Chapter 5: The Integumentary System
Layers of the Skin
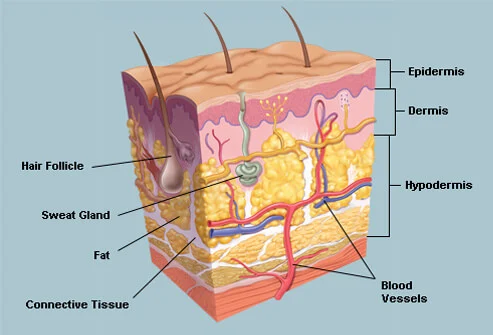
- The skin and its accessory structures make up the integumentary system, which provides the body with overall protection.
- The skin is made of multiple layers of cells and tissues, which are held to underlying structures by connective tissue.
- The skin is composed of two main layers: the epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures. Beneath the dermis lies the hypodermis, which is composed mainly of loose connective and fatty tissues.
The Epidermis
- The epidermis is composed of keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium.
- It is made of four or five layers of epithelial cells, depending on its location in the body.
- Skin that has four layers of cells is referred to as “thin skin.”
- Most of the skin can be classified as thin skin.
- “Thick skin” is found only on the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet.
- A keratinocyte is a cell that manufactures and stores the protein keratin.
- Keratin is an intracellular fibrous protein that gives hair, nails, and skin their hardness and water-resistant properties.
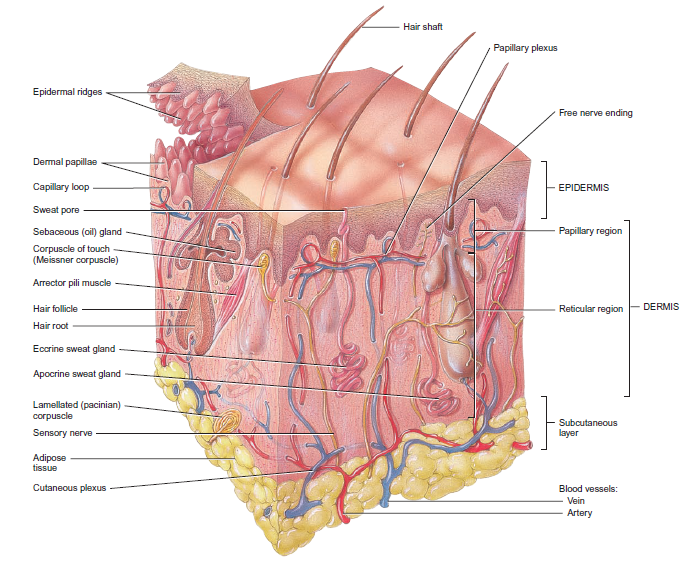
Stratum Basale
- The stratum basale (also called the stratum germinativum) is the deepest epidermal layer and attaches the epidermis to the basal lamina, below which lie the layers of the dermis.
- A finger-like projection, or fold, known as the dermal papilla (plural = dermal papillae) is found in the superficial portion of the dermis.
- A basal cell is a cuboidal-shaped stem cell that is a precursor of the keratinocytes of the epidermis.
- The first is a Merkel cell, which functions as a receptor and is responsible for stimulating sensory nerves that the brain perceives as touch.
- The second is a melanocyte, a cell that produces the pigment melanin.
- Melanin gives hair and skin its color, and also helps protect the living cells of the epidermis from ultraviolet (UV) radiation damage.
Stratum Spinosum
- As the name suggests, the stratum spinosum is spiny in appearance due to the protruding cell processes that join the cells via a structure called a desmosome.
- Interspersed among the keratinocytes of this layer is a type of dendritic cell called the Langerhans cell, which functions as a macrophage by engulfing bacteria, foreign particles, and damaged cells that occur in this layer.
Stratum Granulosum
- The stratum granulosum has a grainy appearance due to further changes to the keratinocytes as they are pushed from the stratum spinosum.
- The cells (three to five layers deep) become flatter, their cell membranes thicken, and they generate large amounts of the proteins keratin, which is fibrous, and keratohyalin, which accumulates as lamellar granules within the cells.
Stratum Lucidum
- The stratum lucidum is a smooth, seemingly translucent layer of the epidermis located just above the stratum granulosum and below the stratum corneum.
- These cells are densely packed with eleiden, a clear protein rich in lipids, derived from keratohyalin, which gives these cells their transparent (i.e., lucid) appearance and provides a barrier to water.
- Stratum Corneum: The stratum corneum is the most superficial layer of the epidermis and is the layer exposed to the outside environment.
Dermis
- The dermis might be considered the “core” of the integumentary system (derma- = “skin”), as distinct from the epidermis (epi- = “upon” or “over”) and hypodermis (hypo- = “below”).
- It contains blood and lymph vessels, nerves, and other structures, such as hair follicles and sweat glands.
- Papillary Layer: The papillary layer is made of loose, areolar connective tissue, which means the collagen and elastin fibers of this layer form a loose mesh.
Reticular Layer
- Underlying the papillary layer is the much thicker reticular layer, composed of dense, irregular connective tissue.
- Elastin fibers provide some elasticity to the skin, enabling movement.
- Hypodermis: The hypodermis (also called the subcutaneous layer or superficial fascia) is a layer directly below the dermis and serves to connect the skin to the underlying fascia (fibrous tissue) of the bones and muscles.
Pigmentation
The melanin is transferred into the keratinocytes via a cellular vesicle called a melanosome.
Melanin occurs in two primary forms. Eumelanin exists as black and brown, whereas pheomelanin provides a red color.
Dark-skinned individuals produce more melanin than those with pale skin.
Accessory Structures of the Skin
Hair
- Hair is a keratinous filament growing out of the epidermis. It is primarily made of dead, keratinized cells.
- Strands of hair originate in an epidermal penetration of the dermis called the hair follicle.
- The hair shaft is the part of the hair not anchored to the follicle, and much of this is exposed at the skin’s surface.
- The rest of the hair, which is anchored in the follicle, lies below the surface of the skin and is referred to as the hair root.
- The hair root ends deep in the dermis at the hair bulb, and includes a layer of mitotically active basal cells called the hair matrix.
- The hair bulb surrounds the hair papilla, which is made of connective tissue and contains blood capillaries and nerve endings from the dermis.
- The medulla forms the central core of the hair, which is surrounded by the cortex, a layer of compressed, keratinized cells that is covered by an outer layer of very hard, keratinized cells known as the cuticle.
- The cells of the internal root sheath surround the root of the growing hair and extend just up to the hair shaft. They are derived from the basal cells of the hair matrix.
- The external root sheath, which is an extension of the epidermis, encloses the hair root.
- The glassy membrane is a thick, clear connective tissue sheath covering the hair root, connecting it to the tissue of the dermis.
- Each hair root is connected to a smooth muscle called the arrector pili that contracts in response to nerve signals from the sympathetic nervous system, making the external hair shaft “stand up.”
Hair Growth
- The first is the anagen phase, during which cells divide rapidly at the root of the hair, pushing the hair shaft up and out.
- The catagen phase lasts only 2 to 3 weeks, and marks a transition from the hair follicle’s active growth.
- Finally, during the telogen phase, the hair follicle is at rest and no new growth occurs.
Nails
- The nail body is formed on the nail bed, and protects the tips of our fingers and toes as they are the farthest extremities and the parts of the body that experience the maximum mechanical stress.
- The nail body forms at the nail root, which has a matrix of proliferating cells from the stratum basale that enables the nail to grow continuously.
- The lateral nail fold overlaps the nail on the sides, helping to anchor the nail body.
- The nail fold that meets the proximal end of the nail body forms the nail cuticle, also called the eponychium.
- The nail bed is rich in blood vessels, making it appear pink, except at the base, where a thick layer of epithelium over the nail matrix forms a crescent-shaped region called the lunula (the “little moon”).
- The area beneath the free edge of the nail, furthest from the cuticle, is called the hyponychium.
Sweat Glands
- When the body becomes warm, sudoriferous glands produce sweat to cool the body.
- An eccrine sweat gland is a type of gland that produces a hypotonic sweat for thermoregulation.
- Eccrine glands are a primary component of thermoregulation in humans and thus help to maintain homeostasis.
- An apocrine sweat gland is usually associated with hair follicles in densely hairy areas, such as armpits and genital regions.
Sebaceous Glands
- A sebaceous gland is a type of oil gland that is found all over the body and helps to lubricate and waterproof the skin and hair.
- Most sebaceous glands are associated with hair follicles.
- They generate and excrete sebum, a mixture of lipids, onto the skin surface, thereby naturally lubricating the dry and dead layer of keratinized cells of the stratum corneum, keeping it pliable.
Protection
- The skin shields the body from wind, water, and UV rays. Keratin and glycolipids in the stratum corneum prevent water loss.
- It protects against dirt, bacteria, and hazardous substances.
- Dermicidin, an antibiotic in sweat, prevents microorganisms from overcolonizing the skin.
Sensory Function
- The epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis have sensory nerve systems that detect touch, surface temperature, and pain, making the skin a sense organ.
- The Meissner corpuscle (tactile corpuscle) and Pacinian corpuscle (lamellated corpuscle) respond to mild touch and vibration, respectively, on the tips of the fingers, which are particularly sensitive to touch.
Thermoregulation
- The integumentary system helps regulate body temperature through its tight association with the sympathetic nervous system, the division of the nervous system involved in our fight-or-flight responses.
- The sympathetic nervous system is continuously monitoring body temperature and initiating appropriate motor responses.
Vitamin D Synthesis
- The epidermal layer of human skin synthesizes vitamin D when exposed to UV radiation. In the presence of sunlight, a form of vitamin D3 called cholecalciferol is synthesized from a derivative of the steroid cholesterol in the skin.
- The absence of sun exposure can lead to a lack of vitamin D in the body, leading to a condition called rickets, a painful condition in children where the bones are misshapen due to a lack of calcium, causing bowleggedness.
Diseases
- One of the most talked about diseases is skin cancer. Cancer is a broad term that describes diseases caused by abnormal cells in the body dividing uncontrollably.
- Most cancers are identified by the organ or tissue in which the cancer originates. One common form of cancer is skin cancer.
- DNA mutations cause cancer. Mutations can lead to uncontrolled cell proliferation and malignancies.
- Some benign tumors produce cells that can metastasis and form cancers in other organs.
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is a form of cancer that affects the mitotically active stem cells in the stratum basale of the epidermis.
Basal cell carcinoma can take several different forms. Similar to other forms of skin cancer, it is readily cured if caught early and treated.
\n Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is a cancer that affects the keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum and presents as lesions commonly found on the scalp, ears, and hands.
It is the second most common skin cancer.
\n Melanoma
A melanoma is a cancer characterized by the uncontrolled growth of melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells in the epidermis.
Typically, a melanoma develops from a mole.
- It is the most fatal of all skin cancers, as it is highly metastatic and can be difficult to detect before it has spread to other organs.
Skin Disorders
Eczema
Eczema is an allergic reaction that manifests as dry, itchy patches of skin that resemble rashes.
It may be accompanied by swelling of the skin, flaking, and in severe cases, bleeding.
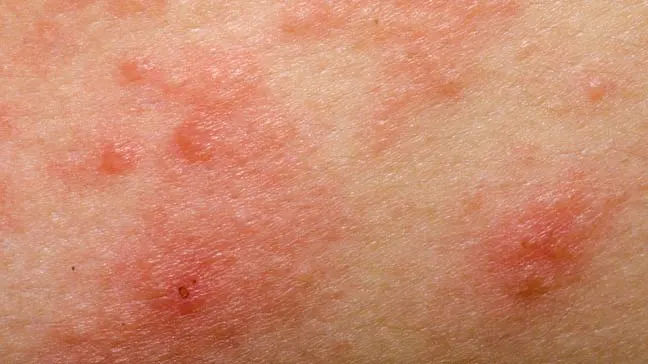
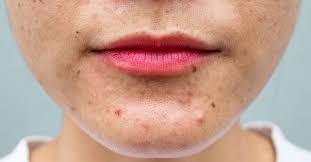
Acne
Acne is a skin disturbance that typically occurs on areas of the skin that are rich in sebaceous glands (face and back).
It is most common along with the onset of puberty due to associated hormonal changes, but can also occur in infants and continue into adulthood.
Injuries
Because the skin is the part of our bodies that meets the world most directly, it is especially vulnerable to injury.
Injuries include burns and wounds, as well as scars and calluses.
- They can be caused by sharp objects, heat, or excessive pressure or friction to the skin.
Skin injuries set off a healing process that occurs in several overlapping stages.
Burns
- A burn results when the skin is damaged by intense heat, radiation, electricity, or chemicals.
- The damage results in the death of skin cells, which can lead to a massive loss of fluid.
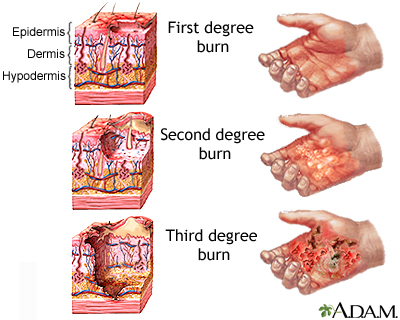
- A first-degree burn is a superficial burn that affects only the epidermis.
- Although the skin may be painful and swollen, these burns typically heal on their own within a few days.
- Mild sunburn fits into the category of a first-degree burn.
- A second-degree burn goes deeper and affects both the epidermis and a portion of the dermis.
- These burns result in swelling and a painful blistering of the skin.
- It is important to keep the burn site clean and sterile to prevent infection.
- If this is done, the burn will heal within several weeks.
- A third-degree burn fully extends into the epidermis and dermis, destroying the tissue and affecting the nerve endings and sensory function.
- These are serious burns that may appear white, red, or black; they require medical attention and will heal slowly without it.
- A fourth-degree burn is even more severe, affecting the underlying muscle and bone.
- Oddly, third and fourth-degree burns are usually not as painful because the nerve endings themselves are damaged.
Scars and Keloids
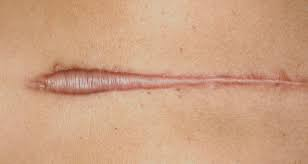
A scar is collagen-rich skin formed after the process of wound healing that differs from normal skin.
- Scarring occurs in cases in which there is repair of skin damage, but the skin fails to regenerate the original skin structure.
Sometimes, there is an overproduction of scar tissue, because the process of collagen formation does not stop when the wound is healed; this results in the formation of a raised or hypertrophic scar called a keloid.
Bedsores and Stretch Marks
Skin and its underlying tissue can be affected by excessive pressure.
- One example of this is called a bedsore.
- Bedsores, also called decubitis ulcers, are caused by constant, long-term, unrelieved pressure on certain body parts that are bony, reducing blood flow to the area and leading to necrosis (tissue death).
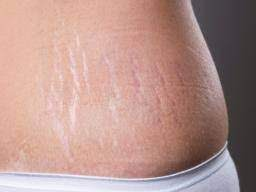
A stretch mark results when the dermis is stretched beyond its limits of elasticity, as the skin stretches to accommodate the excess pressure.
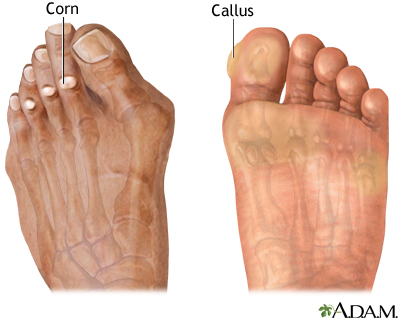
Calluses
When you wear shoes that do not fit well and are a constant source of abrasion on your toes, you tend to form a callus at the point of contact.
Calluses can also form on your fingers if they are subject to constant mechanical stress, such as long periods of writing, playing string instruments, or video games.
A corn is a specialized form of callus.