Exam 3 DNA mutation
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
mutation
an alteration in DNA sequence → major alteration in chromosomal structure
any base-pair change in sequence
single base pair substitution or deletion/insertion of base pairs
can occur in somatic or germ cells or in coding or noncoding regions
point mutation
base substitution
change from one base pair to another
missense mutation
results in new triplet code for different amino acid
nonsense mutation
results in triplet code for stop codon (translation terminated prematurely)
silent mutation
new triplet code still codes for same amino acid
transition base substiution
pyrimidine replaces pyrimidine or purine replaces purine
transversion base substitution
purine and pyrimidine are interchanged
frameshift mutation
result from insertions or deletions of base pair
loss or addition of nucleotides causes a shift in reading frame
frame of triplet reading during translation altered
loss of function mutation
reduces/eliminates function of gene product
null mutation
results in complete loss of function
dominant mutation
results in mutant phenotype in diploid organism
dominant gain-of-function mutation
results in gene with enhanced, negative, or new function
lethal mutations
interrupt essential process and result in death
various inherited biochemical disorders (tay sachs)
lethal conditional mutations
dependent on organisms’ environment
temperature-sensitive mutation
gene product functions at one temperature but not another
ex: temperature sensitive coat color variations in Siamese cats and himalayan rabbits
neutral mutation
occurs in protein-coding region in any part of genome
majority of mutations occur in noncoding region
effect on genetic fitness of organism is neither beneficial nor detrimental
visible (morphological) mutation
seen in phenotype
ex: mendel’s pea characteristics
nutritional mutation
altered nutritional characteristics
ex: loss of ability to synthesize an essential amino acid in bacteria
biochemical mutation
changes in protein function
ex: defective hemoglobin leading to sickle-cell anemia in humans
behavioral mutation
behavior pattern changes
ex: brain mutations affecting drosophila mating behaviors
regulatory mutation
altered gene mutation
ex: mutation affecting expression of the lac operon in E.coli
somatic mutation
occur in any cell except germ cells; are not heritable
germ-line mutation
occur in gametes; are inherited
autosomal mutation
occur within genes located on autosomes
X and Y linked mutations
occur within genes located on X and Y chromosome
recessive autosomal mutation
occurs in somatic cell of diploid organism
is unlikely to result in detectable phenotype
inherited autosomal mutation
are expressed phenotypically in first generation
x-linked recessive mutation
arise in gametes of homogametic female
may be expressed in hemizygous male offspring
E coli + T1 bacteriophage
e coli is susceptible to infection by T1 bacteriophage
some rare strains of E.coli are resistant; resistant strains arise in cultures infected with T1
Luria and Delbruck fluctuation experiment
if mutations are adaptive, T1 resistance will not occur until T1 is added to culture
proportion of resistant cells will be the same for all identical cultures
if mutations occur spontaneously the number of T1 resistant cells will vary
mutation rates in humans
2.5 × 10-8 per site per generation
about 175 mutations per generation
substitutions are 10x more common than insertions or deletions
occur more frequently in males than females
spontaneous mutations
changes in nucleotide sequence that occur naturally
arise from normal biological or chemical processes that alter nitrogenous bases
they are usually mistakes that occur during replication
rates vary but are exceedingly low for all organisms
induced mutations
result from influence of extraneous factors, either natural or artificial
radiation, UV light, natural and synthetic chemicals
factors that cause mutation during replication
replication is imperfect
DNA polymerase occasionally inserts incorrect nucleotides
misincorporated nucleotides persist after proofreading
errors due to mispairing predominantly lead to point mutations
replication slippage
when a loop occurs in template strand during replication, DNA polymerase misses looped out nucleotides and small insertions and deletions occur
most common in repeat sequences (hot spots): contribute to hereditary diseases: Fragile-X, huntington disease
tautomers
alternate chemical forms of purines and pyrimidines
increase chance of mispairing during DNA replication
tautomeric shifts
change the bonding structure allowing for non complementary base pairing
may lead to permanent base-pair changes and mutations
ex: keto from to enol form: removal of a hydrogen atom rearranges chemical bonds, many compounds shift back and forth from one form to another
depurination
loss of nitrogenous bases (usually a purine- guanine or adenine), leading to an apurinic site (without purine)
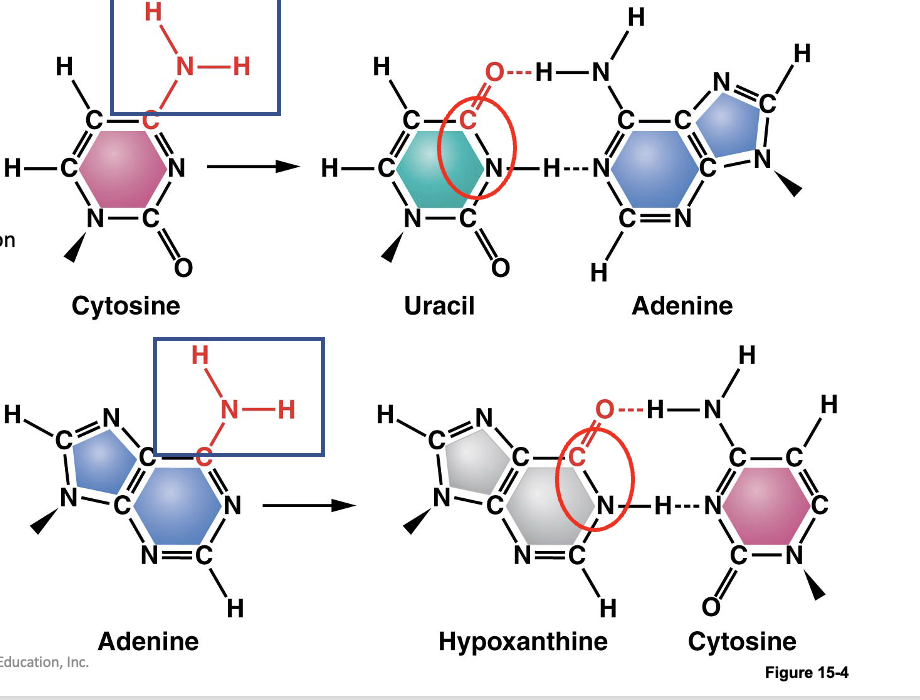
deamination
amino group in cytosine or adenine is converted to uracil and adenine converted to hypoxanthine leading to a proton shift
results in change in base pairing of original bases (A-T converted to G-C)
oxidative damage to DNA
due to by-products of normal cellular processes
exposure to high-energy radiation
superoxides (O2-)
hydroxyl radicals (OH)
hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
free radicals
stable molecules transformed into chemical species containing one or more unpaired electrons
directly or indirectly affect DNA: alter purines and pyrimidines, break phosphodiester bonds, produce deletions, translocations, or fragmentation
diet w/ free radicals
the more you eat, the more ATP is generated
the more ATP you generate the more O2 is broken down into individual, unstable oxygen atoms
oxygen atoms always grab electrons leading to chemical changes in DNA molecules
transposable elements
DNA elements that move within or between genomes
present in all organisms
can act as naturally occurring mutagens
cause inversions, translocations, double-stranded breaks- creates chromosomal damage
mutagens
natural artificial agents that induce mutations
all cells are exposed to them
ex: fungal toxins, cosmic rays, UV light, industrial pollutants, medical x-rays, chemicals in tobacco smoke
base analogs
mutagenic chemicals that mimic DNA bases
can substitute for purines or pyrimidines during nucleic acid biosynthesis
increase tautomeric shifts
increase sensitivity to UV light- mutagenic
ex: 5-bromouracil behaves as thymine analog
alkylating agents
donate alkyl group (CH3 or CH3CH3) to amino or keto groups in nucleotides
alter base-pairing affinity
transition mutations result
ex: mustard gas
intercalating agents
chemicals with dimensions and shapes that wedge between DNA base pairs
this causes base-pair distortions and DNA unwinding → replication errors
ex: ethidium bromide
adduct-forming agents
mutation causing chemicals
covalently binds to DNA, altering conformation and interfering with replication and repair
ex: acetaldehyde or heterocyclic amines (cancer causing chemicals)
UV light
creates pyrimidine dimers; two identical pyrimidines distort DNA conformation
errors can be introduced during DNA replication
ionizing radiation
energy of radiation varies intensely with wavelength: mutagenic are x-rays, gamma rays, cosmic rays
penetrates deeply into tissues, causes ionization of molecules