25 - Slime Molds
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
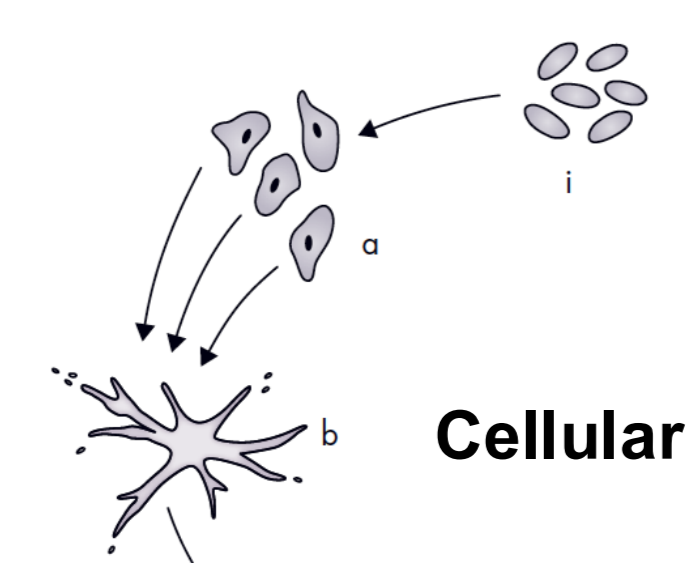
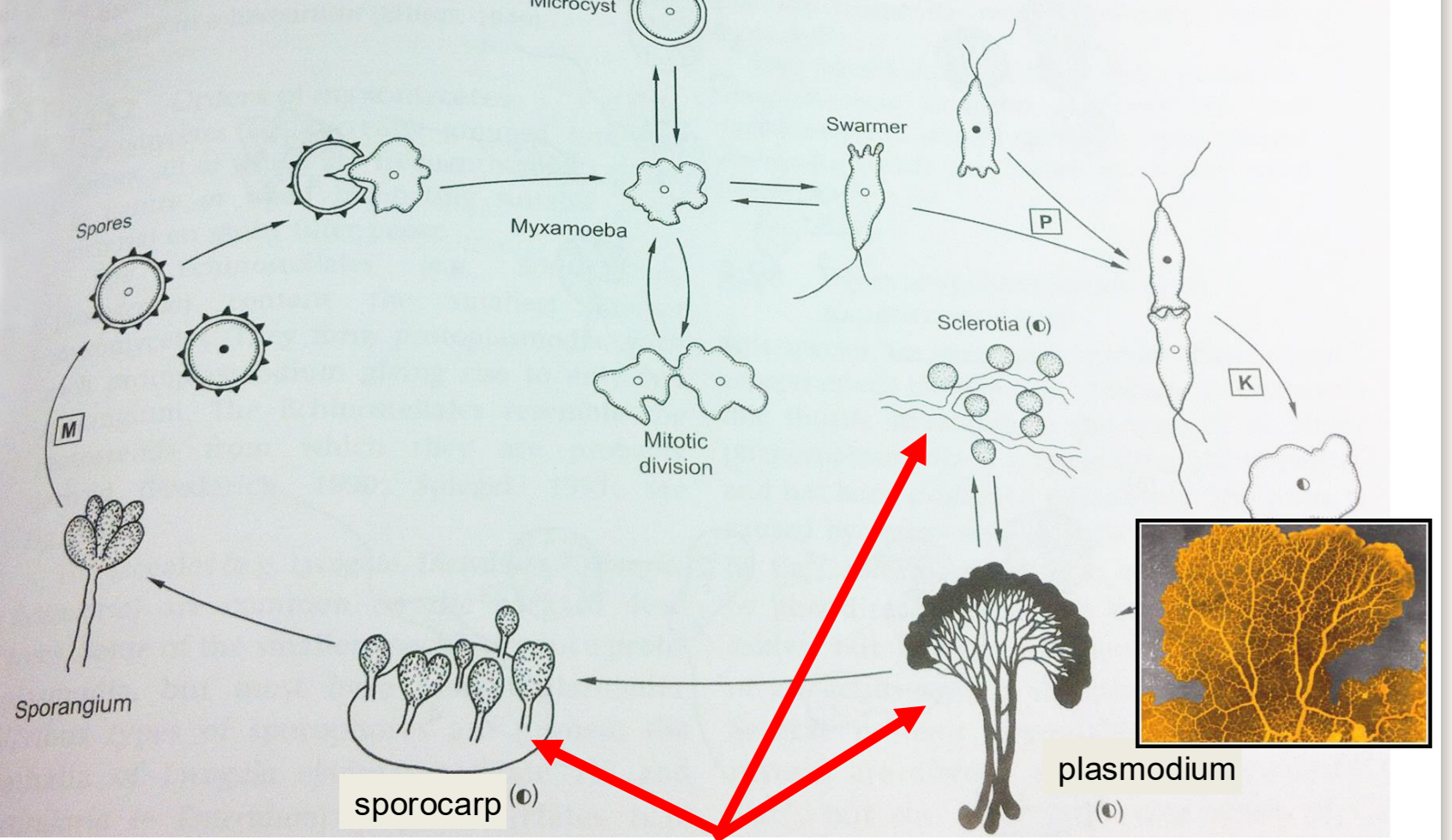
Cellular
individual amoebae that aggregate and form more complex structures
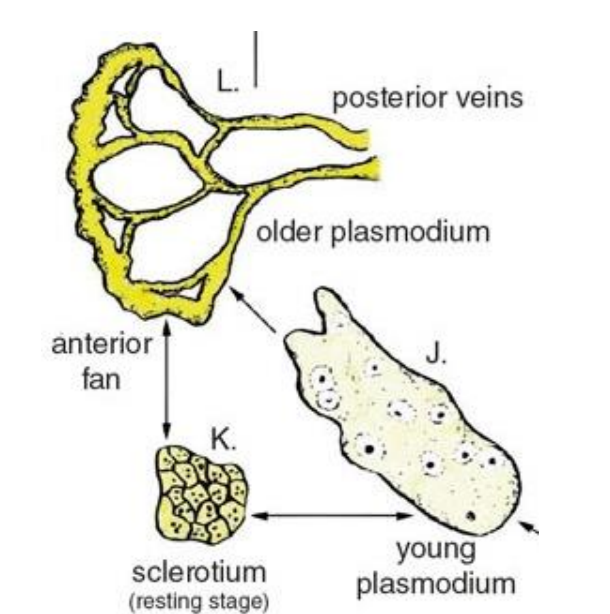
plasmodial
single, multinucleate large cell
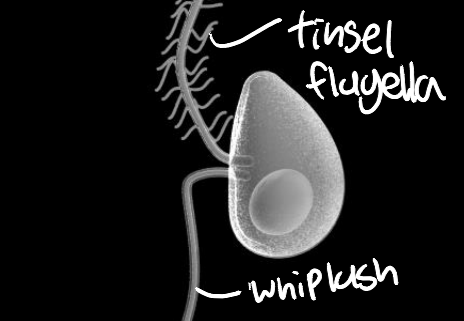
Amoeba
all described slime molds have this phase, typically uninucleate, unicellular, no cell wall, phagocytosis
sorocarp
cellular slime mold fruiting body
sporocarp
plasmodial slime mold fruiting body
Labyrinthulids (net slime molds)
produces slimeways as tracks for cells to glide along, biflagellate zoospores, most marine or estuarine (rarely freshwater), saprobes parasites
Labyrinthula terrestris
rapid blight on turf, occurs due to buildup of sodium, infection through leaf wounds, problematic in golf courses

Labyrinthula zosterae
eelgrass wasting disease, asymptomatic until plant gets stressed, interferes with photosynthesis, outbreak in 1930s killed 90% of eelgrass

Plasmodiophora (endoparasitic slime molds)
multinuculate wall-less protoplasts, cannot move, no phagocytosis, live entirely inside host cells, biflagellate zoospores necrotrophic parasites of vascular plants, hypertrophy and hyperplasia
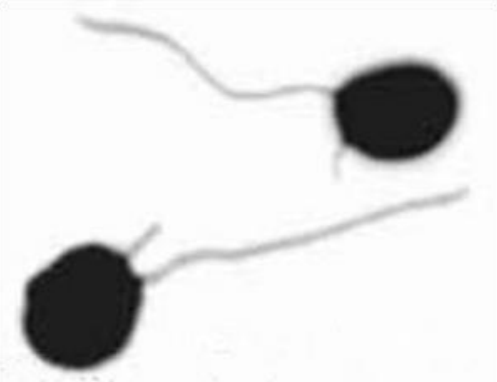
plasmodiophora brassicae
clubroot of cabbage
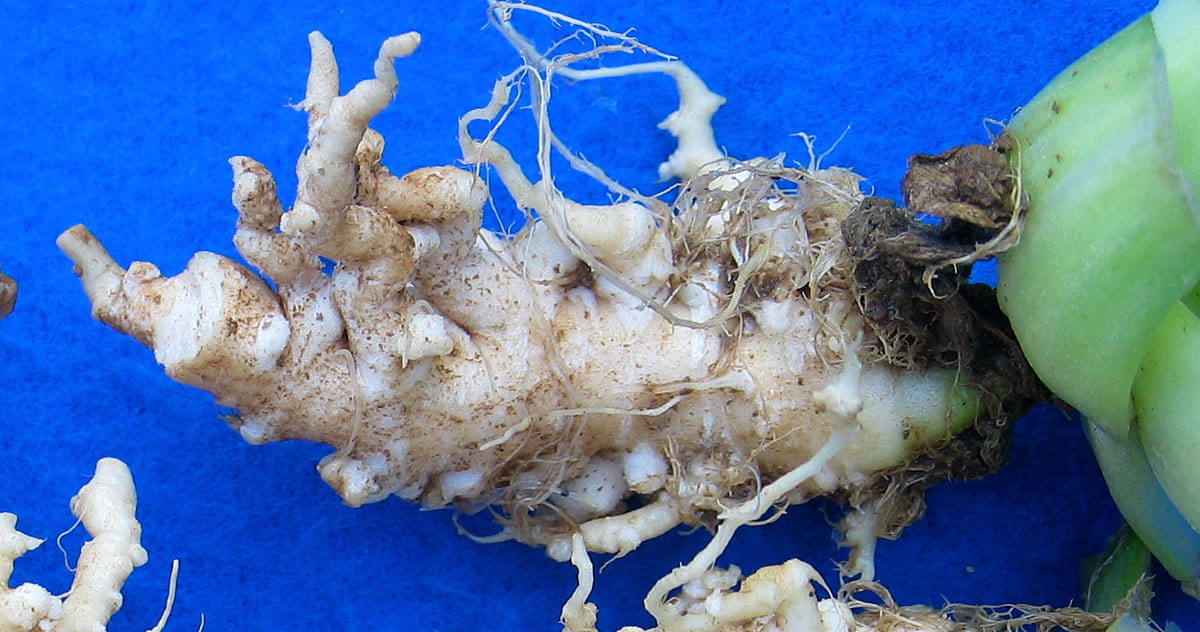

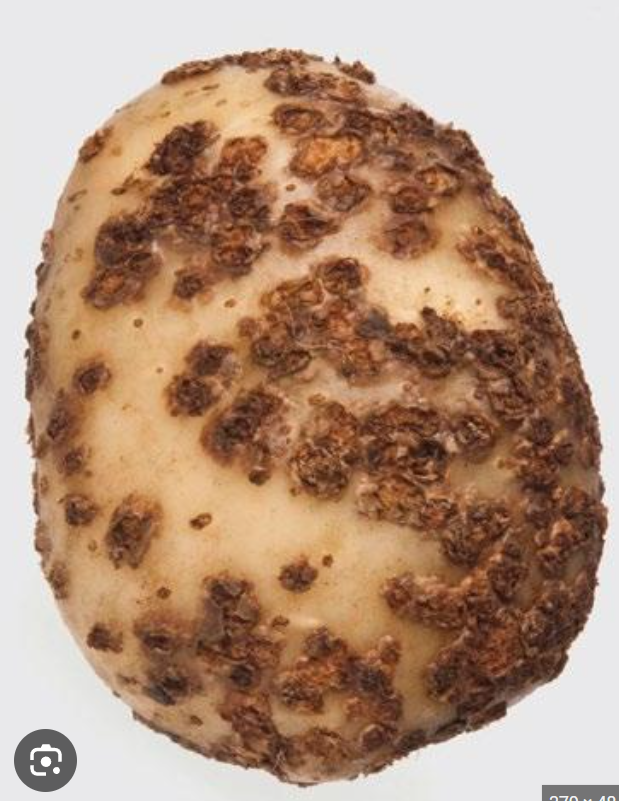
Spongospora subterranea
powdery scab of potatoes

Acrasida (acrasid cellular slime molds)
aggregate behavior, moist soil, organic debris, dung, eats bacteria, yeasts, and decaying vegetation
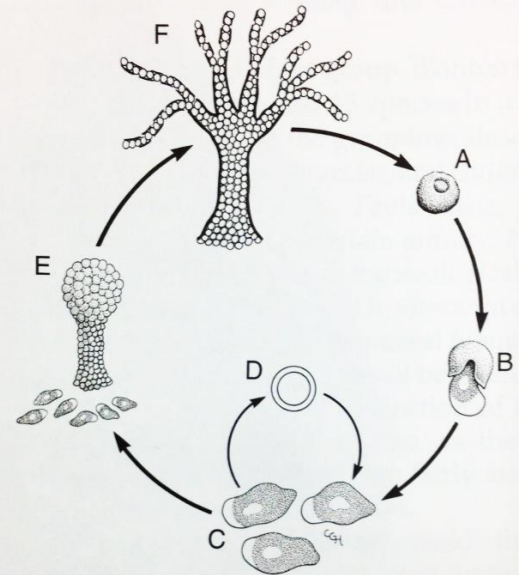
Dictyostelids - cellular slime molds
when they run out of food they aggregate, forming pseudoplasmodium with cAMP, and move as a slug to optimal spore dispersal location
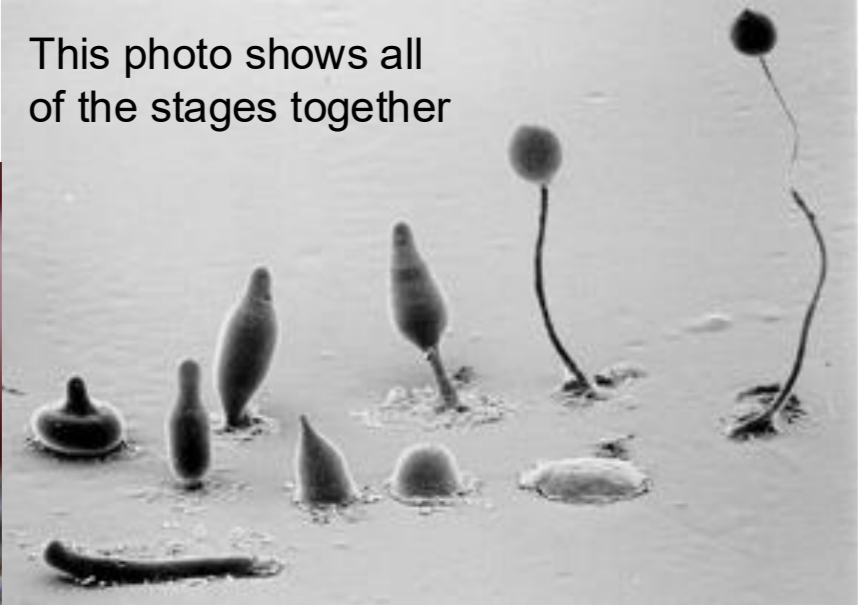
Dictyosteloim discoideum
model organism, entire cycle completed in one day
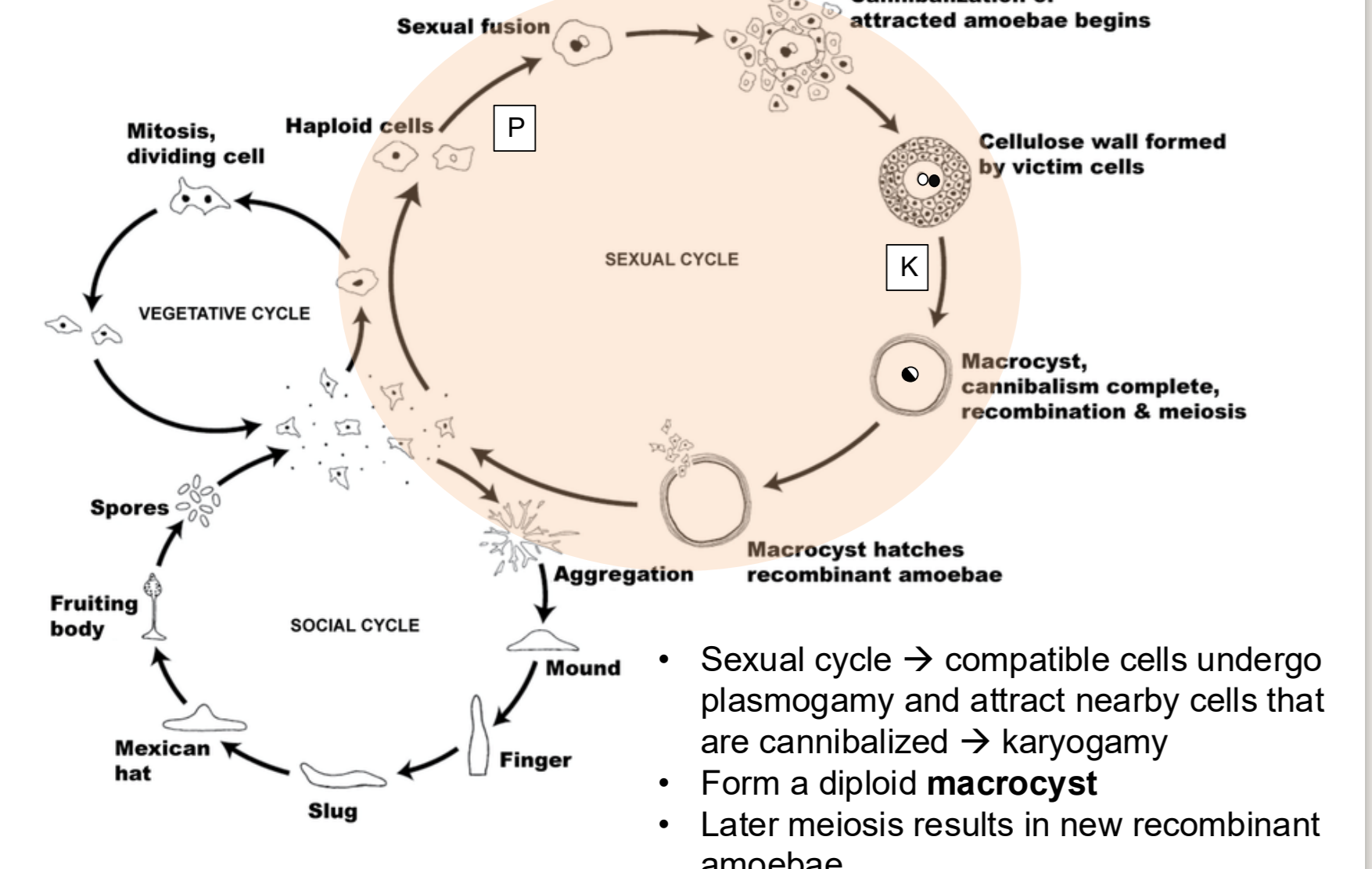
myxogastrids - plasmodial slime molds
no cell wall, can switch between biflagellated and non flagellated body forms,
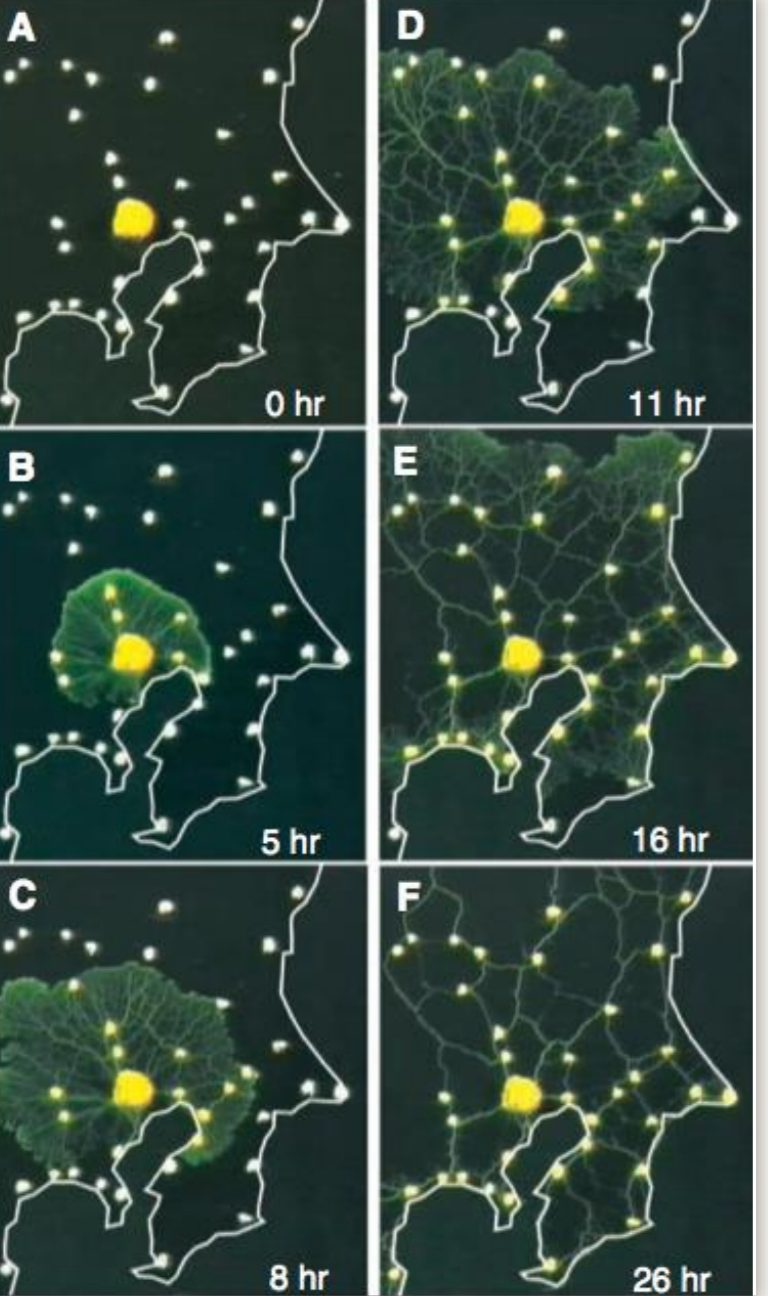
Physarum polyceophalum
external spatioal memory similar to pheromone trail for ants but made of slime
sporangium
several to many stalked or unstalked spore masses that are sepatrate but formed from a common plasmodium
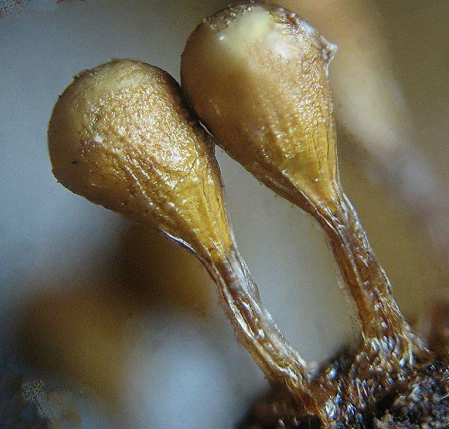

Plasmodiocarp
a spore mass that remains connected and retains the shape of the plasmodium
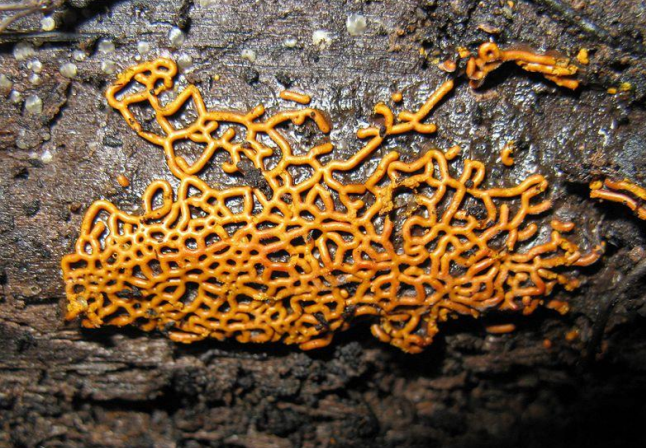

Aethalium
a cushion or puffball shaped sporocarop where almost all of the tissues become spores
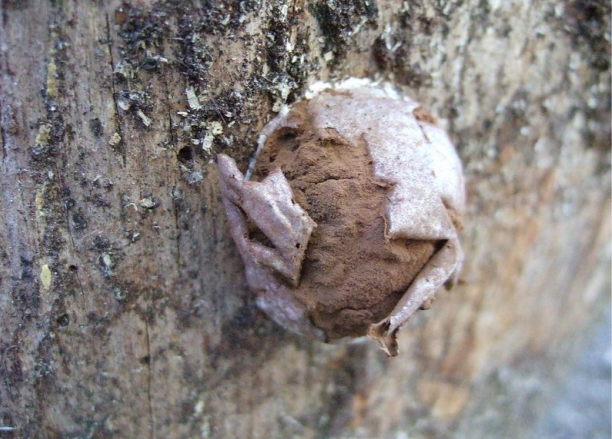

pseudoaethalium
composite structure composed of several sporangia massed together
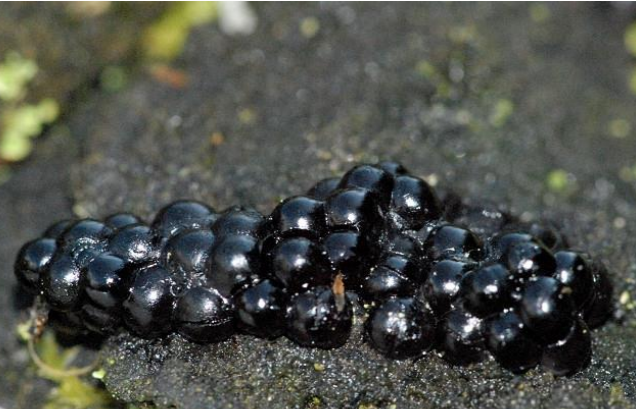

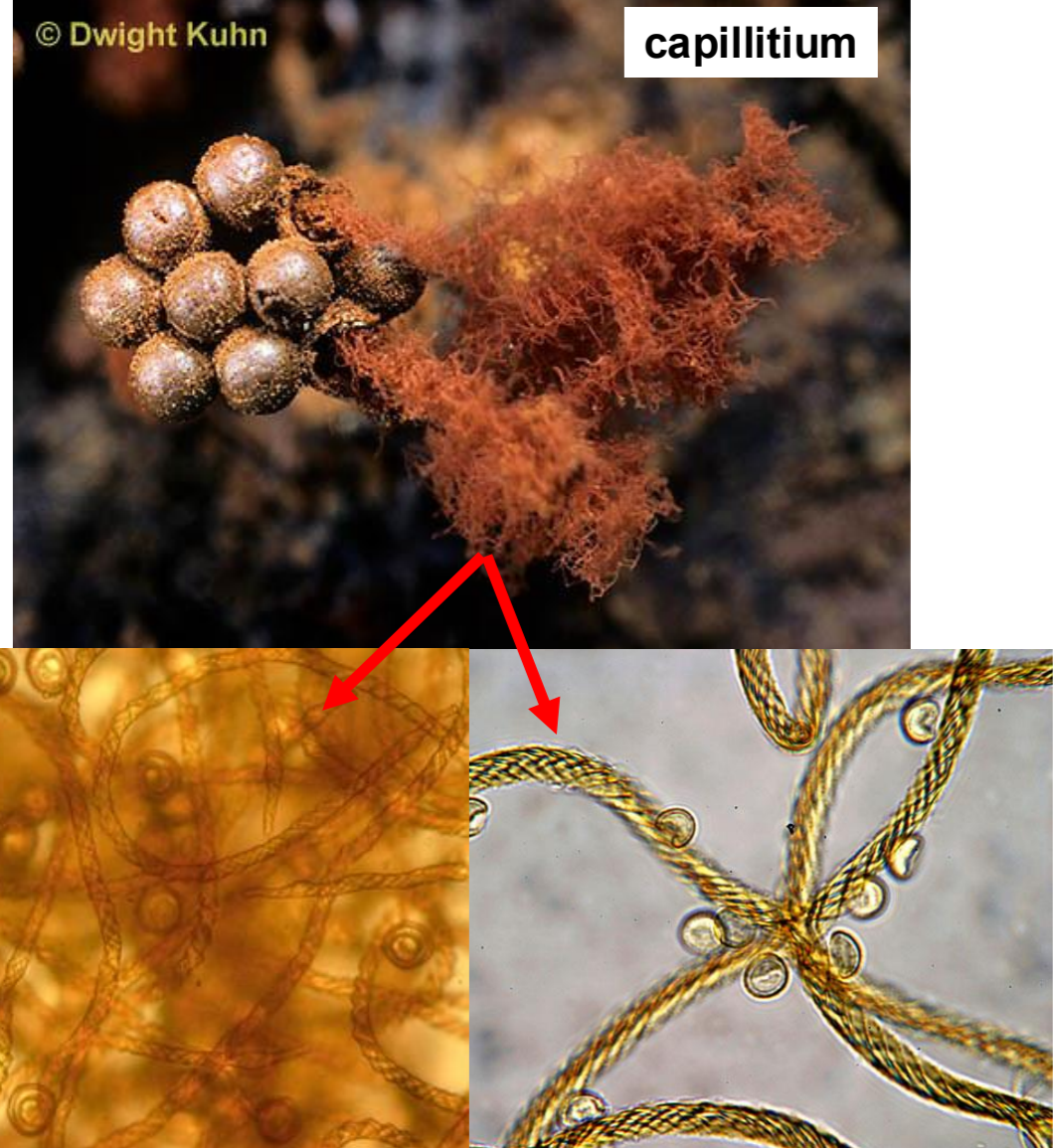
capillitium
thick hyphal-like cords that provide structure and retain the spores for wind dispersal made by caco3 in slime molds

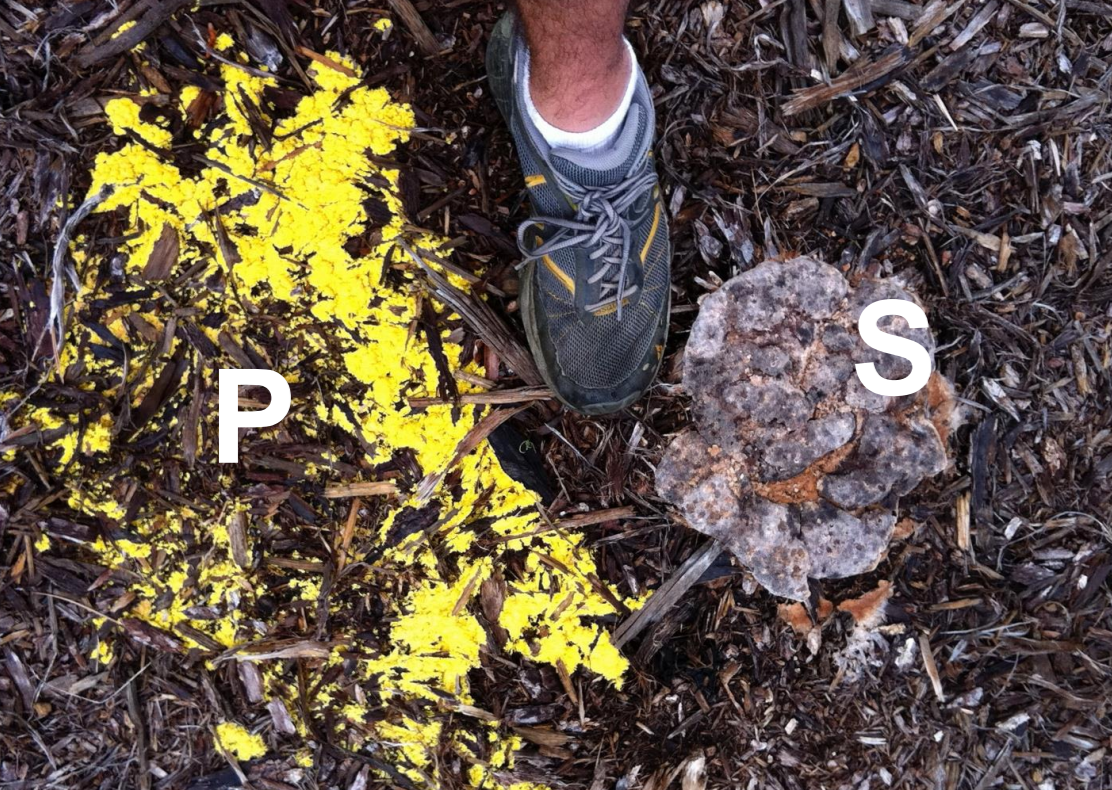
Fuligo septica
dog vomit slime mold

Protostelia
formplasmodia and some can form swarmers
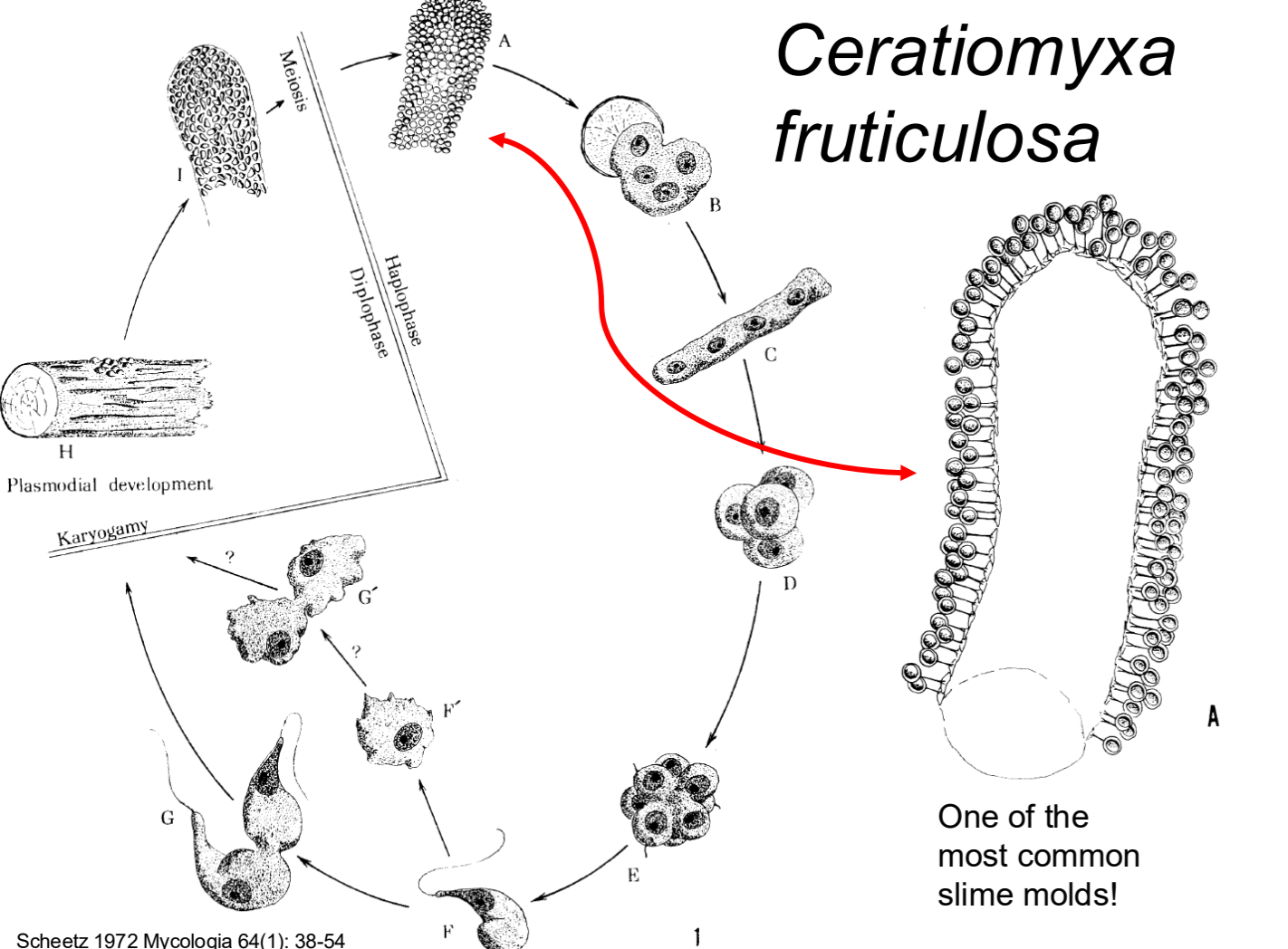
Ceratiomyxa fruticulosa
one of the most common slime molds