D4 Implant Final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:39 AM on 8/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
1
New cards
Disadvantages of a pano: ____% horizontal and
vertical magnification - 25
2
New cards
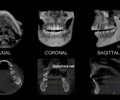
Anatomic planes -
3
New cards
CBCT imaging helps with:
a. Predictability of implant placement
b. imaging of the entire arch \n c. ID bony pathology \n d. All of the above
a. Predictability of implant placement
b. imaging of the entire arch \n c. ID bony pathology \n d. All of the above
D
4
New cards
a. Predictability of implant placement
5
New cards
b. imaging of the entire arch
6
New cards
c. ID bony pathology
7
New cards
d. All of the above - D
8
New cards
CBCT should be used to analyze all of the following except:
9
New cards
a. PA cyst
10
New cards
b. Endodontic pathology
11
New cards
c. Tooth anatomy
12
New cards
d. Fibroma - Fibroma
13
New cards
A \__________________-driven tx plan is created by placing implants in a n ideal relationship to the planned dental restorations and associated supporting bone - prosthetically
14
New cards
Software we use for implants - Invivo
15
New cards
For every 1mm. of palatal positioning, the implant should be placed an additional __mm apically - 1
16
New cards
Depth of implant: \____mm from adjacent CEJ
17
New cards
18
New cards
If implant is placed too deep\= - 3-4
19
New cards
20
New cards
black triangles
21
New cards
Biologic width\= 2.5-3.2mm
22
New cards
23
New cards
24
New cards
25
New cards
\>4mm\= - Challenging and insufficient for development
26
New cards
27
New cards
Insufficiently supported, long term soft tissue complications (deep pockets/recession)
28
New cards
The \_______ platform diameter that fits within the normal root contours should be selected.
29
New cards
30
New cards
The platform should be placed \___mm apically and \___mm lingually to the buccal emergence point. - largest
31
New cards
32
New cards
3,1
33
New cards
What is the key determinant for implant position? - Buccal CEJ or FGM
34
New cards
Presence of interdental papilla
35
New cards
Contact point to crest of bone:
36
New cards
5mm or less
37
New cards
6mm
38
New cards
\>\= 7mm - 100%
39
New cards
56%
40
New cards
27%
41
New cards
Buccal bone thickness- implants should be minimum - 1.5-2mm
42
New cards
Minimum distance between implants.
43
New cards
Between implant and tooth - 3mm
44
New cards
1.5mm
45
New cards
A carrier that transfers the pre-operative plan from a CBCT to the patient for the actual surgery - Digital surgical guide
46
New cards
To achieve an acceptable clinical outcome, the guide should be \________ driven - prosthetically
47
New cards
Conventionally, a \___________ was duplicated and used as a guide for implant placement. - waxed tooth
48
New cards
CAD CAM stands for - Computer aided design
49
New cards
Computer aided manufacture
50
New cards
Printing\= \___________ process
51
New cards
Milling\= \__________ process - additive
52
New cards
subtractive
53
New cards
Uses UV laser to polmerize the drops of resin to desired shape - Sterolithography
54
New cards
Applies drops of polymerizable polymer to the building platform - Triple injecting technology (Polyjet)
55
New cards
Uses a digital projector as a light source to polymerize the liquid resin layer by layer across the platform - Digital light processing (DLP)
56
New cards
Relatively new method uses projecting images in a continuous sequence - Continuous liquid interface production (CLIP)
57
New cards
Before using a surgical guide, what must you do? - Place and glue guide sleeves into the printed part and sterilizing in autoclave
58
New cards
\_______ guide:
59
New cards
2mm sleeves
60
New cards
Guides only the initial osteotomy
61
New cards
No guided kit needed - Pilot drill
62
New cards
Rests over the teeth
63
New cards
Can be used for long span and short span partially edentulous arches - Tooth supported guide
64
New cards
Rests on soft tissue
65
New cards
Used in fully edentulous cases.
66
New cards
Advantages: minimally invasive
67
New cards
Disadvantages: requires anchor pin fixation - Mucosa supported guide
68
New cards
Rests on patient's bone
69
New cards
Fully edentulous cases
70
New cards
Disadvantages: requires anchor pin fixation
71
New cards
**Invasive as the guide is fixed after elevation of mucosa - Bone supported guide
72
New cards
Rests on the bone after flap elevation
73
New cards
Window in the guide guides the level of bone reduction
74
New cards
Anatomage- offers for mandibular cases ONLY
75
New cards
Disadvantages: anchor pins need fixation, hence is invasive - Bone reduction guide
76
New cards
Can virtually extract the teeth
77
New cards
Adv: immediate ext and implant placement cases
78
New cards
Ext or FDP removal accompanied with implant placement. - Extraction guide
79
New cards
Supports zygomatic implants for full edentulous maxillary arches
80
New cards
Requires anchor pin fixation
81
New cards
Zygoma anatomy guided approach - Zygomatic guide
82
New cards
Has base fixation guide (similar to bone reduction guide)
83
New cards
All other guides fit on fixation guide for sequential exts and implant placement
84
New cards
Requires anchor pin fixation
85
New cards
Adv: fully guided, fully guided prosthetic reconstruction, used in DSD - Stackable guide
86
New cards
How close or far off a given set of measurements (observations or readings) are to their true value - Accuracy
87
New cards
How close or dispersed the measurements are to each other. - Precision
88
New cards
Assisted implant surgery showed high trueness and precision. The closer the sleeve to the bone, the more accurate - Static computer
89
New cards
Angulation deviation\- - no statistical difference among the 3 types of guides
90
New cards
Mean deviations between different types of guides were less than \____mm in any direction and less than \___ deg - 2
91
New cards
8
92
New cards
Higher accuracy at the implant head level. The discrepancy was magnified at the \_____ - apex
93
New cards
Are 3D printed surgical guides as accurate at milled? - Yes
94
New cards
Types of dynamic navigation - X-guide
95
New cards
Navident
96
New cards
Robodent
97
New cards
Most scanners are \________ type - non-contact
98
New cards
Set of data points in space, triangulated creating a 3D mesh surface model - Point clouds
99
New cards
Store 3D info as a list vertices joined by edges - OBJ File format
100
New cards
For single, short span sites the accuracy of intra. oral scanners is \____ - high