health semester 1 2025
1/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Bones
Key structures that protect and hold the body in place.
Cartilage
Protects the bone and absorbs impact.
Tendons
Connects muscle to bones.
Ligaments
Connects bones to bones.
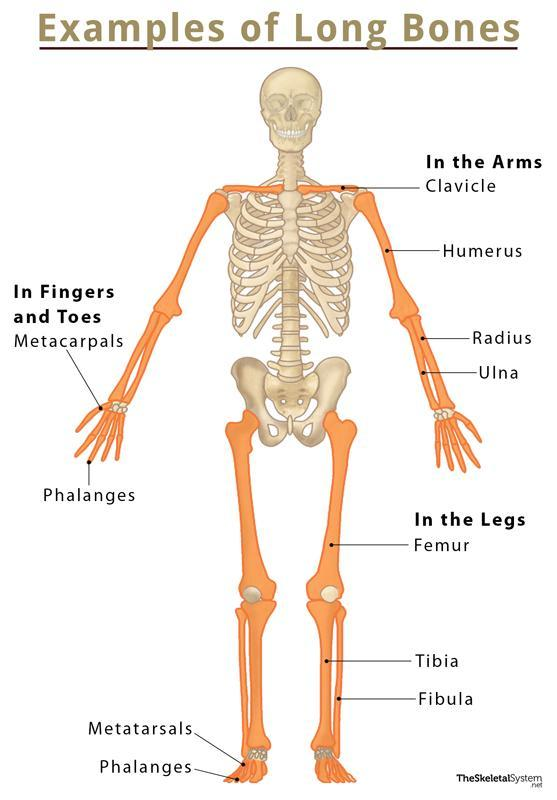
Long bone
Longer bones made to support the body (femur).
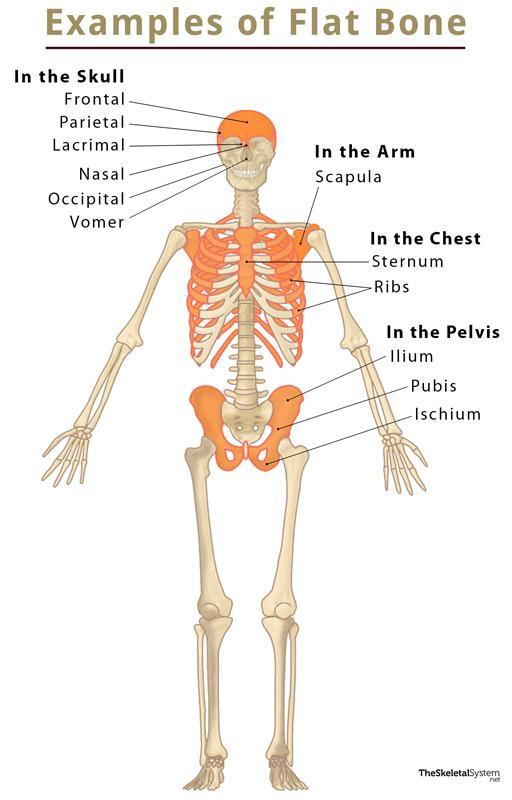
Flat bone
Flat area for muscles to attach (scapula).
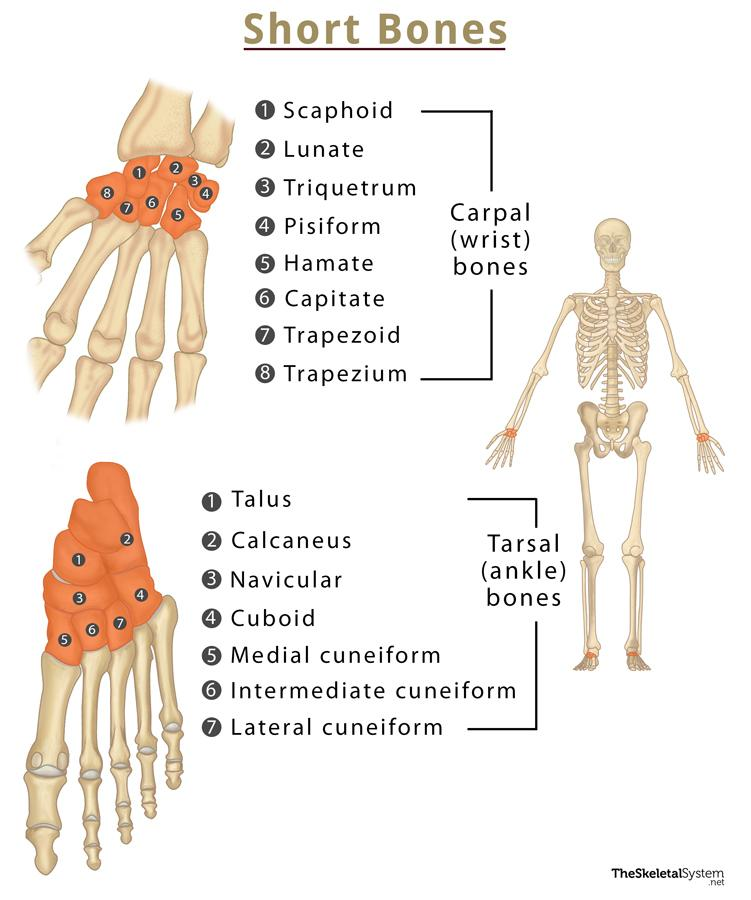
Short bone
Bones that are roughly cubical and provide stability and some movement (carpals).
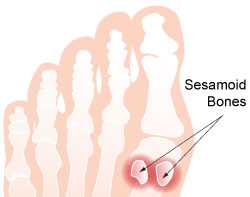
Sesamoid bone
Small bones that protects tendons from stress and wear (patella).
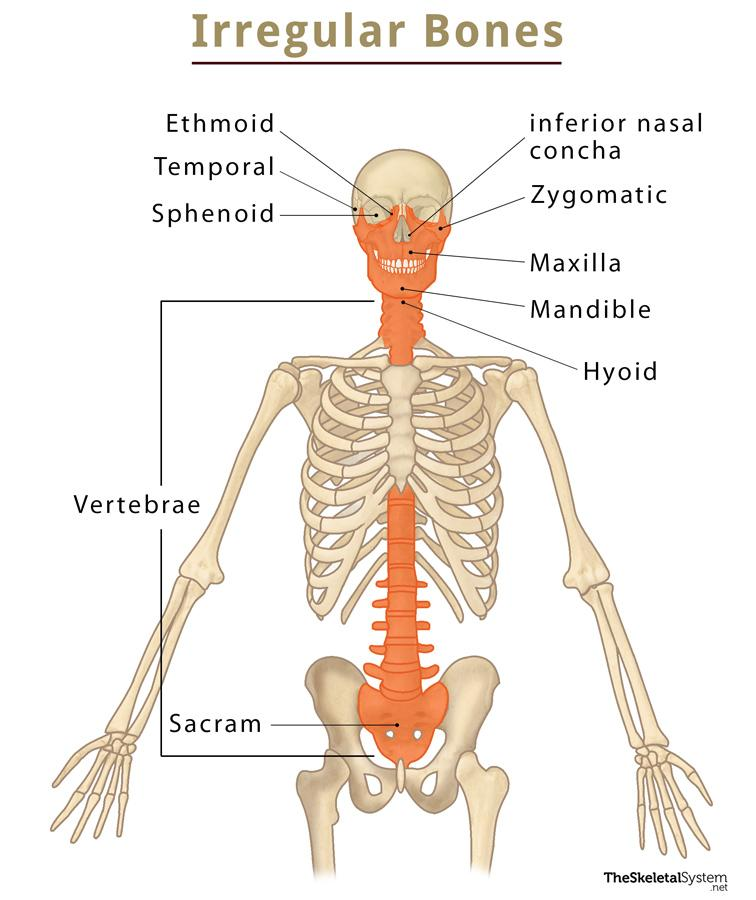
Irregular bone
Have no regular shape (spine).
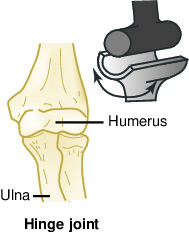
Hinge joint
Allows flexion and extension (elbows & knees).
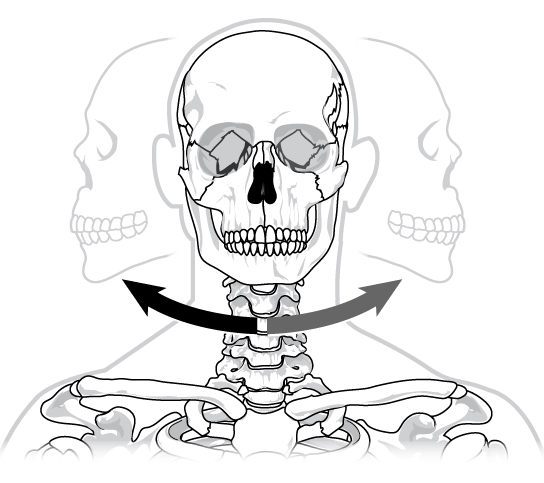
Pivot joint
Rotation of the bone around another (neck & head).
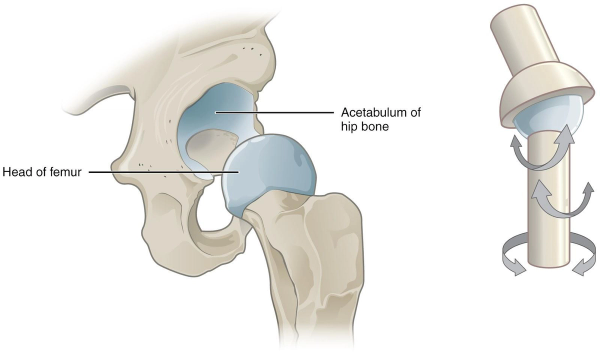
Ball and socket joint
Allows flexion/extension, adduction/abduction, rotation and circumduction (hip & leg).
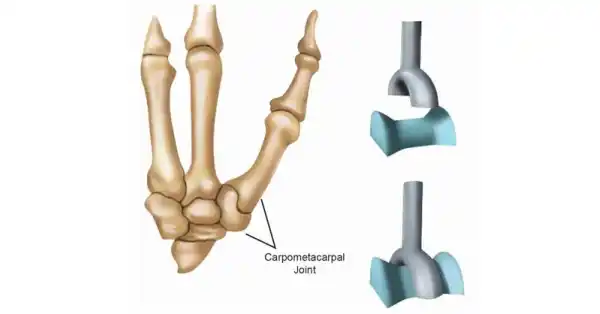
Saddle joint
Allows flexion/extension, adduction (thumb).
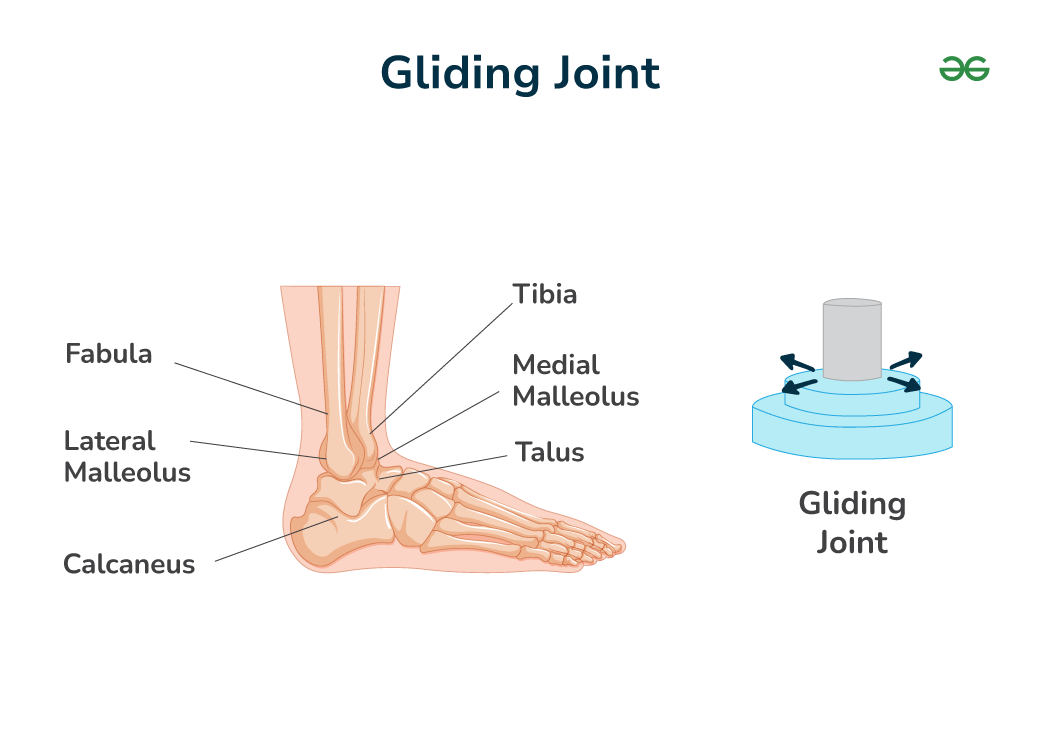
Gliding joint
Allows a gliding movement (wrist).
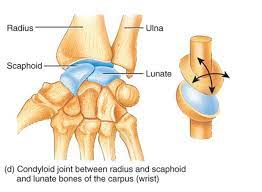
Condyloid joint
Allows flexion/extension and sideways movement (wrist).
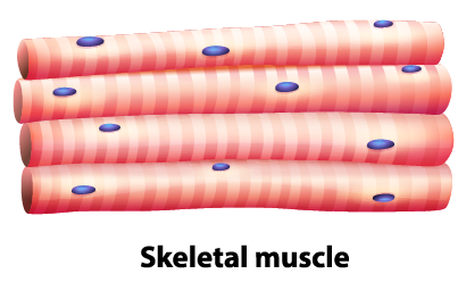
Skeletal muscle
Voluntary muscle that pull on bones to create movement.
Name the three types of joints in the human body.
Immovable fibrous joints, slightly moveable cartilaginous joints, freely moveable synovial joints.
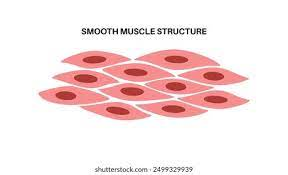
Smooth muscle
Involuntary muscle found on the walls of vital organs.
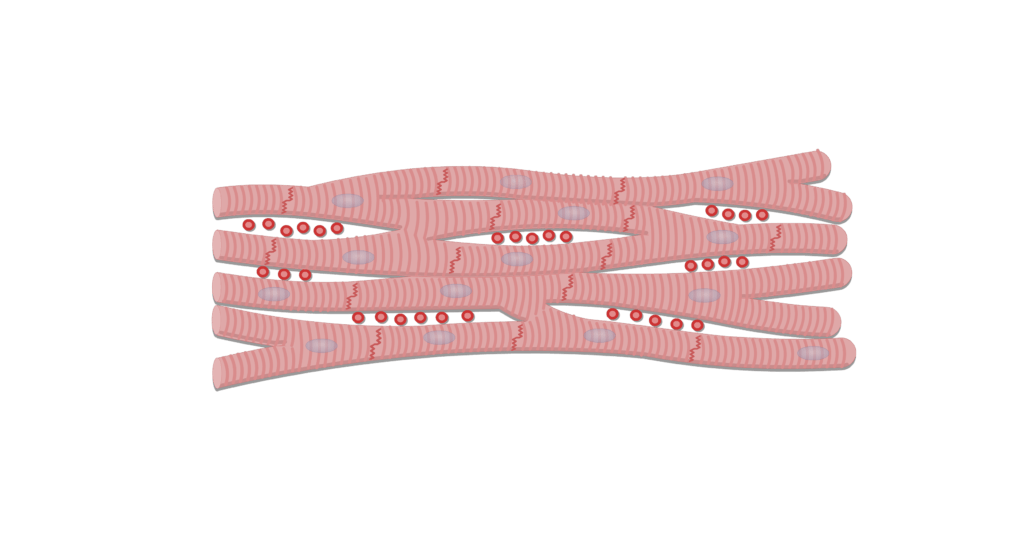
Cardiac muscle
Involuntary muscle found in the heart.
What are the three functions of the muscular system?
Create movement, maintain good posture, maintain bodily functions.
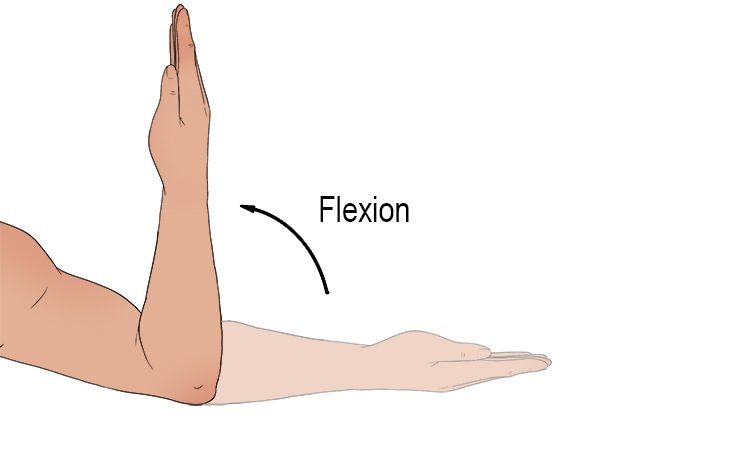
Flexion
Decrease the angle between a joint (bending an arm).
Extension
Increase the angle between a joint (extending arm).
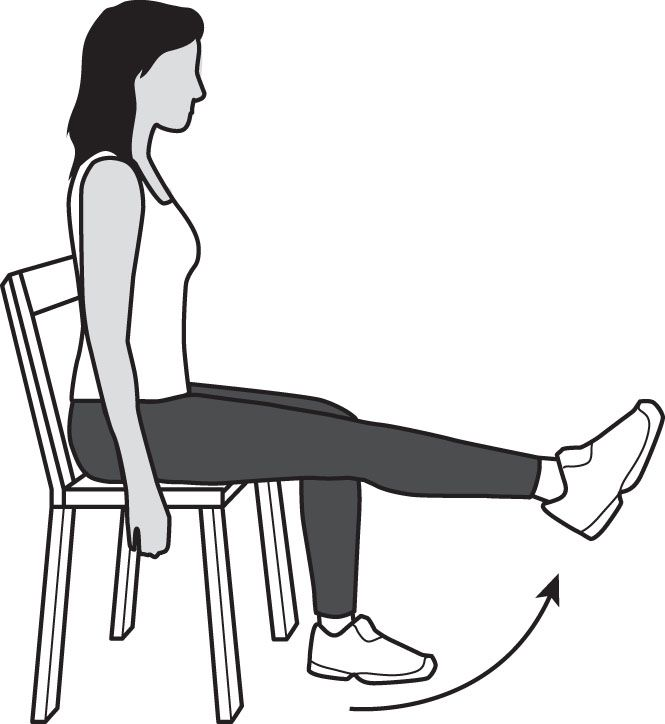
Circumduction
Movement of body part in a circle around joint (windmill stretch).
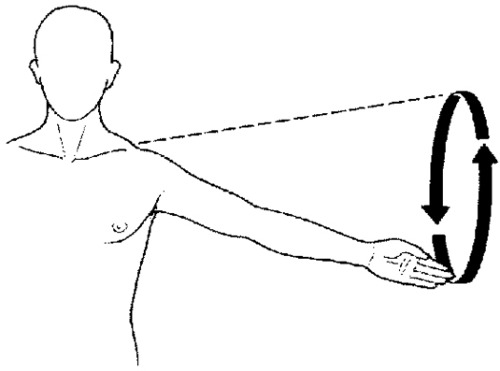
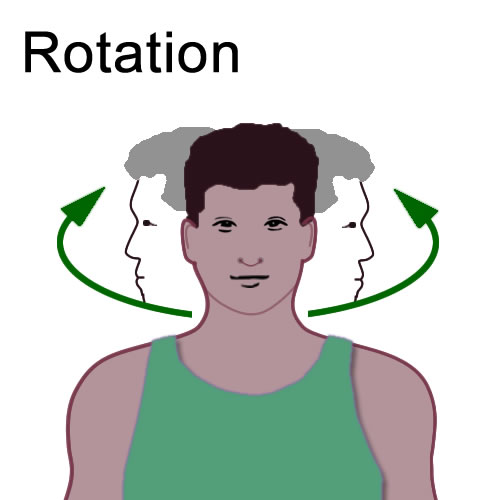
Rotation
Movement of body part around in a line (turning the head).
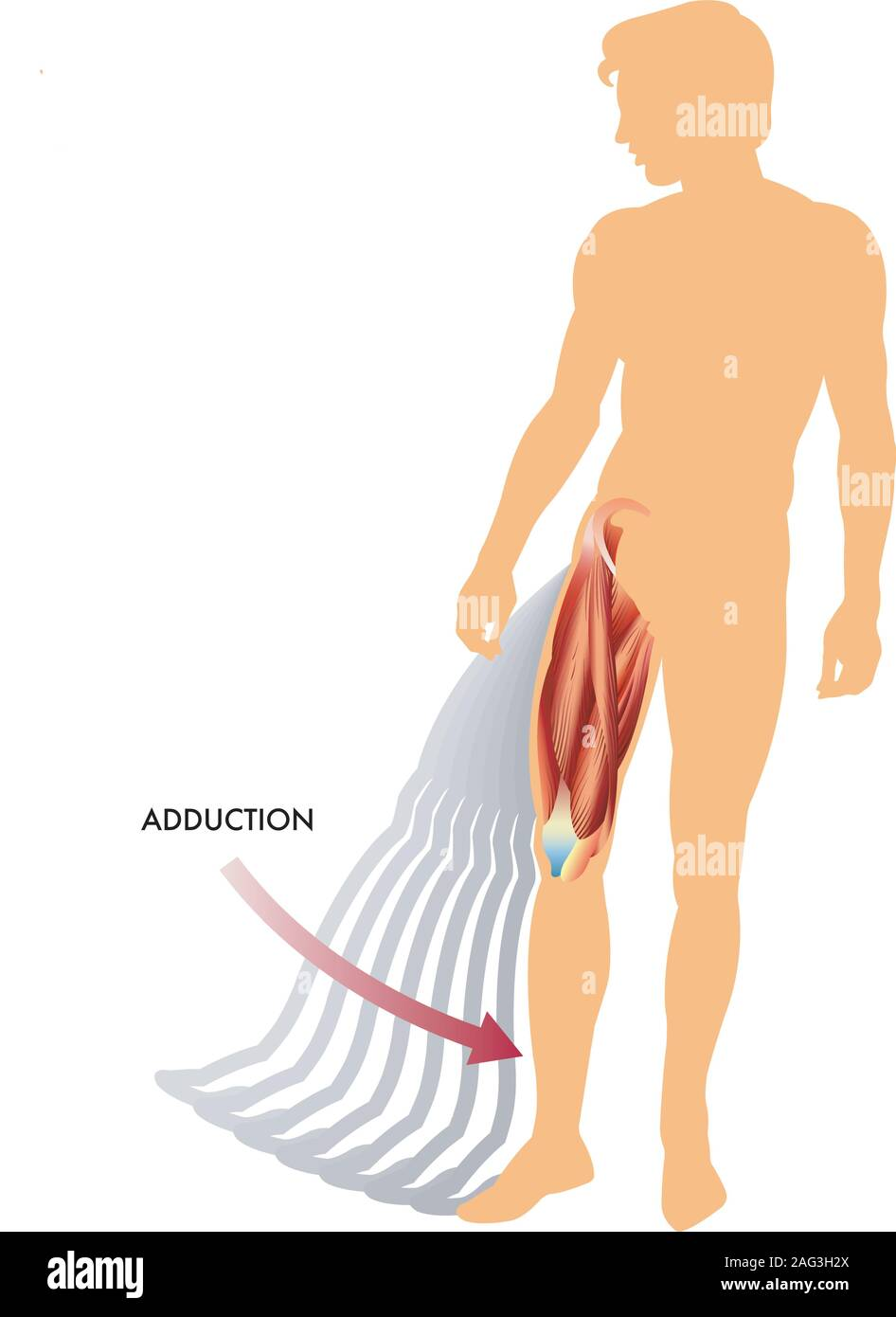
Adduction
Movement of a body part towards the midline of the body (leg raises).
Abduction
Movement of a body part away from the midline of the body (leg raises).