Biochem Test 1 memorization
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
henderson-hasselbalch equation
pH = pKa + log [base]/[acid]
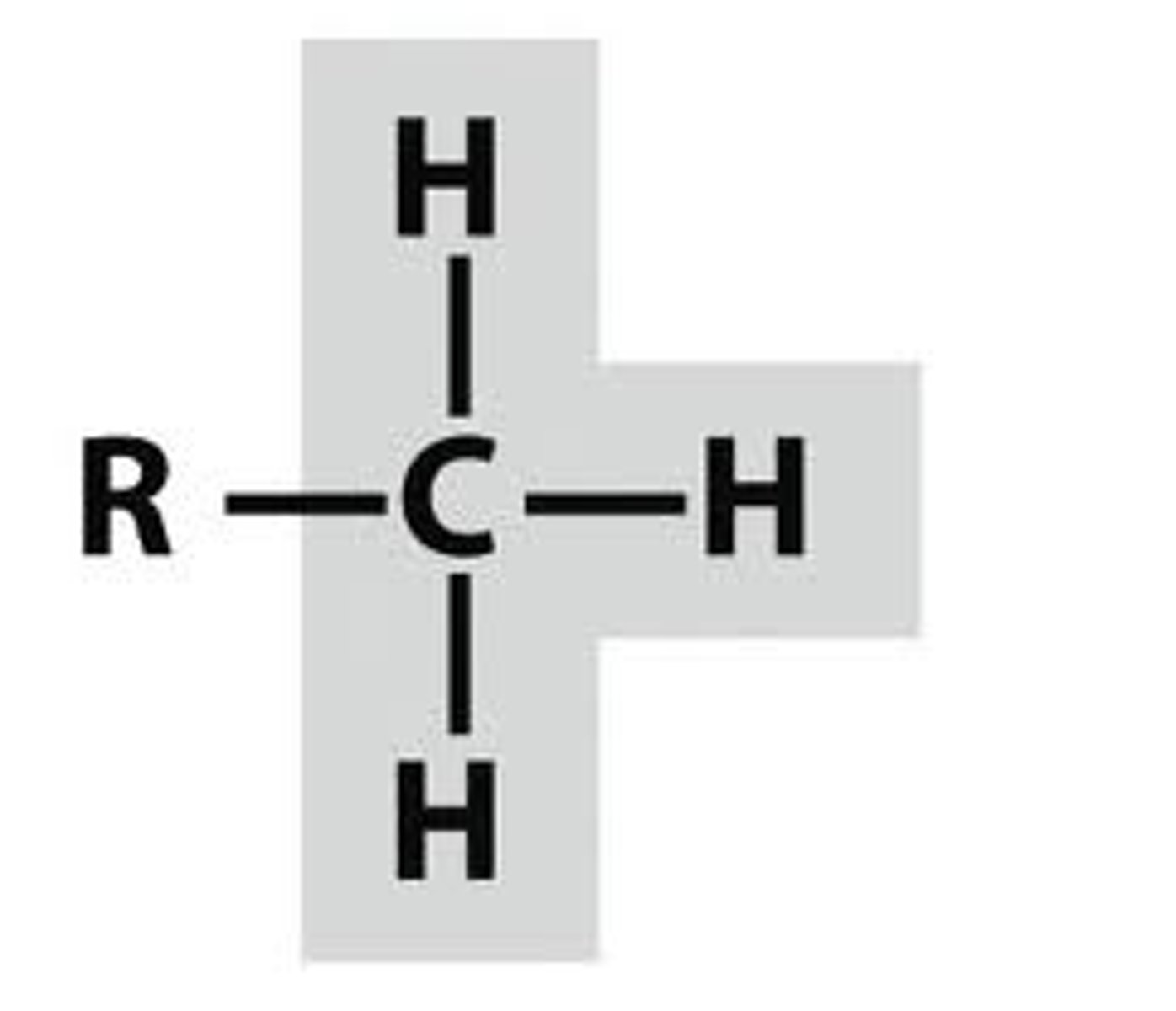
hydrophobic functional group
R-CH3
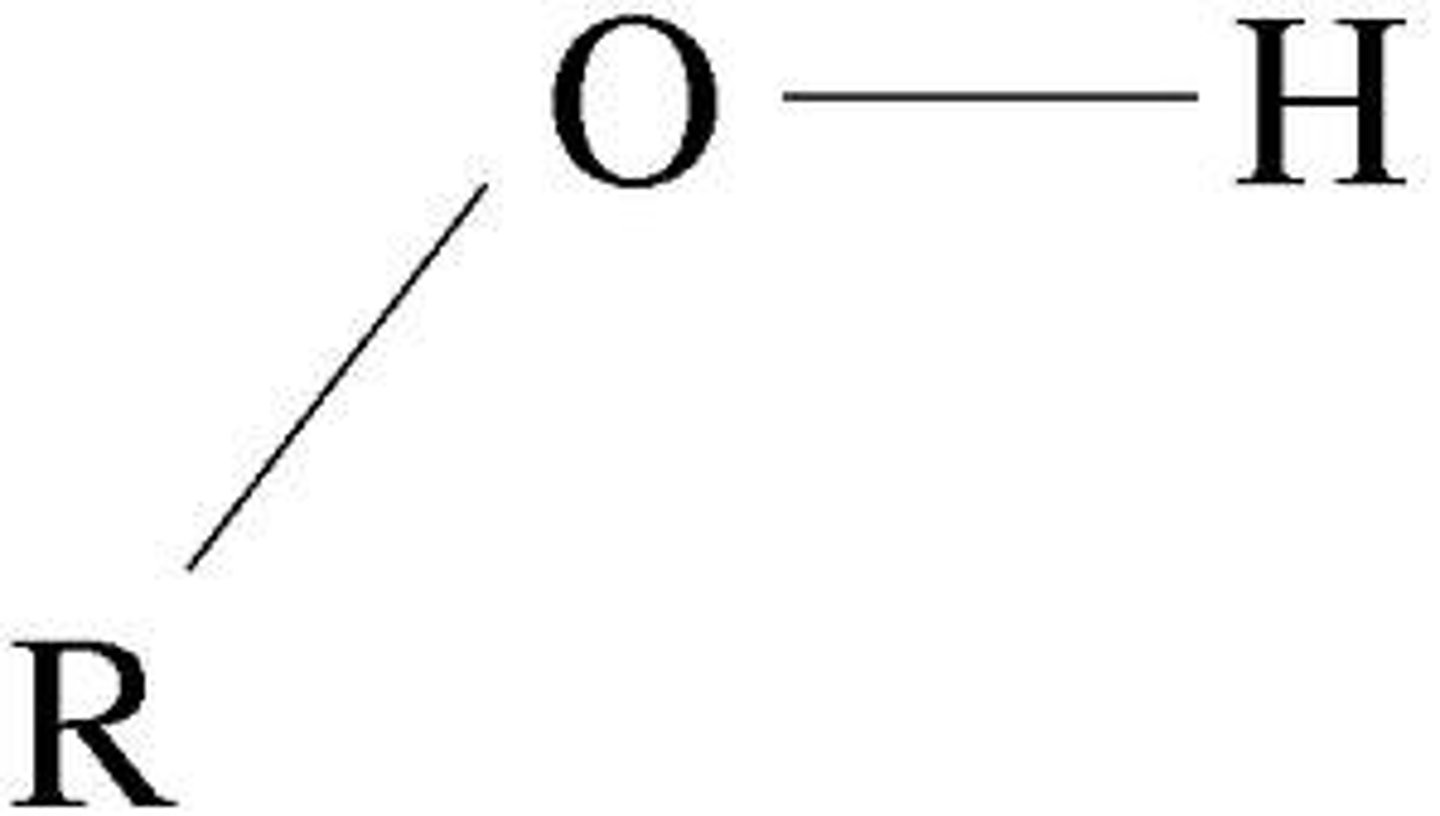
hydroxyl
-OH (alcohol)
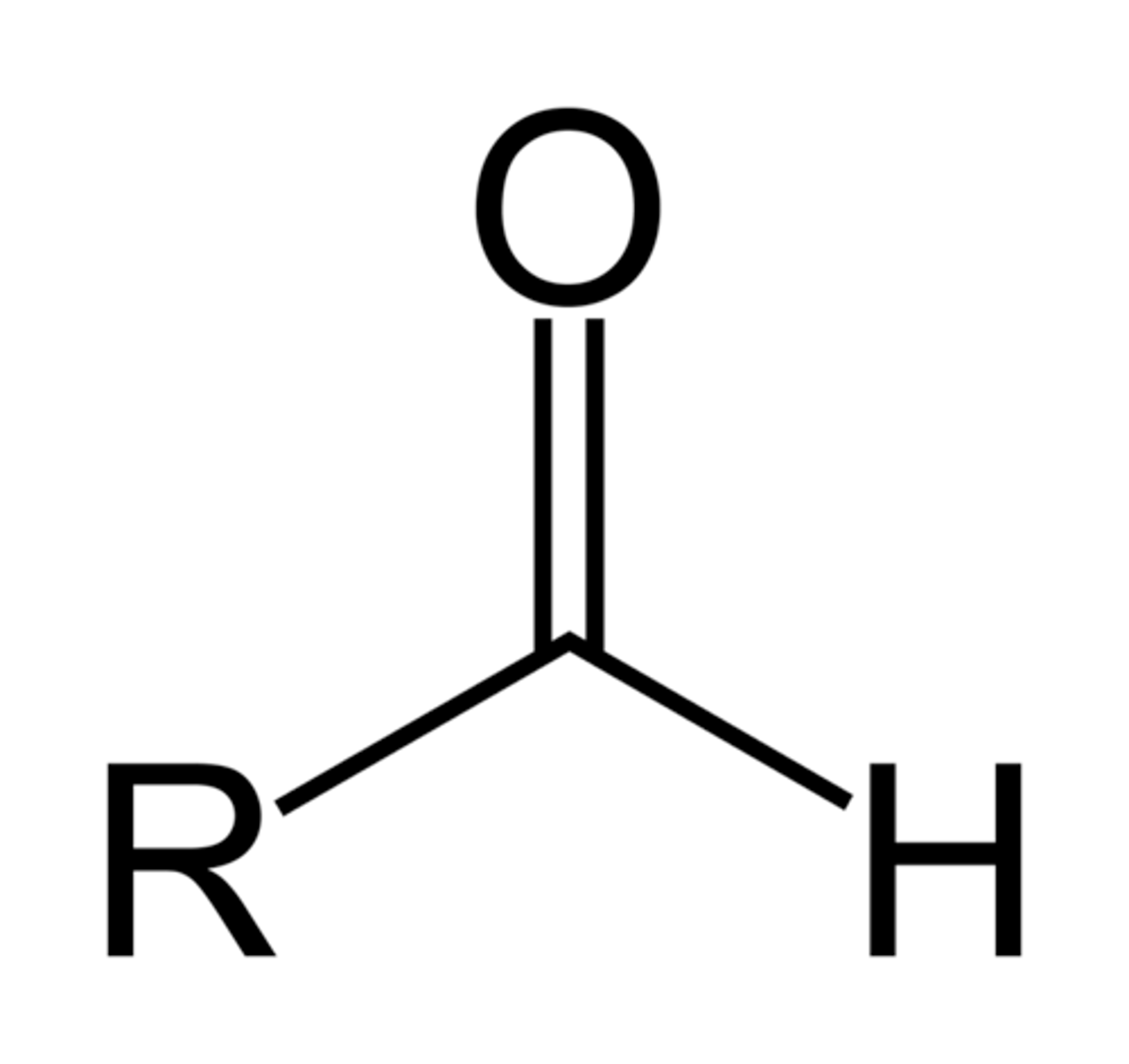
aldehyde
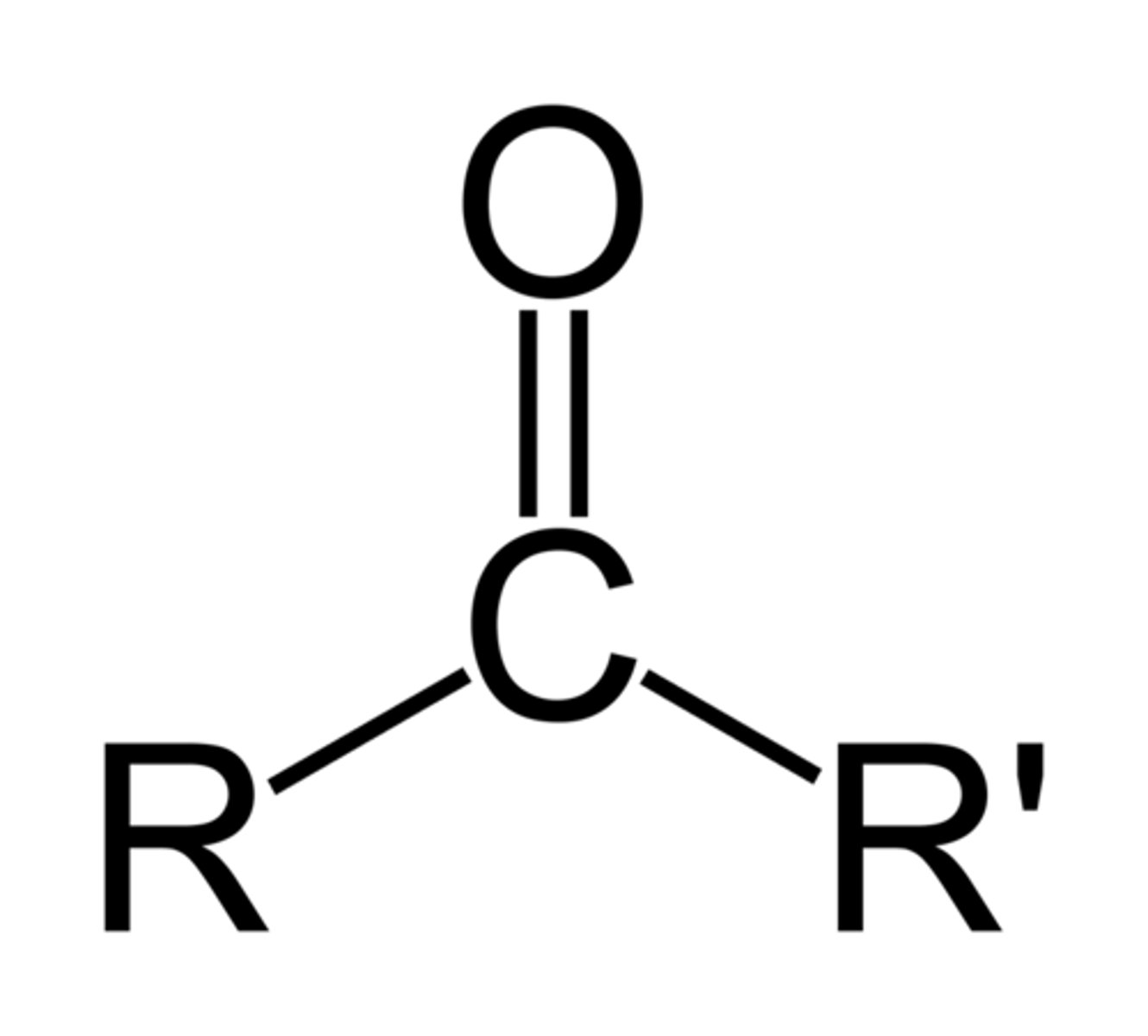
ketone
carboxyl (carboxylic acid)
COOH
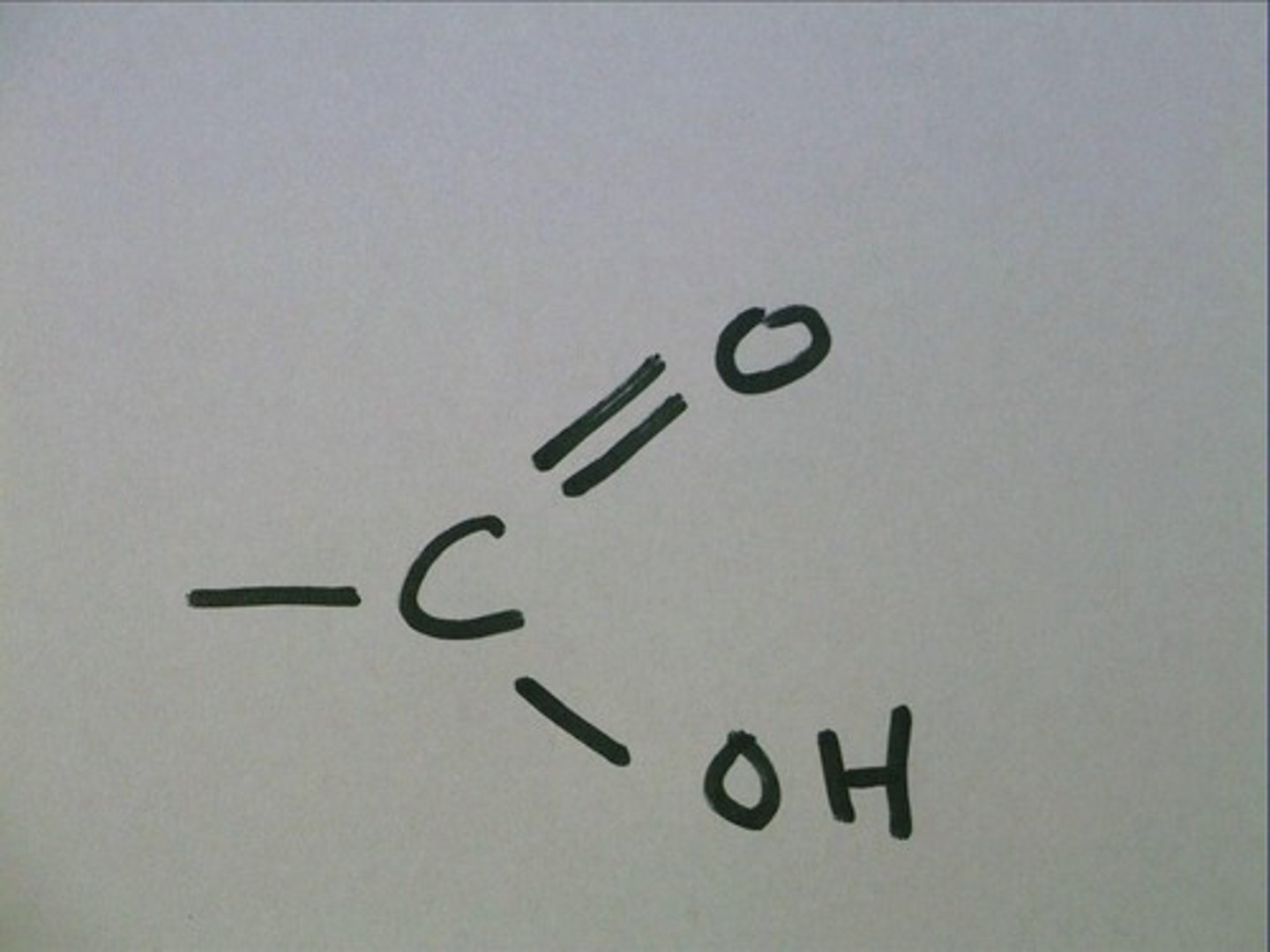
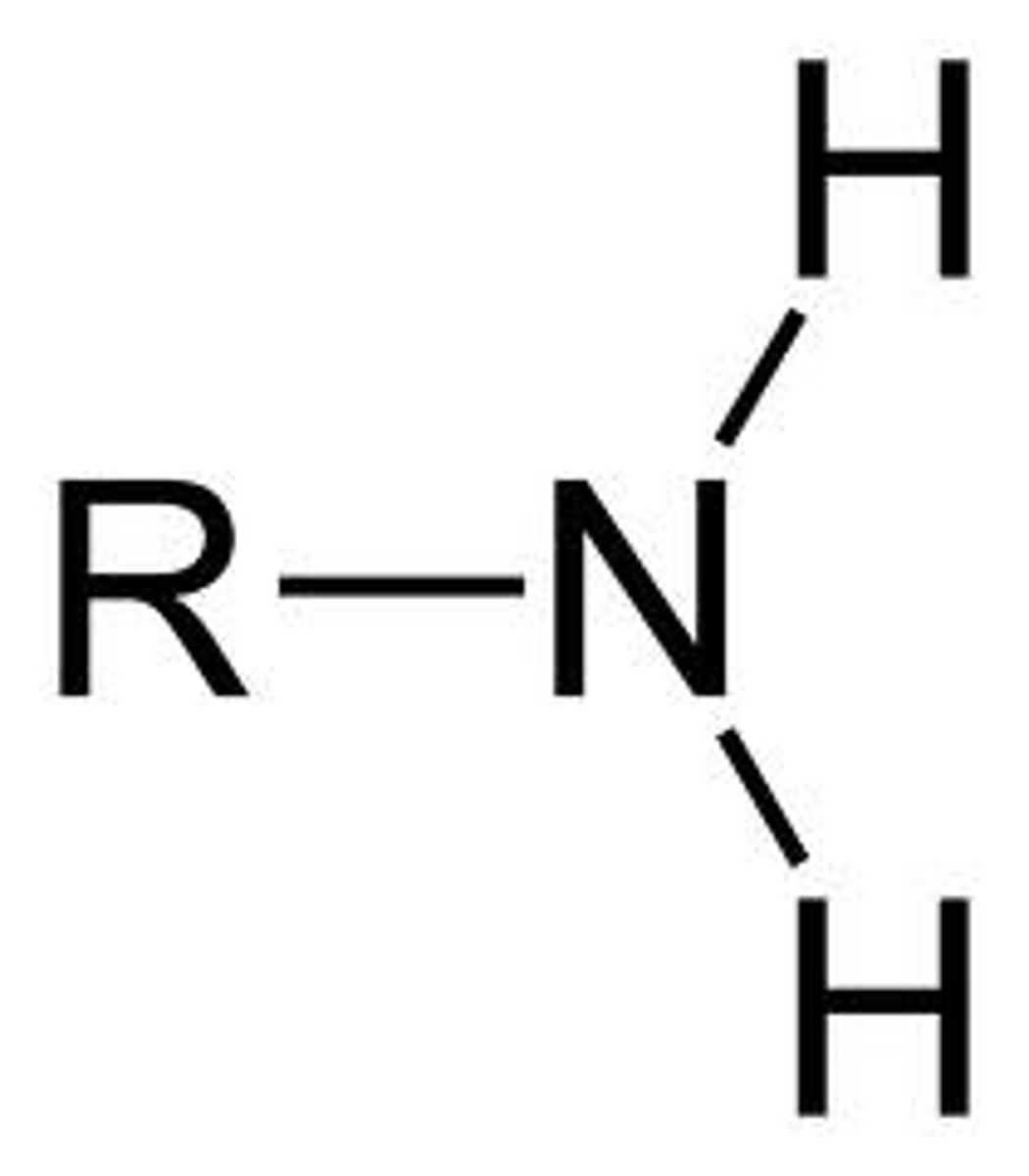
amine
R-NH2
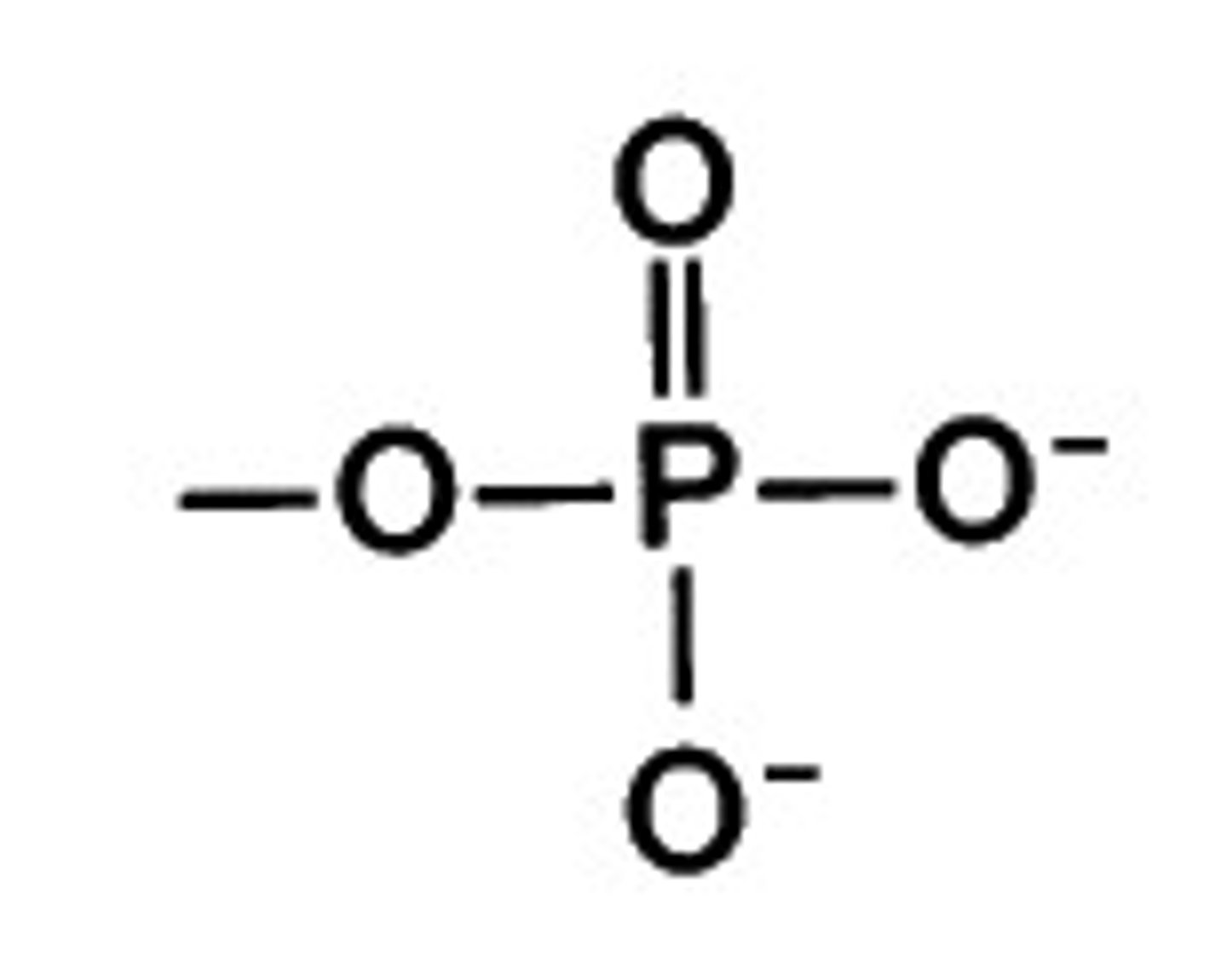
phosphate
sulfhydryl
R-SH (Cysteine)
Glycine
Gly, G, Nonpolar (hydrophobic)
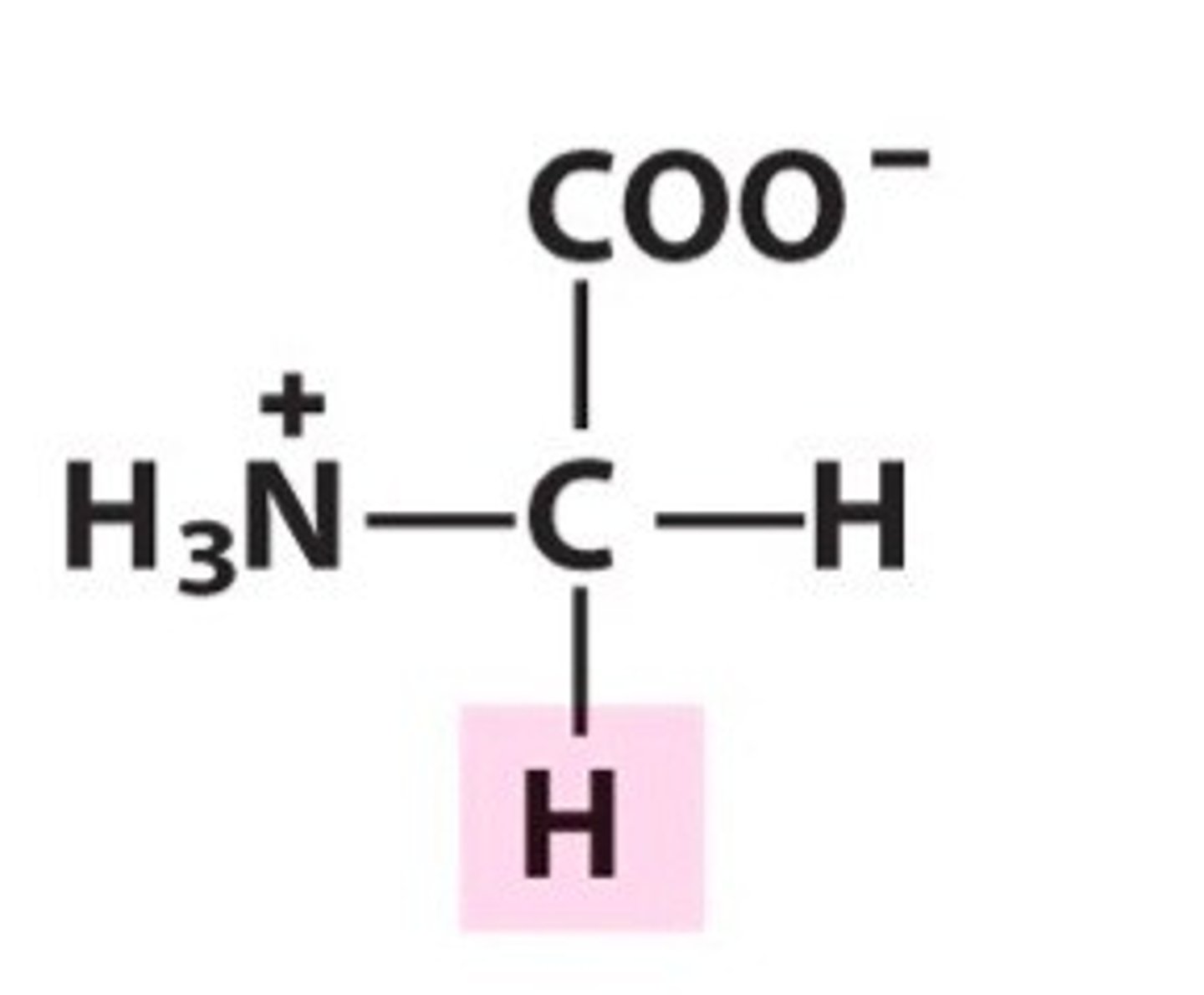
Alanine
Ala, A, nonpolar (hydrophobic)
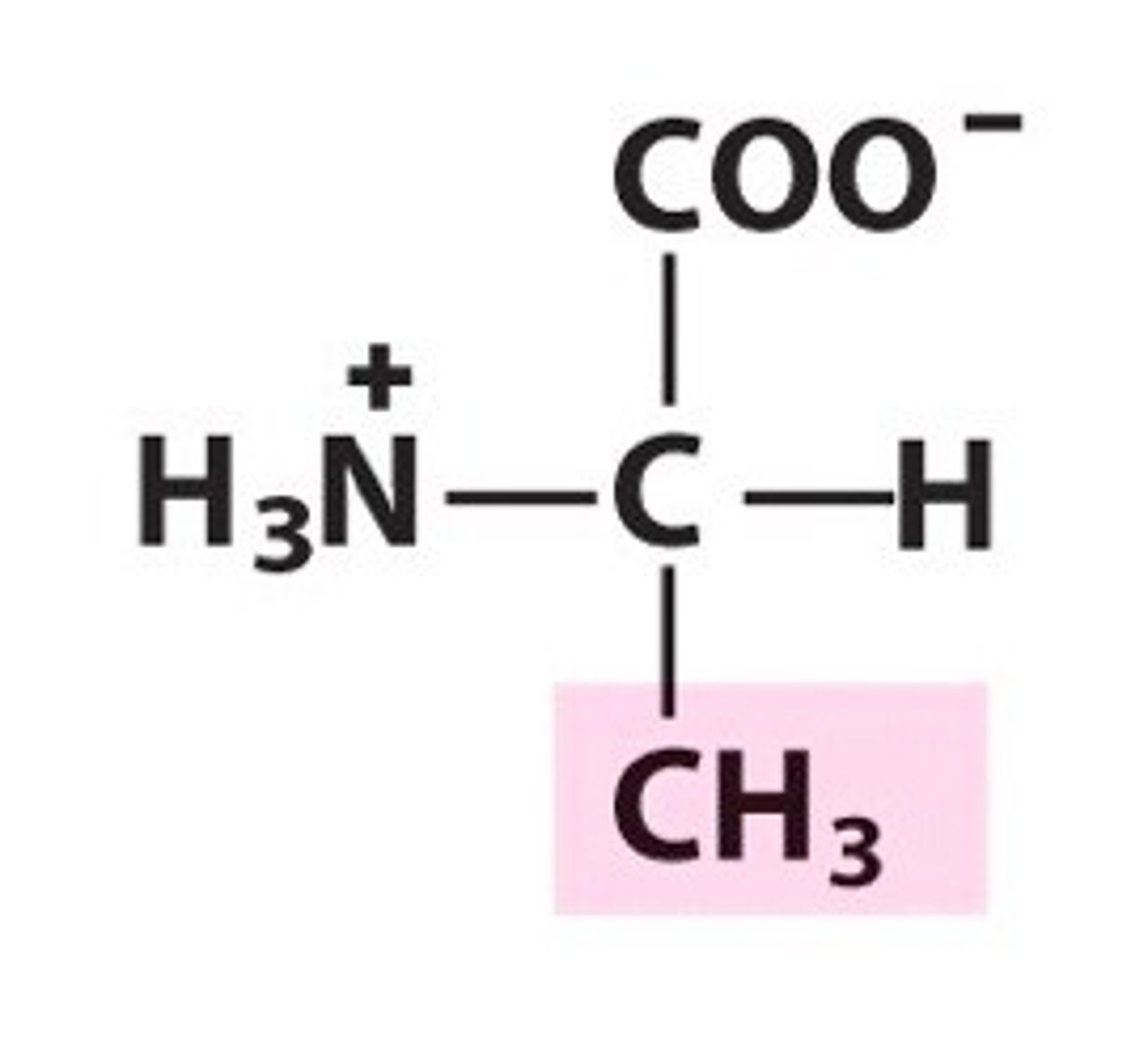
Valine
Val, V, nonpolar, hydrophobic
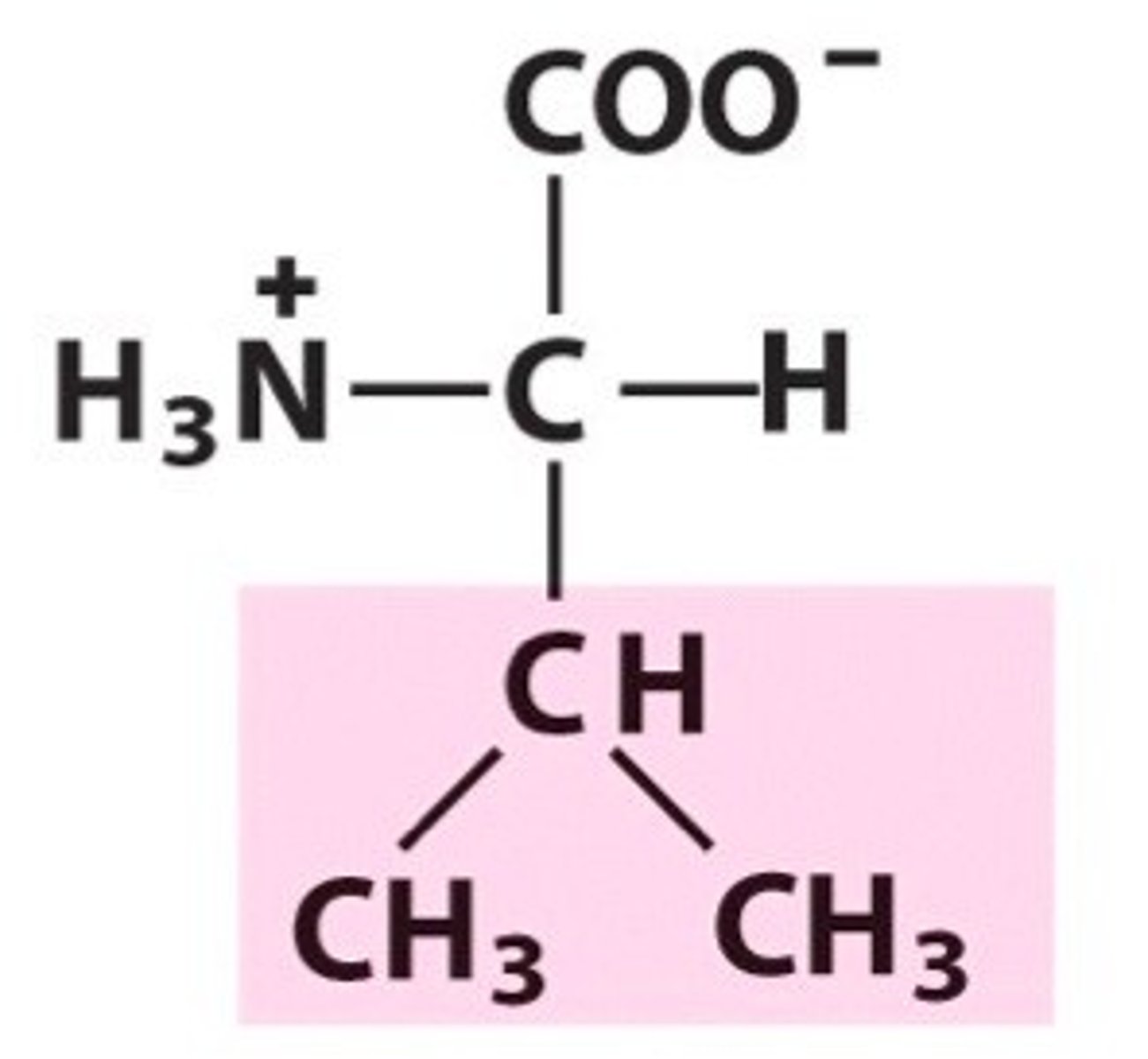
Leucine
Leu, L, nonpolar, hydrophobic
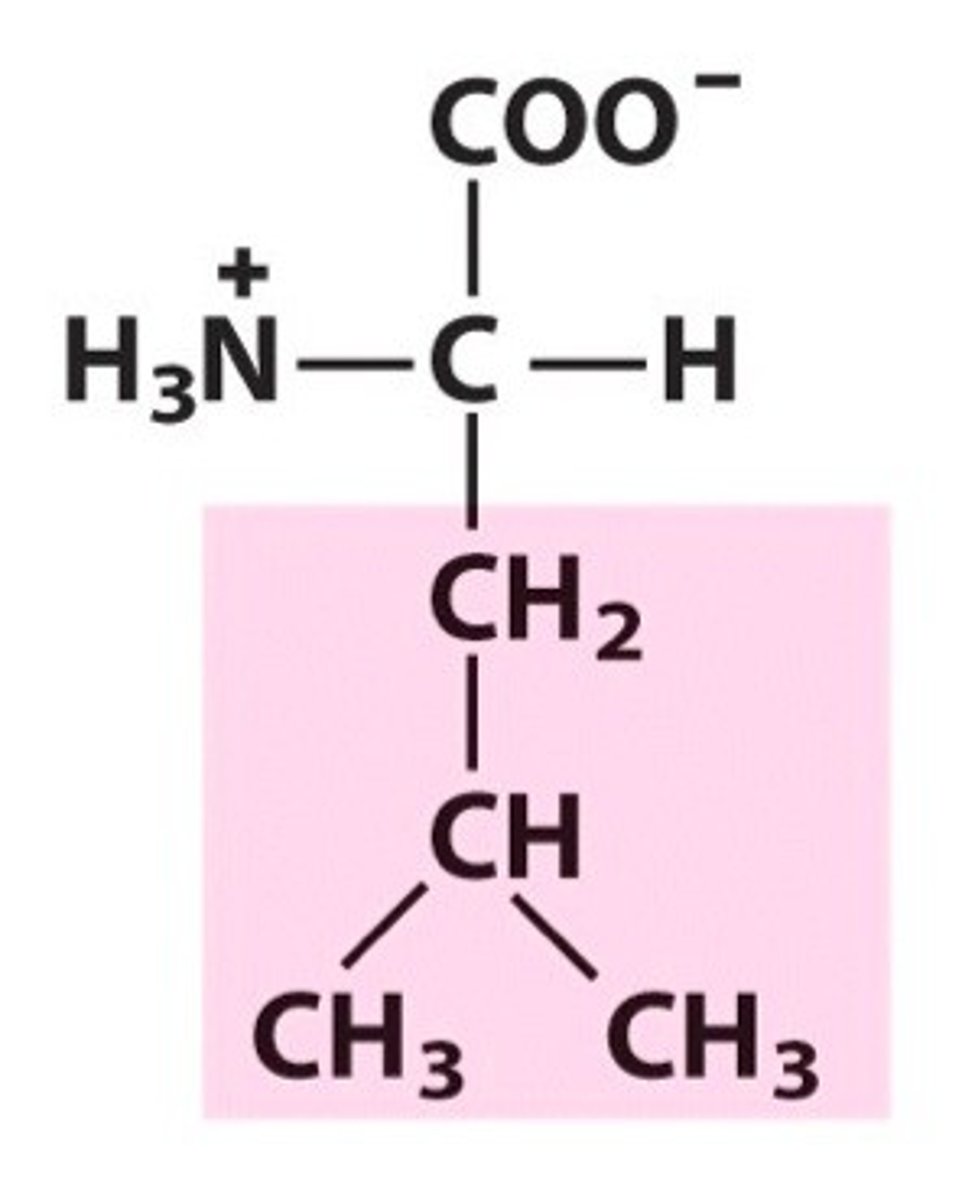
isoleucine
Ile, I, nonpolar, hydrophobic
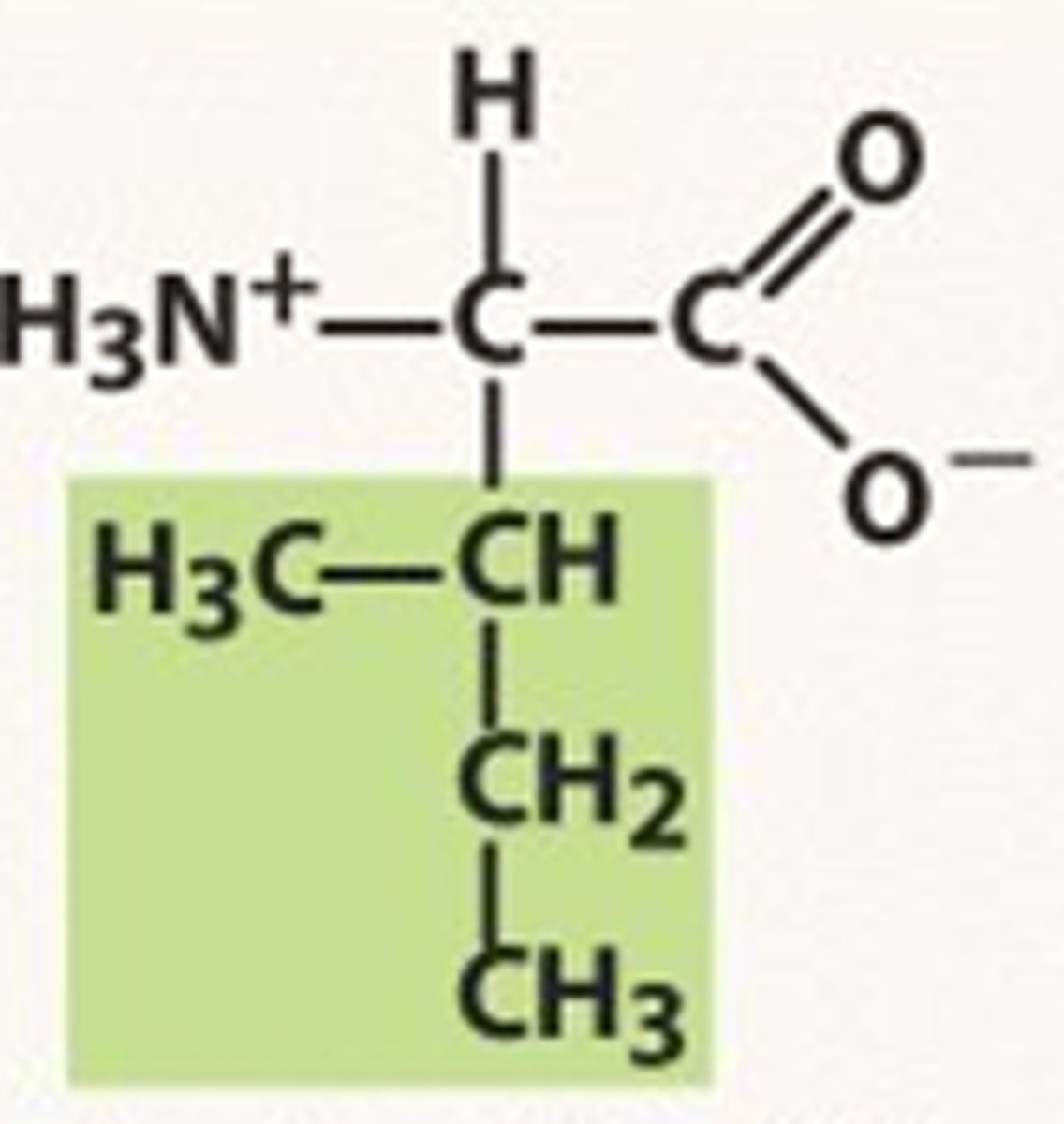
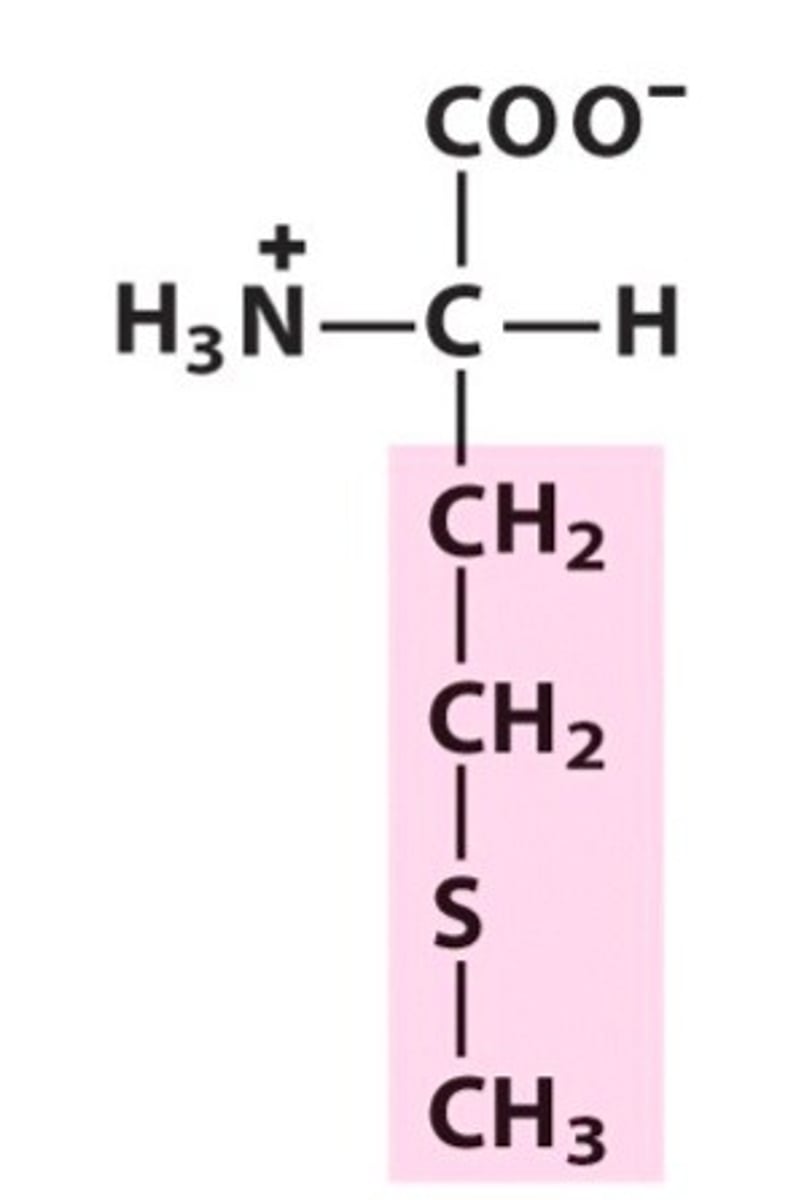
Methionine
Met, M, nonpolar, hydrophobic
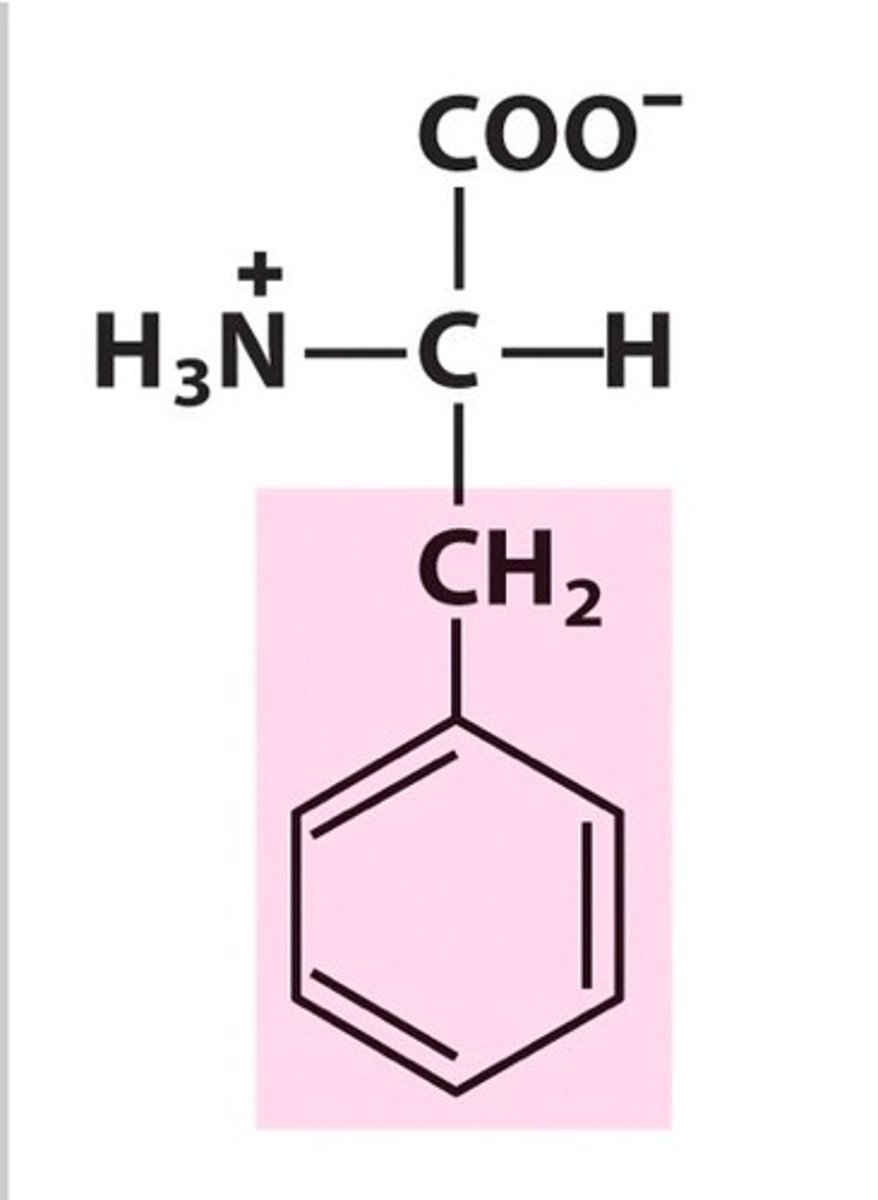
phenylalanine
Phe, F, nonpolar, hydrophobic
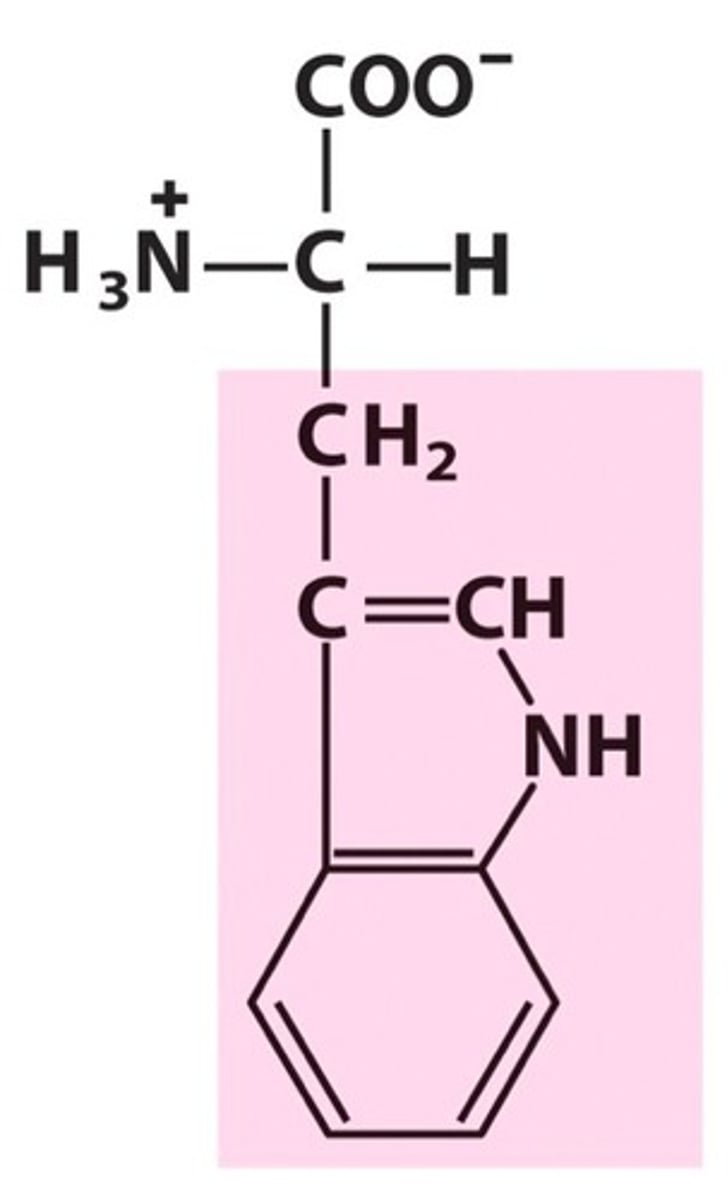
Tryptophan
Trp, W, nonpolar, hydrophobic
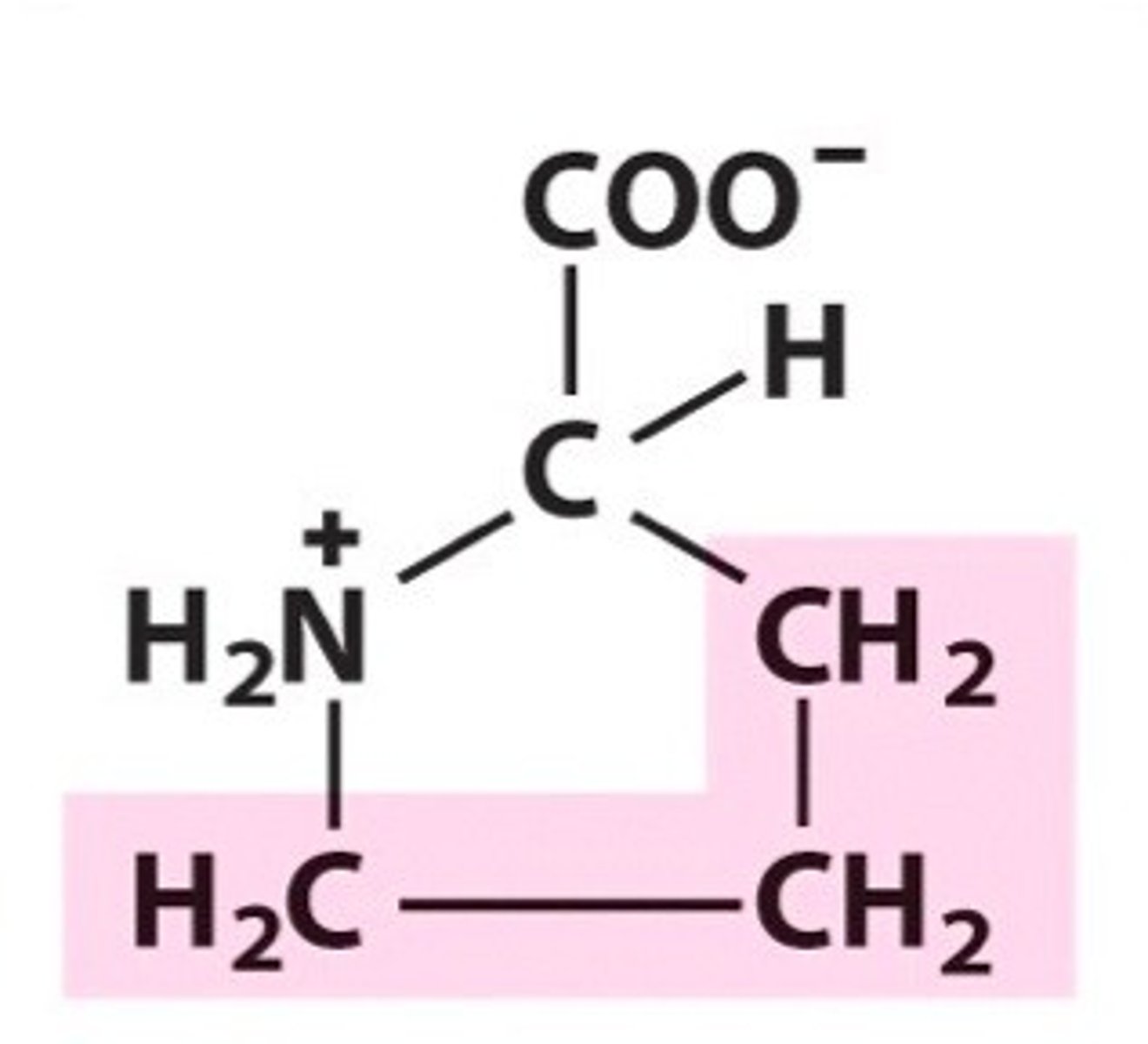
Proline
Pro, P, nonpolar, hydrophobic
Serine
Ser, S, Polar, Hydrophilic
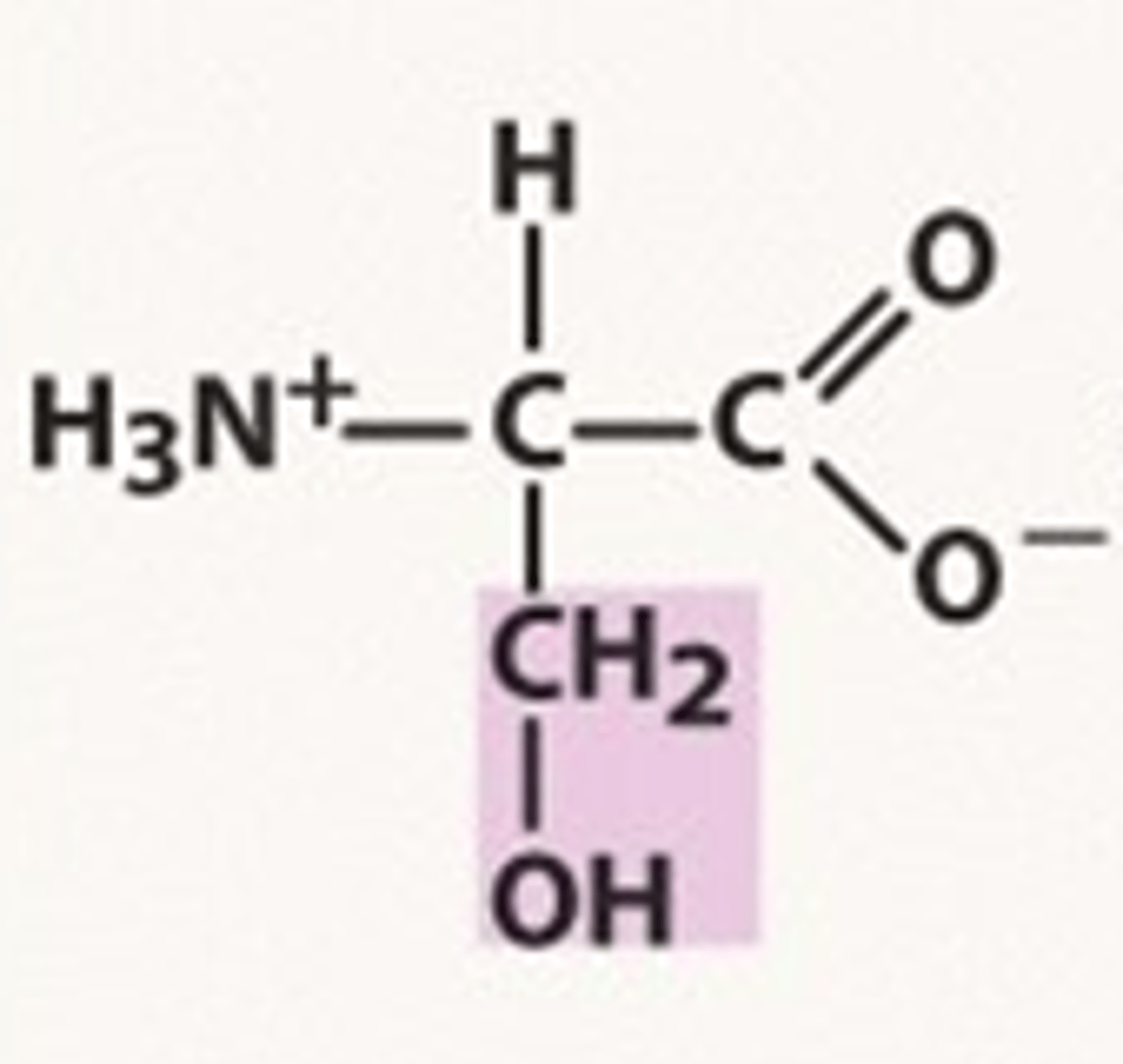
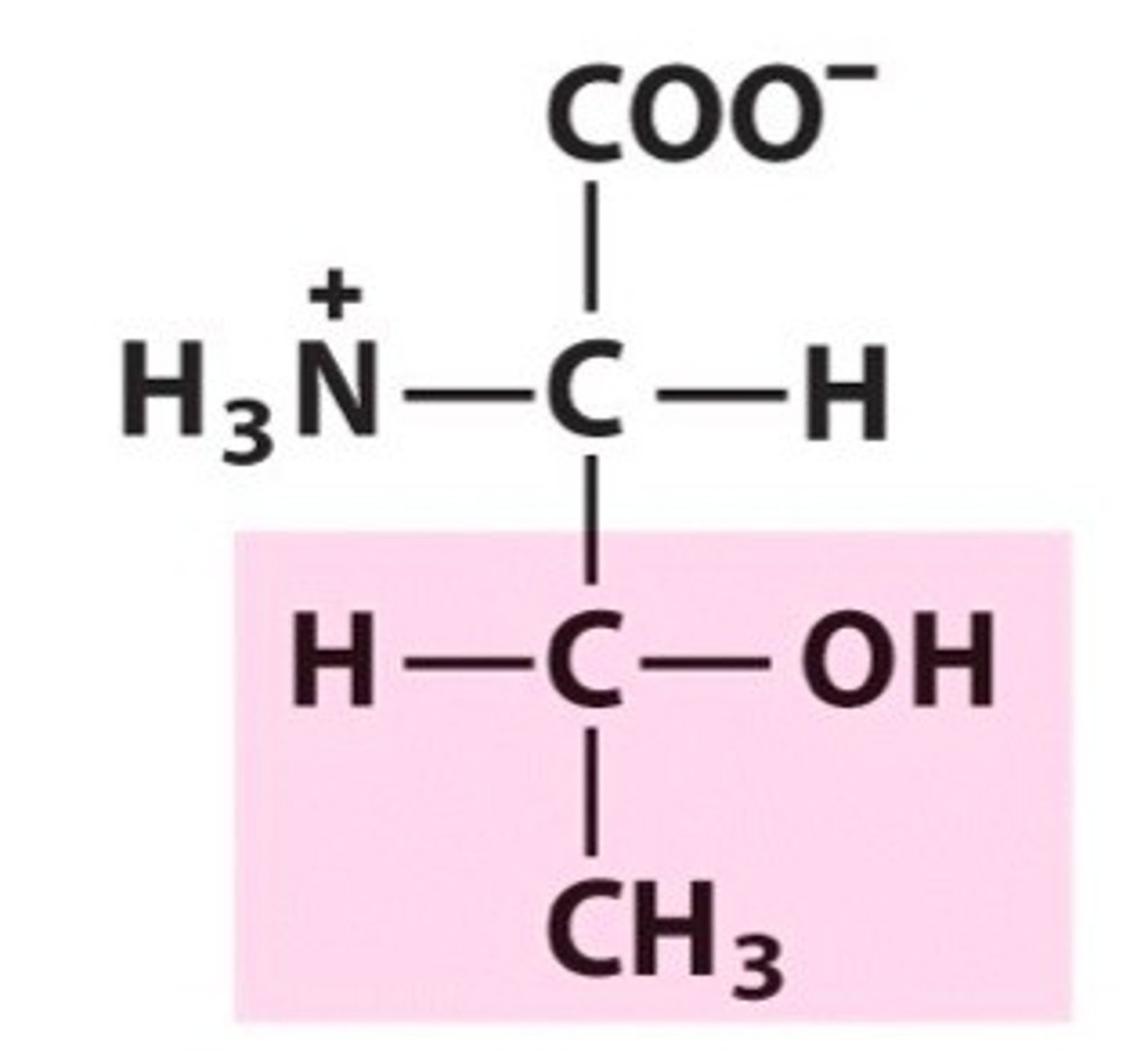
Threonine
Thr, T, Polar, Hydrophilic
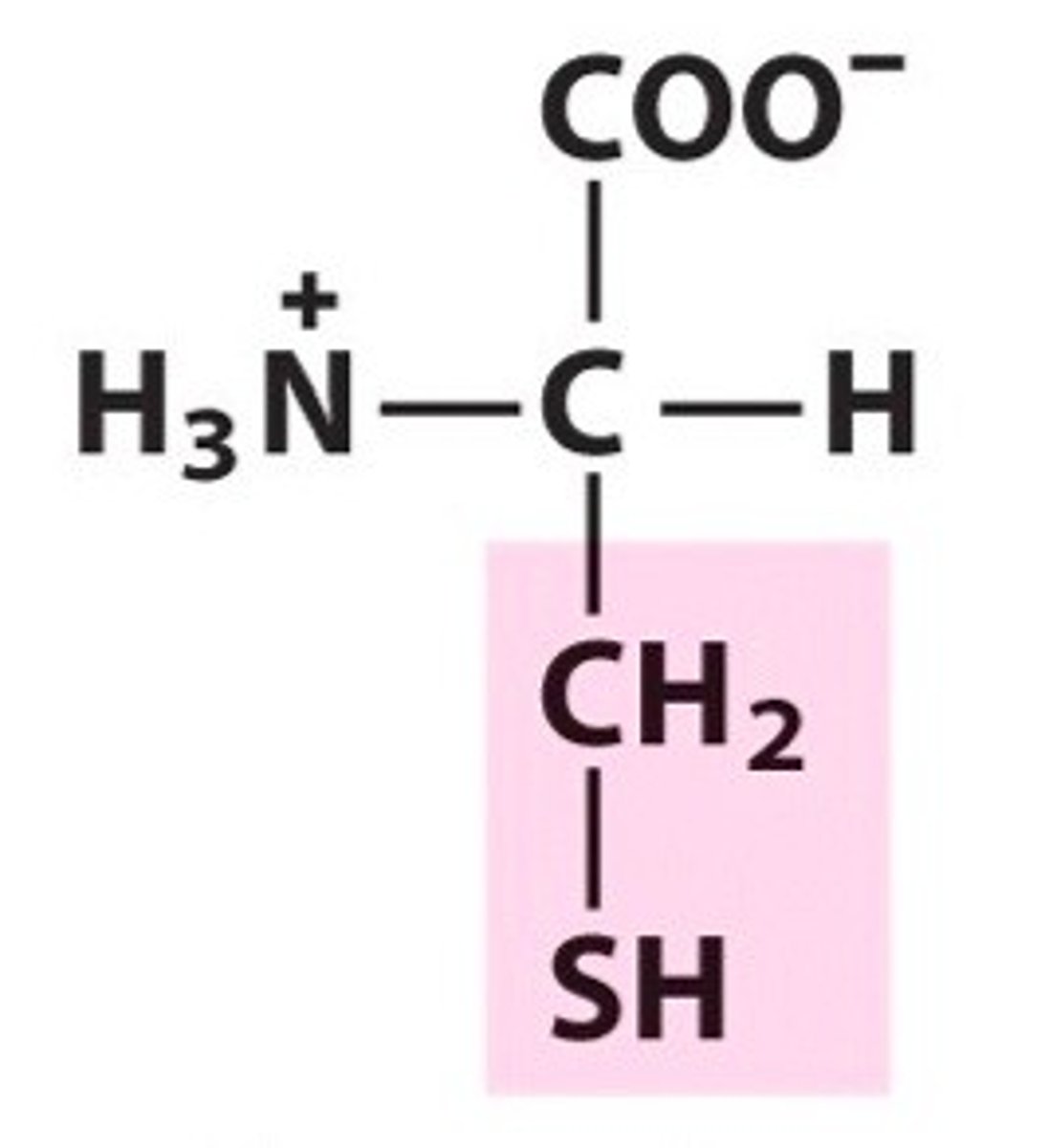
Cysteine
Cys, C, polar, hydrophilic
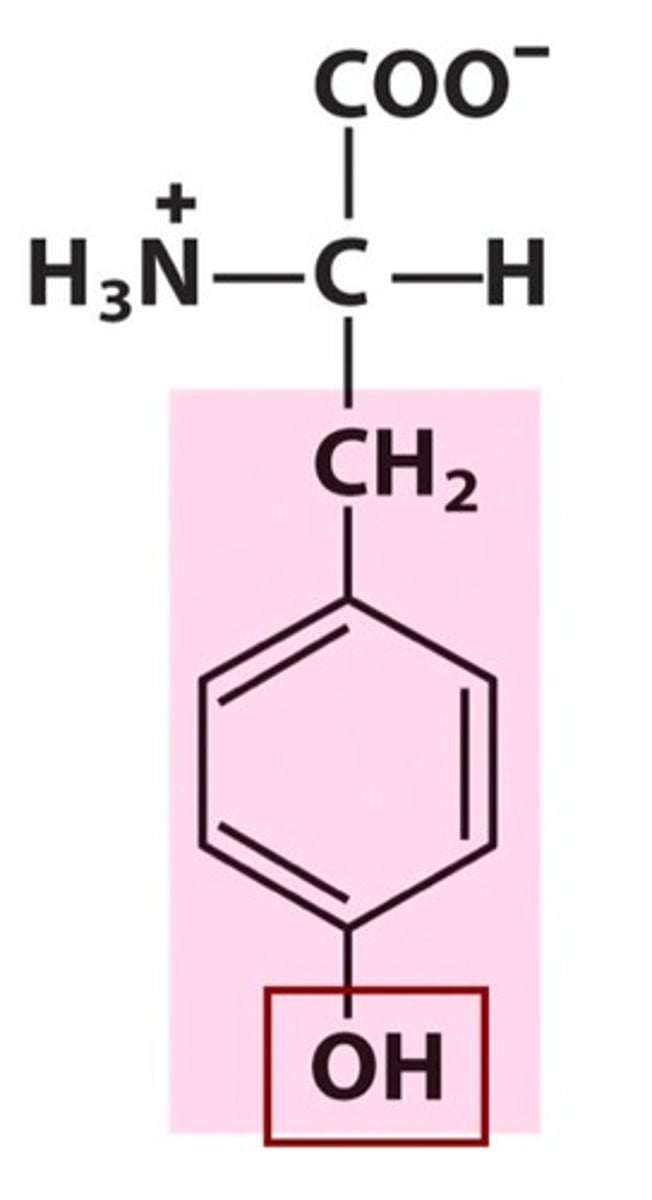
Tyrosine
Tyr, Y, polar, hydrophilic
Asparagine
Asn, N, polar, hydrophilic
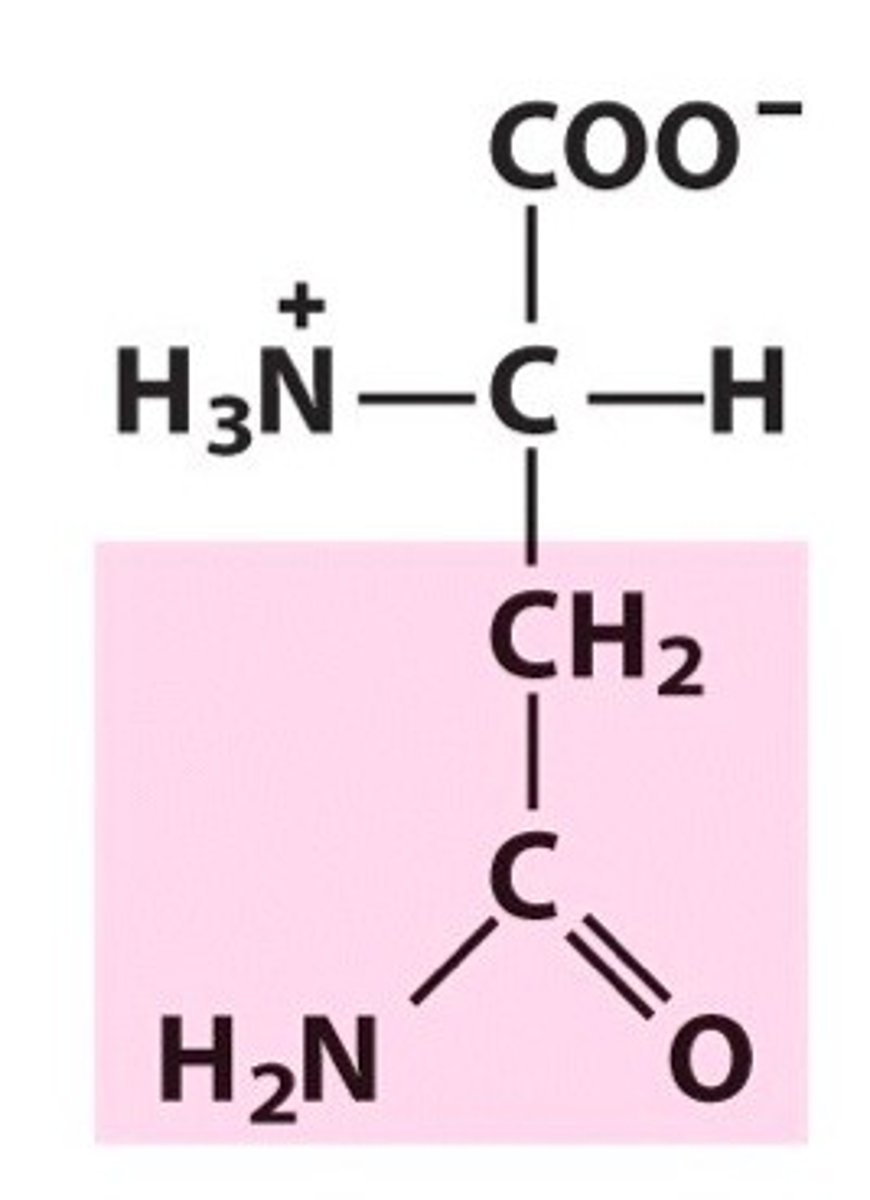
Glutamine
Gln, Q, Polar, Hydrophilic
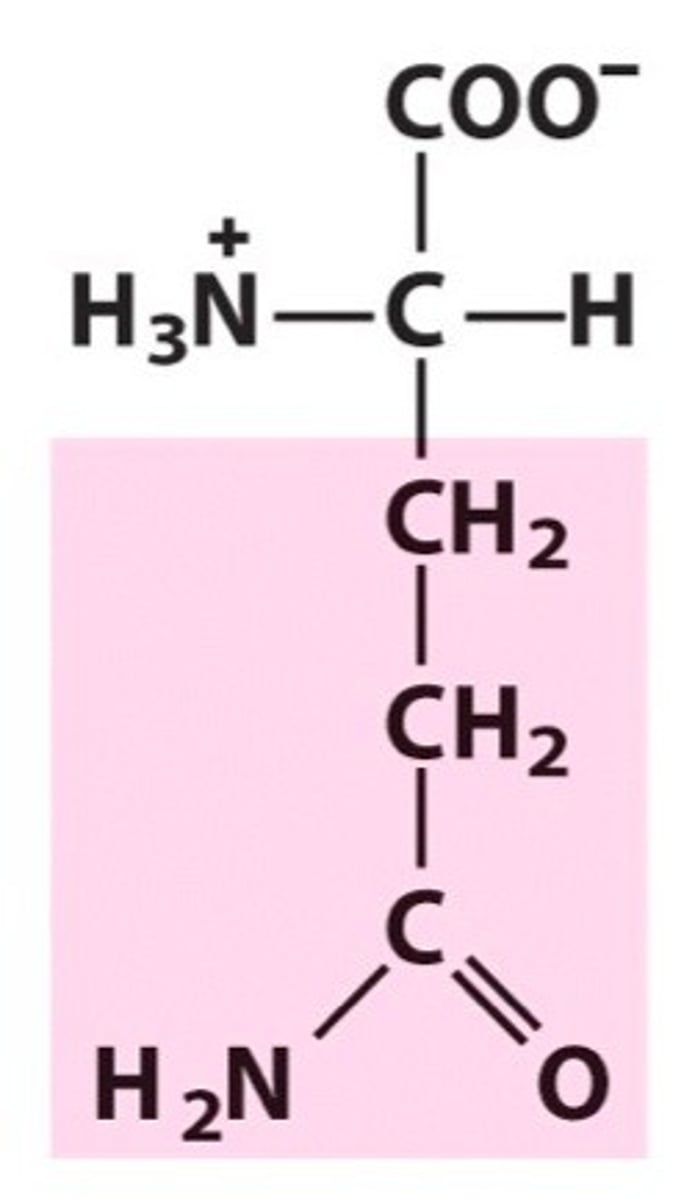
Aspartate
Asp, D, polar negatively charged, Acidic, hydrophilic
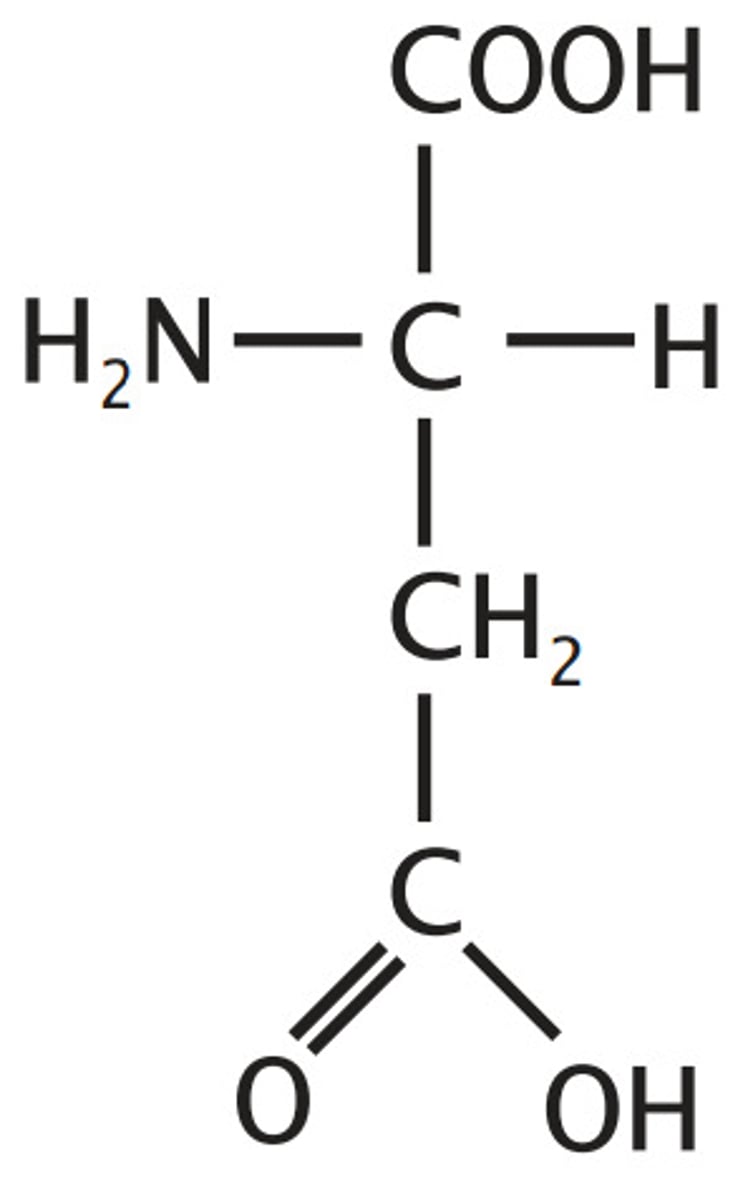
glutamate
glu, E, polar, negatively charged, acidic, hydrophilic
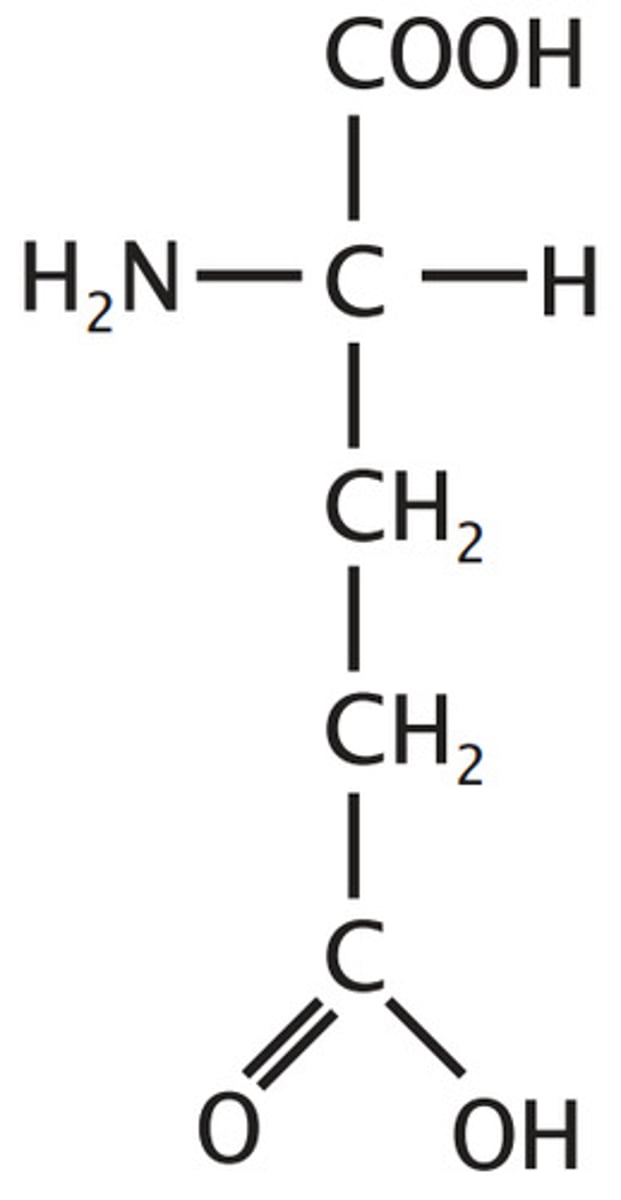
Lysine
Lys, K, polar, basic, positive, hydrophilic
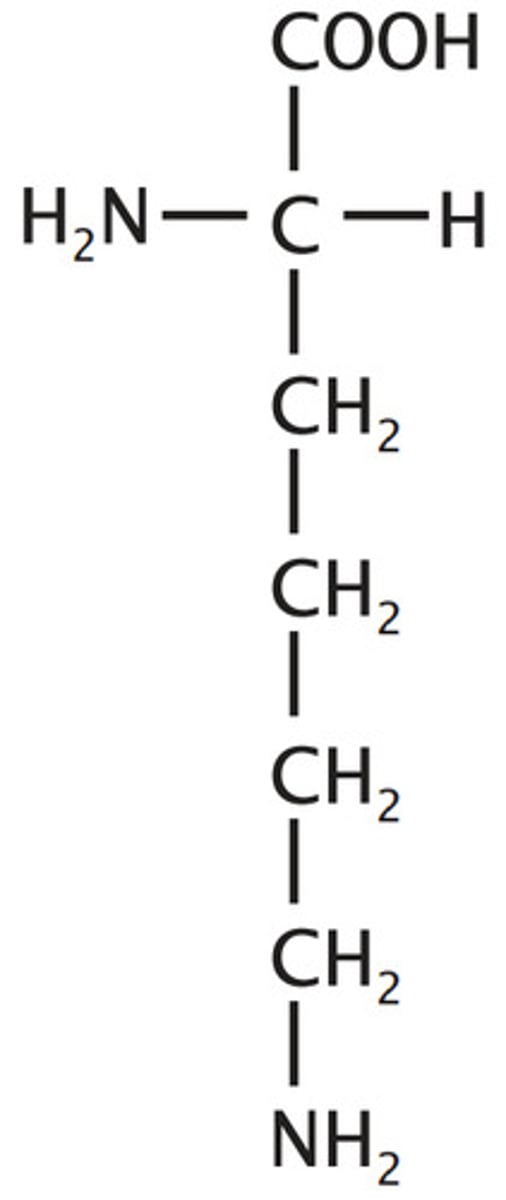
Arginine
Arg, R, Polar, Basic, positive, hydrophilic
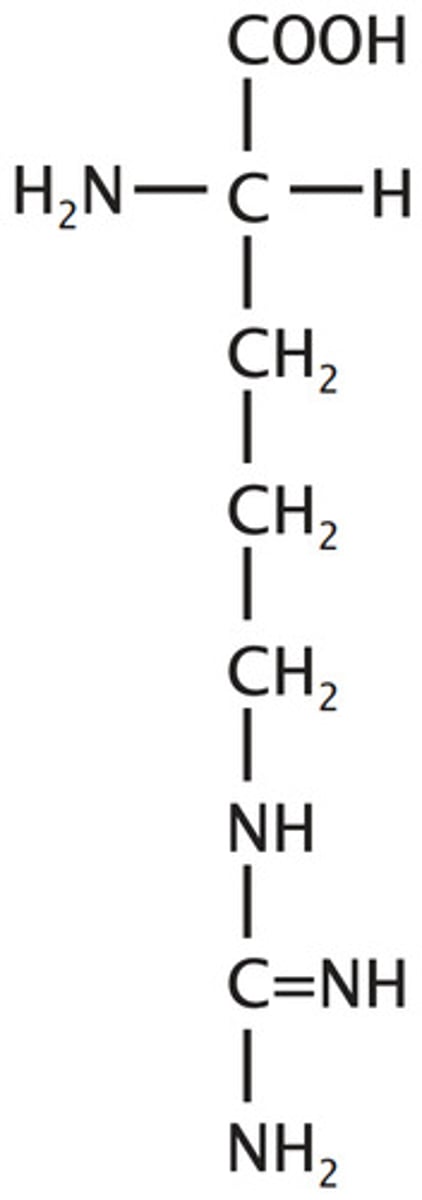
Histidine
His, H, polar, basic, positive, hydrophilic
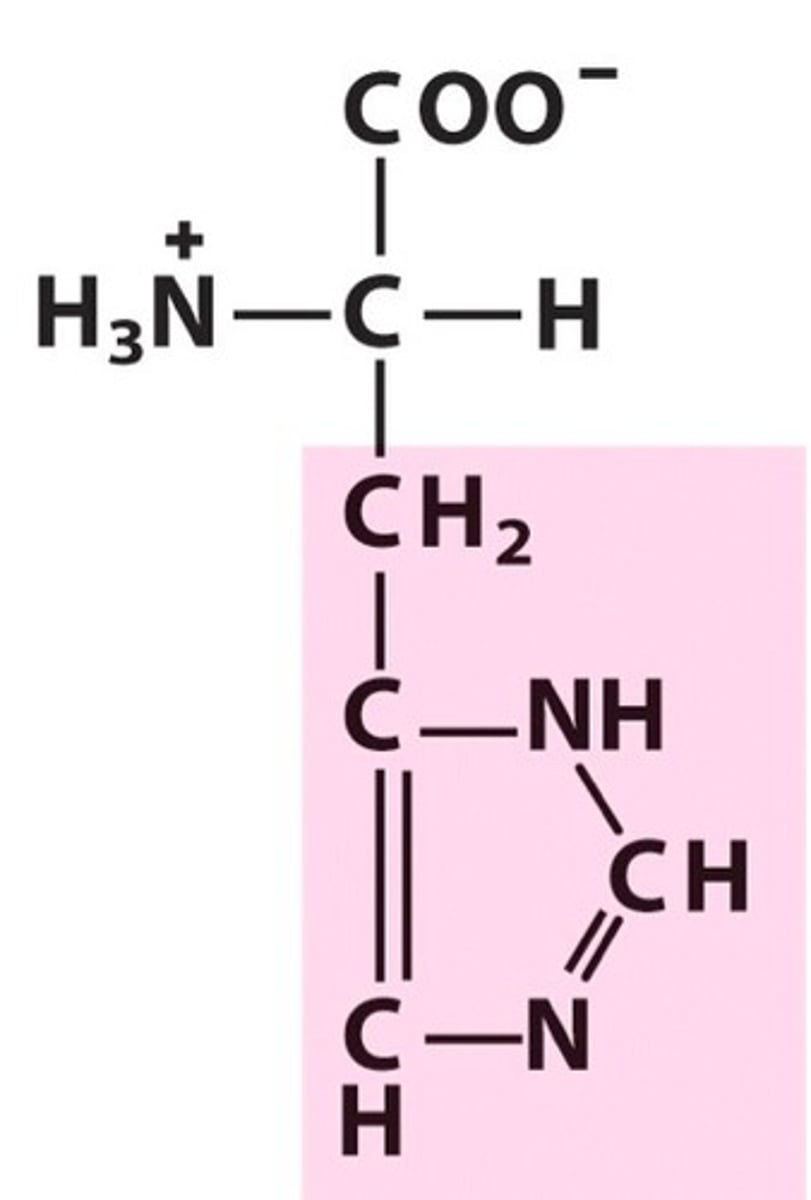
Nonessential amino acids (11)
alanine, arginine, asparagine, aspartic acid, cysteine, glutamic acid, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, tyrosine
Essential amino acids (9)
histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, valine
R-Group PKA and charge:
Terminal carboxyl
3.1
Acid- Neutral
Base- Negative
R-Group PKA and charge:
Terminal amino group
8.0
acid- positive
base- neutral
R-group PKA and charge:
Aspartic Acid/Glutamic Acid
4.1
acid- neutral
base- negative
R-group PKA and charge:
Histidine
6.0
Acid- positive
base- neutral
R-group PKA and charge:
Cysteine
8.3
Acid- neutral
base- negative
R-group PKA and charge:
Tyrosine
10.9
Acid- neutral
base- negative
R-group PKA and charge: Lysine
10.8
acid- positive
base- neutral
R-group pKA and charge: Arginine
12.5
acid- positive
base-neutral
Enzymatic Cleavage: Trypsin
carboxyl side of lysine and arginine residues
Enzymatic cleavage: Thrombin
Carboxyl side of arginine
Enzymatic cleavage: Chymotrypsin
carboxyl side of tyrosine, tryptophan, phenylalanine, leucine, and methionine
Amino acids in proteins of all organisms on earth are _ isomer
L (clockwise)
isoelectric point
The pH value at which the amino acid exists as a zwitterion (no net charge)
steps to find net charge (4)
1) identify all ionizable groups on AA
2) find pKa of ionizable groups
3) identify dominant group (protonated or deprotonated) based on pH
4)Find overall charge on AA
primary structure bond type
peptide bonds or covalent
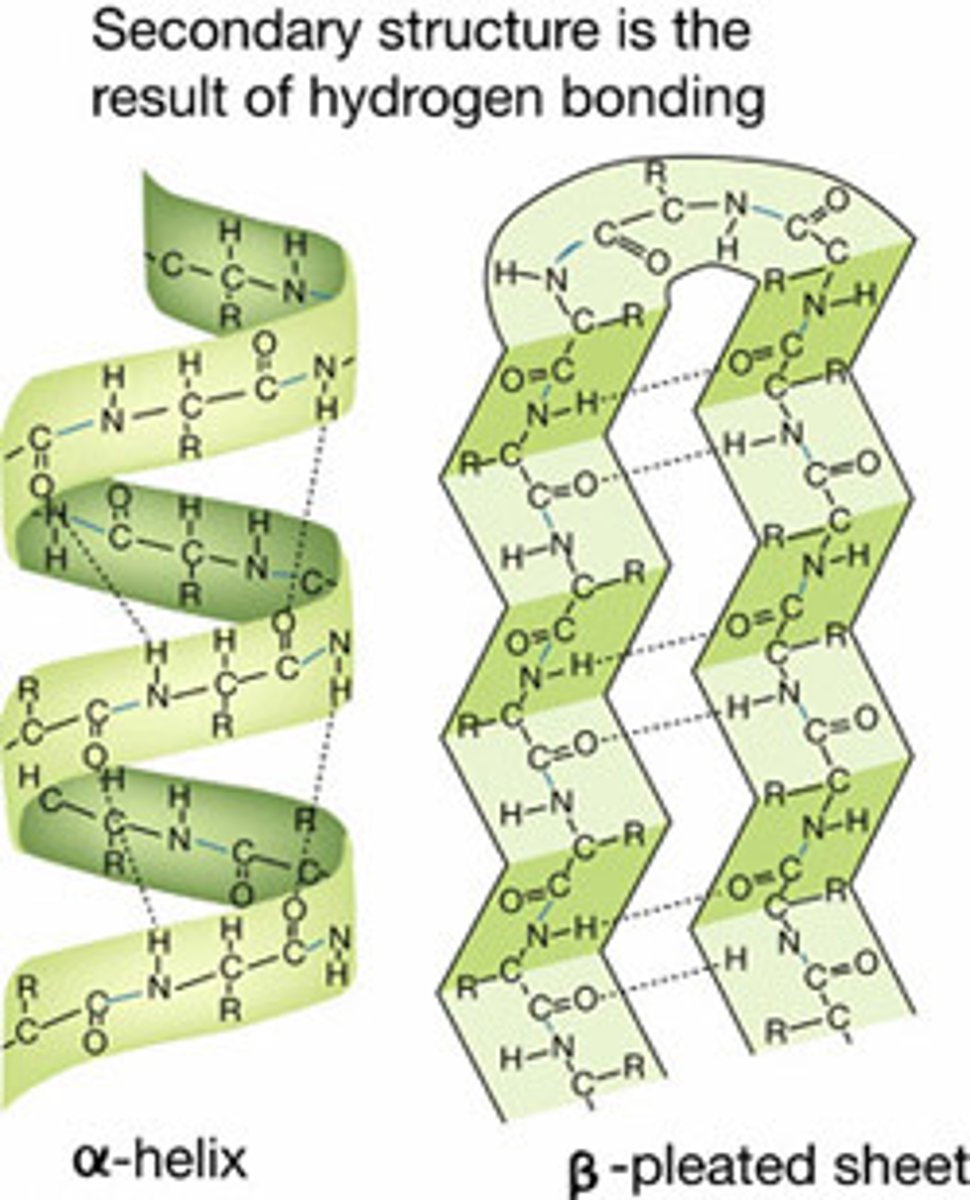
secondary structure bond type
hydrogen bonds between peptide -NH and -CO
secondary structure
Either an alpha helix or beta pleated sheet.
Tertiary Structure bond type
hydrophobic effect- hydrophobic side chains are buried and polar/charged chains are on surface
Van der Waals interactions, H bonds as well
quarternary structure bond type
disulfide bonds
denaturation of protein methods
Thermal
Chemical (urea, BME)
molecular exclusion chromatography (gel filtration)
Small molecules enter spaces in beads, large flow through and elute first
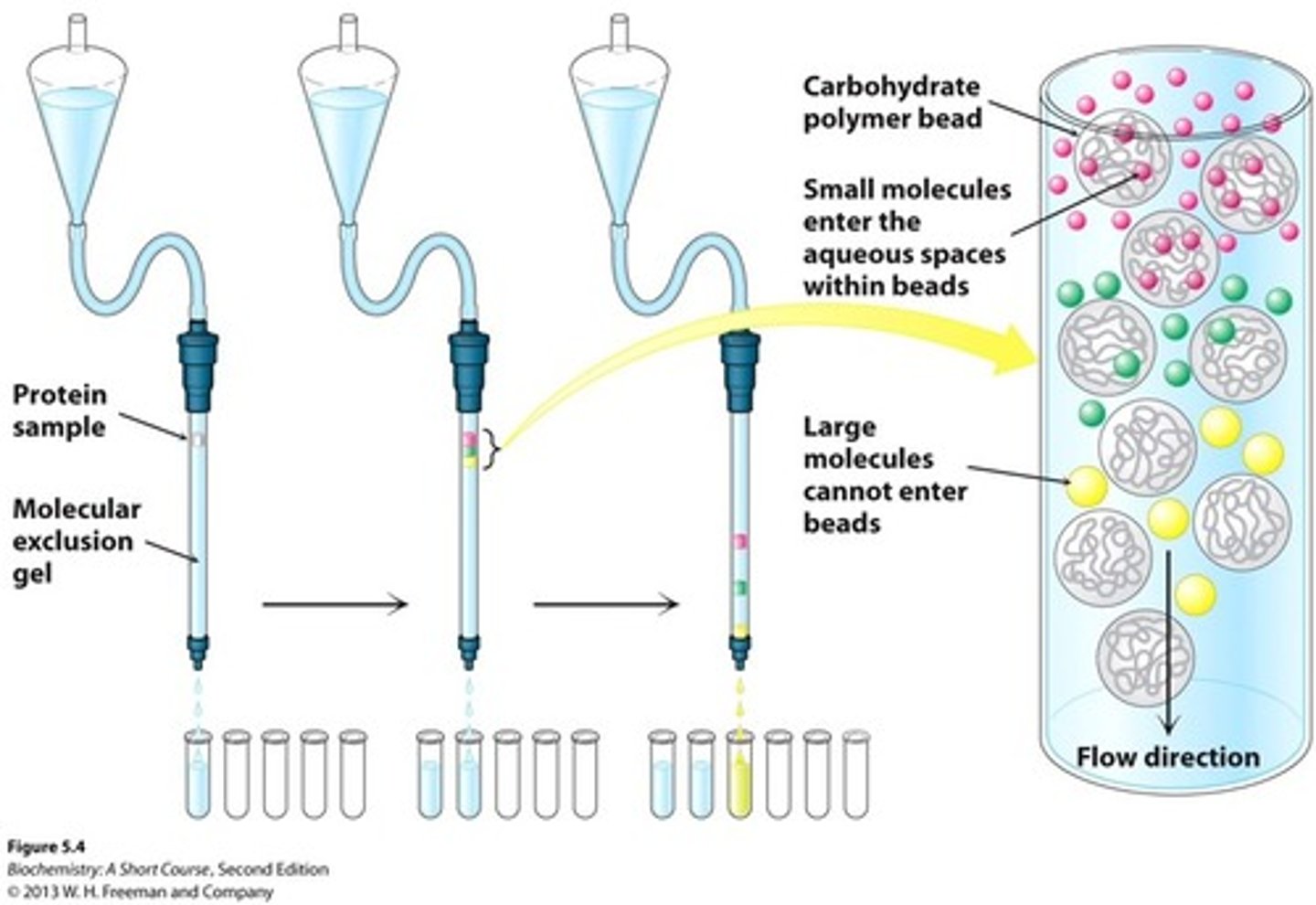
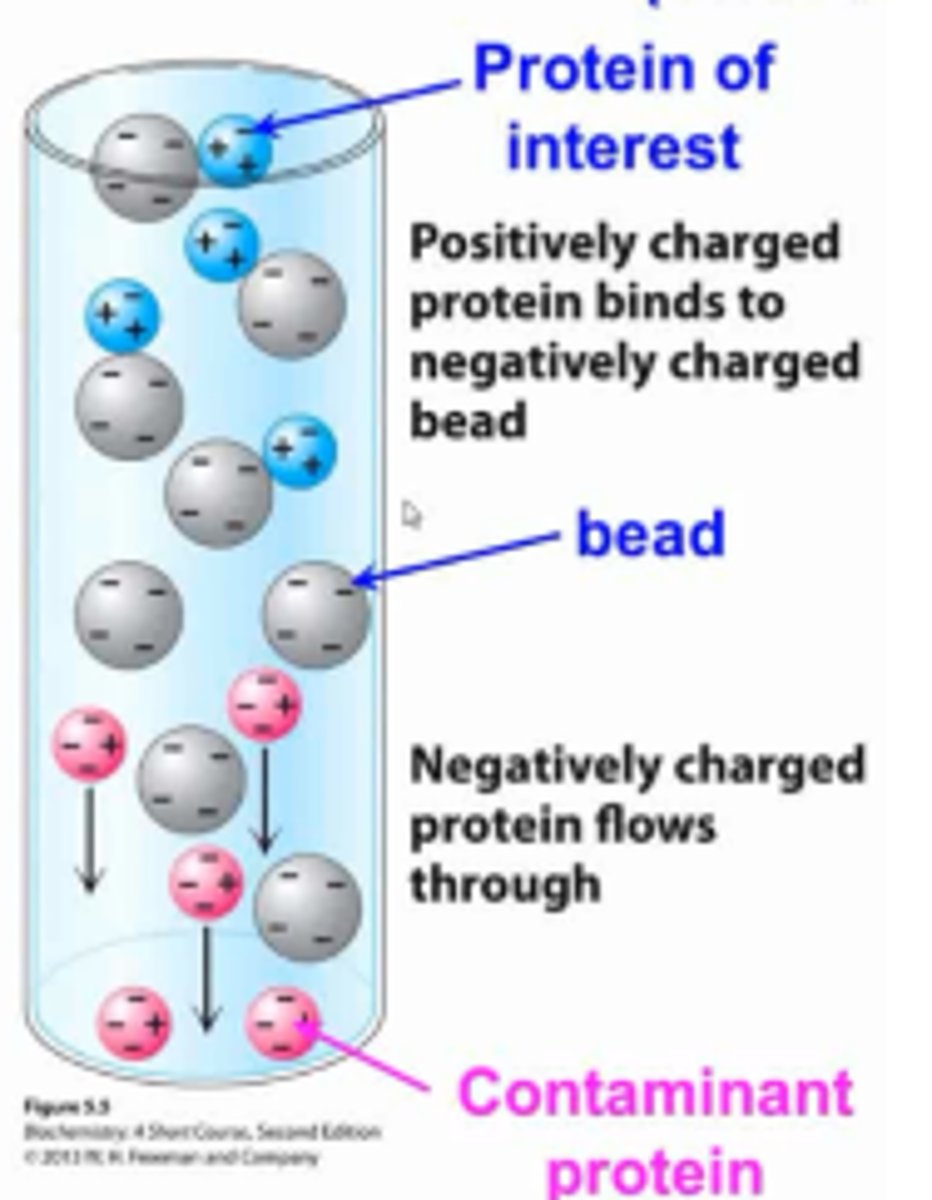
Ion exchange chromatography
negatively charged beads will attract positive proteins, negative proteins will flow through (and vice versa)
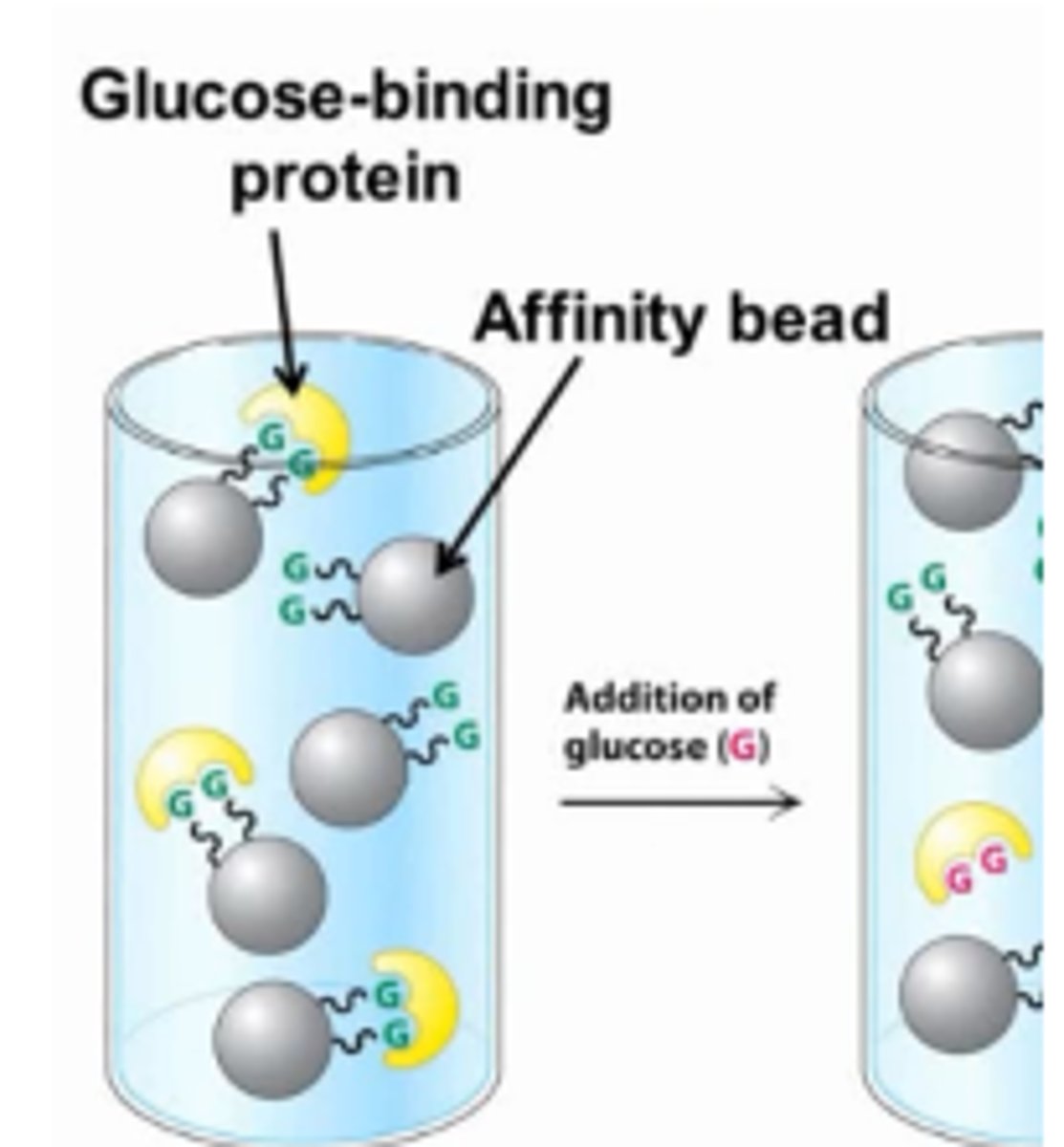
Affinity chromatography
-uses specific interactions to slow down select molecules
-can make use of receptor-ligand, enzyme-substrate, and antigen-antibody interactions
example: beads with glucose attract glucose-binding protein, proteins attach to beads
glucose is then added into cylinder, releasing glucose binding proteins
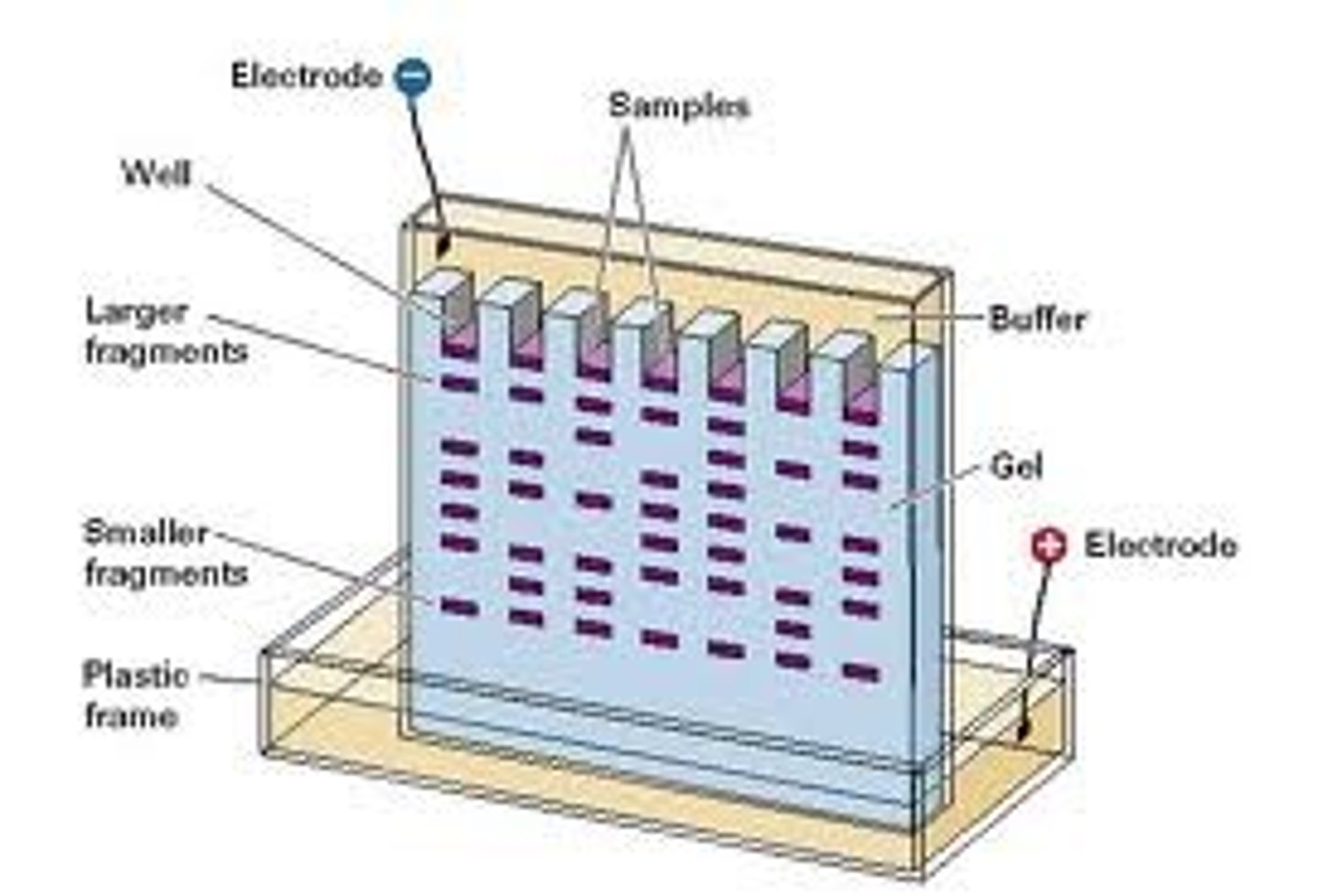
gel electrophoresis
The separation of nucleic acids or proteins, on the basis of their size and electrical charge, by measuring their rate of movement through an electrical field in a gel.
SDS-PAGE
sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
SDS causes proteins to all become negatively charged, and they are then separated purely by mass (smallest travel down to the anode first)