Unit 8: Topic 5, 6, and 7 - Community Ecology, Biodiversity, and Disruptions
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
1
New cards
community
* a group of populations of different species living closely and capable of interacting
2
New cards
habitat
* a place or part of an ecosystem occupied by an organism
3
New cards
ecological niche
* the role and position a species has in its environment
* **fundamental niche:** the niche potentially occupied by the species if there were no limiting factors (predators, competitors, etc)
* realized niched: the portion of the fundamental niche the species actually occupies
* **fundamental niche:** the niche potentially occupied by the species if there were no limiting factors (predators, competitors, etc)
* realized niched: the portion of the fundamental niche the species actually occupies
4
New cards
interspecific interactions
* interactions of individuals from one species with individuals of another species
* competition
* predation
* herbivory
* symbiosis (parasitism, mutualism, commensalism)
* facilitation
* competition
* predation
* herbivory
* symbiosis (parasitism, mutualism, commensalism)
* facilitation
5
New cards
competition
* \
* - / - relationship where individuals of different species compete for limited resources
* competitive exclusion principle
* - / - relationship where individuals of different species compete for limited resources
* competitive exclusion principle
6
New cards
competitive exclusion principle
* two species competing for the same resource cannot coexist permanently
* the competitor with even a slightly better advantage will eliminate the inferior competitor
* the competitor with even a slightly better advantage will eliminate the inferior competitor
7
New cards
niche partitioning
* natural selection drives competing species into different patterns of resource use, or different niches
8
New cards
predation
* + / - relationship where one species (predator) kills and eats the other species (prey)
* adaptations of both predators and prey have been refined by natural selection
* **cryptic coloration:** camouflage
* **Batesian mimicry:** harmless species mimics a harmful one
* **mullein mimicry:** two or more bad-tasting species resemble each other
* adaptations of both predators and prey have been refined by natural selection
* **cryptic coloration:** camouflage
* **Batesian mimicry:** harmless species mimics a harmful one
* **mullein mimicry:** two or more bad-tasting species resemble each other
9
New cards
herbivory
* + / - relationship where one organism eats part of a plant or alga
10
New cards
symbiosis
* when 2 or more species live in direct contact with one another
* parasitism
* mutualism
* commensalism
* parasitism
* mutualism
* commensalism
11
New cards
parasitism
* + / -
* when one organism (parasite) derives nourishment from another (host)
* when one organism (parasite) derives nourishment from another (host)
12
New cards
mutualism
* + / +
* when both organisms benefit from the relationship
* when both organisms benefit from the relationship
13
New cards
commensalism
* + / 0
* when one organism benefits and the other is neither harmed nor benefitted
* when one organism benefits and the other is neither harmed nor benefitted
14
New cards
facilitation
* + / + OR 0 / +
* when one species has a positive effect on the survival and reproduction of another without intimate association of symbiosis
* common in plant species (i.e. some plants make soil more hospitable for other plant species)
* when one species has a positive effect on the survival and reproduction of another without intimate association of symbiosis
* common in plant species (i.e. some plants make soil more hospitable for other plant species)
15
New cards
species diversity
* aka biodiversity
* the variety of different organisms within a community
* **species richness:** the number of **different** species
* **relative abundance:** the **proportion** each species represents of all individuals in the community
NOTE: biodiversity boosts ecosystem productivity; the **greater** the biodiversity in an ecosystem, the **more resilient** it is
* the variety of different organisms within a community
* **species richness:** the number of **different** species
* **relative abundance:** the **proportion** each species represents of all individuals in the community
NOTE: biodiversity boosts ecosystem productivity; the **greater** the biodiversity in an ecosystem, the **more resilient** it is
16
New cards
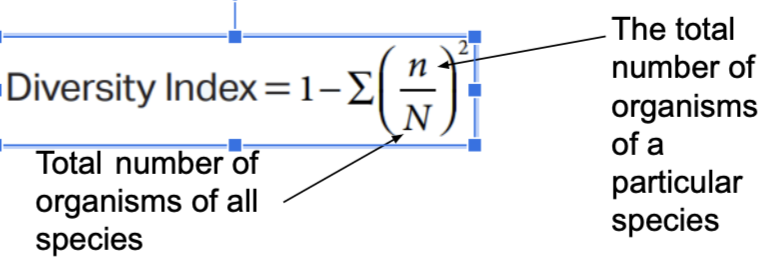
Simpson’s diversity index
* calculate diversity based on species richness and relative abundance
* high diversity index means high biodiversity
* low diversity index means low biodiversity
* high diversity index means high biodiversity
* low diversity index means low biodiversity
17
New cards
invasive species
* organisms that become established outside of their native range/ecosystem, usually by human activity
* ex: a ship brining produce from another country may have insects in the crates holding the produce
* causes harm to the environment
* grow and reproduce quickly
* the intentional or unintentional introduction of an ________________ can allow the species to exploit a new niche that is free of predators and competitors
* ex: a ship brining produce from another country may have insects in the crates holding the produce
* causes harm to the environment
* grow and reproduce quickly
* the intentional or unintentional introduction of an ________________ can allow the species to exploit a new niche that is free of predators and competitors
18
New cards
keystone species
* not usually abundant, but other species in an ecosystem rely on them because of their important ecological niches
* ex: coral
* Coral reefs serve as a _______________ because many other organisms rely upon it as a source of food and protection
* ex: honey bees
* bees are a ______________ because they serve as pollinators
* contribute to maintaining the diversity of the ecosystem
* if ______________ were to be removed from an ecosystem it would have a rippling effect
* often ecosystems collapse
* ex: coral
* Coral reefs serve as a _______________ because many other organisms rely upon it as a source of food and protection
* ex: honey bees
* bees are a ______________ because they serve as pollinators
* contribute to maintaining the diversity of the ecosystem
* if ______________ were to be removed from an ecosystem it would have a rippling effect
* often ecosystems collapse
19
New cards
disturbance
* an event that changes a community by removing organisms from it or altering resource availability
* fires, droughts, human activities, etc.
* fires, droughts, human activities, etc.
20
New cards
ecological succession
* the gradual process by which the species composition of a community changes and develops over time after a disturbance
* primary succession
* secondary succession
* primary succession
* secondary succession
21
New cards
primary succession
* a series of changes on an entirely new (previously lifeless) habitat that has not been colonized
* ex: gradual growth of plants
* ex: gradual growth of plants
22
New cards
secondary succession
* a series of changes that clears an existing community, but leaves the soil intact
* ex: wild fire
* ex: wild fire
23
New cards
human disturbances
* human activity is the strongest disturbance to an ecosystem
* the main threats to biodiversity are:
* habitat loss
* invasive species
* overharvesting
* global change
* have lead to a significant increase in the number of **endangered species**
* the main threats to biodiversity are:
* habitat loss
* invasive species
* overharvesting
* global change
* have lead to a significant increase in the number of **endangered species**
24
New cards
habitat loss
* single greatest threat to biodiversity
* agricultural development and urbanization
* clear cutting, cattle grazing, farmland
* agricultural development and urbanization
* clear cutting, cattle grazing, farmland
25
New cards
overharvesting
* organisms are harvested faster than their population can rebound
* harvesting of ivory in elephants (now banned)
* overfishing
* harvesting of ivory in elephants (now banned)
* overfishing
26
New cards
global change
* alteration to climate, atmospheric chemistry, and ecological systems that reduce the capacity of Earth to sustain life
* air/water pollution
* acid rain
* CO2 emissions
* ocean acidification
* air/water pollution
* acid rain
* CO2 emissions
* ocean acidification
27
New cards
biogeographical factors
* large scale factors that contribute to a range of diversity observed
* **latitude:** species are more diverse in tropics than at the poles due to climate
* **area:** larger areas are more diverse because they offer greater diversity of habitats
* **latitude:** species are more diverse in tropics than at the poles due to climate
* **area:** larger areas are more diverse because they offer greater diversity of habitats
28
New cards
pathogens
* disease causing organisms and viruses
* have the most effect on new habitats or ecosystems with less biodiversity
* have the most effect on new habitats or ecosystems with less biodiversity