E2 - SECONDARY STRUCTURE OF DNA
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Genetic material found in the nucleus
DNA
Makes copy of itself during cell division
DNA
Provide template for RNA biosynthesis or transcription
DNA
Transcribes the genetic information in DNA during RNA biosynthesis or transcription
RNA
Carries and expresses genetic information transcribed via protein biosynthesis or translation in the ribosomes
RNA
DNA structure
Double stranded and Anti-parallel
Components of DNA
Nucleotide, Sugar, Phosphate
Absorbance measurement are measured in these wavelengths
260, 280, and 230
Nucleic acids are seen at this wavelength
260 nm
What is seen in wavelength 260 nm
Presence of aromatic nitrogenous bases (purines and pyrimidines)
Effect of denaturation in absorbance reading in 260 nm
Higher reading due to hyperchromic effect (helix unwinding)
Primary contaminants of Nucleic acids
Proteins
Proteins are seen at what wavelength
280 nm
What is seen in 280nm
Aromatic amino acids Trp, Phe, and Tyr
How to compute for the concentration of DNA
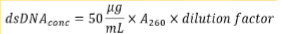
Relative purity can be determined using
A260/A280
Range for good quality nucleic acid in A260/280
1.8 - 2.0
Pure DNA at A260/280
1.8
A260/280 reading lower than 1.8 indicates
Increased contamination of protein
A260/280 reading higher than 1.8 indicates
Contamination by RNA or denatured DNA
Assess the effect of changes in pH on the structural integrity of DNA, reflecting helix-to-coil transition
Viscometry
Factors affecting viscosity in this experiment
Moelcular size/shape and DNA concentration
Formula for Viscosity
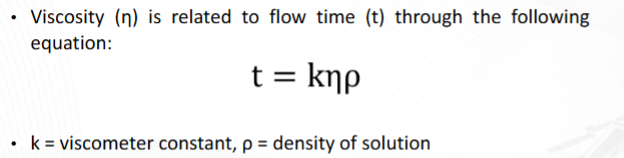
Formula for relative viscosity
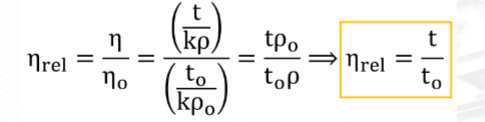
Formula for intrinsic viscosity
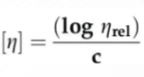
Phosphate group binds to one nucleotide to another through
condesation reaction
bond of phosphate and nculeotide
phosphodiester bond 3’ 5’
why is it challenging to extract DNA compared to proteins
DNA is usually packed in a compact space in the nucleus, deep inside the cell
Why is it difficult to extract DNA completely intact
It is a very long and fragile biomolecule
Factors affecting DNA stabilizing
pH
Temperature
Ionic stregth
Cellular conditions
Mechanical stress
What does pH stabilize
Nucleotides
Ideal pH of H bonds
pH 4 - 10
Ideal pH of Phosphodiester linkages
pH 3 - 12
Ideal pH of N-glycosidic bonds to purine bonds
> pH 3
Temperature where DNA unwinds
80 - 90 C
Temperature where phosphodiester linkages and N-glycosidic bonds breask
Higher than 100C
Ideal ionic stregths for DNA
< 0.05 M weakens H-bonding between complementary strands of DNA
Factors to look into lysis protocol
DNA nucleases must be deactivated and other contaminants must be seperated
Detergents use
Lysing certain membranes and denatrues enzymse
Proteinases use
Degrage nucleases
Chelating agents use
Sequester the metal cofactor of nucleases to deactivate them
RNAses use
Degrade RNA to lower RNA contamination
Where should DNA be stored
In a solution
What happens to a dry DNA
undergoes denaturation
Important thing to consider for mechanical stress
Grinding, shaking, stirring may cause cleavage (shearing or scisson) of DNA chains making the isolated strands shorter or damaged
General protocol for DNA isolation
Lysis/Homogenization
Removal of contaminatns
Precipitation of DNA
Storage
How is DNA precipitated
Adding ice-cold ethanol or isopropyl alcohol
Solution used to store DNA
SSC buffer
Why is SSC buffer used
Maintains DNA stability
Reduces ionic interaction of histones and DNA backbone
Has lower pH to maintain positive charge of histones
Temperature ideal for protein denaturaing
60 C
SSC buffer pH
8
Why is SDS used
protein denaturation, disruption of ionic interaction betwen histones and DNA, inactivated of enzymes
NaCl use
Helps competely dissociate DNA-histone complex and percipitation by increasing inonic strength
Meat tenderizer use
Proteinase, deactivating nucleases
How does nuclease degrade DNA
Cleaves phosphodiester bond
Use of isoamyl alcohol or phenol-chlorofom
Improve phase separation between organic and aqueous layers and remove polar contaminants
EDTA use
Inactivates remaining enzymes, chelates Mg and Ca
Cold alcohol use
Precipitation of DNA, lowers dielectric constant of the solvent by introducing a lower temperature, lowering solubility of DNA
Importance of cold temperatures
Preserves DNA and minimize enzymatic activity
How to compute for protein concentration
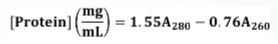
Principle for 320 measurement
Turbidity correction
Purity measurement with turbidity correction
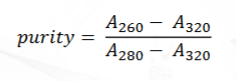
What structure of DNA correlates to decreased viscosity
Coiled DNA
What happens when DNA is neutralized
Denatured DNA should refold back into a double helix
What happens to the viscosity of DNA after adding denaturants
Decreaes