Chapter 11: Understanding Prejudice and Empathy Dynamics
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Prejudice
A preconceived opinion that is not based on reason or actual experience.
RWA
Right wing authoritarianism; characterized by conformity and traditionalism, embracing old-fashioned norms and values.
Empathy
A personality variable that involves the ability to understand and share the feelings of others.
Cultural stereotypes
Generalized views about the characteristics of conservatives and liberals.
Bleeding heart liberal
A term originally not meant as a compliment, referring to perceived excess of compassion.
Political ideology
Multi-dimensional values and beliefs that shape an individual's political preferences.
Ingroup-outgroup bias
The tendency to favor one's own group (ingroup) over others (outgroup).
Empathic Concern (EC)
A measure of empathy; involves having tender, concerned feelings for those less fortunate.
Parochial Empathy
The selectivity in empathy where individuals may be more willing to empathize with ingroup members than outgroup members.
Empathy deficit
The inability to put oneself in someone else's shoes, leading to a lack of understanding of different perspectives.
Social division
The separation of groups based on differing beliefs or characteristics, often exacerbated by selective empathy.
Competition/antagonism
Negative feelings or behaviors directed towards outgroup members.
Support/positive feelings
Affectionate or supportive attitudes directed towards ingroup members.
Empathic motives
The reasons behind individuals' empathetic feelings towards others.
Tribe
A metaphor for any meaningful coalition that can separate people into opposing camps.
Davis, 1983
The author associated with the concept of empathic concern.
-.40**
The correlation coefficient indicating the relationship between SDO and empathic concern.
.60****
The correlation coefficient indicating the relationship between empathic concern and RWA.
Social polarization
The process by which groups become more distinct and divided based on differing ideologies.
Old-fashioned norms/values
Traditional beliefs and practices that are often embraced by individuals with high RWA.
Tender, concerned feelings
Emotional responses that reflect empathy towards those less fortunate.
Empathic motives by Conservatives
Warmth, compassion
Empathic motives by Liberals
Warmth, compassion
Ingroup
A social group with which a person identifies.
Outgroup
A social group with which a person does not identify.
Class exercises
Students need to do at least 10 out of 16 to get their ten points.
Canvas
Platform providing students with individual summaries of points earned/missed.
Exam 2 scores
Median score was 45; students encouraged to meet if scored 40/50 or lower.
Stereotyping and prejudice in the U.S.
Statistics indicate changing perceptions over 50 years among Princeton students.
Percentage of White participants describing African Americans (1933)
84%, 75%, 38%, 26%
Percentage of White participants describing African Americans (1951)
41%, 31%, 24%, 33%
Percentage of White participants describing African Americans (1969)
13%, 26%, 11%, 47%
Percentage of White participants describing African Americans (1982)
6%, 13%, 10%, 29%
Implicit measures of association
Helpful in understanding stereotypes and prejudices.
Social Dominance Orientation (SDO)
A measure of support for inequality between social groups.
Dominance items in SDO
An ideal society requires some groups to be on top and others to be on the bottom.
Equality items in SDO
Group equality should not be our primary goal; we should work to give all groups an equal chance to succeed.
Jim Sidanius
Proposed the Social Dominance Orientation theoretical model.
System justifying ideologies
Concepts that support the status quo and justify social hierarchies.
Congruent trial
A trial where the prime and target are aligned in meaning.
Incongruent trial
A trial where the prime and target are not aligned in meaning.
Social Dominance Orientation (SDO)
A measure that predicts generalized prejudice against various denigrated groups and is related to the endorsement of hierarchy-enhancing social ideologies.
Perceived social system legitimacy
The belief that America is a just society where differences in status between ethnic groups reflect actual group differences.
Differences in status between ethnic groups are the result of injustice.
A reverse coded item indicating that perceived inequalities are unjust.
Protestant Work Ethic (PWE)
The belief that if people work hard, they almost always get what they want.
Even if people work hard, they don't always get ahead.
A reverse coded item reflecting skepticism about the meritocratic nature of society.
Perceived discrimination
The belief that American society treats all ethnic groups equally, contrasted with the reality that ethnic minorities usually don't receive fair treatment.
Belief in a Just World (BJW)
The belief that people get what they deserve, countered by the view that the world is not a just place.
SDO differences: men vs. women
Men are more likely to report higher SDO scores compared to women, who are less likely to embrace the status quo due to historical disadvantages.
SDO differences by ethnicity
People of color often score lower than whites on SDO, but the difference is often not significant.
Surprisingly small differences by ethnicity
Many researchers find that the differences in SDO scores between ethnic groups are modest, with a substantial number of non-Whites showing moderate acceptance of SDO.
Scores range from low to moderate
Most participants, including Whites, rarely show complete agreement with pro-SDO ideologies.
Whites score higher in SDO than non-Whites
On average, Whites score higher in SDO, but the difference is relatively modest.
Support for group-relevant social policies
SDO predicts support for policies that uphold the hierarchical status quo, including punitive criminal justice policies and opposition to social welfare.
Endorsement of group-relevant social ideologies
SDO is related to ideologies such as political conservatism, nationalism, and sexism across various cultures.
Opposition to humanitarian practices
Individuals with high SDO are likely to oppose social welfare and affirmative action.
Just World Beliefs (BJW)
The belief that the world is fundamentally fair and that individuals get what they deserve.
Internal attributions for poverty
The belief that poverty is a result of individual failings rather than systemic issues.
Rape myths
Beliefs that trivialize or deny the severity of sexual assault, often endorsed by those with high SDO.
Karma
The belief that actions have consequences that will affect individuals in the future, often used to justify social inequalities.
Militarism
The belief in the maintenance of a strong military capability and readiness to use it aggressively to defend or promote national interests.
Noblesse oblige
The obligation of the nobility or privileged to act with generosity and nobility toward those less privileged.
Cultural differences in SDO
Variations in SDO scores can be observed across different cultures, reflecting differing societal values and norms.
Social Dominance Orientation (SDO)
A measure of an individual's preference for hierarchy within social systems and the domination of lower-status groups.
Dehumanization
The conviction that certain people lack complex cognitions/emotions characteristic of humanity.
MRI study by Harris and Fiske (2006)
A study that found low activation in the medial frontal cortex when participants viewed pictures of disadvantaged outgroup members.
Ambivalent Sexism
A theory suggesting that men's attitudes towards women contain both negative and seemingly positive elements.
Hostile Sexism
Overtly negative evaluations and stereotypes about a gender, such as the belief that women are incompetent.
Benevolent Sexism
Evaluations of gender that appear positive but are actually damaging to people and gender equity.
Stereotype Content Model
A model proposing that stereotypes can have both positive and negative characteristics based on perceived warmth and competence.
Gender Role Backlash
The phenomenon where individuals who violate traditional gender roles are disliked more than those who conform.
Jennifer Eberhardt's Research
Research examining biases in imprisonment and the accessibility of crime-relevant versus crime-irrelevant objects.
Crime-relevant objects
Objects that are associated with criminal behavior, such as guns.
Crime-irrelevant objects
Objects that are not associated with criminal behavior, such as a tree branch.
Gender role violations
Instances where individuals exhibit attributes inconsistent with traditional gender norms.
Hypothesis 1 (Gender Role Backlash)
The idea that gender role violations directly elicit negativity.
Hypothesis 2 (Gender Role Backlash)
The idea that negativity towards gender role violators is driven by inferences about their sexual orientation.
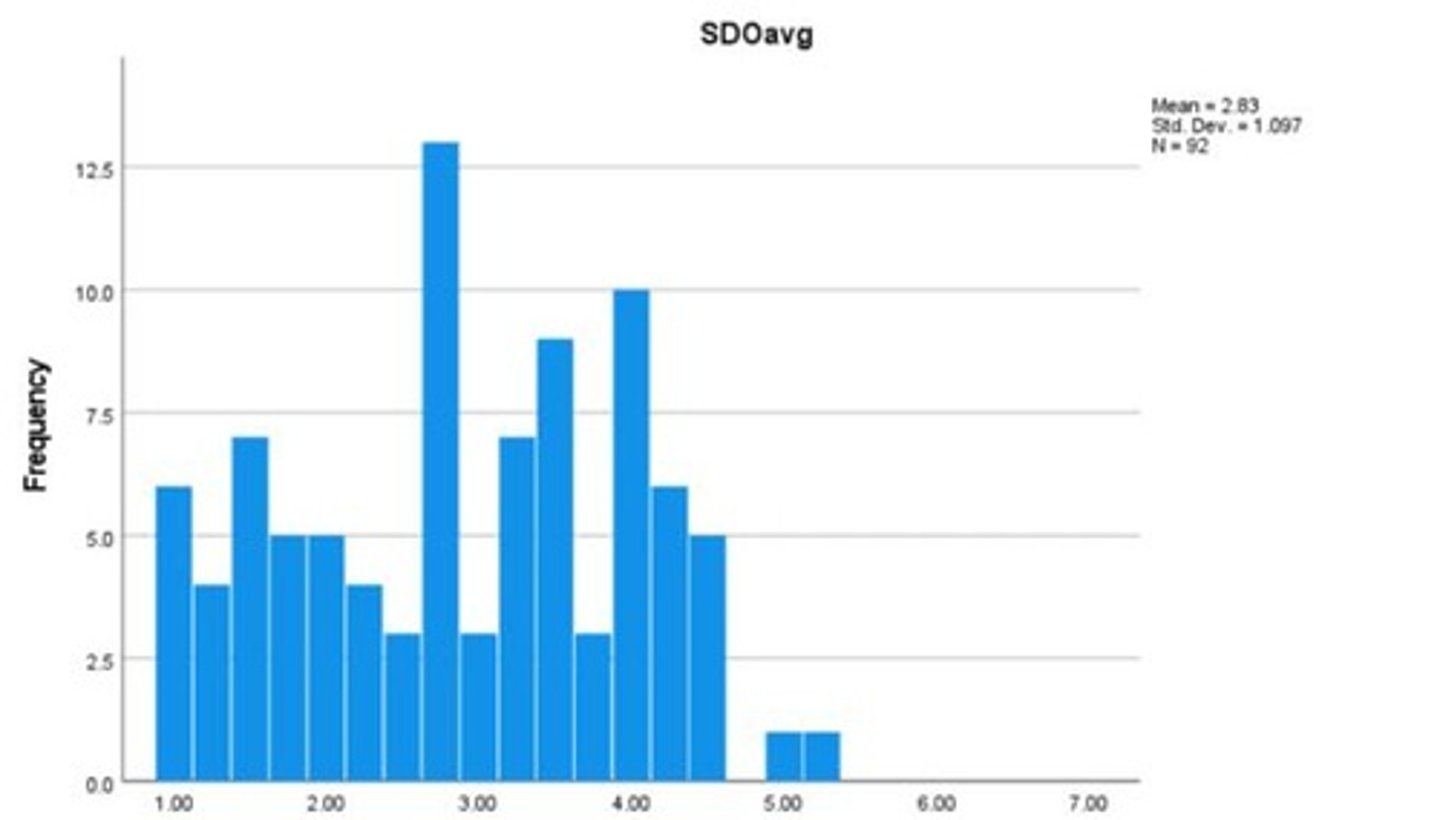
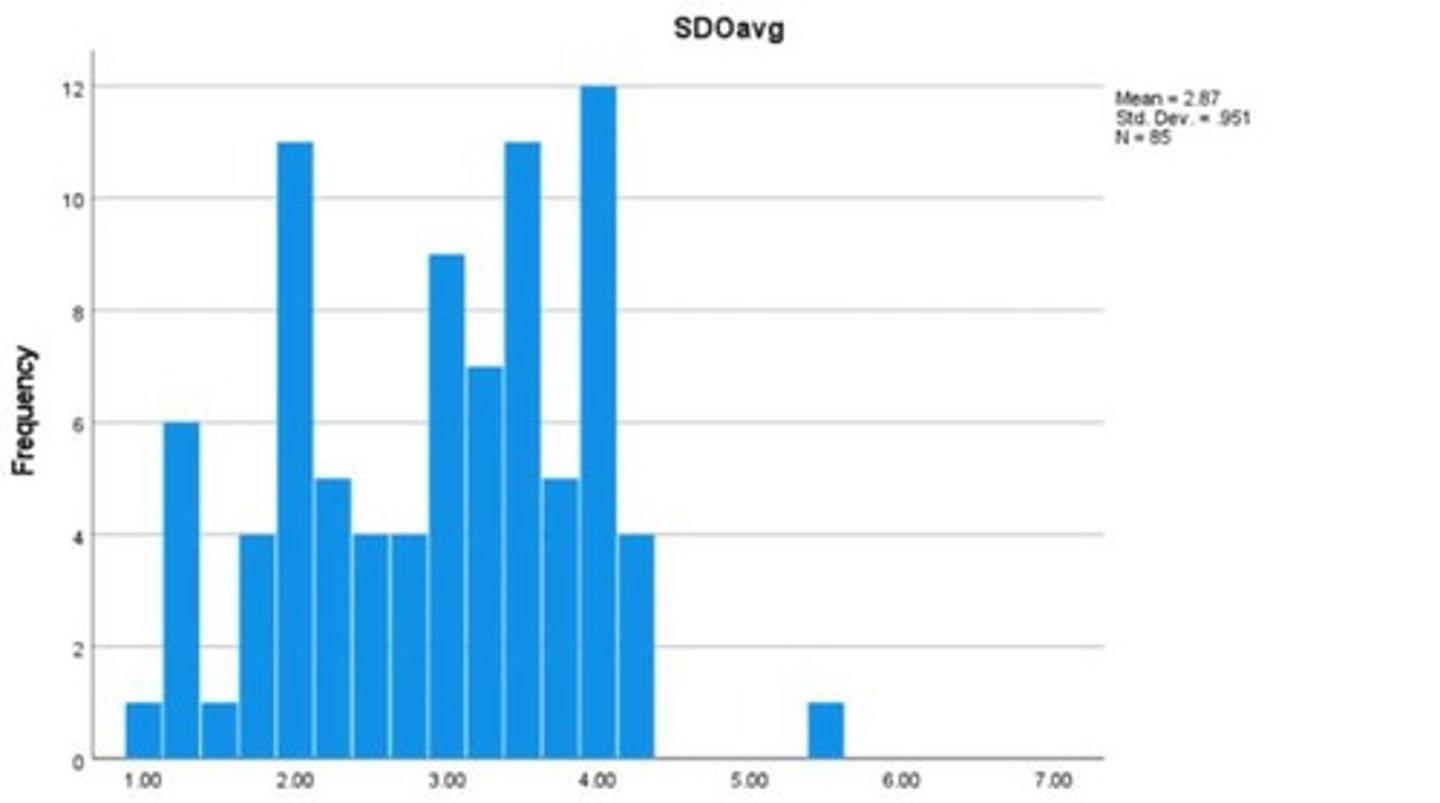
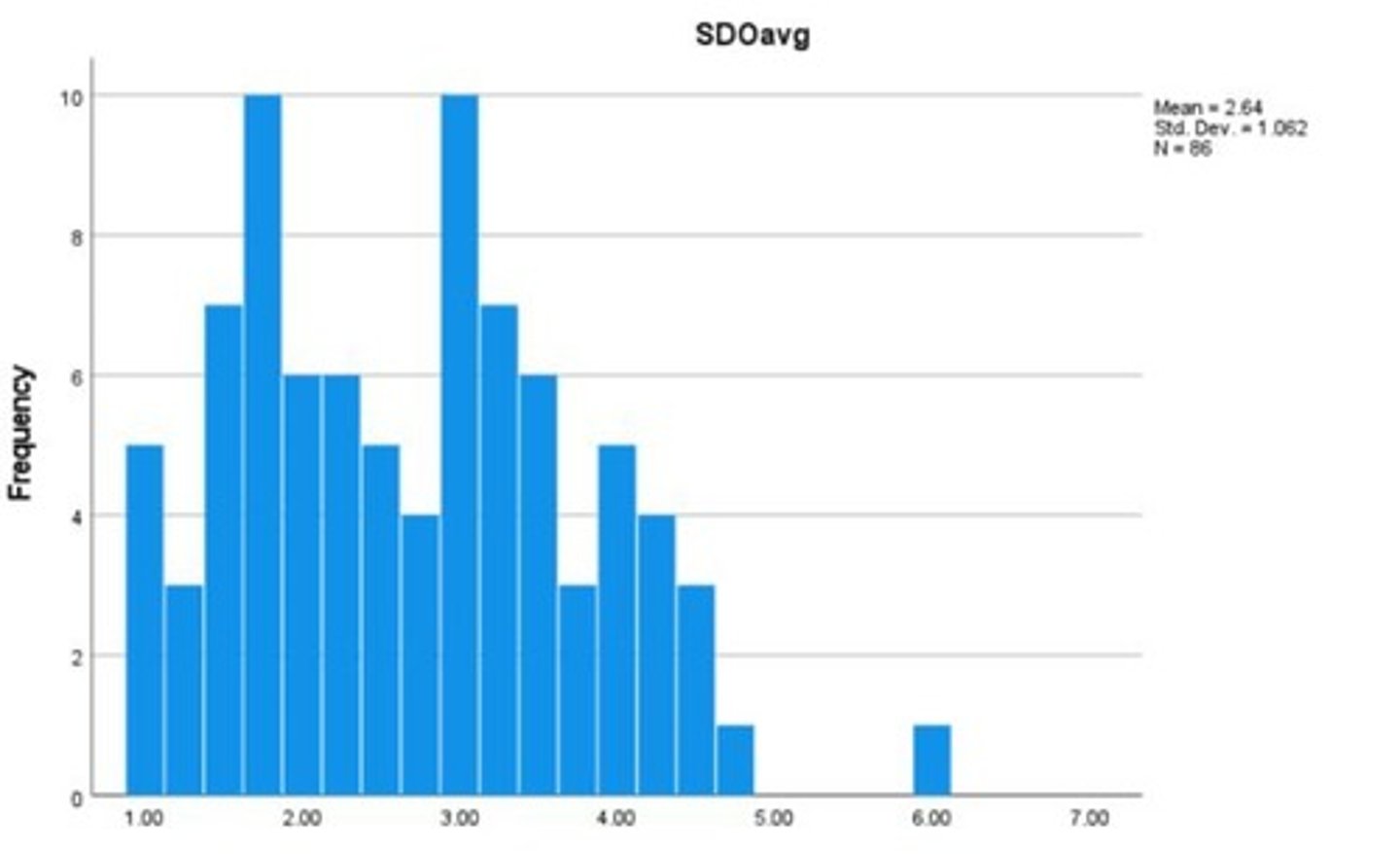
Distribution of SDO scores by ethnicity
A comparison of SDO scores among different ethnic groups, showing modest differences.
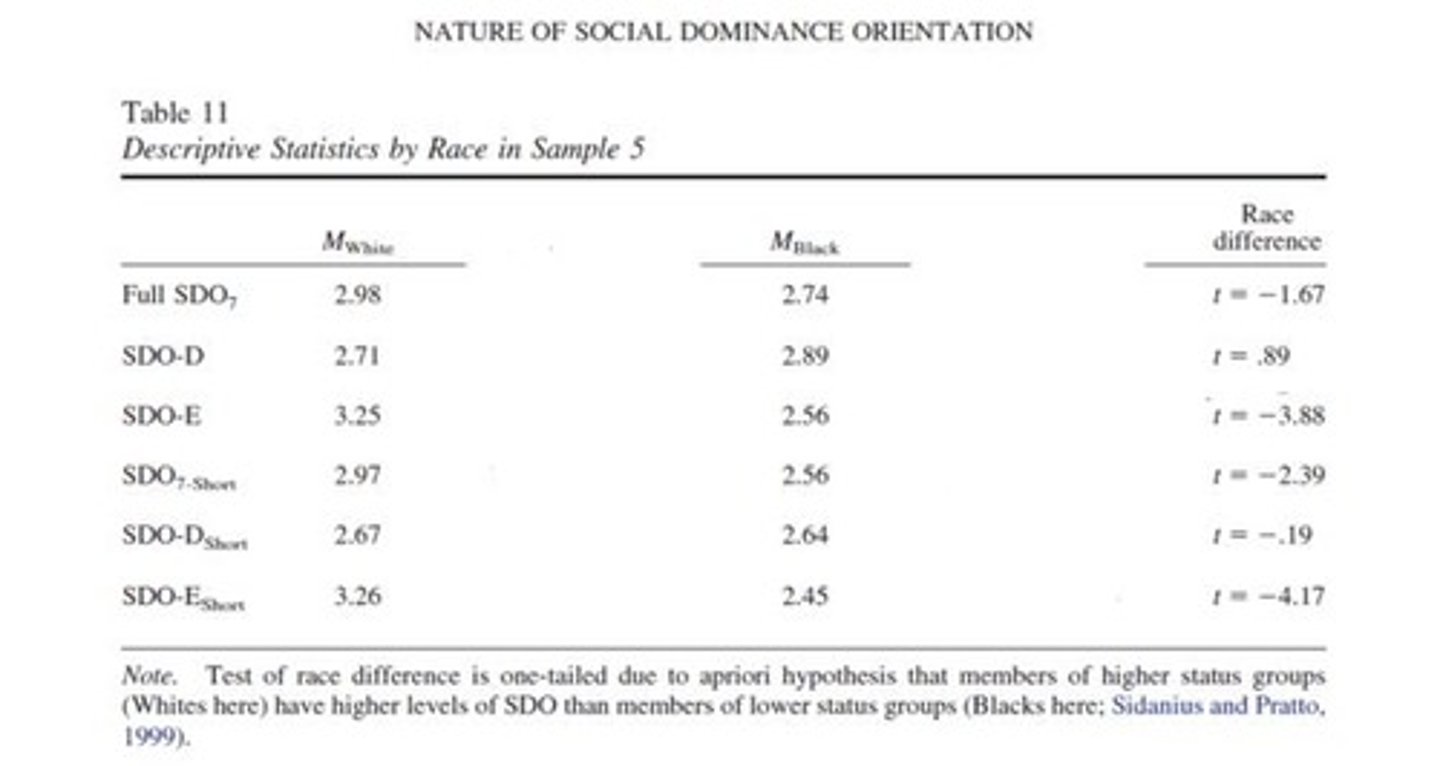
Mean SDO score for Asian-American participants
Mean = 2.90
Median SDO score for Asian-American participants
Median = 3.00
Mean SDO score for White participants
Mean = 3.11
Median SDO score for White participants
Median = 3.21
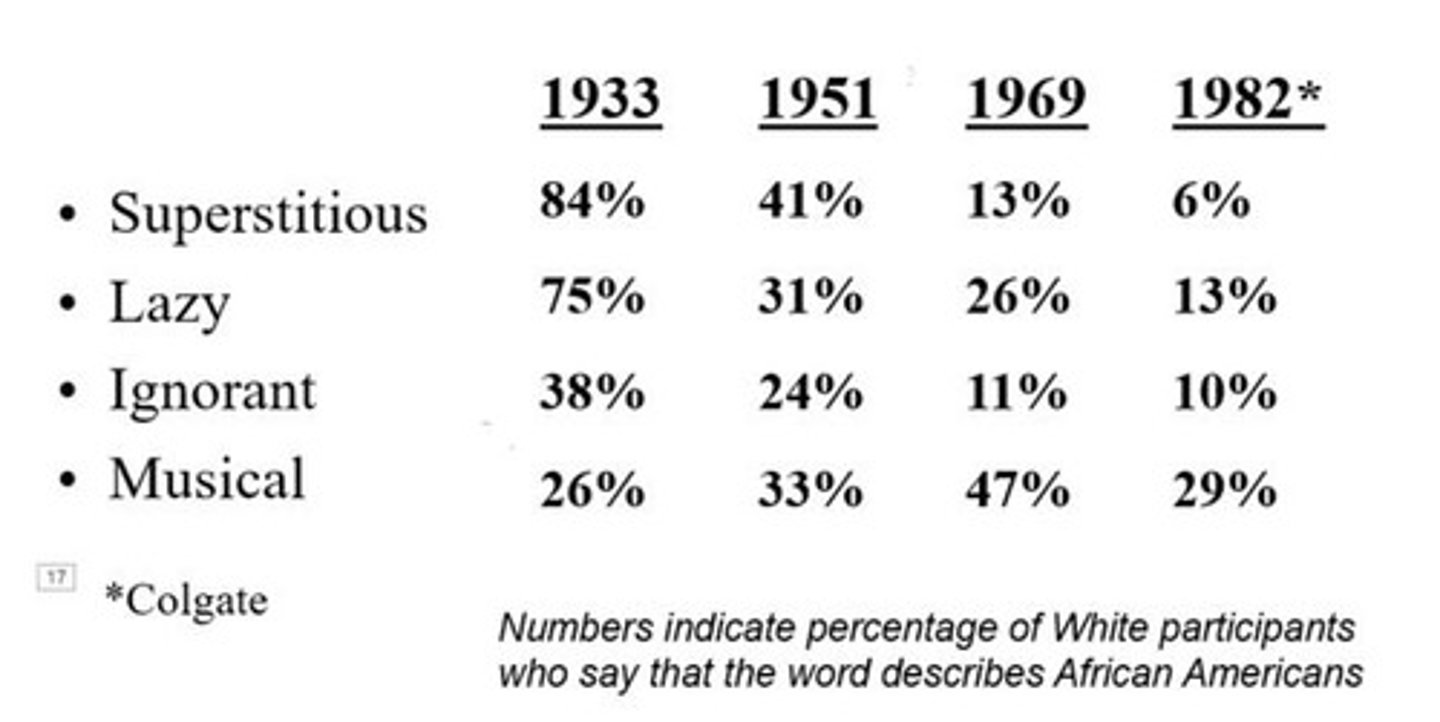
Mean SDO score for Latin-X participants
Mean = 2.42
Median SDO score for Latin-X participants
Median = 2.25
Mean SDO score for Black participants
Mean = 2.64
Median SDO score for Black participants
Median = 2.63
System-justifying ideology
Beliefs that support and rationalize social hierarchies and inequalities.
Old-fashioned sexism
A form of sexism that involves placing women on a pedestal while simultaneously objectifying them.
Perceived warmth and competence
Two independent dimensions that characterize stereotypes according to the stereotype content model.