabled more people to live longer and healthier lives.
Led countries to move to stage 2 of the DTM
Led countries to move to stage 2 of the DTM
31
New cards
Migration
a form of relocation diffusion involving a permanent move from one place to another
32
New cards
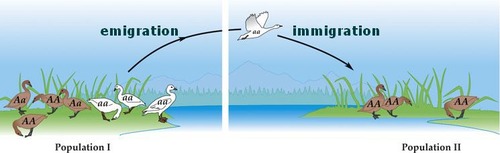
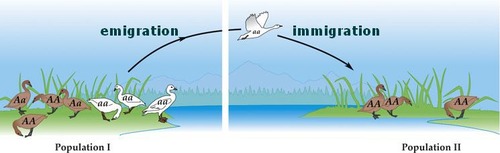
Immigration
Migration to a new location (Country)
Immigration with an I = into a new place
Immigration with an I = into a new place
33
New cards
Emigration
movement of individuals out of a country
Emigration with an E = to leave a place
Emigration with an E = to leave a place
34
New cards
Ravenstein's Laws of Migration
1880s German geographer noted patterns about migration tendencies, demographics etc (why/how/who migrates)
1. Economic reasons
2. Most people migrate Short Distances
3. Long Distance migrants usually move to Urban Areas (major economic activities found here....think Gravity Model)
4. Step Migration
5. Counter-migration
6. Men migrate further than women
7. Long Distance migrants are young adults rather than families with children
8. Rural to Urban
1. Economic reasons
2. Most people migrate Short Distances
3. Long Distance migrants usually move to Urban Areas (major economic activities found here....think Gravity Model)
4. Step Migration
5. Counter-migration
6. Men migrate further than women
7. Long Distance migrants are young adults rather than families with children
8. Rural to Urban
35
New cards
Zelinsky's Model of Migration
Coincides with the DTM
Claims that the type of migration that occurs within a country depends on its level of development
Stage 1: little or no permanent migration (move daily or seasonally)
Stage 2: Rural to Urban AND International migration
Stage 3-5: Migration is internal intraregional
Claims that the type of migration that occurs within a country depends on its level of development
Stage 1: little or no permanent migration (move daily or seasonally)
Stage 2: Rural to Urban AND International migration
Stage 3-5: Migration is internal intraregional
36
New cards
Push/Pull Factors
Conditions that draw people to another location (pull factors) or cause people to leave their homelands and migrate to another region (push factors)
37
New cards
Intervening Opportunity
The presence of a nearer opportunity that greatly diminishes the attractiveness of sites farther away.....pauses ones migration (movement)
38
New cards
Intervening Obstacle
hinders migration.
PHYSICAL FEATURES: mountains, oceans, deserts etc
MAN MADE BARRIERS such as The Berlin Wall, US/Mexico wall, Israeli Green Line Wall, POLITICAL policies restricting immigration, ECONOMIC cost of migrating, CULTURAL obstacles such as language, family pressure, hostility towards immigrants
PHYSICAL FEATURES: mountains, oceans, deserts etc
MAN MADE BARRIERS such as The Berlin Wall, US/Mexico wall, Israeli Green Line Wall, POLITICAL policies restricting immigration, ECONOMIC cost of migrating, CULTURAL obstacles such as language, family pressure, hostility towards immigrants
39
New cards
Forced Migration
Human migration flows in which the movers have no choice but to relocate because of political, economic, environmental and cultural factors
40
New cards
Refugee
A person who has been forced to leave their country in fear of their life
41
New cards
Internally Displaced Person (IDP)
Someone who has been forced to migrate for similar political / cultural reasons as a refugee but has NOT migrated across an international border
42
New cards
Asylum Seeker
Someone who has migrated to another country in the hope of being recognized as a refugee
43
New cards
Voluntary Migration
movement in which people relocate in response to perceived opportunity; not forced.
44
New cards
Transnational Migration
international migration in which people retain strong cultural, emotional, & financial ties with their country of origin
a process of movement and settlement across international borders in which individuals maintain or build multiple networks of connection to their country of origin while at the same time settling in a new country" Transnational migrants work, pray, and express their political interests in several contexts rather than in a single nation-state. Some will put down roots in a host country, maintain strong homeland ties, and belong to religious and political movements that span the globe
a process of movement and settlement across international borders in which individuals maintain or build multiple networks of connection to their country of origin while at the same time settling in a new country" Transnational migrants work, pray, and express their political interests in several contexts rather than in a single nation-state. Some will put down roots in a host country, maintain strong homeland ties, and belong to religious and political movements that span the globe
45
New cards
Transhumance
A seasonal periodic movement of pastoralists and their livestock between highland and lowland pastures

46
New cards
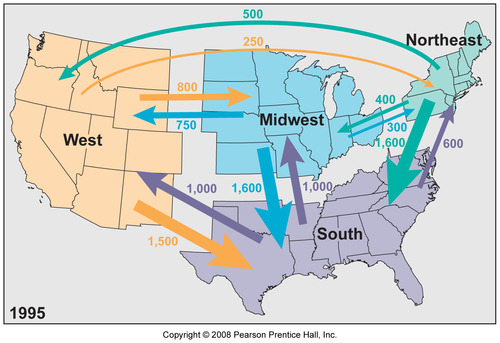
Interregional Migration
Permanent movement from one region of a country to another.
47
New cards
Intraregional Migration
Permanent movement within one region of a country.
48
New cards
Chain Migration
migration of people to a specific location because relatives, friends, or members of the same nationality previously migrated there
49
New cards
Step Migration
a migration in which an eventual long-distance relocation is undertaken in stages... a common pattern is from a small town to larger town to a small city and finally to a large city
50
New cards
Guest Worker
a foreign laborer living and working temporarily in another country
51
New cards
Counter Urbanization
The flow of urban residents leaving cities
52
New cards
Brain Drain
the emigration of highly trained, skilled and/or educated people from a country.
53
New cards
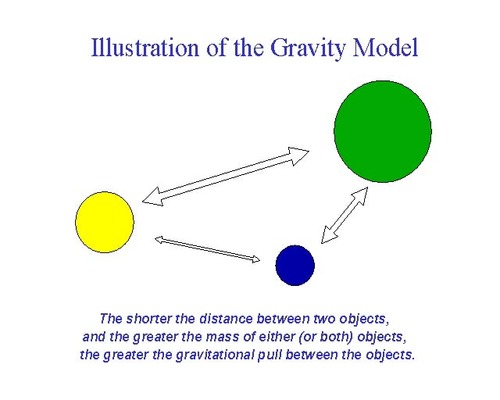
Gravity Model
the belief in the greater pull of larger communities and the assumption that more people are likely to migrate to larger towns/cities vs small towns/cities
54
New cards
Remittances
Money migrants send back to family and friends in their home countries, often in cash, forming an important part of the economy in many poorer countries
55
New cards
Net-out Migration
the difference between the number of people moving into an area (a country, state, or county, for example) and the number moving out.
56
New cards
Net-In Migration
the difference between the number of immigrants (people coming into an area) and the number of emigrants (people leaving an area) throughout the year. When the number of immigrants is larger than the number of emigrants, a positive net migration rate occurs.