Type 1 Type 2 errors and power
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
P-value
The probability assuming Ho is true that the test stat will take on a value as extreme or more extreme than what we observed
Power
The probability that a fixed a level test will reject Ho when a particular alternative value of the parameter is true.
Steps to calculating power
Find the event that causes the test to reject Ho
Find the probability of that event, given an alternative value of the parameter is true
Lower power
Larger σ means
Higher Power
Larger sample size means
Higher alpha level means
Higher Power
Higher power
Alternative further from Ho
Type 1 Error
Reject Ho, but Ho is true
Type 2 Error
Accept Ho, Ha is true
Alpha
Probability of a type 1 error
1-Power
Probability of a type 2 error
2 Samp-Z Test and Samp-Z Confidence Interval
σ1 and σ2 are known, x̄1-x̄2 follows a normal distribution
2 Samp-T Test and Samp T Confidence Interval
σ1 and σ2 are unknown, x̄1-x̄2 follows a t distribution
How to check for normality with a t distribution
Histogram shape for skewness
Comparative box Plot of Outliers
Independence within groups for a t model
Responses in each group are independent of each other
Simple Random Sample
Population is less than 10%
Matched Pairs test
What do you use if the groups are dependent
n<15
No Skewness or outliers
15<n<40
Some skewness but no outliers
n>40
No extreme skewness or outliers
Close to t-distribution
If we can’t assume equal population variance that means it is
Df when you have technology
(n1-1) + (n2-1)
Say yes to pooled
If equal variance
Yes
Do you always assume unequal variance?
Larger than
With pooled procedure the Degrees of Freedom is _____ than the Degrees of Freedom for Unequal Variance
Lower, narrower
Pooled procedures makes a ____ rejection rate and _____ interval
p1-p2
Parameter for Inference of 2 Proportions
Statistic for 2-Samp Proportion Problem
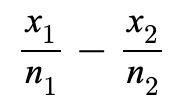
Assumptions for Inference
Sampling distribution of p̂1-p̂2 is normal
Assess if the sample size is large enough to ensure normality
n1 p̂p, n1(1-p̂p) and n2 p̂p, n2(1-p̂p)
Independence within groups
Are samples random and is n less than 10% of population
Independence between groups.
Responses in one group shouldn’t influence responses in other groups.
We don’t know the parameter p
Pool the sample proportion and replace the standard deviation with standard error if ____
How to check normality for 2-prop Z Int
Check n1 p̂1, n1(1-p̂1) and n2 p̂2, n2(1-p̂2) are all more than 10
p-hat of p (p̂p)
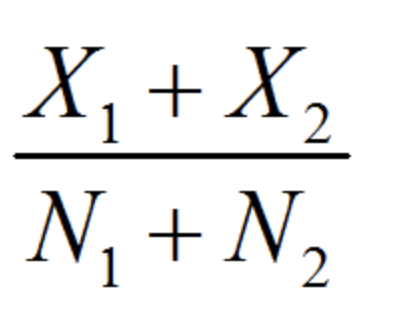
Reject Ho
(p<alpha)
Fail to Reject Ho
(p>alpha)