B4b Transpiration & Translocation
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Not 'tissues and organs in plants', not 'RP investigating water loss in a leaf'
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Transpiration is the movement of ___
water
translocation is the movement of
nutrients: glucose and amino acids
Transpiration occurs through
xylem tissue
translocation occurs through
phloem tissue
Xylem tissue is..
Phloem tissue is…
one/two way
Xylem tissue is one way
Phloem tissue is two way
xylem tissue is made of
xylem tissue is made of dead cells
phloem tissue is made of
phloem tissue is made of living cells
in xylem tissue, the cell wall is made of
in xylem tissue, the cell wall is made of lignin, which makes it stronger
in phloem tissue, the cell wall is made of
in phloem tissue, the cell wall is made of cellulose
in xylem tissue, cell end walls are
in xylem tissue, cell end walls are hollow
in phloem tissue, cell end walls have
in phloem tissue, cell end walls have sieve plates, aka perforations
In translocation, substances are moved through the phloem tissue through which type of transport?
In translocation, substances are moved through the phloem tissue through Active transport
in transpiration, what direction does the water move in?
it is sucked up towards the leaves, from the roots
How does water escape the plant?
The stomata in the leaf need to open to let CO2 in, and water escapes while this happens. The plant has no interest in losing water!
the water then evaporates.
Which 4 conditions affect transpiration?
Temperature
Air movement / windiness
Humidity
Light intensity
Higher temperature = higher or lower rate of transpiration
higher temp = faster transpiration
more wind = higher or lower rate of transpiration
Windier = faster transpiration
More humid = higher or lower rate of transpiration
More humid = slower transpiration
Because it’s already wet outside the plant, so there is a lower concentration gradient so the plant tries less hard to get water out into the air.
Bright light = higher or lower rate of transpiration
more light = faster transpiration
What can we use to measure rate of transpiration?
The humble potometer
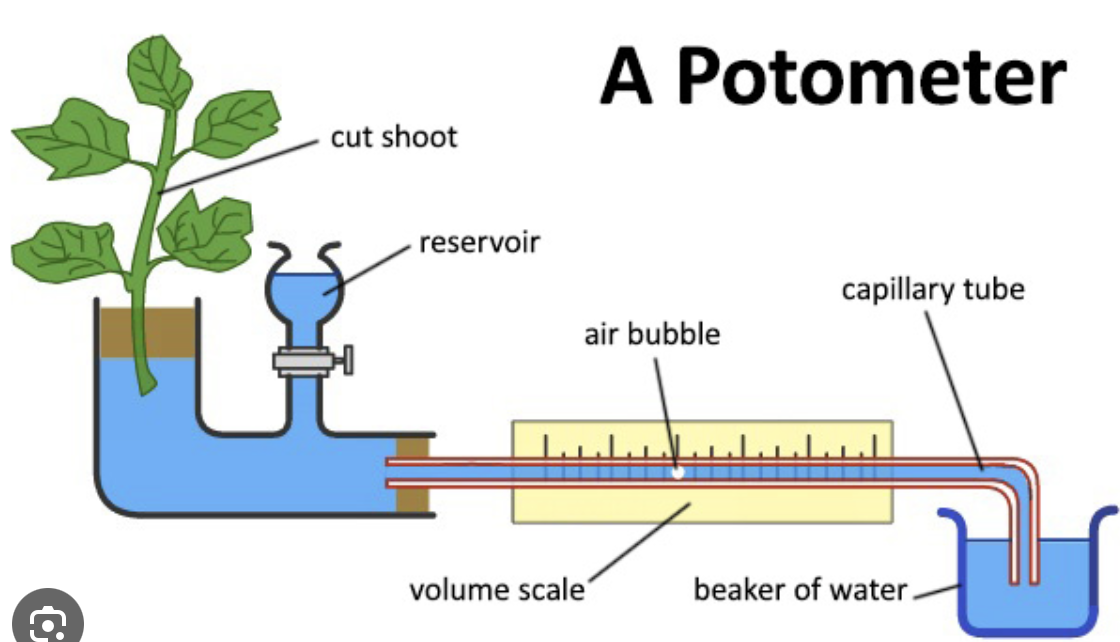
How do we use it?
And how is it reset?
as plant uptakes water, air bubble moves to the left. after a set time, see how far it has moved.
to reset the experiment, open the tap on the reservoir to allow water to flow in the other direction, pushing the bubble back towards the beaker.
4marker: Explain how water from the soil reaches the leaves. Include:
concentration gradient
transpiration
osmosis
root hair cells
evaporation
stomata
see folder, booklet B4b, page 10