ACCT 200 Final Exam MC
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 8:21 PM on 9/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
1
New cards
A company is more likely to use a job order cost system if:
A)it manufactures a large volume of similar products.
B)its production is continuous.
C)it manufactures products with unique characteristics.
D) it uses a periodic inventory system.
A)it manufactures a large volume of similar products.
B)its production is continuous.
C)it manufactures products with unique characteristics.
D) it uses a periodic inventory system.
C)it manufactures products with unique characteristics.
2
New cards
The sources of information for assigning costs to job cost sheets are:
A)invoices, time tickets, and the pre-determined overhead rate.
B)material requisition slips, time tickets, and the actual overhead costs.
C)material requisition slips, payroll register, and the pre-determined overhead rate.
D)material requisition slips, time tickets, and the pre-determined overhead rate.
A)invoices, time tickets, and the pre-determined overhead rate.
B)material requisition slips, time tickets, and the actual overhead costs.
C)material requisition slips, payroll register, and the pre-determined overhead rate.
D)material requisition slips, time tickets, and the pre-determined overhead rate.
D)material requisition slips, time tickets, and the pre-determined overhead rate.
3
New cards
\
The formula for computing the pre-determined manufacturing overhead rate is estimated annual overhead costs divided by estimated annual operating activity, expressed as:
\
A)direct labor cost.
B)direct labor hours.
C)machine hours.
D)Any of the answer choices is correct.
The formula for computing the pre-determined manufacturing overhead rate is estimated annual overhead costs divided by estimated annual operating activity, expressed as:
\
A)direct labor cost.
B)direct labor hours.
C)machine hours.
D)Any of the answer choices is correct.
D)Any of the answer choices is correct.
\
\
4
New cards
Which of the following is true?
A)Job order costing requires less data entry than process costing.
B)Allocation of overhead is easier under job order costing than process costing.
C)Job order costing provides more precise costing for custom jobs than process costing.
D)The use of job order costing has declined because more companies have adopted automated accounting systems.
A)Job order costing requires less data entry than process costing.
B)Allocation of overhead is easier under job order costing than process costing.
C)Job order costing provides more precise costing for custom jobs than process costing.
D)The use of job order costing has declined because more companies have adopted automated accounting systems.
C)Job order costing provides more precise costing for custom jobs than process costing.
5
New cards
The job cost sheet represents
A)labor costs
B)work in process
C)finished goods
D)none of the above
A)labor costs
B)work in process
C)finished goods
D)none of the above
B)work in process
6
New cards
The OAR is the overhead allocation rate.
True
False
True
False
True
7
New cards
Common allocation bases for overhead costs include:
A)Direct labor hours
B)Direct labor hour dollars
C)Machine hours
D)All of the above
A)Direct labor hours
B)Direct labor hour dollars
C)Machine hours
D)All of the above
D)All of the above
8
New cards
When raw materials are requisitioned from raw materials inventory, they become part of
A)Cost of Goods Sold
B)Work in Process
C)Finished Goods
D)None of the above
A)Cost of Goods Sold
B)Work in Process
C)Finished Goods
D)None of the above
B)Work in Process
9
New cards
\
An example of a type of product that would be manufactured in a job costing process is....
An example of a type of product that would be manufactured in a job costing process is....
Aircraft
10
New cards
Which of the following is an example of a Lean Manufacturing system?
A)zero-based budgeting
B)job costing
C)activity-based costing
D)six sigma
A)zero-based budgeting
B)job costing
C)activity-based costing
D)six sigma
D)six sigma
\
\
11
New cards
All of the following are examples of Lean Manufacturing operations except for....
A)front end costing
B)just-in-time inventory
C)value stream mapping
D)point-of-use storage
A)front end costing
B)just-in-time inventory
C)value stream mapping
D)point-of-use storage
A)front end costing
12
New cards
"Lean" is often described by the Japanese word "kaizen", meaning "change for the better”
True
False
True
False
True
\
\
13
New cards
Lean thinking or lean manufacturing is about
A)producing low fat meal plans
B)a manufacturing system to reduce waste and increase efficiency
C)all of the above
D)none of the above
A)producing low fat meal plans
B)a manufacturing system to reduce waste and increase efficiency
C)all of the above
D)none of the above
B)a manufacturing system to reduce waste and increase efficiency
14
New cards
Implementation of a "lean" program could result in all of the following except....
A)less use of materials in production
B)cost efficiencies in labor use
C)fewer quality defects
D)higher inventory levels
A)less use of materials in production
B)cost efficiencies in labor use
C)fewer quality defects
D)higher inventory levels
D)higher inventory levels
15
New cards
Carolina Creations sells
A)services
B)handbags
C)furniture
D)none of the above
A)services
B)handbags
C)furniture
D)none of the above
D)furniture
16
New cards
Which of the following is not an element of manufacturing overhead?
A)sales manager's salary
B)plant manager's salary
C)factory repairman's wages
D)product inspector's salary
A)sales manager's salary
B)plant manager's salary
C)factory repairman's wages
D)product inspector's salary
A)sales manager's salary
\
\
17
New cards
Managerial accounting:
1. is governed by generally accepted accounting principles.
2. places emphasis on special-purpose information.
3. pertains to the entity as a whole and is highly aggregated.
4. is limited to cost data.
1. is governed by generally accepted accounting principles.
2. places emphasis on special-purpose information.
3. pertains to the entity as a whole and is highly aggregated.
4. is limited to cost data.
places emphasis on special-purpose information.
18
New cards
The cost driver in activity-based costing is
1. the number of product units produced
2. the number of direct labor hours
3. the number of machine hours
4. the activity that has the strongest correlation to the costs accumulated in the cost pool.
1. the number of product units produced
2. the number of direct labor hours
3. the number of machine hours
4. the activity that has the strongest correlation to the costs accumulated in the cost pool.
the activity that has the strongest correlation to the costs accumulated in the cost pool.
19
New cards
Activity-based costing can be performed at
1. unit level
2. job or batch level
3. facility level
4. all of the above
1. unit level
2. job or batch level
3. facility level
4. all of the above
all of the above
20
New cards
All of the following are benefits of budgetary planning **except** for:
1. Requires all levels of management to plan ahead.
2. Records the performance of the past financial year.
3. Motivates personnel throughout the organization to meet planned objectives.
4. Facilitates coordination of activities and resources within the organization.
1. Requires all levels of management to plan ahead.
2. Records the performance of the past financial year.
3. Motivates personnel throughout the organization to meet planned objectives.
4. Facilitates coordination of activities and resources within the organization.
Records the performance of the past financial year.
21
New cards
In developing the master budget in a manufacturing organization, it is best to start with the ...
1. Direct Labor budget
2. Direct Materials budget
3. Production budget
4. Sales budget
1. Direct Labor budget
2. Direct Materials budget
3. Production budget
4. Sales budget
Sales budget
22
New cards
A budget:
1. is the responsibility of management accountants.
2. is the primary method of communicating agreed-upon objectives throughout an organization.
3. ignores past performance because it represents management's plans for a future period.
4. may promote efficiency but has no role in valuating performance.
1. is the responsibility of management accountants.
2. is the primary method of communicating agreed-upon objectives throughout an organization.
3. ignores past performance because it represents management's plans for a future period.
4. may promote efficiency but has no role in valuating performance.
is the primary method of communicating agreed-upon objectives throughout an organization.
23
New cards
Compared to budgeting, long-range planning generally has the:
1. Same amount of detail.
2. Longer time period.
3. Same emphasis.
4. Same time period.
1. Same amount of detail.
2. Longer time period.
3. Same emphasis.
4. Same time period.
Longer time period.
24
New cards
In most cases, not-for-profit entities:
1. Prepare budgets using the same steps as those used by profit-oriented businesses.
2. Know budgeted cash receipts at the beginning of a time period , so they budget only for expenditures.
3. Begin the budgeting process by budgeting expenditures rather than receipts.
4. Can ignore budgets because they are not expected to generate net income.
5.
1. Prepare budgets using the same steps as those used by profit-oriented businesses.
2. Know budgeted cash receipts at the beginning of a time period , so they budget only for expenditures.
3. Begin the budgeting process by budgeting expenditures rather than receipts.
4. Can ignore budgets because they are not expected to generate net income.
5.
Prepare budgets using the same steps as those used by profit-oriented businesses.
25
New cards
The three responsibilities of management include...
1. Planning.
2. Organizing / Directing.
3. Controlling.
4. All of the above.
\
1. Planning.
2. Organizing / Directing.
3. Controlling.
4. All of the above.
\
All of the above.
26
New cards
Non-financial information should be considered in the formation of budgets, plans and forecasts.
True
False
True
False
True
27
New cards
Financial plans should include only variable costs.
True
False
True
False
False
28
New cards
One of the three basic differences between budgets and longer range planning is ...
1. Economic entity.
2. Geography.
3. Time period involved.
4. None of the above.
1. Economic entity.
2. Geography.
3. Time period involved.
4. None of the above.
Time period involved.
29
New cards
All of the following are operating budgets **except for** ....
1. Sales budget.
2. Cash budget.
3. Direct Labor budget.
4. Manufacturing overhead budget.
1. Sales budget.
2. Cash budget.
3. Direct Labor budget.
4. Manufacturing overhead budget.
Cash budget.
30
New cards
An objective of doing a cash budget could be...
1. to determine if the company should file for bankruptcy.
2. to determine if there is sufficient cash to invest in additional property.
3. to determine if cash would be available to recover operations in the event of a disaster,
4. all of the provided answers are correct
1. to determine if the company should file for bankruptcy.
2. to determine if there is sufficient cash to invest in additional property.
3. to determine if cash would be available to recover operations in the event of a disaster,
4. all of the provided answers are correct
all of the provided answers are correct
31
New cards
Components of a cash budget include all of the following except
1. cash receipts
2. net income
3. beginning cash balance
4. financing
5.
1. cash receipts
2. net income
3. beginning cash balance
4. financing
5.
net income
32
New cards
Which of the line items below are relevant in a cash budget / forecast
1. depreciation expense related to equipment
2. estimated bad debt expense
3. cash to be paid for the purchase of new equipment
4. all of the provided answers are correct
1. depreciation expense related to equipment
2. estimated bad debt expense
3. cash to be paid for the purchase of new equipment
4. all of the provided answers are correct
cash to be paid for the purchase of new equipment
33
New cards
The following budgets are all financial budgets except for the
\
A)combined cash budget.
B)budgeted balance sheet.
C)budgeted income statement.
D)capital expenditures budget.
\
\
A)combined cash budget.
B)budgeted balance sheet.
C)budgeted income statement.
D)capital expenditures budget.
\
1. budgeted income statement.
34
New cards
Budgets are
1. required by Generally Accepted Accounting Principles.
2. future oriented.
3. only used by large corporations.
4. prepared by the controller only for the entire organization.
1. required by Generally Accepted Accounting Principles.
2. future oriented.
3. only used by large corporations.
4. prepared by the controller only for the entire organization.
future oriented.
35
New cards
\
Budgetary control involves all but one of the following:
1. modifying future plans
2. analyzing differences
3. using static but not flexible budgets
4. determining differences between actual and planned results
Budgetary control involves all but one of the following:
1. modifying future plans
2. analyzing differences
3. using static but not flexible budgets
4. determining differences between actual and planned results
using static but not flexible budgets
36
New cards
A static budget is:
1. a projection of budget data at several levels of activity within the relevant range of activity
2. a projection of budget data at a single level of activity
3. compared to a flexible budget in a budget report
4. never appropriate in evaluating a manager's effectiveness in controlling costs
1. a projection of budget data at several levels of activity within the relevant range of activity
2. a projection of budget data at a single level of activity
3. compared to a flexible budget in a budget report
4. never appropriate in evaluating a manager's effectiveness in controlling costs
a projection of budget data at a single level of activity
37
New cards
A static budget is useful in controlling costs when cost behavior is:
1. mixed
2. fixed
3. variable
4. linear
\
1. mixed
2. fixed
3. variable
4. linear
\
fixed
38
New cards
A controllable cost is ...
1. a cost that the CEO is prescribing
2. a cost that is variable
3. a cost that is fixed
4. a cost over which a manager has control
1. a cost that the CEO is prescribing
2. a cost that is variable
3. a cost that is fixed
4. a cost over which a manager has control
a cost over which a manager has control
39
New cards
A budgetary process is more useful if it is adaptable to changes in operating conditions
True
False
True
False
True
40
New cards
Cost behavior analysis
1. helps management plan operations
2. applies to all types of businesses and entities
3. helps management decide between alternative courses of action
4. all of the above
1. helps management plan operations
2. applies to all types of businesses and entities
3. helps management decide between alternative courses of action
4. all of the above
all of the above
41
New cards
Fixed costs are costs that
1. Vary in total directly and proportionately with changes in the activity level.
2. Remain the same per unit at every activity level.
3. Neither of the above.
4. Both (a) and (b) above.
1. Vary in total directly and proportionately with changes in the activity level.
2. Remain the same per unit at every activity level.
3. Neither of the above.
4. Both (a) and (b) above.
Neither of the above.
42
New cards
Contribution margin is
1. revenue remaining after deducting cost of goods sold.
2. expressible in $ and/or %.
3. expressible as an amount per unit.
4. revenues less variable costs less fixed costs.
1. revenue remaining after deducting cost of goods sold.
2. expressible in $ and/or %.
3. expressible as an amount per unit.
4. revenues less variable costs less fixed costs.
expressible in $ and/or %.
43
New cards
The Dalton Convention Center was built in 1991 with the expectation that it would be heavily used for expositions, customers and vendors, and company training events for what industry?
1. furniture industry.
2. shoe industry.
3. carpet industry.
4. none of the above.
1. furniture industry.
2. shoe industry.
3. carpet industry.
4. none of the above.
carpet industry.
44
New cards
Which one of the following is a name for the range over which a company expects to operate?
1. Mixed range
2. Relevant range
3. Fixed range
4. Variable range
1. Mixed range
2. Relevant range
3. Fixed range
4. Variable range
Relevant range
45
New cards
Managerial accounting differs from financial accounting in that managerial accounting...
1. is used primarily by external decision makers.
2. is required by Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
3. emphasizes data relevance over data objectivity.
4. tends to report on the company as a whole rather than segments of the company.
1. is used primarily by external decision makers.
2. is required by Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
3. emphasizes data relevance over data objectivity.
4. tends to report on the company as a whole rather than segments of the company.
emphasizes data relevance over data objectivity.
46
New cards
At the breakeven point, the contribution margin equals total
1. variable costs
2. sales revenues
3. selling and administrative costs
4. fixed costs
1. variable costs
2. sales revenues
3. selling and administrative costs
4. fixed costs
fixed costs
47
New cards
An overly optimistic sales budget may result in ...
1. increases in selling prices late in the year.
2. insufficient inventories.
3. increased sales during the year.
4. excessive inventories.
1. increases in selling prices late in the year.
2. insufficient inventories.
3. increased sales during the year.
4. excessive inventories.
excessive inventories.
48
New cards
Which of the following is not a proper matching?
1. long-range planning
1. long-range planning
budgeting
49
New cards
If there were
1) 60,000 pounds of raw materials on hand in the raw materials stockroom on January 1,
2) 120,000 pounds are desired for inventory at January 31, and
3) 410,000 pounds are required for January's production,
How many pounds of raw material should be purchased in January?
1. 350,000 pounds
2. 530,000 pounds
3. 290,000 pounds
4. 470,000 pounds
\
1) 60,000 pounds of raw materials on hand in the raw materials stockroom on January 1,
2) 120,000 pounds are desired for inventory at January 31, and
3) 410,000 pounds are required for January's production,
How many pounds of raw material should be purchased in January?
1. 350,000 pounds
2. 530,000 pounds
3. 290,000 pounds
4. 470,000 pounds
\
470,000 pounds → Total Raw Materials Needed = 410,000+120,000 = 530,000 but 60,000 on hand so 530,000-60,000 = 470,000
50
New cards
Which of the following statements about a budgeted income statement is not true?
1. The budgeted income statement is prepared after the financial budgets are prepared.
2. The budgeted income statement is the end product of the operating budgets.
3. The budgeted income statement s used as a control mechanism on financial performance over the course of the year.
4. The budgeted income statement is prepared using the individual operating budgets.
1. The budgeted income statement is prepared after the financial budgets are prepared.
2. The budgeted income statement is the end product of the operating budgets.
3. The budgeted income statement s used as a control mechanism on financial performance over the course of the year.
4. The budgeted income statement is prepared using the individual operating budgets.
The budgeted income statement is prepared after the financial budgets are prepared.
51
New cards
Assume a company uses direct labor hours (DLH) to allocated overhead (OH). Complete the statement below from the terms listed.
Overhead Allocation Rate
Estimated DLH
Actual DLH
Actual OH Costs
In budgeting OH for the year, a business unit will use the following formula:
____________________________ x _______________________________
1. Overhead Allocation Rate
2. Estimated DLH
3. Actual DLH
4. Actual OH Costs
Overhead Allocation Rate
Estimated DLH
Actual DLH
Actual OH Costs
In budgeting OH for the year, a business unit will use the following formula:
____________________________ x _______________________________
1. Overhead Allocation Rate
2. Estimated DLH
3. Actual DLH
4. Actual OH Costs
Overhead Allocation Rate \* Estimated DLH
52
New cards
Assume a company uses direct labor hours (DLH) to allocated overhead (OH). Complete the statement below from the terms listed.
Overhead Allocation Rate
Estimated DLH
Actual DLH
Actual OH Costs
In allocating OH to manufacturing jobs over the course of the year, a business unit will apply the following formula:
____________________________ x _______________________________
1. Overhead Allocation Rate
2. Estimated DLH
3. Actual DLH
4. Actual OH Costs
Overhead Allocation Rate
Estimated DLH
Actual DLH
Actual OH Costs
In allocating OH to manufacturing jobs over the course of the year, a business unit will apply the following formula:
____________________________ x _______________________________
1. Overhead Allocation Rate
2. Estimated DLH
3. Actual DLH
4. Actual OH Costs
Overhead Allocation Rate \* Actual DLH
53
New cards
Cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis is a key factor in many decisions, including choice of product lines, pricing of products, marketing strategy, and use of productive facilities. A calculation used in a CVP analysis is the breakeven point.
Once the breakeven point is reached, operating income will increase by the ....
1. gross margin per unit for each additional unit sold
2. contribution margin per unit for each additional unit sold
3. fixed costs per unit for each additional unit sold
4. variable costs per unit for each additional unit sold
Once the breakeven point is reached, operating income will increase by the ....
1. gross margin per unit for each additional unit sold
2. contribution margin per unit for each additional unit sold
3. fixed costs per unit for each additional unit sold
4. variable costs per unit for each additional unit sold
contribution margin per unit for each additional unit sold
54
New cards
Which of the following is not part of manufacturing overhead?
1. period costs, such as depreciation on office computers
2. indirect materials, such as machine lubricants
3. indirect labor, such as a plant forklift operators' wages
4. other indirect manufacturing costs, such as plant utilities
1. period costs, such as depreciation on office computers
2. indirect materials, such as machine lubricants
3. indirect labor, such as a plant forklift operators' wages
4. other indirect manufacturing costs, such as plant utilities
period costs, such as depreciation on office computers
55
New cards
At January 1, 2016, Shark Corp has a beginning inventory of 2,000 surfboards. Shark estimates it will sell 10,000 units during the first quarter of 2016 with a 12% increase in sales each quarter. Shark's policy is to maintain an ending inventory equal to 25% of the next quarter's sales. Each surfboard costs $100 and is sold for $150. How much is budgeted sales revenue for the third quarter of 2016?
1. $450,000
2. $1,950,000
3. $1,881,600
4. $1,254,400
1. $450,000
2. $1,950,000
3. $1,881,600
4. $1,254,400
$1,881,600 ;
* Q1: 10,000 surfboards
* Q2: 10,000 x 1.12 = 11,200 surfboards
* Q3: 11,200 x 1.12 = 12,544 surfboards
* Q4: 12,544 x 1.12 = 14,077 surfboards;
* Q1 ending inventory: 25% x 11,200 = 2,800 surfboards
* Q2 ending inventory: 25% x 12,544 = 3,136 surfboards
* Q3 ending inventory: 25% x 14,077 = 3,519 surfboards;
* Q1 required production: 10,000 + 2,800 - 2,000 = 10,800 surfboards
* Q2 required production: 11,200 + 3,136 - 2,800 = 11,536 surfboards
* Q3 required production: 12,544 + 3,519 - 3,136 = 13,927 surfboards
* Q1 COGS: 10,800 x $100 = $1,080,000
* Q2 COGS: 11,536 x $100 = $1,153,600
* Q3 COGS: 13,927 x $100 = $1,392,700;
* Q3 sales revenue: (12,544 x $150) - $1,392,700 = $1,881,600
* Q1: 10,000 surfboards
* Q2: 10,000 x 1.12 = 11,200 surfboards
* Q3: 11,200 x 1.12 = 12,544 surfboards
* Q4: 12,544 x 1.12 = 14,077 surfboards;
* Q1 ending inventory: 25% x 11,200 = 2,800 surfboards
* Q2 ending inventory: 25% x 12,544 = 3,136 surfboards
* Q3 ending inventory: 25% x 14,077 = 3,519 surfboards;
* Q1 required production: 10,000 + 2,800 - 2,000 = 10,800 surfboards
* Q2 required production: 11,200 + 3,136 - 2,800 = 11,536 surfboards
* Q3 required production: 12,544 + 3,519 - 3,136 = 13,927 surfboards
* Q1 COGS: 10,800 x $100 = $1,080,000
* Q2 COGS: 11,536 x $100 = $1,153,600
* Q3 COGS: 13,927 x $100 = $1,392,700;
* Q3 sales revenue: (12,544 x $150) - $1,392,700 = $1,881,600
56
New cards
A budget is most likely to be effective if....
1. it is used to assess blame when things do not occur according to plans.
2. it is not used to evaluate a manager's performance.
3. employees and managers at the lower levels do not get involved in the budgeting process.
4. it has top management support.
1. it is used to assess blame when things do not occur according to plans.
2. it is not used to evaluate a manager's performance.
3. employees and managers at the lower levels do not get involved in the budgeting process.
4. it has top management support.
it has top management support.
57
New cards
Peter’s Production had estimated $2,170,000 of manufacturing overhead for the year and 55,000 direct labor hours. By the end of the year, the company had actually incurred $2,050,000 of manufacturing overhead costs and had used a total of 57,000 direct labor hours on various jobs.
What was the predetermined MOH rate per direct labor hour for the year?
( You may show your calculations on the provided scratch paper.)
1. $ 37.27 per DLH
2. $ 39.45 per DLH
3. $ 35.96 per DLH
4. $ 38.07 per DLH
\
Was MOH over-allocated or under-allocated for the year?
1. over-allocated
2. under-allocated
3. none of the above
4. all of the above
\
What was the predetermined MOH rate per direct labor hour for the year?
( You may show your calculations on the provided scratch paper.)
1. $ 37.27 per DLH
2. $ 39.45 per DLH
3. $ 35.96 per DLH
4. $ 38.07 per DLH
\
Was MOH over-allocated or under-allocated for the year?
1. over-allocated
2. under-allocated
3. none of the above
4. all of the above
\
$ 39.45 per DLH;
Predetermined MOH rate per DLH = $2,170,000 / 55,000 DLH
Predetermined MOH rate per DLH = $39.45 per DLH
\
over-allocated
OAR > Actual MOH
Predetermined MOH rate per DLH = $2,170,000 / 55,000 DLH
Predetermined MOH rate per DLH = $39.45 per DLH
\
over-allocated
OAR > Actual MOH
58
New cards
Peter’s Production had estimated $2,170,000 of manufacturing overhead for the year and 55,000 direct labor hours. By the end of the year, the company had actually incurred $2,050,000 of manufacturing overhead costs and had used a total of 57,000 direct labor hours on various jobs.
By how much was MOH over-allocated or under-allocated for the year?
1. $120,000
2. $78,650
3. $198,650
4. none of the above
By how much was MOH over-allocated or under-allocated for the year?
1. $120,000
2. $78,650
3. $198,650
4. none of the above
$198,650; OAR = 39.45 x 57,000 DLH therefore, Total allocated MOH cost = $2,248,650
\
Actual OH = 2,050,000
\
Over-allocated = 2,248,650 - 2,050,000 = 198,650
\
Actual OH = 2,050,000
\
Over-allocated = 2,248,650 - 2,050,000 = 198,650
59
New cards
At the end of the year, manufacturers will take any immaterial over- or under- allocated overhead and record it as a period cost.
True
False
True
False
False
\
\
60
New cards
\
Which of the following would decrease unit contribution margin the most?
1. a 15% decrease in selling price
2. a 15% decrease in variable costs
3. a 15% increase in variable costs
4. a 15% decrease in fixed costs
Which of the following would decrease unit contribution margin the most?
1. a 15% decrease in selling price
2. a 15% decrease in variable costs
3. a 15% increase in variable costs
4. a 15% decrease in fixed costs
a 15% decrease in selling price
61
New cards
\
In an activity-based costing system, cost reduction is accomplished by identifying and eliminating:
__All Cost Drivers__ __Non-Value Added Activities__
A. No No
B. Yes Yes
C. No Yes
D. Yes No
Indicate which line is correct.
A
B
C
D
In an activity-based costing system, cost reduction is accomplished by identifying and eliminating:
__All Cost Drivers__ __Non-Value Added Activities__
A. No No
B. Yes Yes
C. No Yes
D. Yes No
Indicate which line is correct.
A
B
C
D
D
62
New cards
What does a contribution margin statement highlight?
1. the costs that behave as fixed v variable costs.
2. the costs that must be covered for the operation to breakeven
3. all of the above
4. none of the above
1. the costs that behave as fixed v variable costs.
2. the costs that must be covered for the operation to breakeven
3. all of the above
4. none of the above
all of the above
63
New cards
"Relevant range" is the range over which variable costs are expected to behave inconsistently.
True
False
True
False
False
64
New cards
A cash budget shows anticipated cash flows in three sections. What are they?
1. operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities
2. cash items, capital items, and non-cash items.
3. cash receipts, cash disbursements, and financing.
4. none of the above
1. operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities
2. cash items, capital items, and non-cash items.
3. cash receipts, cash disbursements, and financing.
4. none of the above
operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities
65
New cards
Dolce Co. estimates its sales at 180,000 units in the first quarter and that sales will increase by 18,000 units each quarter over the year. Each unit sells for $25. Of total sales, 40% of the sales are for cash. Of the credit customers, 70% pay within the quarter. The remainder is received in the quarter following the sale. Cash collections for Q2 are budgeted at...
$ 1,980,000
$ 3,780,000
$ 4,059,000
$ 4,869,000
$ 1,980,000
$ 3,780,000
$ 4,059,000
$ 4,869,000
$ 4,869,000;
\
The first step in calculating the cash collections for Q2 is to calculate the total credit sales for Q1 and Q2.
Total credit sales for Q1 = 60% x $25 x 180,000 = $2,700,000
Total credit sales for Q2 = 82% x $25 x 198,000 = $4,059,000 ($25 is multiplied by 198,000 because sales are expected to increase by 18,000 units each quarter).
Of the credit sales in Q1, 30% will be collected in Q1 and 70% will be collected in Q2. Therefore, cash collections from credit sales in Q2 related to Q1 sales will be:
$2,700,000 x 70% = $1,890,000
For the credit sales in Q2, 70% is expected to be collected in Q2 and the remaining 30% will be collected in Q3. Therefore, cash collections from credit sales in Q2 will be:
$4,059,000 x 70% = $2,841,300
The total cash collections for Q2 will be:
Cash collections from Q1 credit sales + Cash collections from Q2 credit sales = $1,890,000 + $2,841,300 = $4,731,300
However, the question is asking for the cash collections for Q2, so we need to subtract the credit sales for Q2 that will be collected in Q3:
$4,731,300 - ($4,059,000 x 30%) = $4,731,300 - $1,217,700 = $3,513,600
Therefore, the correct answer is $4,869,000.
\
The first step in calculating the cash collections for Q2 is to calculate the total credit sales for Q1 and Q2.
Total credit sales for Q1 = 60% x $25 x 180,000 = $2,700,000
Total credit sales for Q2 = 82% x $25 x 198,000 = $4,059,000 ($25 is multiplied by 198,000 because sales are expected to increase by 18,000 units each quarter).
Of the credit sales in Q1, 30% will be collected in Q1 and 70% will be collected in Q2. Therefore, cash collections from credit sales in Q2 related to Q1 sales will be:
$2,700,000 x 70% = $1,890,000
For the credit sales in Q2, 70% is expected to be collected in Q2 and the remaining 30% will be collected in Q3. Therefore, cash collections from credit sales in Q2 will be:
$4,059,000 x 70% = $2,841,300
The total cash collections for Q2 will be:
Cash collections from Q1 credit sales + Cash collections from Q2 credit sales = $1,890,000 + $2,841,300 = $4,731,300
However, the question is asking for the cash collections for Q2, so we need to subtract the credit sales for Q2 that will be collected in Q3:
$4,731,300 - ($4,059,000 x 30%) = $4,731,300 - $1,217,700 = $3,513,600
Therefore, the correct answer is $4,869,000.
66
New cards
Why are budgets useful in the planning process?
1. They provide management with information about the company's past performance.
2. They communicate goals and provide a basis for valuation.
3. They guarantee the company will be profitable if it meets its objectives.
4. They enable the budget committee to earn their paycheck.
1. They provide management with information about the company's past performance.
2. They communicate goals and provide a basis for valuation.
3. They guarantee the company will be profitable if it meets its objectives.
4. They enable the budget committee to earn their paycheck.
They communicate goals and provide a basis for valuation.
67
New cards
A company is concerned about its operating performance, as summarized below:
Revenues (*at $12.50 per unit*) $ 300,000
Fixed costs $ 160,000
Net loss $ ( 40,000)
What variable costs did it incur?
$160,000
$120,000
$200,000
$180,000
Revenues (*at $12.50 per unit*) $ 300,000
Fixed costs $ 160,000
Net loss $ ( 40,000)
What variable costs did it incur?
$160,000
$120,000
$200,000
$180,000
$180,000
\
\
68
New cards
A company is concerned about its operating performance, as summarized below:
Revenues (*at $12.50 per unit*) $ 300,000
Fixed costs $ 160,000
Net loss $ ( 40,000)
How many units were produced?
24,000 units
14,400 units
12,800 units
there is insufficient information to answer this question
Revenues (*at $12.50 per unit*) $ 300,000
Fixed costs $ 160,000
Net loss $ ( 40,000)
How many units were produced?
24,000 units
14,400 units
12,800 units
there is insufficient information to answer this question
there is insufficient information to answer this question
69
New cards
A company is concerned about its operating performance, as summarized below:
Revenues (*at $12.50 per unit*) $ 300,000
Fixed costs $ 160,000
Net loss $ ( 40,000)
How many additional units should the company have sold to break-even?
32,000
24,000
16,000
8,000
Revenues (*at $12.50 per unit*) $ 300,000
Fixed costs $ 160,000
Net loss $ ( 40,000)
How many additional units should the company have sold to break-even?
32,000
24,000
16,000
8,000
8,000
70
New cards
The concept of "job costing" can be applied in a service firm. The real difference between job costing at manufacturing companies and service firms is that most costs at service firms are PRODUCT costs, rather than PERIOD (operating expenses) costs.
True
False
True
False
False
71
New cards
\
The FS has had two social events this year: 1) an outing to a local basketball game, for which the FS incurred $230 in costs (tickets and transport), and 2) a holiday party, for which the FS incurred $170 in costs. The FS is proposing to hold two further events in the second half of the year: 1) the end-of-year party, for which the FS expects to incur $250 in costs, and 2) an outing to a game and party venue.
**QUESTION**: How much does the AS have in their budget to spend on the outing to the game and party venue?
$ 400
$ 150
$ 350
$ 750
The FS has had two social events this year: 1) an outing to a local basketball game, for which the FS incurred $230 in costs (tickets and transport), and 2) a holiday party, for which the FS incurred $170 in costs. The FS is proposing to hold two further events in the second half of the year: 1) the end-of-year party, for which the FS expects to incur $250 in costs, and 2) an outing to a game and party venue.
**QUESTION**: How much does the AS have in their budget to spend on the outing to the game and party venue?
$ 400
$ 150
$ 350
$ 750
$ 350
72
New cards
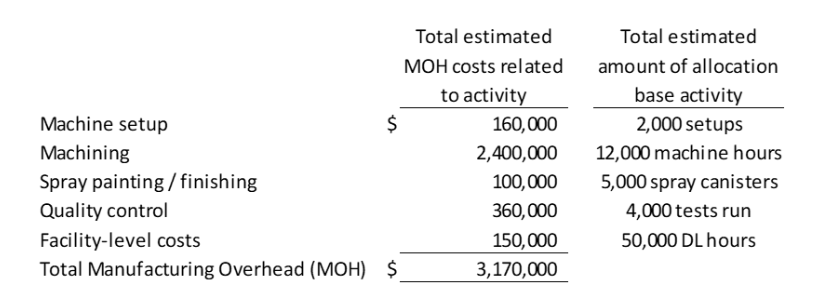
Walter's Washing Machines is considering adopting an activity-based costing system. The following manufacturing activities, indirect manufacturing costs, and cost drivers have been identified:
\
\
**QUESTION: At what rate are facility level costs being allocated?**
$80/setup
$200/machine hour
$3/direct labor hour
$12.50/machine hour
\
\
**QUESTION: At what rate are facility level costs being allocated?**
$80/setup
$200/machine hour
$3/direct labor hour
$12.50/machine hour
$3/direct labor hour
73
New cards
According to GAAP, expenses are recognized when:
1. they contribute to the production of revenue.
2. they are billed by the supplier.
3. the invoice is received.
4. they are paid.
1. they contribute to the production of revenue.
2. they are billed by the supplier.
3. the invoice is received.
4. they are paid.
they contribute to the production of revenue.
74
New cards
Accrued expenses are expenses paid in cash and recorded as assets before they are used or consumed.
True
False
True
False
False
75
New cards
Tyson Inc had the following accounts and balances at the end of the financial reporting period:
Accounts payable $ 25,000
Accounts receivable 5,000
Buildings 70,000
Cash 10,000
Unearned service revenue 10,000
Equipment 35,000
Land 35,000
Common Stock 10,000
Based on the ending account balances above, what should be the balance for ending retained earnings?
$ 125,000
$ 110,000
$ 140,000
$ 120,000
Accounts payable $ 25,000
Accounts receivable 5,000
Buildings 70,000
Cash 10,000
Unearned service revenue 10,000
Equipment 35,000
Land 35,000
Common Stock 10,000
Based on the ending account balances above, what should be the balance for ending retained earnings?
$ 125,000
$ 110,000
$ 140,000
$ 120,000
$ 110,000
76
New cards
In a double-entry accounting system, the total of all debits must equal the total of all credits.
True
False
True
False
True
77
New cards
In which of the following sequences are the financial statements usually prepared?
1. balance sheet, statement of cash flows, income statement, and statement of retained earnings,
2. balance sheet, statement of retained earnings, statement of cash flows, and income statement
3. income statement, balance sheet, statement of retained earnings, and statement of cash flows
4. income statement, statement of retained earnings, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows
1. balance sheet, statement of cash flows, income statement, and statement of retained earnings,
2. balance sheet, statement of retained earnings, statement of cash flows, and income statement
3. income statement, balance sheet, statement of retained earnings, and statement of cash flows
4. income statement, statement of retained earnings, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows
income statement, statement of retained earnings, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows
78
New cards
Depreciation is a process of:
1. appraisal
2. cash accumulation
3. cost allocation
4. valuation
1. appraisal
2. cash accumulation
3. cost allocation
4. valuation
cost allocation
79
New cards
The liability created by a business when it purchases material on credit from suppliers is termed a(n):
1. account receivable
2. expense
3. account payable
4. inventory
1. account receivable
2. expense
3. account payable
4. inventory
account payable
80
New cards
Consider management's explanations of the key assumptions and estimates used in the determination of material account balances in the financial statements. State whether management's explanations are most likely to be detailed in management discussion and analysis (MD&A), the notes to the financial statements, or the auditor’s report:
1. none of the provided answers are correct
2. management discussion and analysis (MD&A)
3. auditor’s report
4. notes to the financial statements
1. none of the provided answers are correct
2. management discussion and analysis (MD&A)
3. auditor’s report
4. notes to the financial statements
notes to the financial statements
81
New cards
Gao Inc. follows GAAP and applies the expense recognition principle. Gao Inc repairs a car on August 31 and calls the customer to tell them the vehicle is ready for pick-up. The customer picks up the vehicle on September 1 and mails the payment to Gao Inc on September 5. Gao Inc receives the check in the mail on September 8 and deposits the check in the bank on September 10th.
On what date should Gao Inc recognize the revenue?
\
August 31
September 1
September 10
September 8
On what date should Gao Inc recognize the revenue?
\
August 31
September 1
September 10
September 8
August 31
82
New cards
Transaction analysis is the process of reviewing source documents to determine the dual effect on the accounting equation and the specific elements involved.
True
False
True
False
True
83
New cards
GAAP uses the accounting basis by which organizations record economic events in the period in which the events occur, regardless of when cash exchanged hands; this is called:
depreciation
revenue recognition
cash-based accounting
accrual-based accounting
depreciation
revenue recognition
cash-based accounting
accrual-based accounting
accrual-based accounting
84
New cards
Which of the following statements is true:
1. amounts paid out as dividends are not expenses.
2. amounts received from issuing stock are revenues.
3. amounts paid out as dividends are reported on the income statement.
4. amounts received from issued stock are reported on the income statement.
1. amounts paid out as dividends are not expenses.
2. amounts received from issuing stock are revenues.
3. amounts paid out as dividends are reported on the income statement.
4. amounts received from issued stock are reported on the income statement.
amounts paid out as dividends are not expenses.
85
New cards
The purpose of corporate governance is to help build an environment of trust, transparency and accountability necessary for fostering long-term investment, financial stability and business integrity, thereby supporting stronger growth and more inclusive societies.
True
False
True
False
True
86
New cards
Ludlow Machine Shop started the year with total assets of $120,000 and total liabilities of $80,000. During the year, the business recorded $600,000 in revenues, $510,000 in expenses, and dividends of $20,000. Stockholders' equity at the end of the year was:
$ 135,000
$ 110,000
$ 130,000
$ 150,000
$ 135,000
$ 110,000
$ 130,000
$ 150,000
$ 110,000
87
New cards
Which of the following financial statements is concerned with the company at a point in time?
1. balance sheet
2. income statement
3. statement of cash flows
4. statement of retained earnings
1. balance sheet
2. income statement
3. statement of cash flows
4. statement of retained earnings
balance sheet
88
New cards
Both investments by stockholders and revenues decrease stockholders’ equity.
True
False
True
False
False
89
New cards
The right to receive money in the future is called a(n):
1. account payable
2. revenue
3. account receivable
4. liability
\
1. account payable
2. revenue
3. account receivable
4. liability
\
account receivable
90
New cards
\
When goods are purchased for resale by a company, it increases:
1. net income
2. expenses
3. revenues
4. inventory
When goods are purchased for resale by a company, it increases:
1. net income
2. expenses
3. revenues
4. inventory
inventory
91
New cards
State whether management's description of its ability to fund operations and expansion is most closely associated with the management discussion and analysis (MD&A), the notes to the financial statements, or the auditor’s report:
1. all of the provided answers are correct
2. management discussion and analysis (MD&A)
3. auditor’s report
4. notes to the financial statements
1. all of the provided answers are correct
2. management discussion and analysis (MD&A)
3. auditor’s report
4. notes to the financial statements
management discussion and analysis (MD&A)
92
New cards
Adjusting entries include one income statement account and one balance sheet account.
True
False
True
False
True
93
New cards
Internal control is used in a business to:
1. ensure compliance with laws and regulations
2. enhance the accuracy and reliability of its financial records
3. all of the provided answers are correct
4. safeguard its assets
1. ensure compliance with laws and regulations
2. enhance the accuracy and reliability of its financial records
3. all of the provided answers are correct
4. safeguard its assets
all of the provided answers are correct
94
New cards
In the Auditors' Report that accompanies audited financial statements, external auditors attest to the accuracy of the financial statments.
True
False
True
False
False
95
New cards
After closing entries are posted, all permanent accounts should have a zero balance.
True
False
True
False
False
96
New cards
The cost of assets consumed or services used is also known as a(n):
1. revenue
2. liability
3. expense
4. asset
1. revenue
2. liability
3. expense
4. asset
expense
97
New cards
The basis accounting equation is ___ = _ + stockholders' equity
\
\
assets, liabilities
98
New cards
When a company pays its insurance premium in advance of the policy coverage period, the journal entry includes a debit to ....
1. Cash
2. Insurance Expense
3. Accounts Payable
4. Prepaid Insurance Expense
1. Cash
2. Insurance Expense
3. Accounts Payable
4. Prepaid Insurance Expense
Prepaid Insurance Expense
99
New cards
You would expect to see the following in the footnotes to the financial statements:
Matters to be voted upon by the shareholders of the Company at the next annual shareholders' meeting
True
False
Matters to be voted upon by the shareholders of the Company at the next annual shareholders' meeting
True
False
False
100
New cards
Which of the following types of accounts are considered **permanent** accounts?
1. dividends
2. assets
3. none of the provided answers are correct
4. revenues
1. dividends
2. assets
3. none of the provided answers are correct
4. revenues
assets