Integumentary system
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANP 1106
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
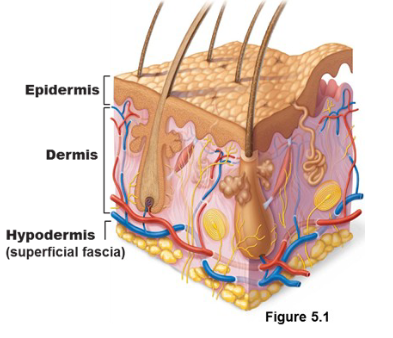
Structure of skin
Is 1.5 -4 mm consisting of 2 distinct regions
includes: epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis
Epidermis
Superficial epithelial region: layered-thick
keratinized stratified(multilayered) squamous(flat) epithelium
The outermost protective shield of the body
avascular
Dermis
Dense connective tissue ; vascularized
makes up most of the skin
leathery layer is made up of dense connective tissue
Hypodermis
Superficial fascia(connective tissue that wraps around)
not part of the skin, hence subcutaneous
Mostly adipose tissue/areolar connective tissue
anchors skin to muscles with ability to slide
acts as shock absorber and an insulator to reduce heat loss
stores fat
4 types of epidermal cells
Keratinocytes
Melanocytes
Dendritic (Langerhans) cells
Tactile (merkel) cells
Keratinocytes
Make up 95% of thin cells
arise from stratum basale
What is the main function of keratinocytes? To make keratin
What is the lifespan of a keratinocyte? 28-56 days
What is epidermal growth factor? is a protein that stimulates cell growth and differentiation by binding to its receptor, EGFR
Melanocytes
Produce melanin which is packed into melanosomes;
deepest layer of epidermis(basale)
numerous branching processes for melanosomes transfer to adjacent cells.
Why is melanin important? To protect nucleus from damaging UV rays of the sun
Dendritic (Langerhans) cells
epidermal dendritic cells (star-shaped);
present in stratum spinosum
migrate to epidermis from bone marrow.
Can differentiate into macrophages
macrophages activate immune system and ingest foreign substances
Tactile (Merkel) Cells
present at the epidermis/dermis boundary
have disc-like sensory nerve ending forms touch receptors
Epidermal cells and layers of the epiderm
stratum = layers
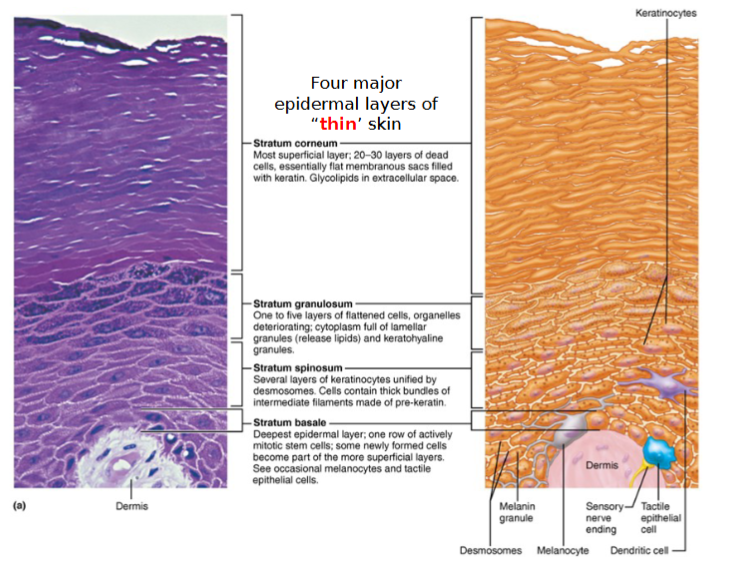
5 distinct layers of epidermis
Thick Skin: Contains 5 layers (strata) and is found in high abrasion(hands, feet)
Thin skin contains only 4 strata(omit stratum lucidum)
5 layers of skin:
Stratum corneum
Stratum lucidum
Stratum granulosum
Strum spinosum
Stratum Basale
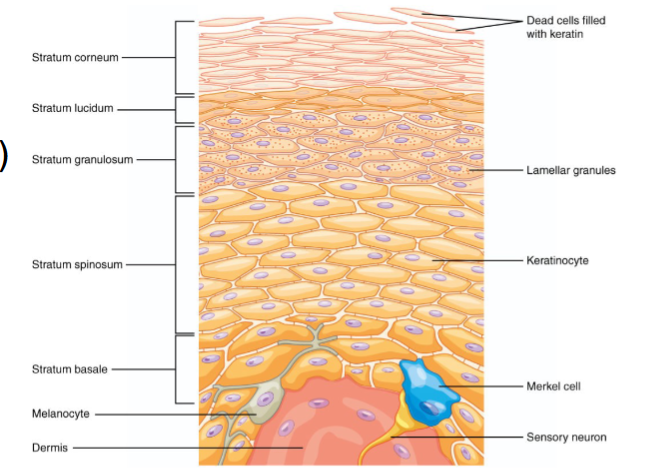
Stratum basale (basal layer)
the deepest epidermal layer, is also called the stratum germinativum
consists of a single row of stem cells that continuously proliferate and differentiate to maintain epidermis
contains youngest keratinocytes, melanocytes & tactile epithelial cells
Stratum Spinosum (prickly layer)
contain dendritic cells and many rows of flattened dividing keratinocytes
its cells contain thick bundles of intermediate filaments, consisting of prekeratin anchored to desmosomes
Stratum granulosum (granular layer)
consist of 1-5 layers and where keratinization (hardening) begins
granules promote hardening and waterproofing
these cells flatten, their nuclei and organelles begin to disintegrate and forms 2 types of granules
keratohyaline granules
lamellar granules
keratinocytes stop dividing and die due to distance from capillaries and glycolipids coating
keratohyaline granules
provides ‘glue’ that binds prekeratin intermediate filaments to from keratin
lamellar granules
contain a water-resistant glycolipid that is secreted into the extracellular space.
Together with tight junctions, the glycolipid slow water loss across the epidermis.
Stratum Lucidum (clear layer)
found only in THICK skin
is a thin transulecent band above the stratum granulosum
consists of rows of flat, dead keratinocytes
its cells are identical to those of stratum corneum
Stratum Corneum (horny layer)
the outermost epidermal layer that accounts for ~3/4 of epidermal thickness
keratin and proteins accumulate inside the plasma membrane of its cells to protect skin from abrasion/penetration
glycolipid between its cells keeps it waterproof
is a layer of completely dead cells and are shed to be replaced (ie. dandruff, flakes)
Dermis
Strong, flexible connective tissue
cells include fibroblasts, macrophages, some mast cells. and WBCs
Semi-fluid matrix heavily embedded with collagen, elastin, and reticular fibers
Fibers in matrix bind body together
Makes up the hide used to make leather
Contains nerves, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels, epidermal hair follicles, oil glands and sweat glands
Has only 2 layers
2 layers of the dermis
Papillary dermis
Reticular dermis
Papillary dermis
made up of interwoven mat of areolar CT fibers interspersed with blood vessels
has peg-like projections on its surface, AKA dermal papillae
is the superficial region of dermis that indents the overlying epidermis
contains either capillary loops or free nerve endings (tactile/meissner corpuscles and pain receptors)
create friction ridges
Reticular dermis
largest layer of skin
made up of deeper, thick dense irregular CT (thick bundles of collagen fibers running in different directions but mostly parallel to skin surface)
source of lines of cleavage (tension) lines(AKA collagen-free areas)
important for surgery bc it takes less time to heal
has Pacinian corpuscles (pressure receptors), sweat/oil glands, hair root
collagen fibers give strength/resiliency & maintain skin hydration
elastic fibers provide stretch-recoil properties of skin
Friction ridges
On palms of hands (& fingers), soles of feet,
formed when dermal papillae lie on top of dermal ridges, which extend from the surface as epidermal ridges known as friction ridges
Definitively develop pre-birth
Persistent during life except for permanent scarring
Details are unique and never repeat
Overall patterns may vary within limits allowing classification
function of friction ridges
enhance gripping ability
contribute to sense of touch
sweat pores in ridges leave unique fingerprint pattern
What is the physiological basis of stretch marks or striae?
occurs due to extreme stretching during short period of time
AKA scar tissue resulting from the tears in collagen and elastic fibers
*keloids are deep scarring in tissue and dermis is projected and covered. a severe form of striae
What happens when you get a blister?
bubble of fluid has accumulated in separated epidermis and underlying dermis
heals fairly easily
flexure lines
part of reticular layer that are dermal folds at or near joints, where dermis is tightly secured to deeper structures
occurs due to skin’s inability to slide easily for joint movement causing deep skin crease
common in wrist, toes, etc
Melanin
only pigment made in the skin; derived from tyrosine; two forms that range in color from reddish yellow to brownish black
Eumelanin: darker brown
Pheomelanin: less effective type (reddish brown)
melanin production is made by tyrosinase, an enzyme in melanocytes
What is the role of melanocytes contributing to skins of different colors/tanning ability
skin colour dependent on type and relative amount of melanin & keratinocyte retention of the pigment
What damage does sun do to the skin
Elastic fibers clump, causing skin to become leathery
Temporarily depresses immune system
Cause alterations(mutation) in DNA that may lead to skin cancer
UV light destroys folic acid
folic acid is needed for DNA synthesis
How does sunscreen protect your skin?
exogenous form of protection similar to what melanin does
it reflects the UV light away from cells them from UV damage
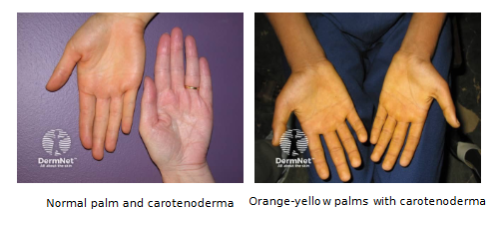
Carotene
yellow to orange pigment found in plant products - e.g.: carrots
deposits in keratinocytes (esp. stratum corneum) & hypodermis
carotenoderma: excess carotene
Most obvious in palms and soles
Hemoglobin
from capillary circulation & gives skin a pinkish hue (explains the transparent epidermis of Caucasian skin).
localized in dermis
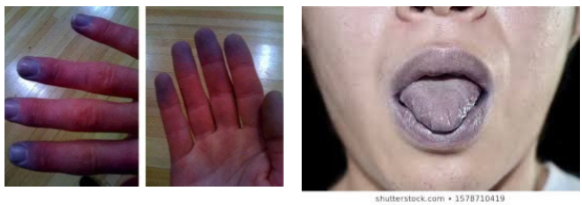
What is cyanosis?
When hemoglobin is poorly oxygenated, giving the skin a bluish-gray tint.
especially obvious in the oral mucous membranes and nail beds, particularly in darker-skinned individuals.
can be a sign of respiratory or cardiovascular problems.
Accessory structures of the skin
Hair
hair follicles
nails
sweat glands
sebaceous glands
Hair
AKA pili
flexible strands of dead, keratinized cells produced by hair follicles
none on palms, soles, lips, nipples, & portions of external genitalia
function of hair
sense insects on skin
guard head from physical trauma, heat loss, sun
shield eyes
filter particles from inhaled air
composition of hair
hard keratin
(more durable, doesn’t flake) – more cysteine-cysteine bonds that gives it less flexibility, more strength
Soft keratin
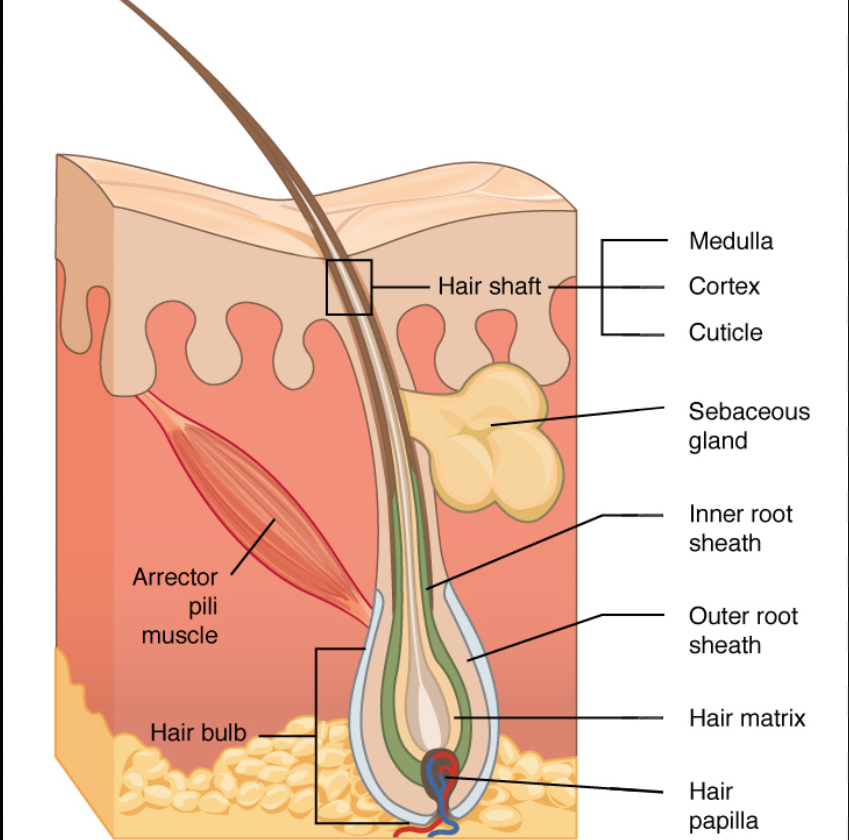
6 main parts of hair
shaft
projects above the skin’s surface (keratinization complete).
Has 3 layers: cuticle, medulla, cortex
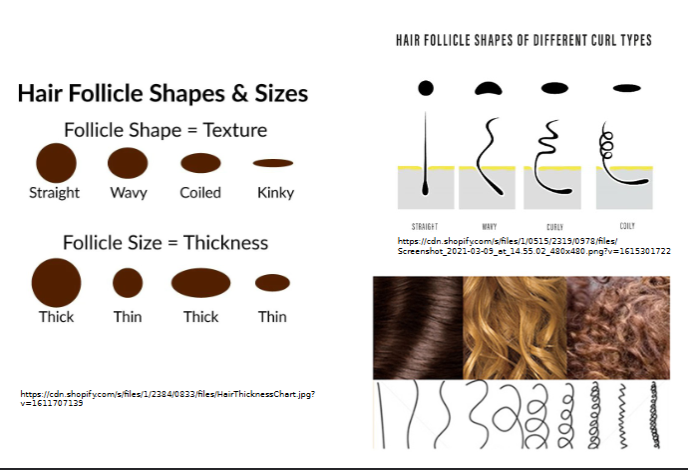
shape/size determines hair texture
root
the part embedded in the skin (contained within hair follicles
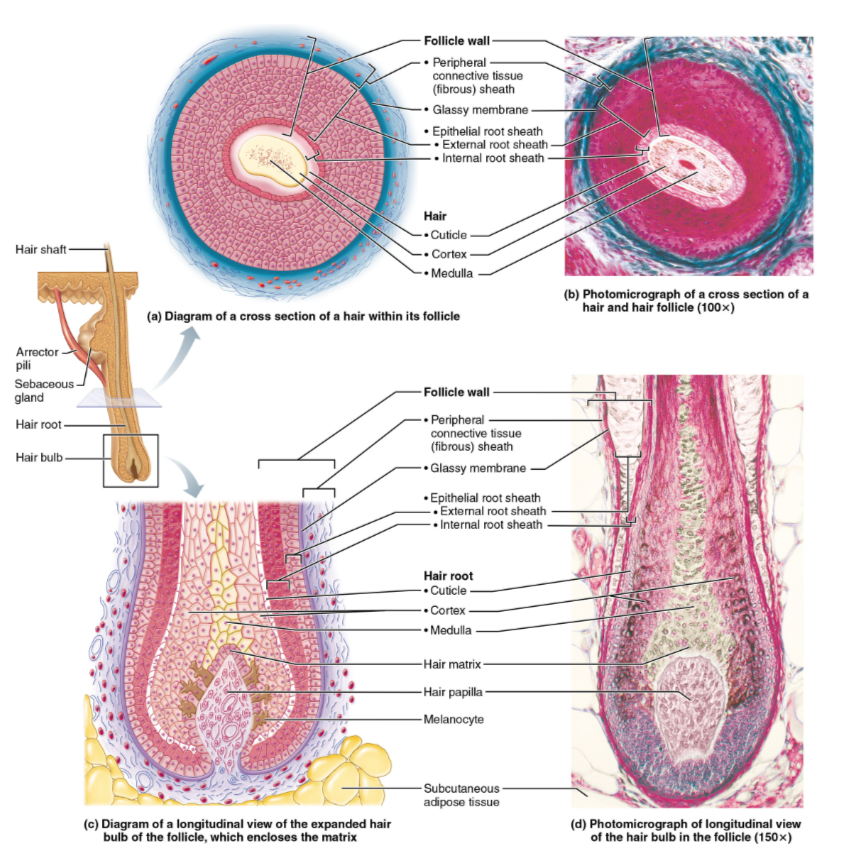
Bulb
expanded deep end of follicle- has papilla/root hair plexus
Follicle: outer CT root sheath and inner epithelial root sheath; hair matrix
Arrector pili muscle: 1/follicle; contract to pull hair up and dimple skin. causes goosebumps
found outside the wall of hair follicle
Sebaceous gland: holocrine gland that secretes sebum (oily- lubrication and waterproofing; bactericidal)
coily hair
shaft is flat and ribbonlike in cross section
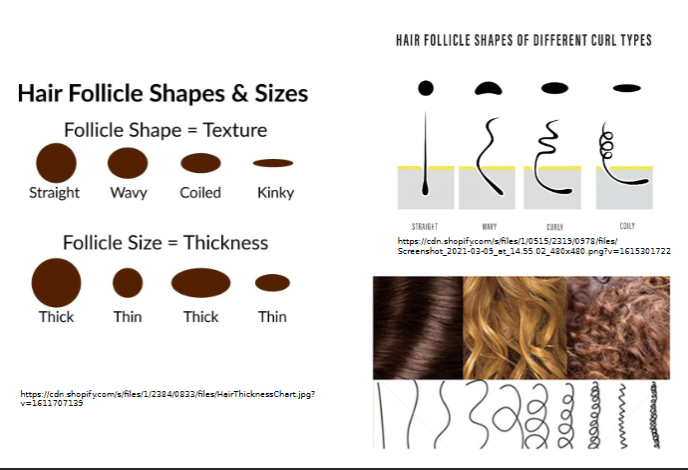
silky and wavy hair
shaft is oval
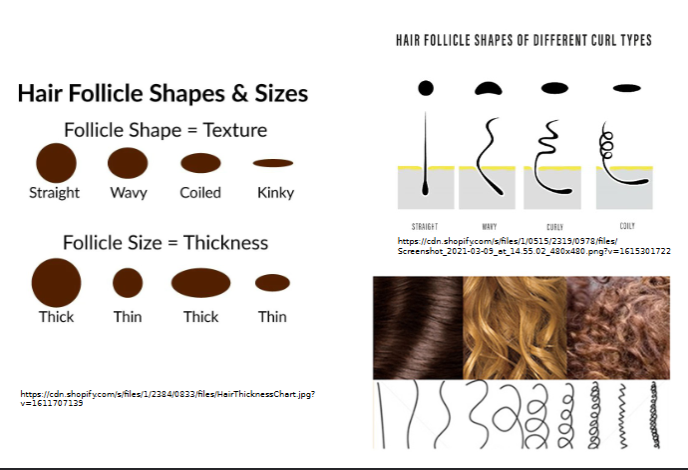
straight hair shaft shape
round
3 layers of hair shaft
cuticle: single layer of overlapping cells
Cortex: several layers of flattened keratinocytes; pigment is here
medulla: large cells separated by air spaces-absent in fine (vellus) hair
absence of it makes hair softer in females than males
What are split ends
caused by damage to cuticle
normally sits flat, but become raised or missing scales
ends of hair are not as smooth
What happens when hair is turning gray or white?
happens bc of change in color due to melanocytes
melanocytes produce less melanin until they stop completely
are replaced by air bubbles, which lack color =gray hair
caused by age, stress, vitamin deficiency
Structure of hair follicles
hair papilla
Dermal papilla containing a knot of capillaries that supplies nutrient to growing hair
if destroyed=no more hair growth
hair matrix
Actively dividing area of bulb that produces hair cells
as matrix makes new cells, it pushes older ones upward
Vellus hair
pale, fine body hair of children and adult females
terminal hair
coarse, long hair
found on scalp and eyebrows
at puberty
appears in axillary and pubic regions of both sexes
also on face and neck of males
nutrition and hormones affect hair growth
growth rate=~2mm/week
growth cycles of follicles
active growth phase followed by regression/resting phase
each follicle has only certain number of growth cycles before it is done
which hair has longer active phase-eyebrow or head hair?
head hair has longer active phases (~4 yrs), which is why they grow long before they are shed
eyebrow hair is active for only few months so they never grow very long
What is hirsutism
excessive hair growth
must be terminal hair on face, neck, chest particularly women (ie. PCOS)
occurs due to excess androgen production
Balding(alopecia/hair loss) with age
hair grows fastest between teen years and 40s
after 40s, hair shed faster than replaces
by 60-65, hair thins
later years, terminal hair replaced by vellus hair causing wispy hair
male pattern baldness
a type of true baldness
genetically determined, gender influenced
altered response of hair follicle to androgen that shortens growth cycles
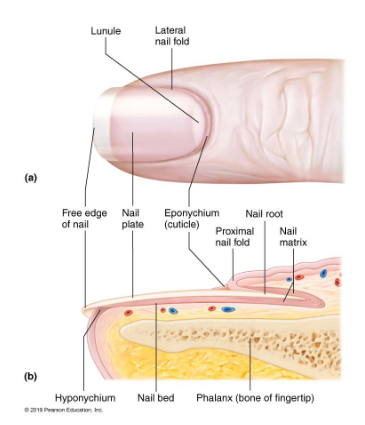
Nails
scale-like modification of epidermis that contain hard keratin-protective useful tool
free edge, body, nail folds,-2 lateral and 1 proximal
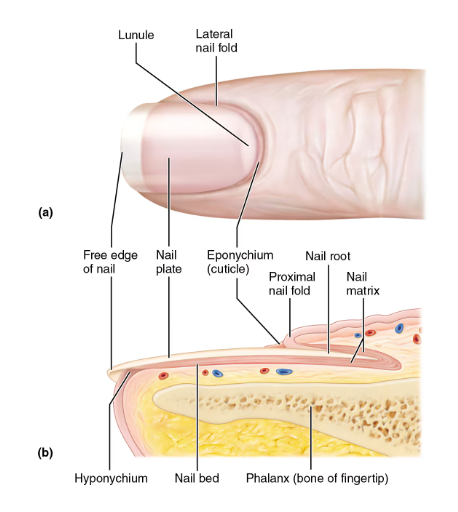
Parts of a nail
nail root: embedded in skin
nail plate: body visible attached portion
nail bed: epidermis underneath keratinized nail plate
nail matrix: thickened portion of bed responsible for nail growth
lunule: thickened nail matrix, appears white,
nail folds
eponychium: nail fold that projects onto surface of nail body AKA cuticle
hyponychium: area under free edge of plate that accumulates dirt
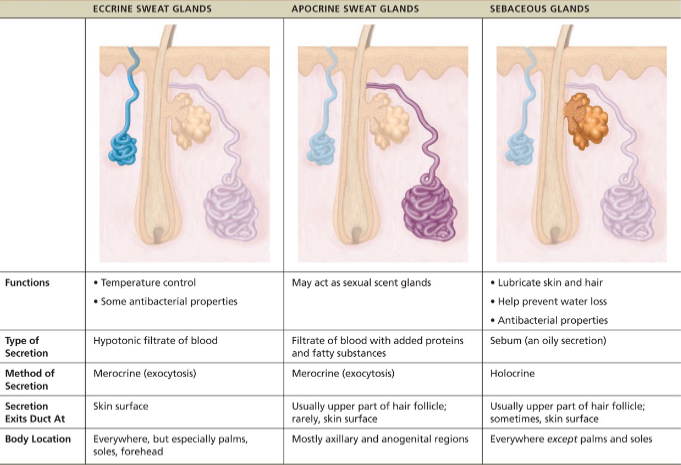
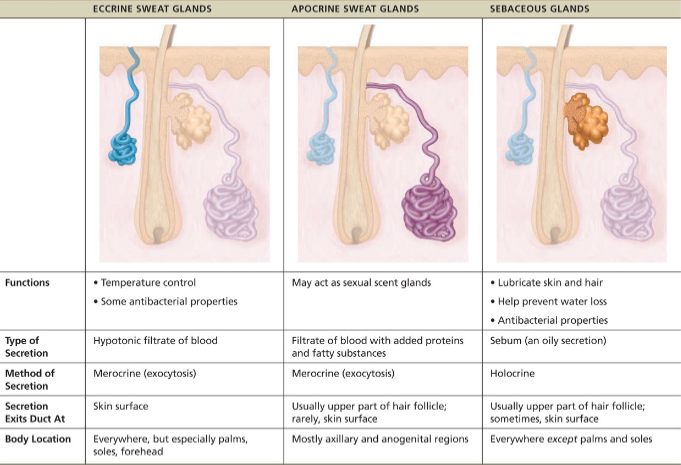
Sweat glands(sudoriferous glands)
all skin surfaces except nipples & parts of external genitalia contain sweat glands/~3mil/person
2 types
eccrine and apocrine
what is sweat
99% of water + salts, vitamin C, antibodies, dermcidin, traces of metabolic wastes like urea, uric acid, ammonia
pH ~4-6
regulated by ANS
prevents body from overheating
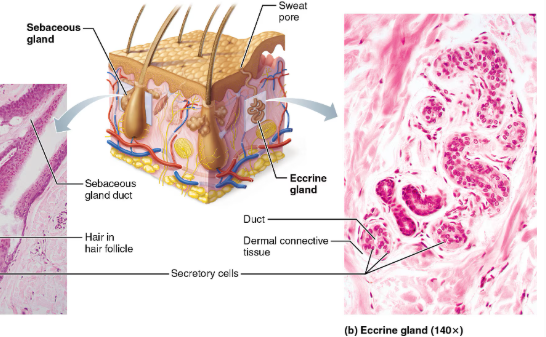
Eccrine(merocrine)
simple coiled tubular glands with pore at surface to release sweat
more numerous than apocrine
abundant on palms, soles and forehead
function in thermoregulation
regulated by the SNS
secrete sweat
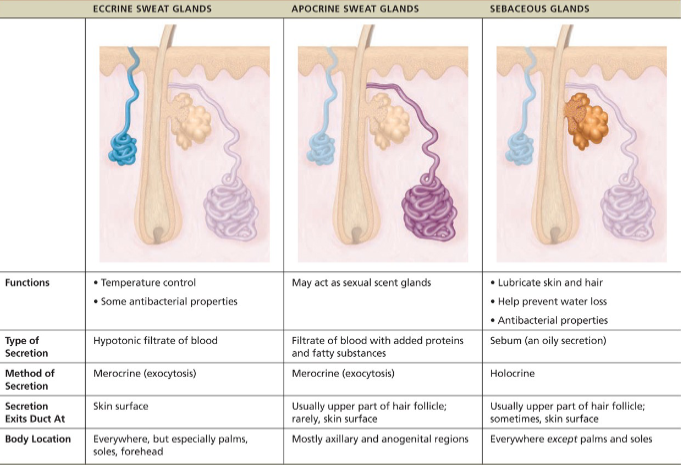
Apocrine
axillary & anogenital areas; larger; ducts empty into follicles
lies deeper in dermis
are also merocrine glands
same as sweat but with fatty substances and some proteins -odorless until decomposed by skin bacteria leading to body odor
viscous with mily/yellowish color
begin functioning at puberty due to androgrens
activated by SNS in times of stress
2 types of modified apocrine sweat glands
ceruminous: secrete wax (cerumen) in external ear canal. produced by nearby sebaceous gland
mammary: secrete milk
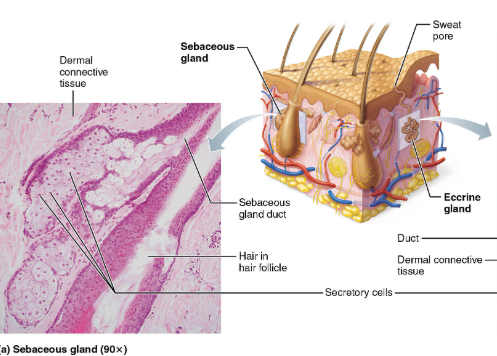
Sebaceous (oil glands)
are simple branched alveolar glands
widely distributed holocrine glands, except for thick skin of palms and soles
most develop from hair follicles and secrete into hair follicles
relatively inactive until puberty
Secretes sebum
oily secretion
bactericidal (bacteria-killing) properties
softens hair and skin
Acne
usually an infectious inflammation of sebaceous glands, resulting in pimples (pustules or cysts)
whiteheads, or closed comedones, are blocked sebaceous glands
if secretion is oxidized, whitehead becomes blackhead, AKA open comedones
overactive sebaceous glands in infants can cause seborrhea, known as ‘cradle cap’
begin as pink, raised lesions on scalp that turn yellow/brown and slough off

6 Major function of skin
protection
thermoregulation
cutaneous sensation
metabolic function
excretion: some N-containing wastes; NaCl
blood reservoir
Protection as function of skin
chemical barrier:
acidic skin secretions (acid mantle) retards bacterial replication
sweat also contains dermcidin and other anti-bacterial agents
melanin protects against UV-induced damage
Physical barrier:
barrier to trauma and bacterial invasion; also waterproofing
biological barrier:
Langerhans cells of epidermis and macrophages in dermis
not impermeable to gases, fat-soluble vitamins, steroids
Thermoregulation as function of skin
sweating (o.5-12L fluid/day)
insensible perspiration: routine and unnoticeable sweating
sensible: visible output of sweat
evaporation of the sweat is what cools the body
Cutaneous Sensation as function of skin
Skin is supplied with cutaneous sensory receptors that are part of NS. are AKA exteroceptors
they respond to external stimuli on the body
Metabolic function of the skin
vit D. synthesis needed for absorption of Ca 2+
keratinocyte enzymes aid in conversion of topically-applied cortisone by hydrocortisone
Blood reservoir as function of skin
dermis can hold about 5% of total blood volume
NS can constrict dermal blood vessels to make it more available to other organs and muscles
Excretion as a function of the skin
body eliminates limited amounts of nitrogen-containing wastes (ammonia, urea, and uric acid) in sweat
Profuse sweating is an important avenue for water and salt (sodium chloride) loss
define burn
tissue damage caused by heat, electricity, radiation, chemicals
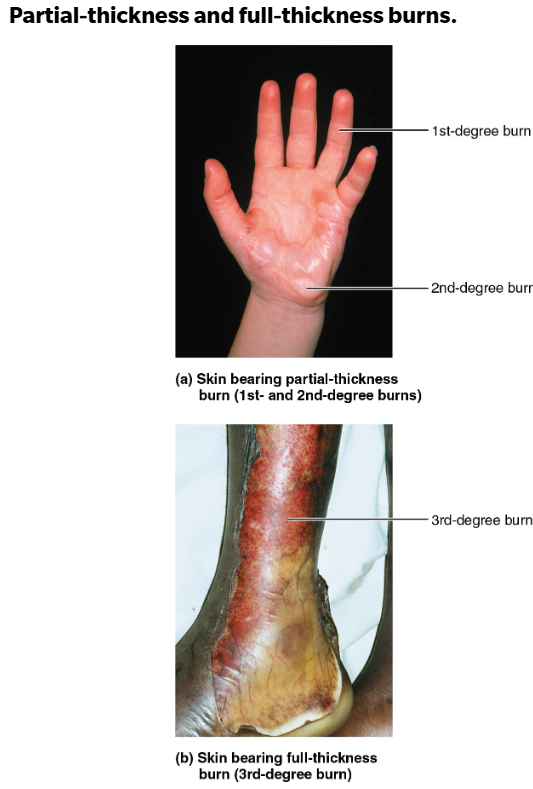
Types of burn severity(depth)
First degree: only epidermis damaged
redness, swelling, pain. heals quickly(ie. sunburn); partial thickness burn
Second degree: epidermis & upper dermis
blisters, redness; partial thickness burn
Third degree: entire thickness of skin (epidermis + dermis)
appears gray-white, cherry red, or blackened
nerve endings/sensory receptors are destroyed so it doesn’t feel painful
What are the 2 main concerns for burns
fluid loss
loss of fluid→ loss of blood volume→ hypovolemic shock
infection
potential for repair of third degree burn
depends on severity
ie. skin grafting=for smaller area of burn
artificial skin=stem cells are grown and transplanted for larger burns
skin bank= stored/frozen for ~2 years
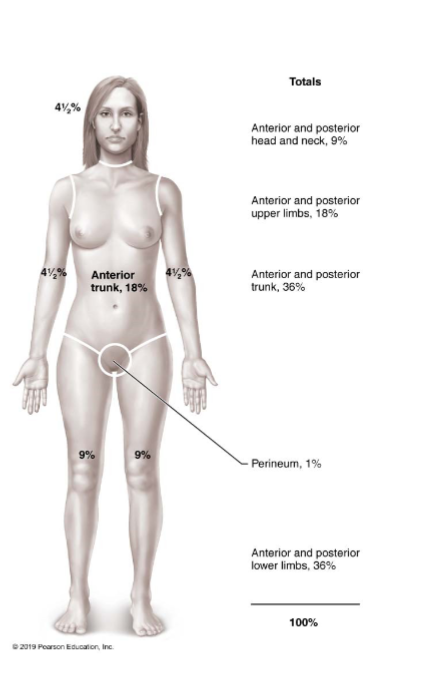
Rule of Nines for evaluating burns
Used to estimate volume of fluid loss
Body is broken into 11 sections, with each section representing 9% of body surface (except genitals, which account for 1%)
Ex: 41/2% means that amount of fluid is lost in that area and must be restored