Static Electricity
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What are the factors affecting the electric force between two point charges?
Electric force increases when:
magnitude of charges increases and / or;
distance between charges decreases
What is the conservation of electric charge?
The conservation of electric charge states that electric charge cannot be created nor destroyed. They are only transferred from one object to another. Net charge of a system remains constant unless some charge enters or leaves the system.
Electric field (definition)
Region in which an electric charge experiences an electric force
Electric field representation
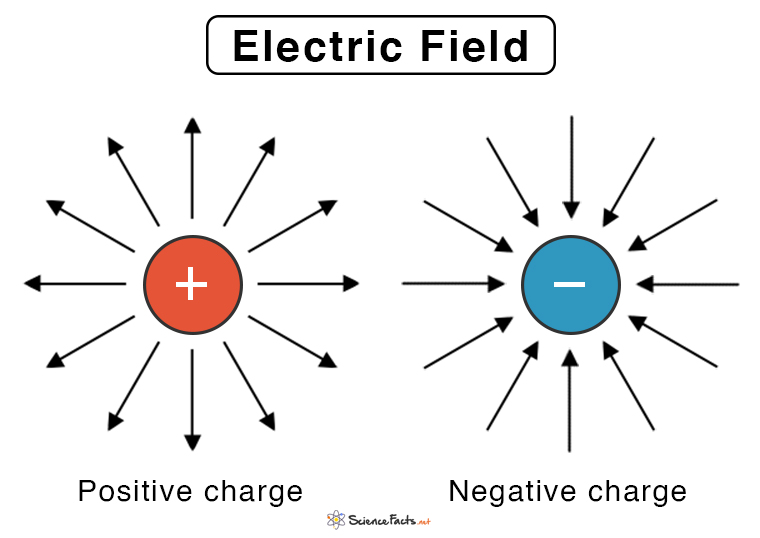
What are the characteristics of electrical insulators and conductors?
Insulators | Conductors | |
|---|---|---|
Ability to conduct electricity | Low | High |
Motion of charged particles | Not free to move about within insulator | Free to move within conductor |
Method of charging | By friction- when electrical insulators become charged, electrons remain at the surface where the material has been rubbed | By contact or induction |
How are electrical insulators charged? (If A is negatively charged and B is positively charged)
Answering Technique:
During rubbing, some of the electrons from B are removed from their atoms and are transferred to A
A has an excess of electrons and is now negatively charged
B has a deficit of electrons and is now positively charged
Why this happens:
Different elements have different characteristics, electrons of some atoms are held more strongly by their nuclei than other electrons in other atoms
Less tightly held electrons from B are attracted and transferred to A
Since A and B are both insulators, their electrons cannot move freely throughout the materials
The vacant electron sites in B cannot be refiled by other electrons in B
How are electrical conductors charged by contact?
Positively charged object (A) touches neutral object (B).
Free moving electrons from B flow towards A as opposite charges attract.
B now has a deficit of electrons and is thus positively charged
Induction (Definintion)
The process of charging a conductor without contact between the conductor and the charging body
How are electrical conductors charged by induction? (Answering technique)
As like charges repel/ unlike charges attract, free moving electrons are attracted/ repelled (where), excess positive charges are left (where)
When separated, objects now have an equal number of excess opposite charges. The free moving electrons on each object redistribute themselves equally apart on the surface
How are electrical conductors charged by induction? EARTH (Answering technique)
As like charges repel/ unlike charges attract, free moving electrons are attracted/ repelled (where), excess positive charges are left (where)
The flow of electrons from the Earth neutralises the excess positive charges on the object/ Excess free moving electrons flow away from object to earth
The free moving electrons on object redistribute themselves equally apart on the surface, object is positively/ negatively charged
How are neutral conductors attracted to charged conductors?
Electrons in neutral object are attracted/ repelled to (where) , excess positive charges are left (where)
Since unlike charges attract, neutral conductor attracted to charged conductor
How are electrical insulators discharged?
Heating
Charged object brought towards flame
Heat from flame ionises surrounding air particles
Ions are attracted and neutralises charges on object
Humid conditions
How are electrical conductors discharged?
Earthing
When a charged conductor is earthed, a path is provided for
excess free moving electrons to flow away from conductor
electrons to flow to the conductor to neutralise excess positive charges
Hazards of electrostatics
Ignition of flammable substances
Electric charges may build up on vehicles due to friction between road and rotating tires
Sudden discharge may cause sparks and can ignite flammable items carried by vehicles
Damage to electronics
Antistatic material have thin layer of metallised film, which acts as an electrostatic shield
Lightning
Lightning conductors provide a conducting path for electrons to flow
Applications
read yourself i lazy