GA Thoracic Organs of Respiration
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
146 Terms
the trachea begins right below the:
cricoid cartilage
The phrenic nerve is derived from spinal nerves:
C3-C5
The visceral pleura is supplied by ________ fibers carried by the thoracic splanchnic nerves.
GVA
The lingula is part of the:
upper lobe of the left lung
The secondary bronchi are also known as the:
lobar bronchi
what are the components of the lower respiratory tract?
trachea, bronchi, lungs
what type of cartilage makes up the trachea?
hyaline cartilage
what structure separates the trachea from the upper vs lower respiratory tract?
larynx, lowest part of cartilage is cricoid cartilage
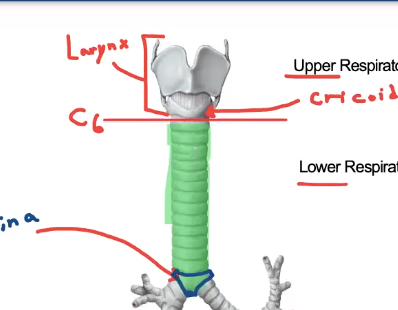
what vertebral level indicates where the trachea begins?
C6
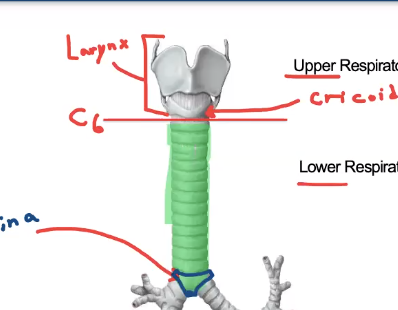
what cartilage indicates the last tracheal cartilage?
carina
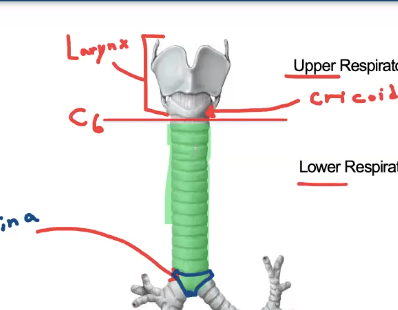
what vertebral level is the carina?
T4/T5
what two structures branch off of the carina?
left and right mainstem bronchi
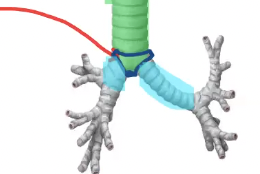
what is another name for the right and left mainstem bronchi?
right and left primary bronchi
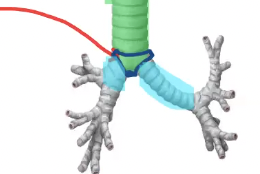
what are the three main differences between the right and left primary bronchi?
left mainstem bronchus is longer and right is shorter, right mainstem has a larger lumen (thicker), right mainstem more in line with trachea/vertically oriented (left takes a hard left/horizontally/obliquely oriented)
why is the left mainstem bronchus longer than the right?
left lung pushes further lateral because of the heart so bronchus has to reach further
Secondary bronchi are also known as ____
lobar bronchi (1 bronchi per lobe)
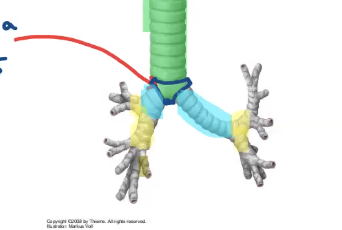
how many lobar bronchi are on the left?
2
how many lobar bronchi are on the right?
3
Tertiary bronchi are also known as ______.
segmental bronchi
what is directly anterior to the trachea?
aortic arch
what is directly posterior to the trachea?
esophagus
The tracheal rings are open _______.
posteriorly
why is the trachea open posteriorly?
to allow for esophagus expanding if swallowing large ball of food
what muscle bridges the gap between the opened tracheal rings?
trachealis
during a deep inspiration, what level might the carina be at?
T6
when the diaphragm contracts it moves in what direction?
downward
what are the two membranes of the pleural sac?
visceral and parietal pleuras
what type of membrane is the pleural sac?
serous
what is the function/purpose of a serous membrane?
lubricating membrane
Visceral pleura is in direct contact with ______.
the lung itself

Parietal pleura is in contact with _____.
the wall, thoracic cavity
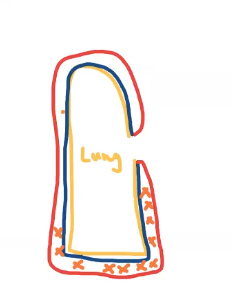
Pleural cavity is
the space between the visceral pleura and parietal pleura (potential space), contains a thin layer of serous fluid
where do serous membranes come from (embryologically)?
lateral plate mesoderm
costal pleura is in direct contact with _____
the ribs
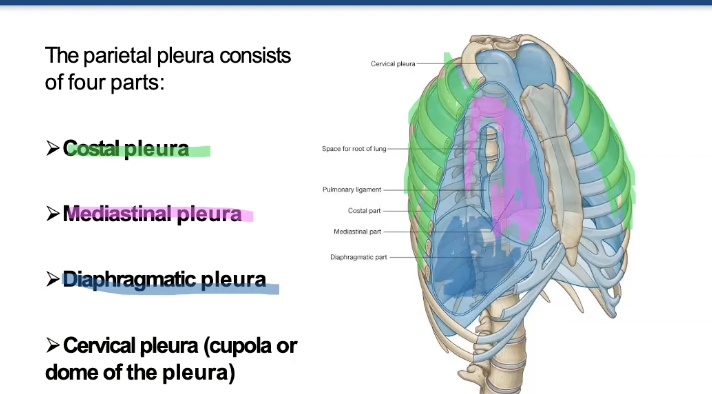
what are the four parts of the parietal pleura?
costal, mediastinal, diaphragmatic, cervical pleura
What is another name for the cervical pleura?
cupola or dome of the pleura
what are the boundaries of the inferior border of the parietal pleura?
anteriorly rib 8, laterally rib 10, posteriorly T12
Pleural spaces are also known as ____.
recesses
What are the two recesses in the pleural cavity?
costodiaphragmatic and costomediastinal
what is the lowest point in the pleural cavity?
costodiaphragmatic recess
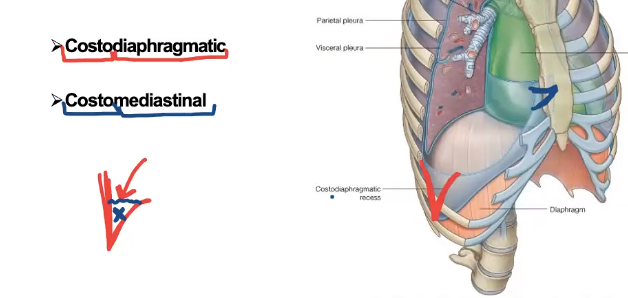
what fits into the costodiaphragmatic recess?
inferior border of the lung
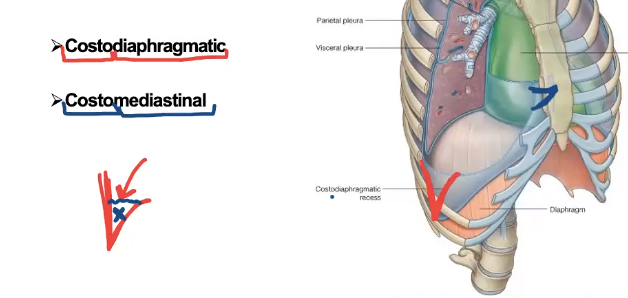
what fits into the costomediastinal recess?
anterior border of the lungs
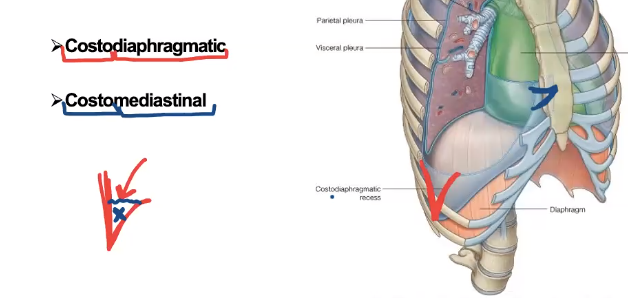
The base of the lung is also known as
the diaphragmatic surface
Base of the lung location
most inferior portion of the lung
what are the three surfaces of the lung?
diaphragmatic, mediastinal, costal surfaces
Each surface of the lung is separated by ____
a border
What are the three borders of the lung?
inferior, anterior, posterior borders
What are the contents of the root and hilum? (no photo)
a pulmonary artery, two pulmonary veins, a main bronchus, bronchial vessels, nerves, lymphatics
The anterior border separates what two surfaces?
costal and mediastinal
The inferior border separates what two surfaces?
costal and diaphragmatic surface/base
what separates the lung into lobes?
fissure (slice-like opening)
The oblique fissure of the left lung separates…
the superior and inferior lobes
The oblique fissure on the right lung separates…
the inferior lobe from the other two
The horizontal/transverse fissure separates…
the superior and medial lobes
What anterior landmark is the horizontal/transverse fissure at?
4th rib/costal cartilage
What lateral landmark is the horizontal/transverse fissure at?
6th rib
The ribs slope _____ as they travel forward
inferiorly
The inferior border of the lung is found posteriorly at the level of?
T10
The inferior border of the lung is found laterally at the level of?
rib 8
The inferior border of the lung is found anteriorly at the level of?
rib 6
What level is the inferior boundary of the parietal pleura posteriorly?
T12
What level is the inferior boundary of the parietal pleura laterally?
rib 10
What level is the inferior boundary of the parietal pleura anteriorly?
rib 8
why does the left lung only have two lobes?
gave up middle lobe to make room for the heart
is the left or right lung taller?
left
Lingula
landmark found on the superior lobe of the left lung
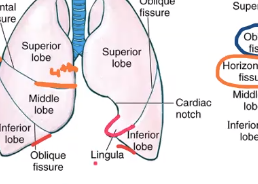
T/F Functionally speaking the lingula is a lobe of its own.
True
What landmark can be used to distinguish the lingula from the rest of the superior lobe?
cardiac notch
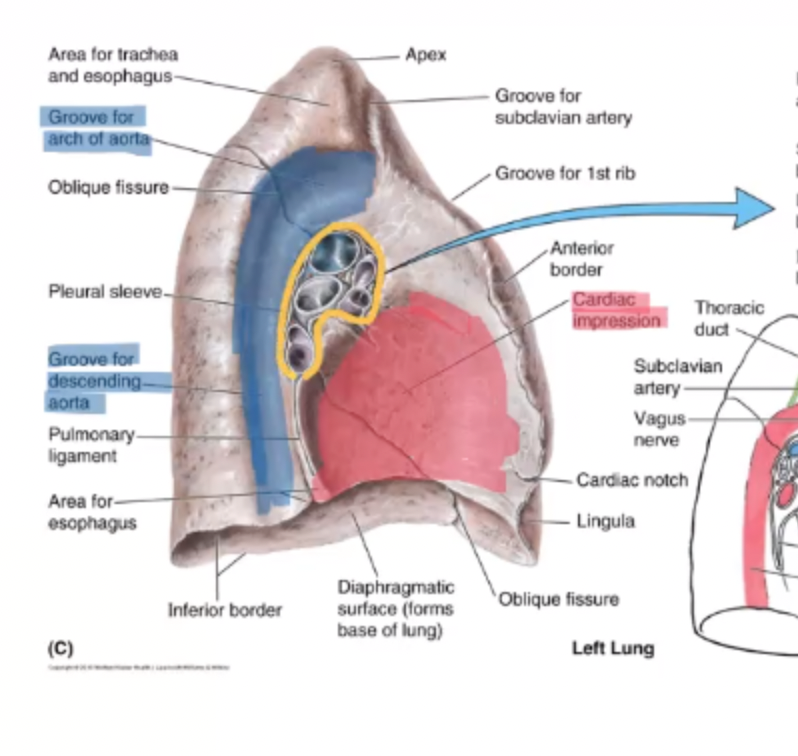
Cardiac notch
shallow depression on the anterior border of the left lung
The root of the lung is made up of the contents of the _____.
hilum
Hilum definition
doorway in and out of any organ
Structures of the root/hilum
pulmonary artery, two pulmonary veins, main bronchus, bronchial vessels, nerves, lymphatics
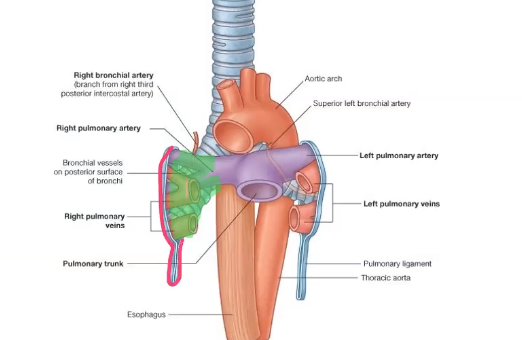
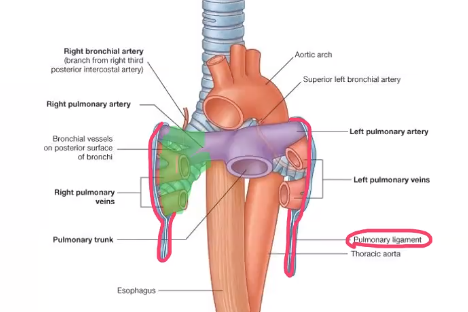
Pulmonary ligament
loose sleeve around the root of the lung, allows the lungs to expand, where visceral and parietal pleura meet
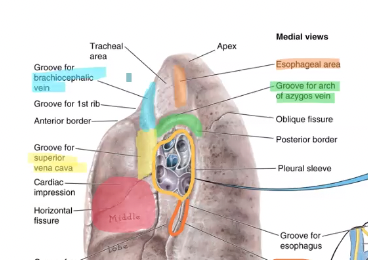
Cardiac impression
red
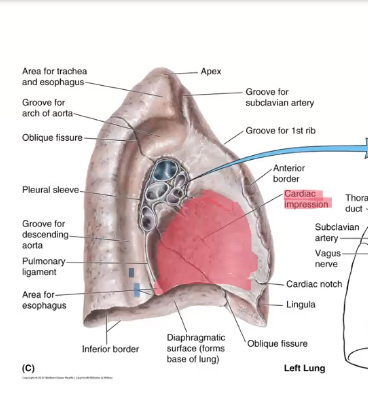
Groove for descending thoracic aorta
blue
what is the most superior structure in the left lung’s hilum?
pulmonary artery
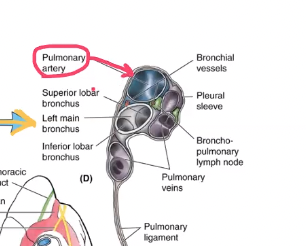
What structure is anterior an inferior to the left lung’s hilum’s pulmonary artery?
left mainstem bronchus
What structure is anterior and inferior to the left lung’s hilum’s mainstem bronchus?
pulmonary veins
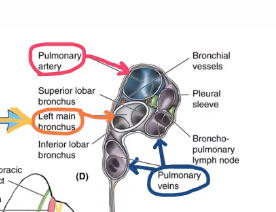
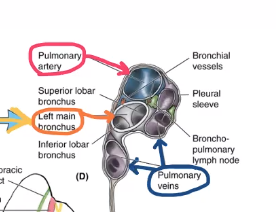
what is the most posterior/superior structure in the right lung’s hilum?
main stem bronchus
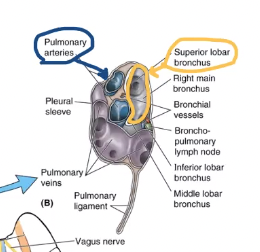
what structure is anterior to the bronchus of the right lung’s hilum?
pulmonary artery
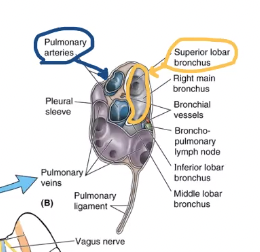
what is anterior and inferior to the right lung’s hilum’s pulmonary artery?
pulmonary veins
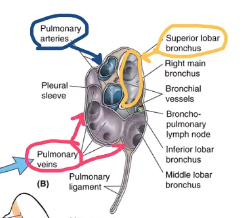
The cardiac impression larger on the right or left lung?
left
what are the grooves found on the right lung?
cardiac, inferior vena cava, esophagus, azygous vein, brachiocephalic vein
Bronchopulmonary segment
each have own blood supply, tertiary bronchus, each lobe can be subdivided, are physiologically independent
Segmental bronchus branches into…
large subsegmental bronchus
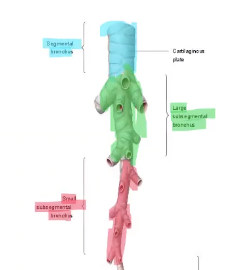
Large subsegmental bronchus branches into…
small subsegmental bronchus
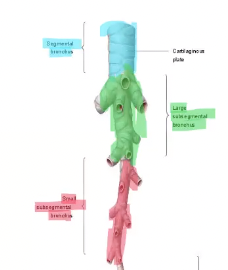
Small subsegmental bronchus branches into…
bronchioles then terminal bronchioles
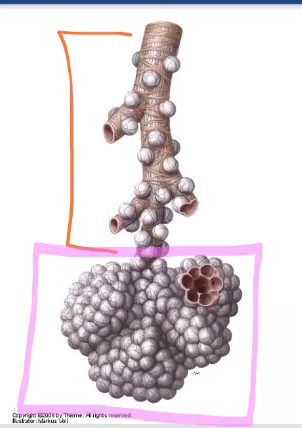
what is the difference between bronchi and bronchioles?
Bronchioles don’t have hyaline cartilage like everything else above
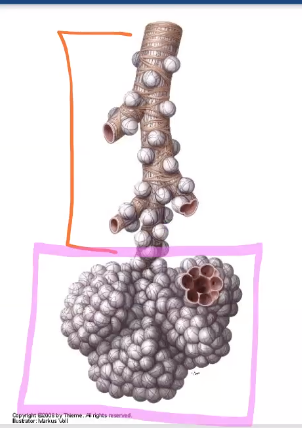
Terminal bronchioles give rise to…
alveolar sacks
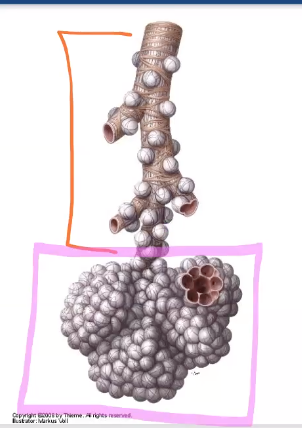
Terminal bronchiole is also known as the….
respiratory bronchioles (individual alveoles there)
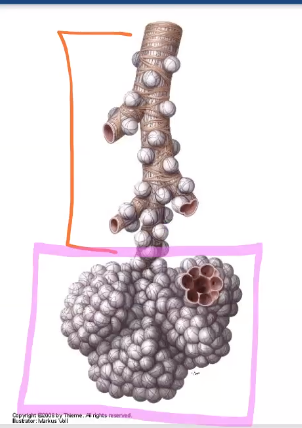
What are the two types of cells making up the walls of the alveoli?
Type I and Type 2 pneumocytes
Type 1 pneumocytes
squamous cells (flat, plate-like), oxygen doesn’t have to travel far to get through wall of cell, gas exchange
Type 2 pneumocytes
cuboidal (harder for gas exchange), secrete surfactant (reduce surface tension, prevents alveolar sack from collapsing)
Type 2 pneumocytes clinical application
7 months of development, then Type 2 begin functioning, so baby born earlier than 7 months the surface tension too much and respiratory distress
where does exchange of respiratory fluids occur?
alveolar sacks
Bronchial arteries are a branch off of ______.
descending thoracic aorta
The left bronchiole vein drains into the _____
accessory hemiazygous vein
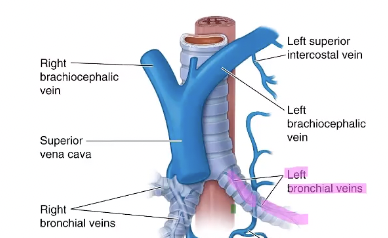
The right bronchiole vein drains into the _____.
azygous vein
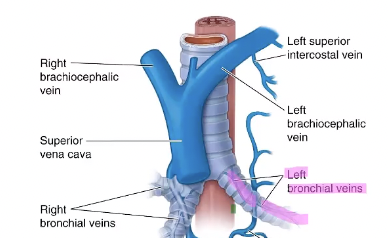
where does the majority of the right lung lymph drain into?
right lymphatic duct
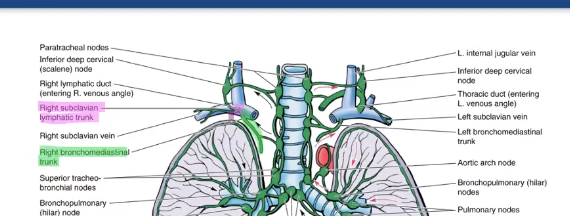
where does the left lung lymphatics drain into?
lymphatic duct