Vas week 5: Arterial UE & LE duplex imaging bookwork
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
The normal PSV of the distal superficial femoral artery is:
94 + 14cm/s
The characteristic waveform from an arteriovenous (AV) fistula created by iatrogenic trauma is
High velocity, low resistance
What type of waveform pattern is common in the neck of a pseudoaneurysm?
To and Fro
Research has noted that a monophasic waveform accompanied by a PSV of ____ is highly indicative of iliac artery _____
<45cm/s, occlusion
An important complication of popliteal aneurysm is:
emboli
When evaluating for popliteal entrapment, measure the PSV of the distal popliteal artery at the level of:
Gastrocnemius muscle head
What percentage of patients with femoral aneurysms also have popliteal aneurysms?
3%
what type of waveform is typically observed in venous segment proximal to an AVF
Turbulant
Which peripheral artery most commonly becomes aneurysmal?
popliteal
Collaterals often enter/exit arteries at what angle?
90 degrees
What percentage of male patients with a popliteal aneurysm might also have an abdominal aneurysm?
64%
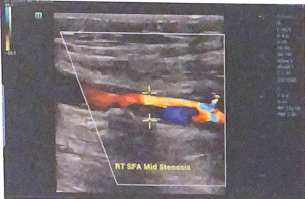
Calculate the VR and fill in the last column of chart below. do velocity ratios suggest a hemodynamically significant stenosis between the arterial segments?
These ratios suggest a significant stenosis at the mid SFA level
When the stenosis is >70%, expect the velocities to be at least _____ compared to the proximal arterial segment
triple
a 15% lumenal reduction corresponds to _____% area reduction
75
Expect the PSV throughout a normal artery to be relatively _____
uniform
“Parvus tardus” is another term some use to describe a ____ waveform
monophasic
a _____ waveform indicates a downstream occlusion
stacatto
Between ____ cm and ____ cm is the typical range for the diameter of a pseudoaneurysm neck
1 - 5
The arterial layer typically involved in an arterial dissection is the _____
intima
Popliteal aneurysms usually occur ____
Bilaterally
what is the formula for calculating the velocity ratio between two segments?
Vr = v2 / v1
Define the term "AV fistula”
Abnormal connection between artery and vein
how does an adventitial cyst affect flow through the popliteal artery?
focal stenosis or occlusion might be observed on the duplex scan
why does color flow sometimes underestimate the luminal reduction of the artery?
color flow often “bleeds’ over the plaque in b-mode
Define “arteriomegaly”
uniform arterial dilatation throughout an artery
What is the difference between an aneurysmal and ectatic artery.
ectatic refers to diameters that are larger throughout the segment, though not yet aneurysmal. aneurysm would be 1.5-2 times larger than the prox segment measured
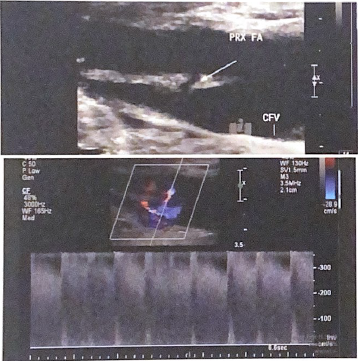
The following B-mode image and spectral doppler tracing are from a lower extremity arterial exam. there appears to be a connection between the artery and adjacent vein. what condition is present in this lower extremity? Describe what evidence from the spectral tracing supports your interpretation.
It is a arteriovenous fistula (AVF). spectral tracing demonstrates a high velocity, low resistance signal typical of an AVF
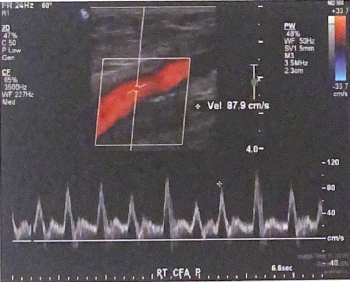
This image was recorded proximal to an AVF. Describe how the arterial waveform is affected because of the finding distally.
arterial signal prox to an avf loses resistance rather than the normal high resistance triphasic waveform, with flow below the baseline, expected in a normal limb.
Are the calipers placed in this image to measure the true or residual lumen?
they are measuring the true lumen, placed from outer wall to the outer wall of the artery
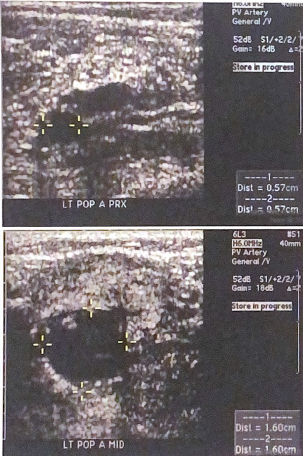
Consider the popliteal artery diameters measured in the images below. is there evidence of a popliteal aneurysm? why or why not?
Yes because an aneurysm is defined as a focal enlargement of an artery at least twice the diameter of the prox segment. the mid segment diameter at 1.6 is greater than twice the diameter of the prox segment at 0.57

Describe the condition in this image
Arterial dissection
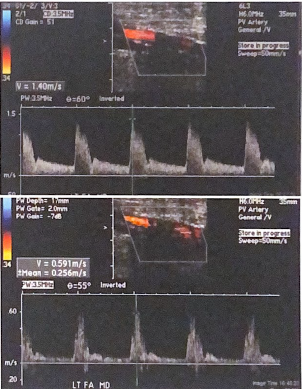
The following images were documented around calcification in the SFA; the first image is before the shadowing and the second image is after. is there evidence of a hemodynamically significant stenosis under the arterial shadowing?
No because the velocity measured after calcification is less than half the velocity recorded before the calcification. The waveform has not significantly changed. the distal waveform does not exhibit strong post stenotic turbulence
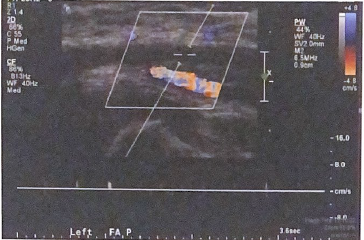
List three good technical practices used to document the occlusion in this image
lower color scale
decreased doppler scale
large doppler gate
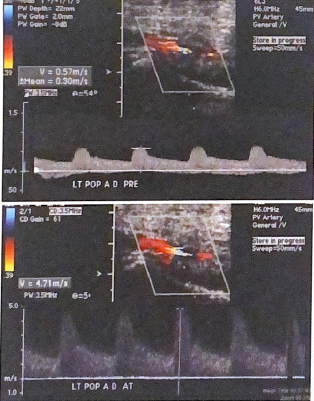
Calculate the Vr for the popliteal artery in these images, is there a hemodynamically significant stenosis in the left distal popliteal artery?
Vr= 4.71 / 0.57 = 8.3
Since velocity has more than tripled from prox segment, this would be considered a hemodynamically significant stenosis
The protocol for post-occlusive reactive hyperemia (PORH) testing includes inflation of a pressure cuff _____ mmHg over the brachial artery pressure at rest for ____ min
30 mmHg for 5 min
The typical shape of an upper extremity aneurysm is:
Fusiform
what is the percentage of subclavian steal cases involving the left arm
85%
upper extremity arterial plaque is most commonly found in which arteries?
subclavian and axillary
a normal peak systolic velocity for the ulnar artery is typically:
50cm/s
subclavian steal syndrome is possible when which of the following conditions is noted, even though brachial pressures do not differ significantly?
To and for vertebral flow
the typical flow pattern in the neck of a pseudoaneurysm is
to and fo
a staccato waveform pattern indicates
distal arterial occlusion
where are collateral vessels often observed by duplex imaging in the case of an occlusion?
proximal and / or distal to the occlusion
The false lumen of an arterial dissection can progress into which of the following conditions?
pseudoaneurysm
the internal thoracic artery typically can be visualized coming off the subclavian artery at a _____ degree angle
90
The _____ artery is most likely to be involved in an upper extremity arterial dissection
subclavian
a _____ waveform is expected in the arterial segment at the site of an AVF
low resistant
The minimum increase in upper extremity velocity ratio from one segment to the next is _____ for a significant stenosis
2.0
when using PORH testing in conjunction with duplex imaging, ______ vertebral flow ill be observed on the ipsilateral side in cases positive for subclavian steal syndrome
reversed or retrograde
Since arterial calcification prohibits visualization of the entire artery, the technologist should use indirect signs such as a change in _____ from before and after the calcified segment
waveform
since the clavicle prohibits visualization of the entire subclavian artery, the technologist should use a change in_____ from above and below the bony structure to determine if there is an obstruction
waveform
intralumenal thrombus within an aneurysm can be a source of ______
emboli
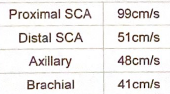
Calculate the velocity ratio between the distal subclavian and axillary arteries. show calculation
48/51=0.94
When scanning the upper extremity of a cancer patient with a history of radiation treatment, arterial narrowing is often caused by what mechanism
intimal hyperplasia or cellular damage after radiation therapy
When do patients experience symptoms linked to thoracic outlet syndrome?
symptoms often come on with certain positional changes
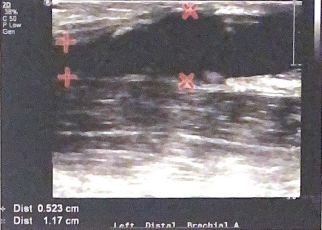
in this image, do the diameters measured support the diagnoses of arterial aneurysm? why or why not?
no because there is a diameter increase distally of more than 1.5-2 times the prox segment. from 0.523 to 1.117 is an increase of 2.23 times
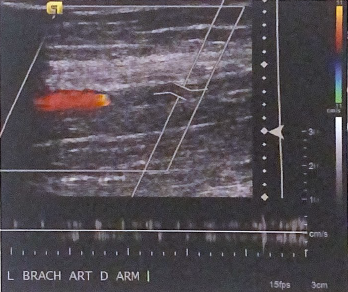
What is most likely interpretation of arterial flow in the brachial artery according to this duplex image?
arterial occlusion due to the lack of color flow with appropriate settings ad no spectral doppler flow determined
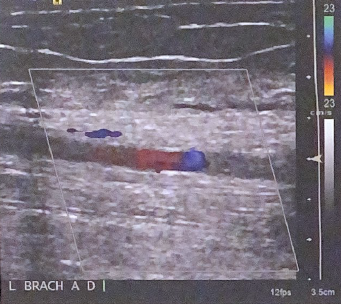
Describe how this image could be optimized for better color flow in the artery. List at least 2 settings that could be adjusted
decrease color scale, make color box smaller and concentrated around artery. can also try to increase color gain
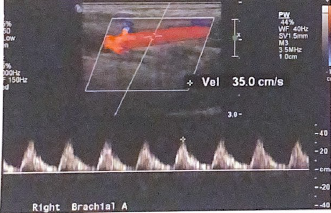
According to published studies, is this PSV in the following image within normal limits?
no it is not for brachial artery. it typically is between 50-120 cm/s
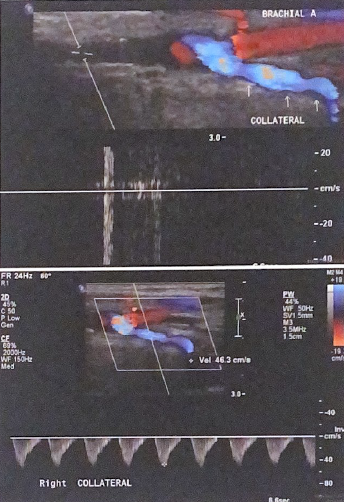
in the top image, there is no flow detected by spectral doppler in the proximal arterial segment. Explain the flow direction documented by color and doppler flow in the collateral brachial artery distally (bottom image)
since artery is occluded proximally, the collateral artery is flowing retrograde in order to provide the brachial artery with antegrade blood flow
Define “aneurysm”
a focal enlargement at least 1.5-2 times the diameter of the proximal arterial segment
Why might a peripheral IV line be a limitation to a duplex scanning?
Visualization can be limited because you cannot scan directly over the site
Define “vasospasm” and list which upper extremity artery is typically affected
temporary constriction of the arteries. digital arrtey’s are often affected