Nervous System Anatomy
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/78
Last updated 12:20 AM on 11/18/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
1
New cards
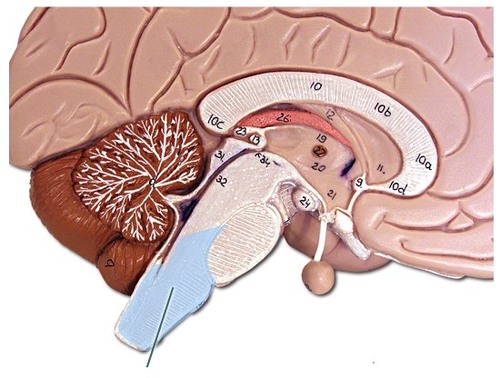
spinal cord
a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column
2
New cards
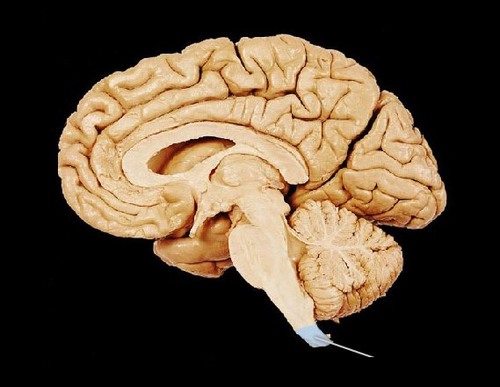
cerebellum
a major feature of the hindbrain responsible for body movements and balance
3
New cards
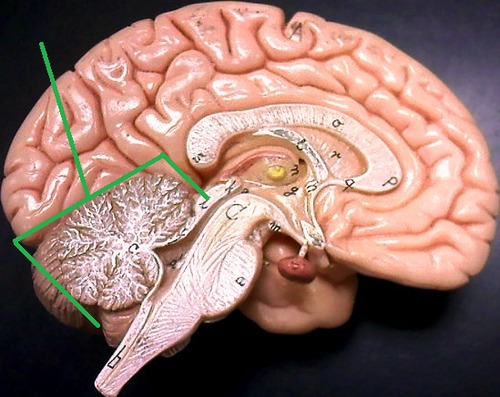
cerebrum
the principal and most anterior part of the brain in vertebrates, located in the front area of the skull and consisting of two hemispheres, left and right, separated by a fissure
4
New cards
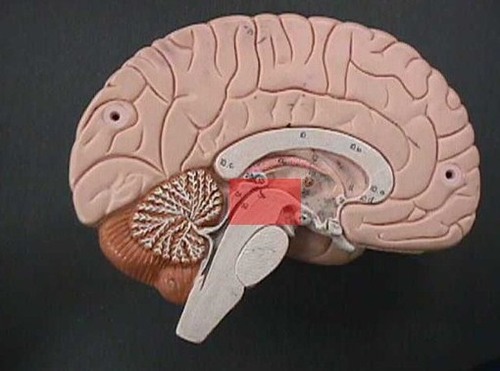
midbrain
relays sensory and motor impulses; serves important functions in motor movement, particularly movements of the eye, and in auditory and visual processing.
5
New cards
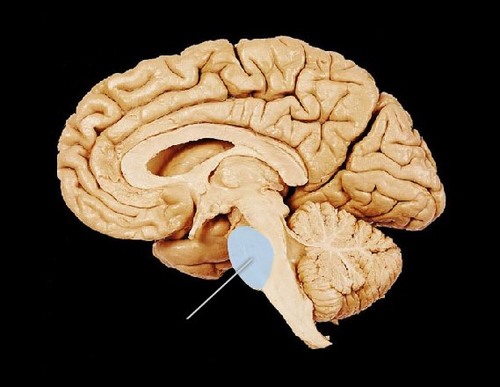
pons
part of the brain stem, assists with regulation of breathing
6
New cards
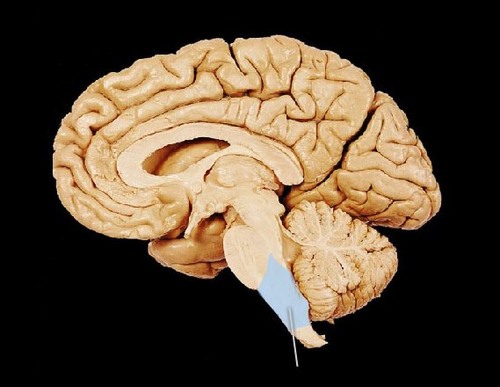
medulla oblongata
part of brain stem, regulates heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing, and controls the reflexes of coughing, sneezing, and vomiting
7
New cards
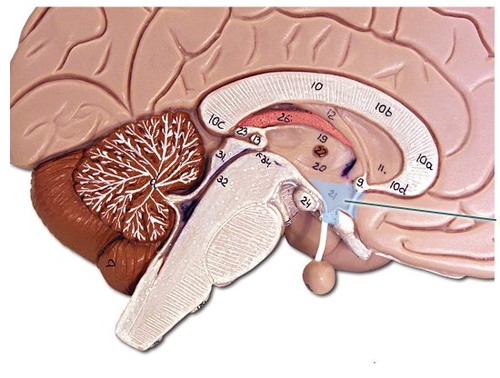
hypothalamus
lower portion of diencephalon which acts as an autonomic center regulating metabolism, heart rate, blood pressure, thirst, hunger, energy level, and body temperature
8
New cards
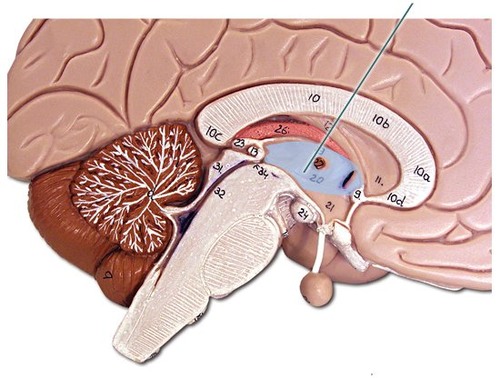
thalamus
middle portion of diencephalon which relays sensory impulses up to the sensory cortex (aka the cerebrum); regulates sleep and consciousness
9
New cards
corpus callosum
a thick band of nerve fibers that divides the cerebral cortex lobes into left and right hemispheres and acts as the connection between the two.
10
New cards
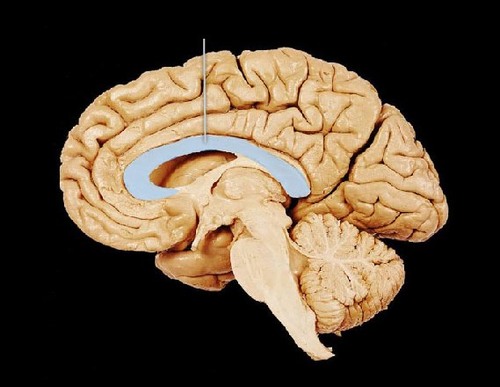
meninges
three layers of protective tissue between the brain and skull
11
New cards
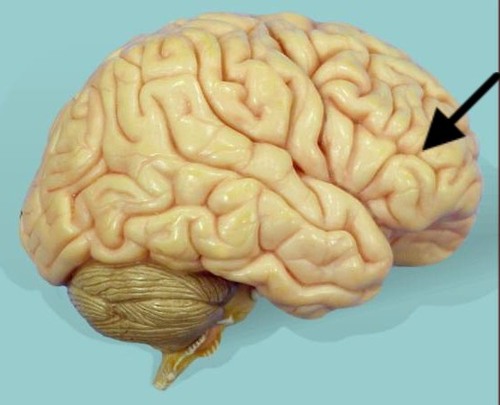
frontal lobe
cerebrum lobe responsible for memory, intelligence, behavior, emotions, motor function, and smell
12
New cards
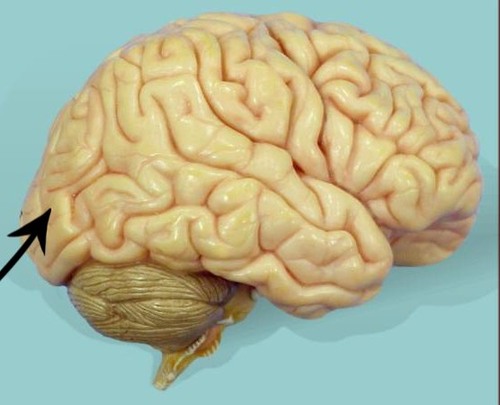
occipital lobe
cerebrum lobe responsible for vision and speech
13
New cards
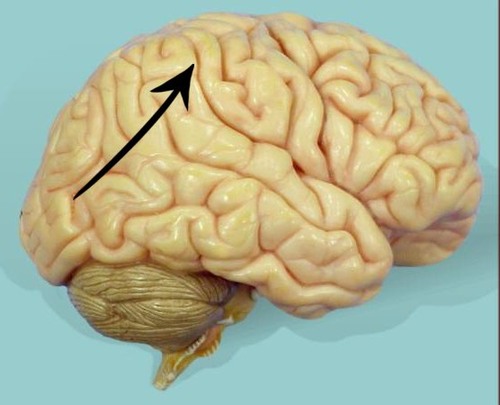
parietal lobe
lobe responsible for somatic sensations (pain, touch, temperature perception), and speech
14
New cards
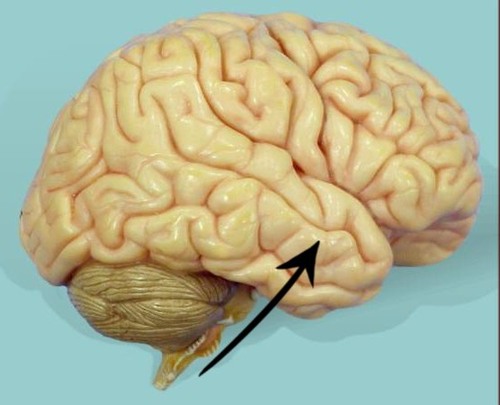
temporal lobe
lobe responsible for hearing, smell, memory, speech, and emotion
15
New cards
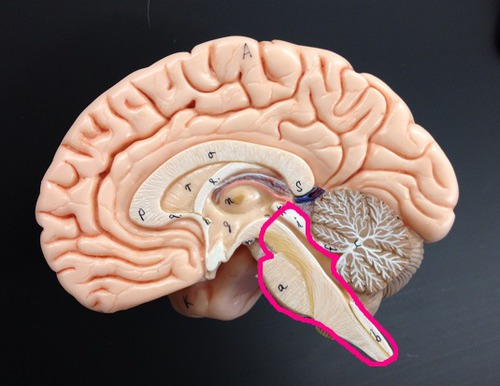
brain stem
Portion of brain that contains the pons, medulla oblongata, and the beginning of the spinal cord, controls the flow of messages between the brain and the rest of the body, and it also controls basic body functions
16
New cards
Broca's area
area on left frontal lobe responsible for tongue and lip movements
17
New cards
primary motor cortex
area in frontal lobe responsible for sending impulses to muscles
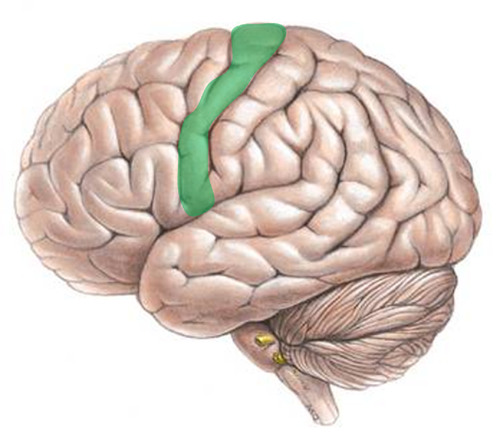
18
New cards
primary somatic sensory cortex
area in parietal lobe responsible for interpreting sensory impulses from the body
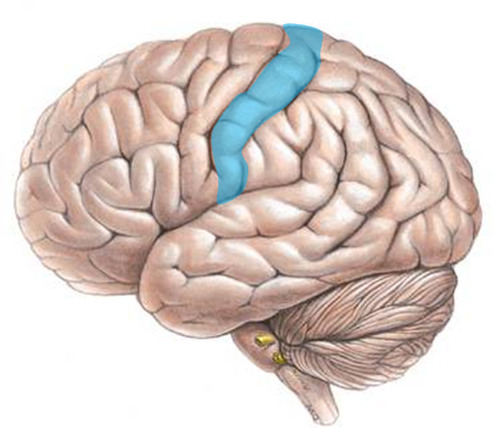
19
New cards
dura mater
outermost meninges layer
20
New cards
sensory input
also known as the afferent pathway; the gathering information about changes in the environment
21
New cards
motor output
also known as the efferent pathway; the response sent from the CNS to the rest of the body
22
New cards
CNS
composed of brain and spinal cord
23
New cards
autonomic NS
involuntary control of cardiac and smooth muscles
24
New cards
Somatic NS
voluntary control of skeletal muscles
25
New cards
parasympathetic
part of autonomic N.S. responsible for "rest and digest" actions
26
New cards
sympathetic NS
part of the autonomic N.S. responsible for response to potential danger
27
New cards
neuroglia
neuron supporting cells of the nervous system
28
New cards
Astrocytes
neuroglia that protects neurons from harmful substances in the blood
29
New cards
ependymal
neuroglia that form a protective covering around the spinal cord and cavities of the brain
30
New cards
oligodendrocytes
neuroglia that produce myelin sheaths around nerve fibers in the CNS
31
New cards
Schwann cells
neuroglia that produce myelin sheaths around nerve fibers in the PNS
32
New cards
dendrites
conduct impulses toward the cell body of a neuron
33
New cards
axons
conduct impulses away from the cell body of a neuron
34
New cards
myelin sheath
insulating material on axon fibers that increase the rate of impulse transmission
35
New cards
neurotransmitter
a chemical messanger that sends a message from the axon terminals to a muscle or nearby neuron
36
New cards
synaptic cleft
a gap between axon terminals and nearby muscles or neurons
37
New cards
Nodes of Ranvier
areas on an axon without a myelin sheath; also known as gray matter
38
New cards
action potential
another name for a nerve impulse
39
New cards
depolarization
the inflow of sodium ions resulting in a more positive environment inside the neuron and the propagation of an action potential.
40
New cards
repolarization
the outflow of potassium ions resulting in the return of a more positive environment outside the neuron.
41
New cards
fissure
a deep grove in the brain
42
New cards
describe the major functions of the medulla...
carries out and regulates life sustaining functions that are done involuntarily (without thinking).
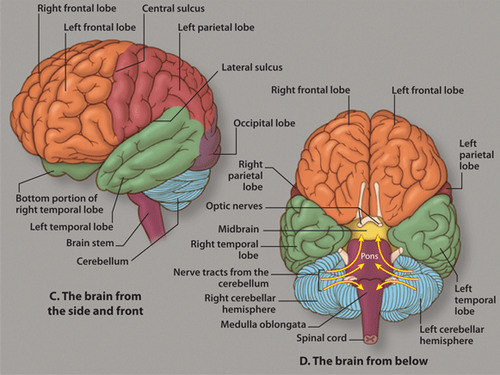
43
New cards
temporal lobe
responsible for processing auditory information from the ears
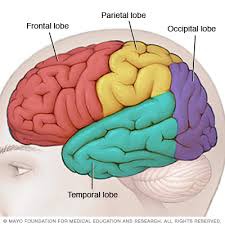
44
New cards
parietal lobe
processes sensory things that have to do with temperature, touch, and taste
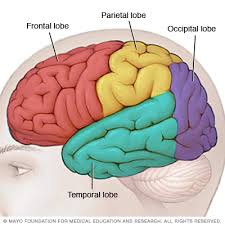
45
New cards
frontal lobe
carries out higher mental processes such as thinking, decision making, and planning. (This is where our personality is formed
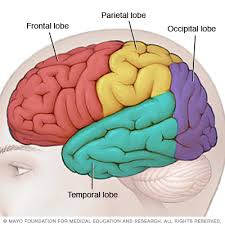
46
New cards
occipital lobe
responsible for processing visual information from the eyes. It helps you correctly understand what you are seeing
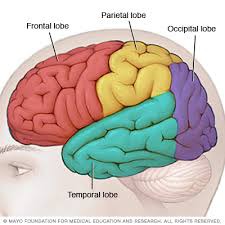
47
New cards
describe the major functions of the cerebral cortex
the cerebral cortex is where the four lobes are located
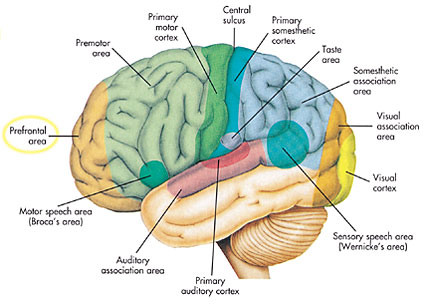
48
New cards
the cerebrum cortex is...
associated with higher brain function such as thought and action
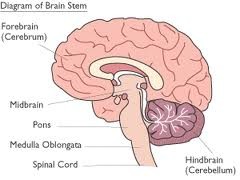
49
New cards
what is a thalamus gland?
the thalamus serves as a relay station for impulses traveling to and from the spinal cord, brain stem, cerebellum, and cerebrum
50
New cards
describe the major functions of the cerebellum...
responsible for balance and coordination of muscles and the body. It is extremely important for being able to preform everyday voluntary things
51
New cards
Nervous system
Major communication system in the body. Functions in sensing, processing, communicating between the cells throughout the entire body
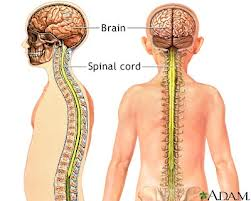
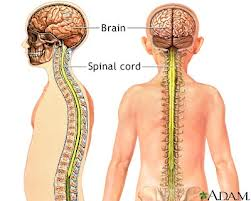
52
New cards
Central Nervous system
Consists of the brain and spinal cord
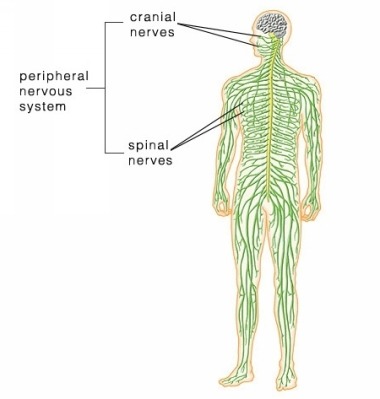
53
New cards
Peripheral nervous system
Consists of cranial and spinal nerves
54
New cards
Afferent pathway
Input. Away from the periphery to the CNS. Brain functions as the integrator. Includes somatic, special, and visceral senses
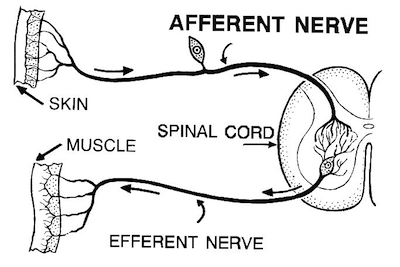
55
New cards
Efferent pathway
Output. Leaves the CNS and travels to the periphery. Includes somatic and automatic nervous systems and sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways
56
New cards
Neurons
Interconnect and communicate with each other. From the brain to spinal, to peripheral nerves, to the effector organs to allow us to react to our surroundings. Use electrical and chemical signals
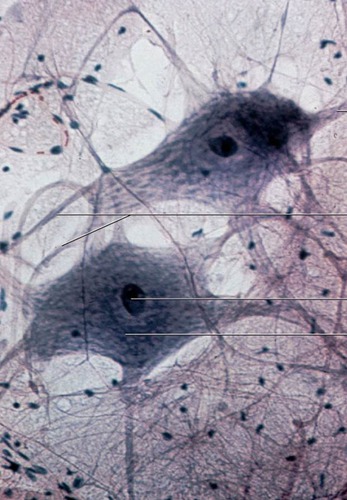
57
New cards
Ventricles
Cavities filled with CSF, lined with ependymal cells
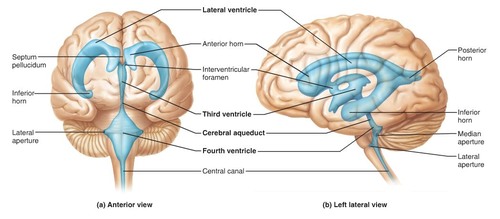
58
New cards
CSF
Secreted from support cells. Support the brain, regulate cell environment. Circulates through ventricular system. Produced by ependymal cells, supports/cushions against trauma, regulates environment of the brain
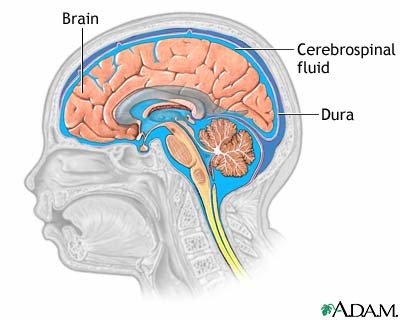
59
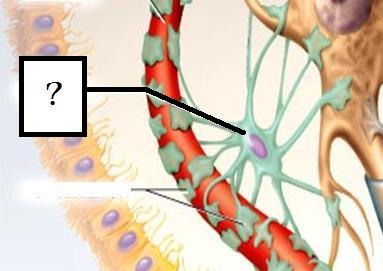
New cards
Astrocytes
Regulate extracellular environment (ions, neurotransmitters).
60
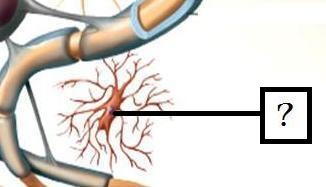
New cards
Microglia
Immune function (phagocytize bacteria and debris, release cytokines)
61
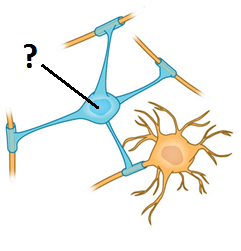
New cards
Oligodendrocytes
Myelinate central nerves multiple nerves at a time
62
New cards
Myelin
Protect axon from outside ions. Act like electrical tape. Made from schwann cells in the periphery and oligodendrocytes in the CNS
63
New cards
Ependymal cells
Secrete CSF, ions, proteins, etc. Line the ventricles
64
New cards
Dura mater
Thick/tough leathery sponge beneath the skull
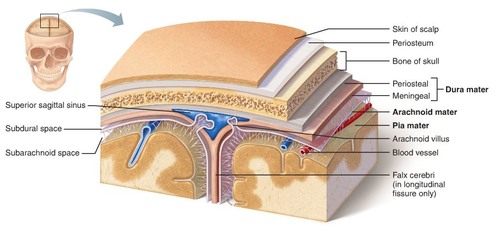
65
New cards
Cerebrum
Most of the brain function. Higher level cognitive functions. Sensory integration, movement initiation, memory, emotion, consciousness
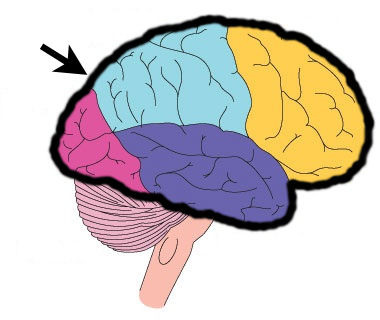
66
New cards
Brain stem
Autonomic funtions. Cardiovascular, respiratory control
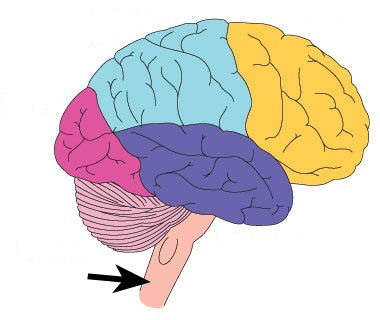
67
New cards
Dendrites
Inpput- receive incoming signals. Multiple, short
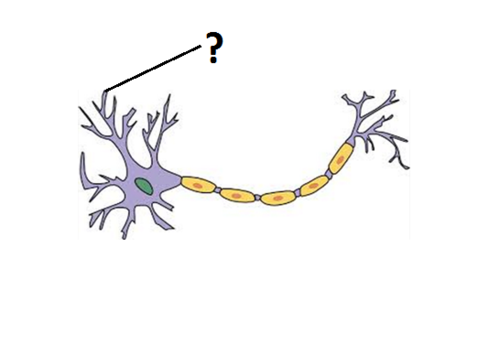
68
New cards
Axons
Output- send signal "away." Single, long (up to 1M). Uniform diameter, often myelinated
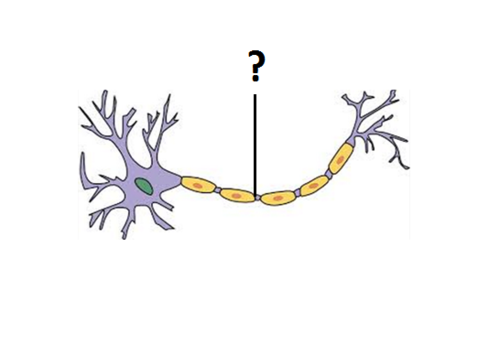
69
New cards
Cerebrum Lobes
Four major lobes. Frontal, parietal, occipital, temportal
70
New cards
Occipital lobe
Primary visual cortex (sight)
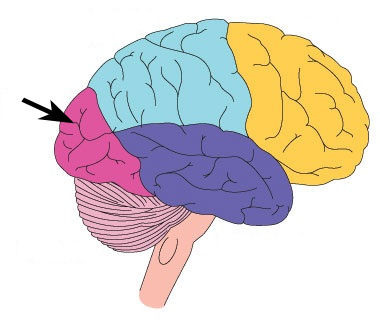
71
New cards
Temporal lobe
Primary auditory cortex (hearing)
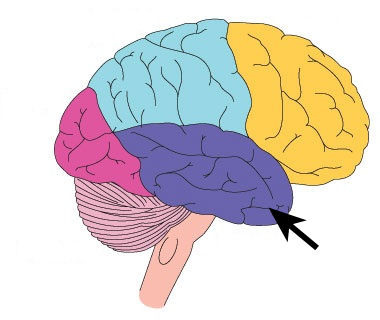
72
New cards
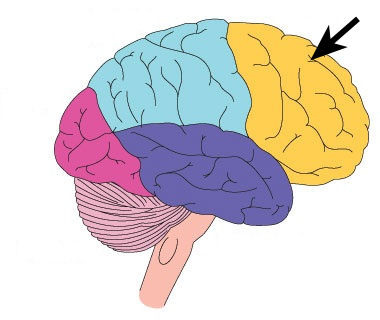
Frontal lobe
Primary motor cortex (voluntary movement)
73
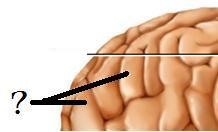
New cards
Gyri
Bumps
74
New cards
Sulci
Grooves
75
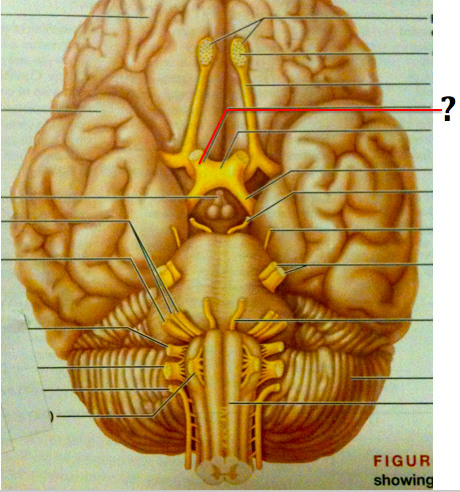
New cards
Optic nerve
Vision
76
New cards
Thalamus
Relay center to/from cortex. All sensory information first stops at thalamus before proceeding to cortex. Multiple sub-nuclei "integrate" incoming sensory signals.
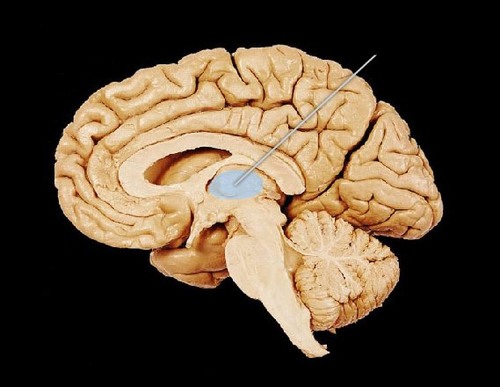
77
New cards
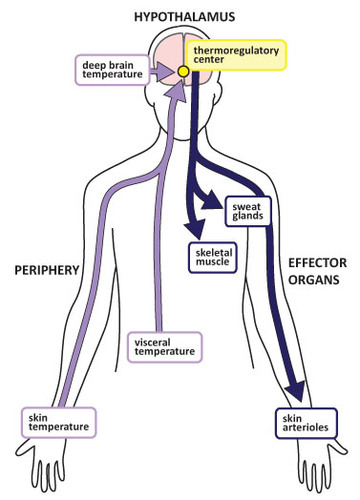
Hypothalamus
Maintains homeostasis by regulating metabolic processes (temperature, hunger, thirst, etc.)
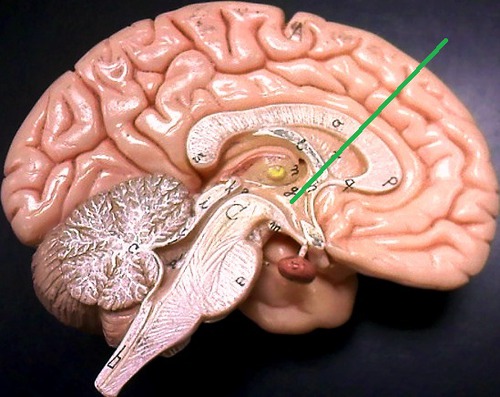
78
New cards
Cerebellum
Coordinates motor output and regulates muscle tone. Compares intended movement coming from the motor cortex with actual movement sensation coming from the joints and muscles and makes corrections. Based on past experiences
79
New cards
Medulla Oblongata
Contains autonomic nuclei that control fundamental life processes required for human life. Respiration, heart rate, etc.