tissues— cartilage, bone, blood
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
description, function, and location of blood (general)
description: cells and platelets in fluid matrix; function: transports gases, defends against disease, clotting; location: throughout the body in a closed system of blood vessels and heart chambers
description, function, and location of bone (general)
description: cells in solid matrix; function: supports, protects, provides framework; location: bones of skeleton, middle ear
description, function, and location of fibrocartilage (general)
description: cells in solid-gel matrix; function: supports, protects, absorbs shock; location: between bony parts of spinal column, parts of pelvic girdle, and knee
description, function, and location of elastic cartilage (general)
description: cells in solid-gel matrix; function: supports, protects, provides flexible framework; location: framework of external ear and part of larynx
description, function, and location of hyaline cartilage (general)
description: cells in solid-gel matrix; function: supports, protects, provides framework; location: ends of bones, nose, and rings in walls of respiratory passages
define cartilage and its function. what are the characteristics of cartilage connective tissue?
Cartilage is a rigid connective tissue that provides support, protection (of underlying tissues), framework (for many developing bones), and attachments.
Cartilage connective tissues lacks direct blood supply, which results in slow healing and infrequent dividing of chondrocytes. Near cartilage cells obtain nutrients from blood vessels in the perichondrium via diffusion, aided by water.
ECM of cartilage
ECM of cartilage is largely composed of collagen fibers embedded in a solid-gel ground substance, which is rich in chondrocytes (cartilage cells)
describe a cartilaginous structure
a cartilaginous structure is enclosed in a covering connective tissue— the perichondrium
name the 3 types of cartilage
hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage
define hyaline cartilage and its function
hyaline cartilage is the most common type of cartilage. it has very fine collagen fibers in its ECM and looks somewhat like white glass. It is found on the ends of bones in any joint and is the supporting rings of the respiratory passages. Parts of an embryo skeleton begin as hyaline cartilage that bone gradually replaces— important in the development an growth of most bones.
define elastic cartilage and its function
elastic cartilage has a dense network of elastic fibers in its ECM, making it flexible. It provides framework for the external ears and for parts of the larynx.
define fibrocartilage and its function
fibrocartilage contains many cartilage fibers in its ECM, making it a very tough tissue. It often forms pads (e.g. intervertebral discs), functioning as a shock absorber for structures subjected to pressure (e.g. vertebrae, knees, pelvic girdle)
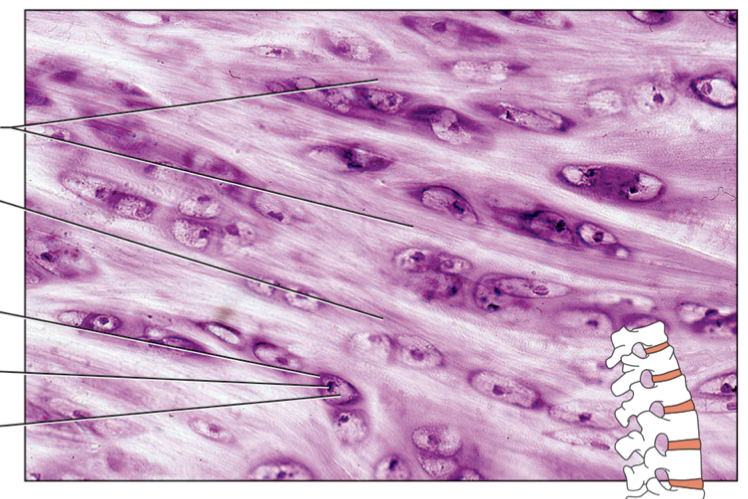
name the components of the connective tissue from top to bottom. name the specific type of connective tissue
in the ECM: collagen fibers, ground substance, lacuna, nucleus, chondrocyte; fibrocartilage
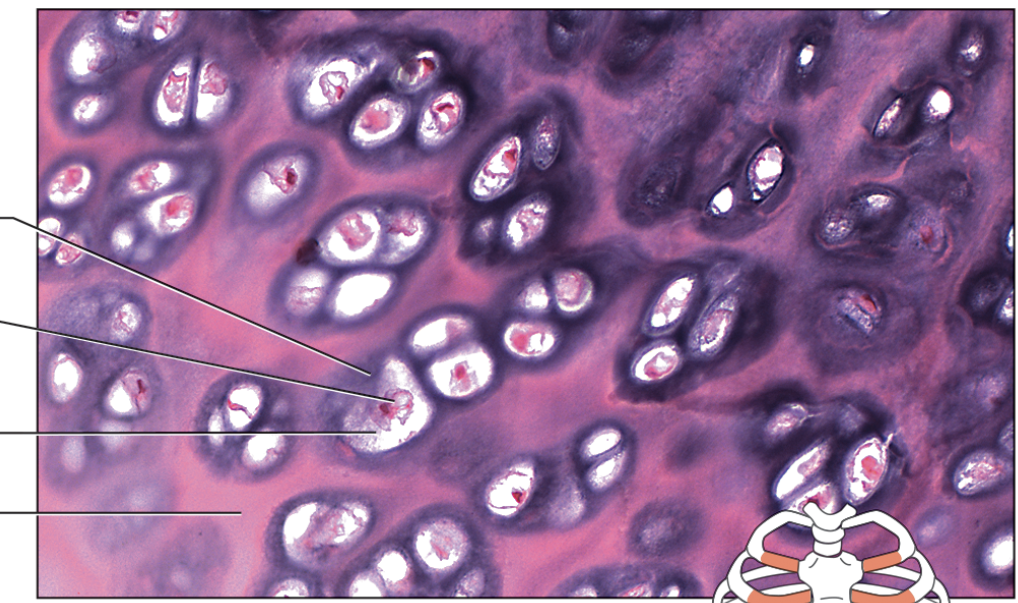
name the components of the connective tissue from top to bottom. name the specific type of connective tissue
lacuna, nucleus, chondrocyte, ECM; hyaline cartilage
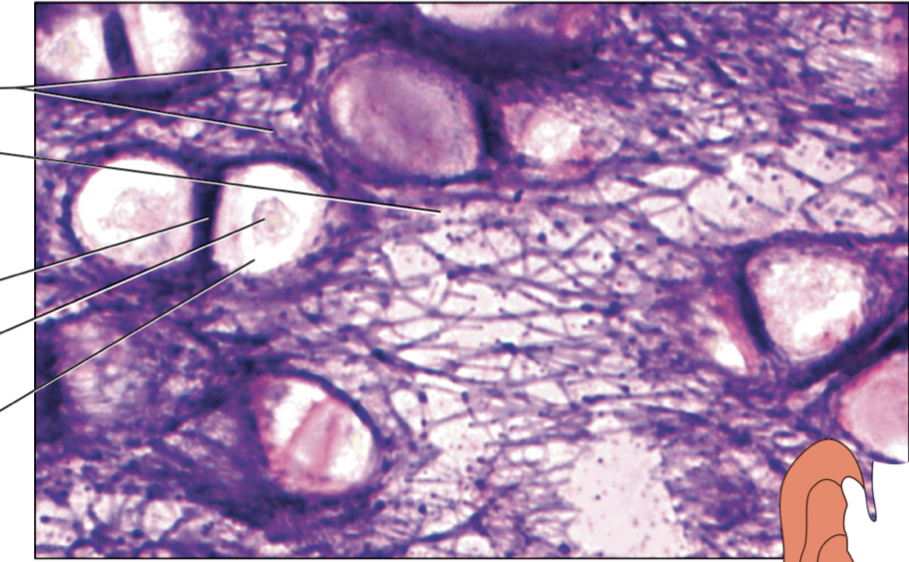
name the components of the connective tissue from top to bottom. name the specific type of connective tissue
in the ECM: elastic fibers, ground substance, lacuna, nucleus, chondrocyte; elastic cartilage
define osseous/bone tissue and its function(s)
osseous tissue is the most rigid connective tissue due to mineral salts (calcium phosphate and calcium carbonates) between cells. Its ECM has many collagen fibers, which are flexible and reinforce the mineral components of bone. It internally supports body structures by protecting vital structures in the cranial and thoracic cavities and is an attachment for muscles. It contains red marrow, and stores and releases inorganic chemicals
name the 2 types of osseous/bone connective tissue
compact and spongy bone tissue
define compact bone and its function(s)
compact bone contains osteoblasts that deposit bone matrix in thin layers which contain blood vessels and osteocytes that are concentrically clustered around a central canal from a cylinder-shaped unit (osteon). Each central canal contains blood vessels so every bone cell is near a nutrient supply. Gap junctions allow materials to move rapidly between blood vessels and bone cells, allowing bone to heal more rapidly than cartilage.
define spongy bone and its function(s)
spongy bone makes up the interior portion of a bone in which bone matrix is deposited around osteocytes, resulting in boney plates with spaces between them. These spaces lighten the weight of the bone and provides spaces for bone marrow
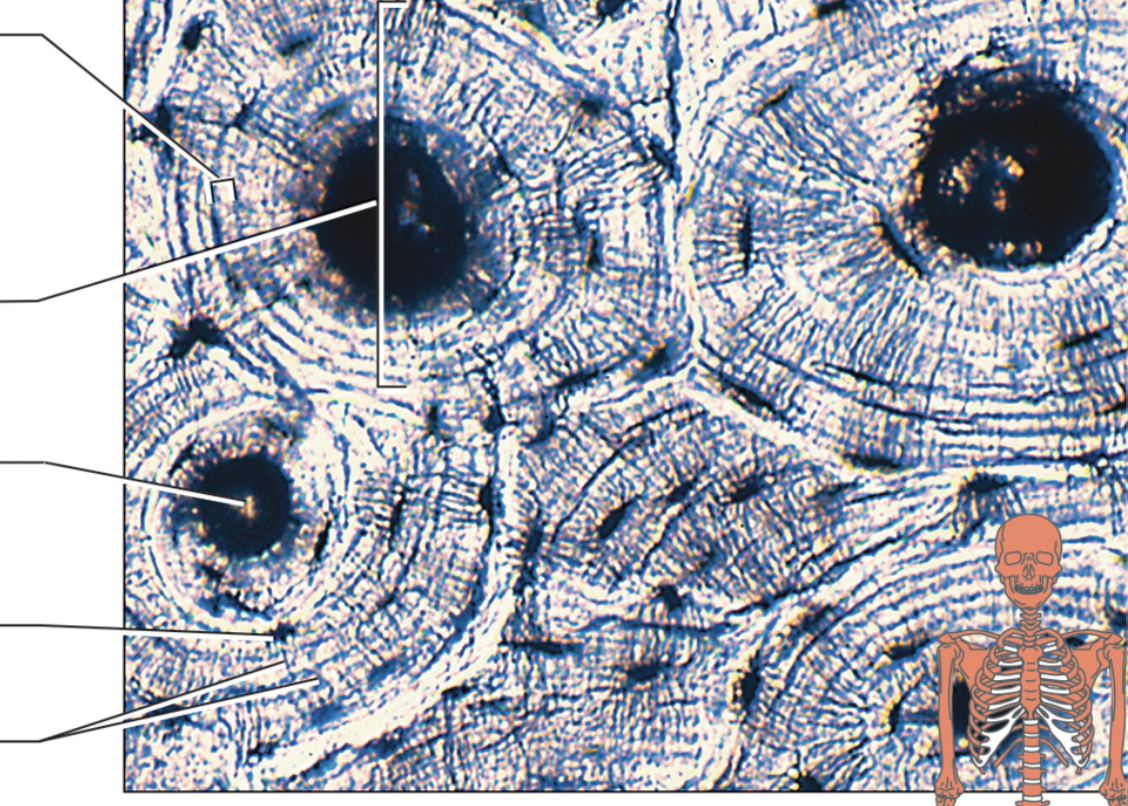
name the components of the connective tissue from top to bottom. name the specific type of connective tissue
osseous/bone connective tissue
define blood and its function(s)
blood consists of red blood cells that function entirely in the blood vessels and white blood cells that typically migrate from the blood through capillary walls to connective tissues where they carry on major activity until they die