4.5 Energy changes
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Students should be able to distinguish between exothermic and endothermic reactions on the basis of the temperature change of the surroundings
Exothermic reactions transfer energy from the reacting molecules to the surroundings so in an exothermic reaction the temperature of the surroundings increases. Burning (combustion), certain oxidation reactions and neutralisation are all examples of exothermic reactions.
Endothermic reactions take in energy from their surroundings so the temperature of the surroundings decreases. Thermal decomposition (a chemical reaction that happens when a compound breaks down when heated) is an example of an exothermic reaction.
Students should be able to evaluate uses and applications of exothermic and endothermic reactions given appropriate information.
Examples and uses of exothermic reactions are hand warmers, self-heating cans for food, combustion, many oxidation reactions & neutralisation
Examples and uses of endothermic reactions are thermal decomposition, reaction between citric acid & sodium hydrogencarbonate, and sports injury packs
Required practical 4: investigate the variables that affect temperature changes in reacting solutions such as, eg acid plus metals, acid plus carbonates, neutralisations, displacement of metals.
The neutralisation reaction between HCl and the alkali sodium hydroxide. We will add increasing volumes of sodium hydroxide solution to HCl and in each experiment measure the maximum temperature reached. In this practical the independent variable is the volume of sodium hydroxide, the dependent variable is the temperature reached. The control variables are the volume of HCl and the concentrations of both HCl and the sodium hydroxide solution.
Start by measuring 30cm3 of dilute HCl into a measuring cylinder.
Transfer the acid into a polystyrene cup.
Stand the polystyrene cup inside a beaker which stops the cup from falling over.
With a thermometer, measure the temperature of the acid and record this in a table.
Measure 5cm3 of sodium hydroxide solution with a measuring cylinder and transfer this into the polystyrene cup.
Fit a plastic lid to the cup and place a thermometer through the hole in the lid with the bulb of the thermometer into the solution.
With the thermometer gently stir the solution.
As the reaction is exothermic energy is released meaning the temperature of the solution will increase.
The temperature on the thermometer will rise and when it stops changing record the highest temperature that was reached.
Rinse out and dry the polystyrene cup and repeat the whole experiment using 5cm3 more of sodium hydroxide solution each time until 40cm3 of sodium hydroxide solution is reached.
At this point repeat the whole experiment one more time so there are two sets of results which can be used to calculate a mean value for the maximum temperature reached for each volume of sodium hydroxide solution. Use the same volume and concentration of HCl each time and the same starting temperature.
Plot a graph of results and the data will show: as we increase the volume of sodium hydroxide solution, the temperature reached increases because more particles of sodium hydroxide react with the HCl and as it is exothermic more energy is released every time so a higher temperature is reached every time. At a certain volume of sodium hydroxide solution the maximum temperature reached starts to decrease as we are adding so much sodium hydroxide that there is not enough HCl so some of the sodium hydroxide is not able to react so the amount of energy released by the reaction has reached a maximum.
The reason for using a polystyrene cup with a lid is because we want to reduce heat losses as we are measuring temperature. Polystyrene is a good thermal insulator so heat loss to this sides and bottom is reduced and the lid prevents heat loss to the air.
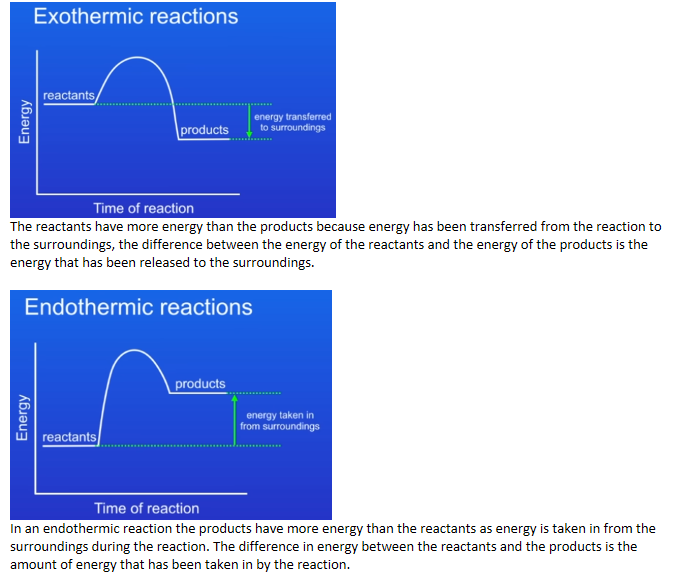
Students should be able to draw simple reaction profiles (energy level diagrams) for exothermic and endothermic reactions showing the relative energies of reactants and products, the activation energy and the overall energy change, with a curved line to show the energy as the reaction proceeds
In an exothermic reaction the reactants have more energy than the products because energy has been transferred from the reaction to the surroundings, the difference between the energy of the reactants and the energy of the products is the energy that has been released to the surroundings.
In an endothermic reaction the products have more energy than the reactants as energy is taken in from the surroundings during the reaction. The difference in energy between the reactants and the products is the amount of energy that has been taken in by the reaction.
Activation energy
Activation energy is the energy needed for a reaction to occur.
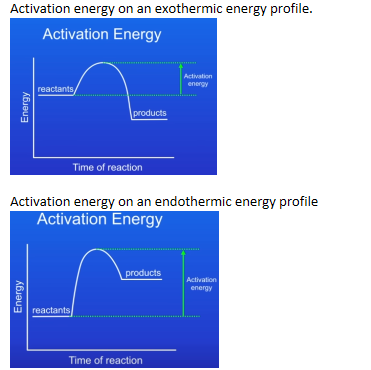
In both exothermic and endothermic reactions the energy rises to a peak, this is called the activation energy. Reactions can only occur when particles collide with sufficient energy (the minimum amount of energy required for particles to react) and this is called the activation energy. The activation energy is from the reactants to the peak of the curve.
Students should be able to calculate the energy transferred in chemical reactions using bond energies supplied.
As energy is released to the surroundings in an exothermic reaction the energy change of the reaction is shown as a negative change. The opposite is true for endothermic reactions (energy change shown as positive). When we break a chemical bond, energy is required and this is an endothermic process and making bonds is exothermic. Every chemical bond has an energy value which tells us the energy required to break the bond.
Students should be able to interpret data for relative reactivity of different metals and evaluate the use of cells.
If two metals are placed in an electrolyte we can produce electricity. An electrolyte is simply a solution that can conduct electricity for example a solution of an ionic compound. If two metals in an electrolyte solution are connected to a voltmeter a pd will be shown as an electric current will flow through the wire. A cell can only produce electricity for a certain period of time as the chemicals run out. Cells will only produce electricity if we use metals with different reactivities. The reactivity series goes;
METALS | ABREVIATION |
Most Reactive |
|
Potassium | Please |
Sodium | Send |
Lithium | Lions |
Calcium | Cats |
Magnesium | Monkeys |
Aluminium | And |
Carbon | Cute |
Zinc | Zebras |
Iron | Into |
Tin | Ten |
Hydrogen | Hot |
Copper | Countries |
Silver | Signed |
Gold | Gordon |
Least Reactive |
|
Carbon and hydrogen are non-metals, they are included in the series as they are useful in extracting metals from their oxides by reduction processes.
The size of the pd depends on the difference in reactivity of the two metals chosen so a cell containing magnesium and copper will have a large pd but a cell containing zinc and tin will have a smaller pd.
The electrolyte also effects the pd but no more information is needed.
Students should be able to evaluate the use of hydrogen fuel cells in comparison with rechargeable cells and batteries
In alkaline batteries the chemicals eventually run out and no more electricity is produced and as these reactions are non-reversible the batteries are non-rechargeable. Rechargeable batteries can be recharged as the reactions can be reversed when we apply an electrical current.
In a fuel cell a fuel such as hydrogen is reacted with either pure oxygen or air. Inside a fuel cell a chemical reaction takes place producing an electric current. For the hydrogen fuel cell the only waste product produced is water.
The advantages of hydrogen fuel cells include; hydrogen will produce electricity for as long as hydrogen is provided whereas rechargeable batteries run out and need to be recharged. Hydrogen fuel cells do not get less efficient as the longer they run however rechargeable batteries can store less electricity the more charging cycles they go through and eventually need to be replaced. Hydrogen fuel cells can also be a source of water for example for astronauts on spacecraft. There are however also some problems with hydrogen fuel cells for example the hydrogen gas itself is explosive and is very difficult to store safely and there are far fewer dangerous chemicals in rechargeable batteries however if manufactured incorrectly rechargeable batteries can catch fire. Hydrogen fuel cells produce a relatively low pd so several are needed together whereas rechargeable batteries produce a greater pd than a hydrogen fuel cell.
Students should be able to write the half equations for the electrode reactions in the hydrogen fuel cell (HT only).
At the negative electrode hydrogen molecules split into hydrogen ions and electrons shown as 2H2 --> 4H+ + 4e- . The electrons pass through the wire and that's the electrical current. At the positive electrode, oxygen molecules combine with the hydrogen ions and the electrons shown as O2 + 4H+ + 4e- --> 2H2O (water). Overall in the hydrogen fuel cell hydrogen is combining with oxygen so the hydrogen is being oxidised so the overall equation is 2H2 + O2 --> 2H2O.
What happens to energy in a chemical reaction?
It is conserved. The amount of energy at the end of the reaction is the same as the amount of energy at the start.
Neutralisation reaction Practical
1)Put 25cm3 of 0.25mol/dm3 of HCL and NaOH in separate beakers
2)Place beakers in 25C water bath till same temperature
3)Add HCL then NaOH into polystyrene cup with lid
4)Take temp every 30secs and record highest
5) Repeat using 0.5mol/dm3 and 1 mol/dm3
What is the equation for energy change of reaction?
Sum of bond energies broken - sum of bonds energies made
What is an electrochemicalcell?
A basic system made up of 2 different electrodes in contact with electrolyte
What is an electrolyte?
A liquid that contains ions which react with electrodes
What does the voltage of a cell depend on?
The bigger the difference in reactivity, the bigger the voltage
The electrolyte used as different ions react differently with electrodes
What is a battery?
2 or more cells in series
What are the types of battery?
Non rechargeable(Alkaline)- chemical reactions stop when one reactant is used up
Rechargeable- chemical reactions reversed when external current supplied
What is a fuel cell?
An electrical cell that is supplied with a fuel and oxygen, and uses energy from the reaction between them to produce electrical energy efficiently.
How does a fuel cell work?
When the fuel enters the cell it becomes oxidised and sets up a potential difference within the cells
What does a hydrogen fuel cell produce?
Hydrogen is oxidized to produce clean water and release energy
What is the equation at the anode for a hydrogen fuel cell?
2H2 -> 4H+ + 4e- Oxidised
Hydrogen loses electrons and H+ ions move to cathode
What is the equation at the cathode for a hydrogen fuel cell?
4H+ + 4e- + 02 -> 2H20 Reduction
Oxygen gains electrons and reacts with H+ ions to make water
What are the advantages of hydrogen fuel cells
They produce water which is not a pollutant
They are lightweight and small
renewable
Can travel further before refueling in comparison to rechargeable cells
No toxic chemical to dispose of at end of cell life
What are the disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cells?
- hydrogen is highly flammable
- hydrogen is sometimes produced for the cell by non-renewable sources
- hydrogen is difficult to store
Why is excess zinc oxide used rather than excess hydrochloric acid?
Excess zinc oxide can be filtered out as it doesn’t dissolve but excess hydrochloric acid cannot be filtered out.