Media Studies Terminology
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
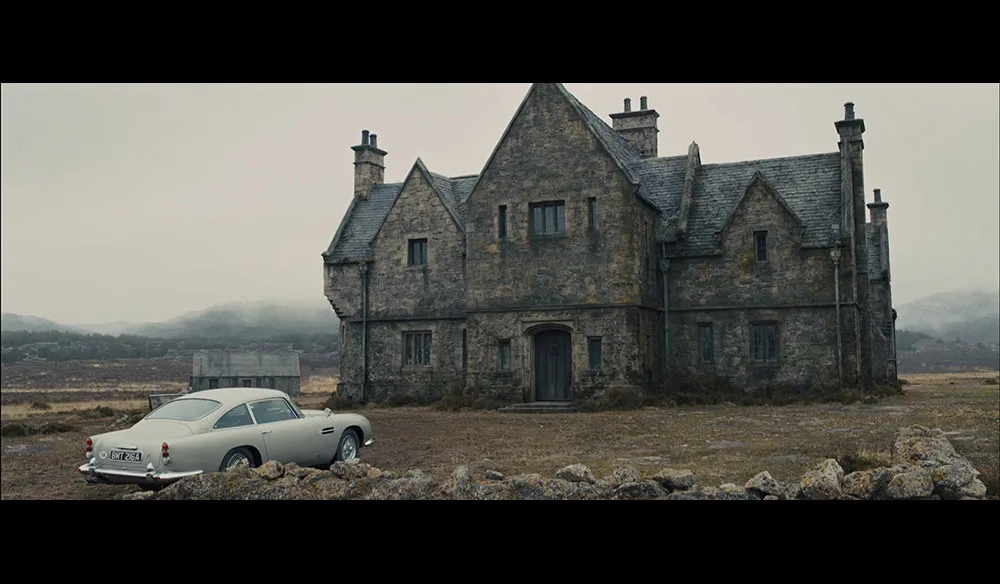

What kind of shot is this?
ESTABLISHING SHOT
Used to set the scene, showcase setting for details
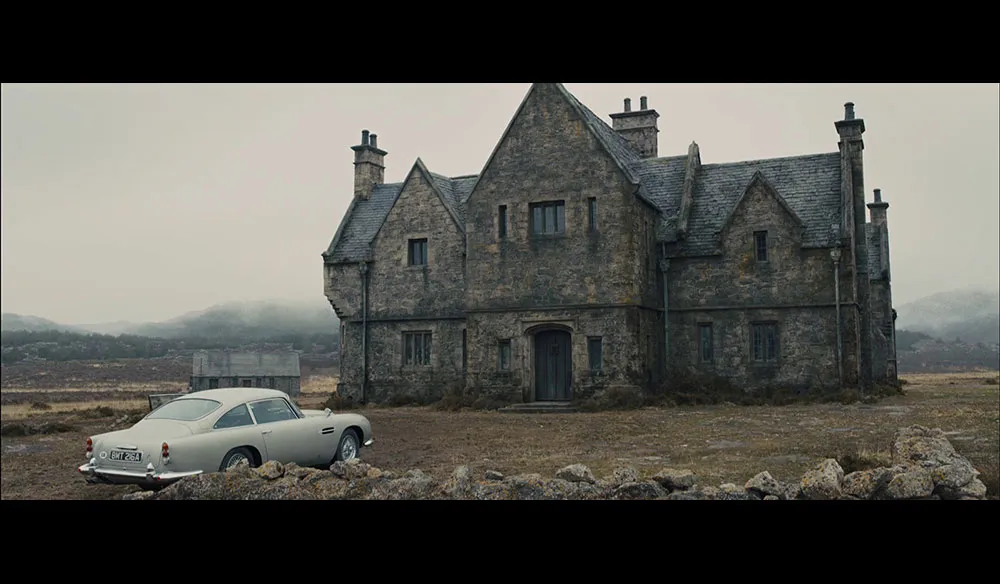


What kind of shot is this?
MASTER SHOT
Similar to an establishing shot, it sets up the scene by showing KEY SIGNIFIERS. Establishing shot = showcases location & master shot = the main characters.
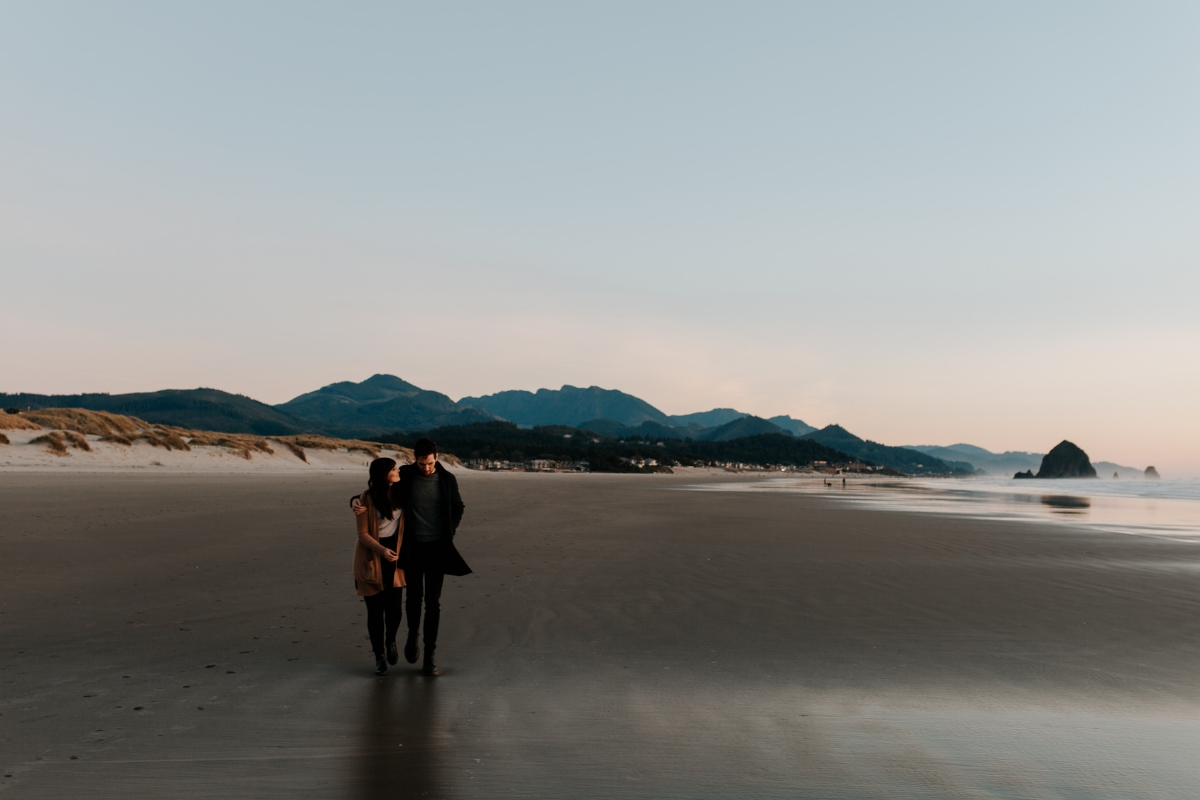


What kind of shot is this?
LONG SHOT
A view of a scene that is shot from a considerable distance, so that people appear as indistinct shapes
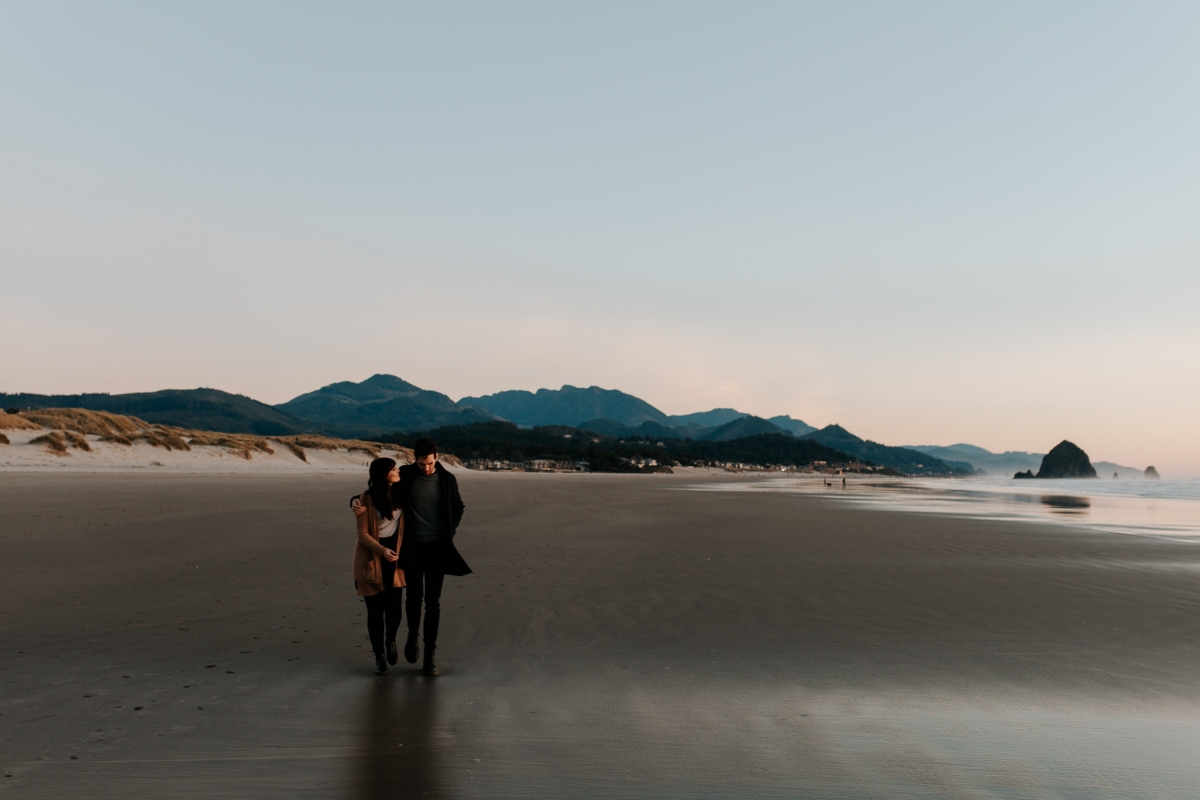


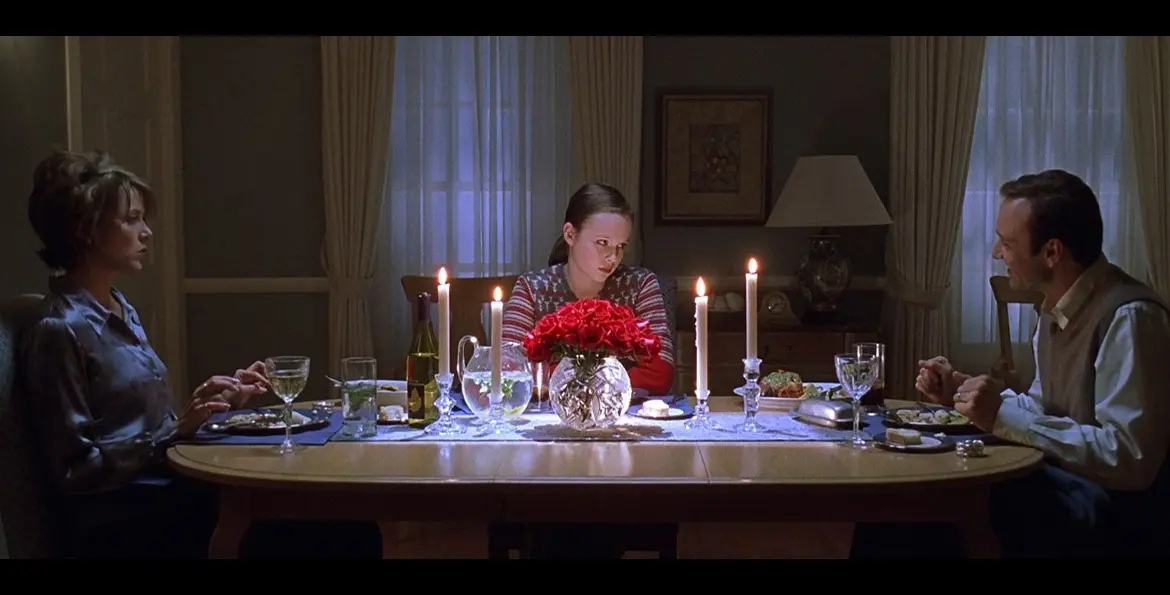
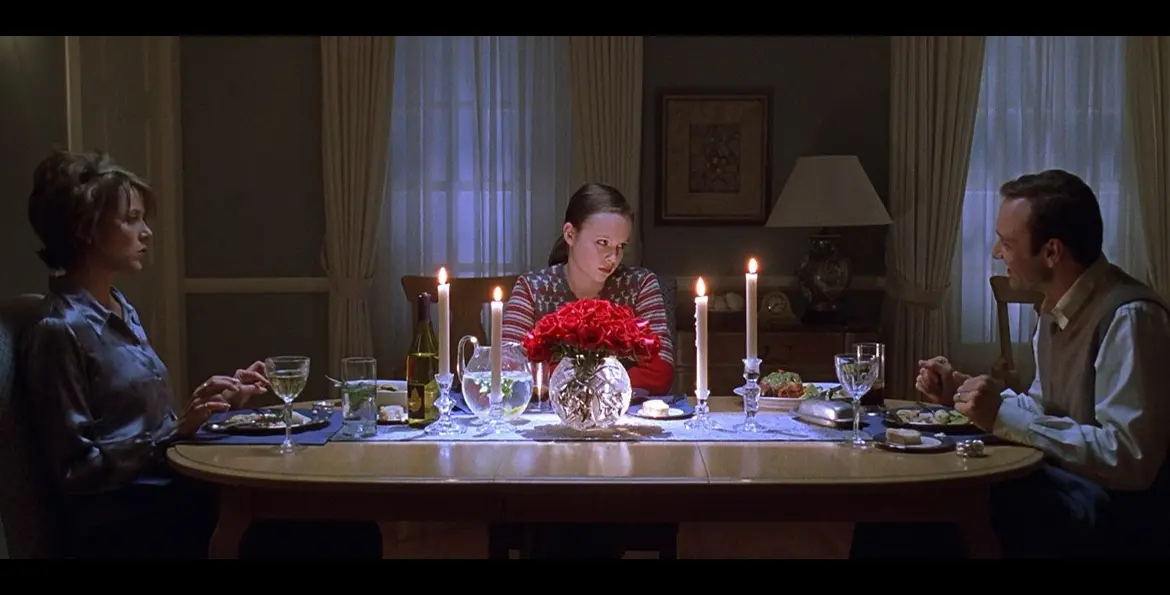
What kind of shot is this?
MEDIUM SHOT
Shows a character to waist up, can also be used in a 2 shot (2 ppl) or 3 shot (3 ppl)
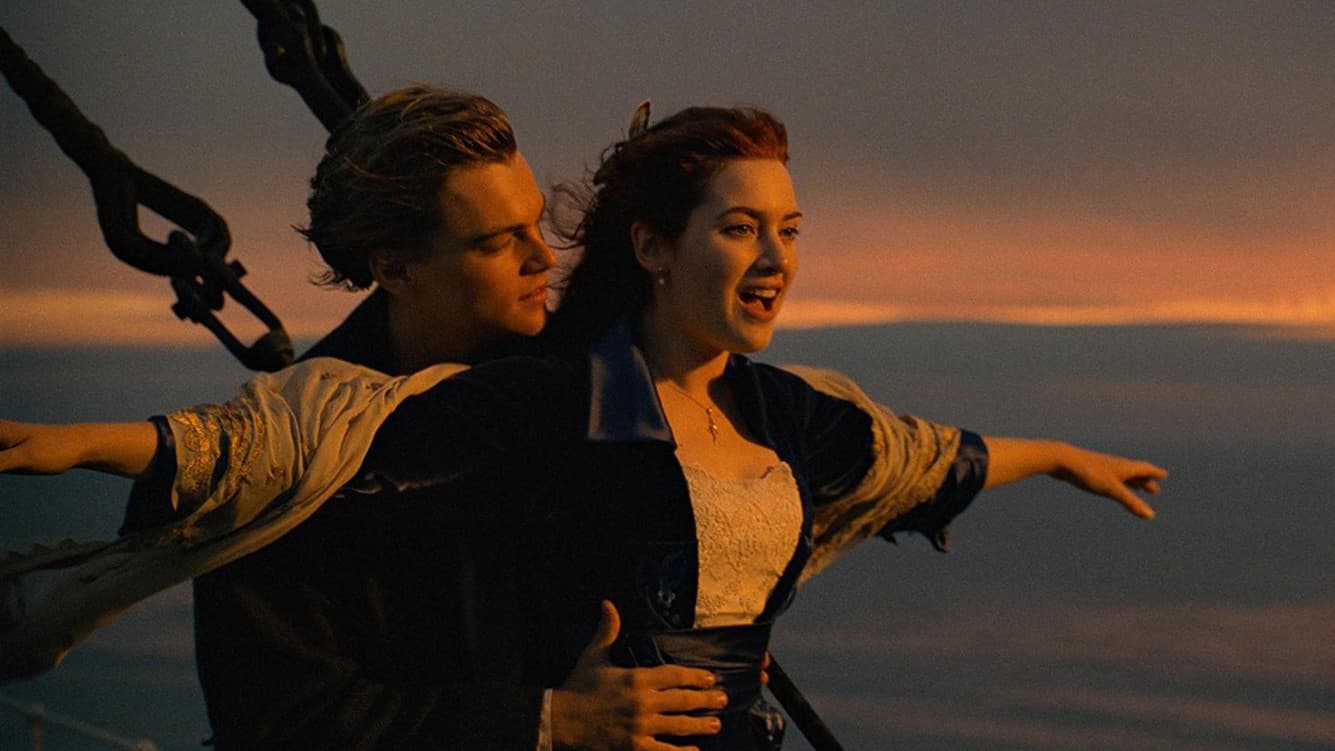

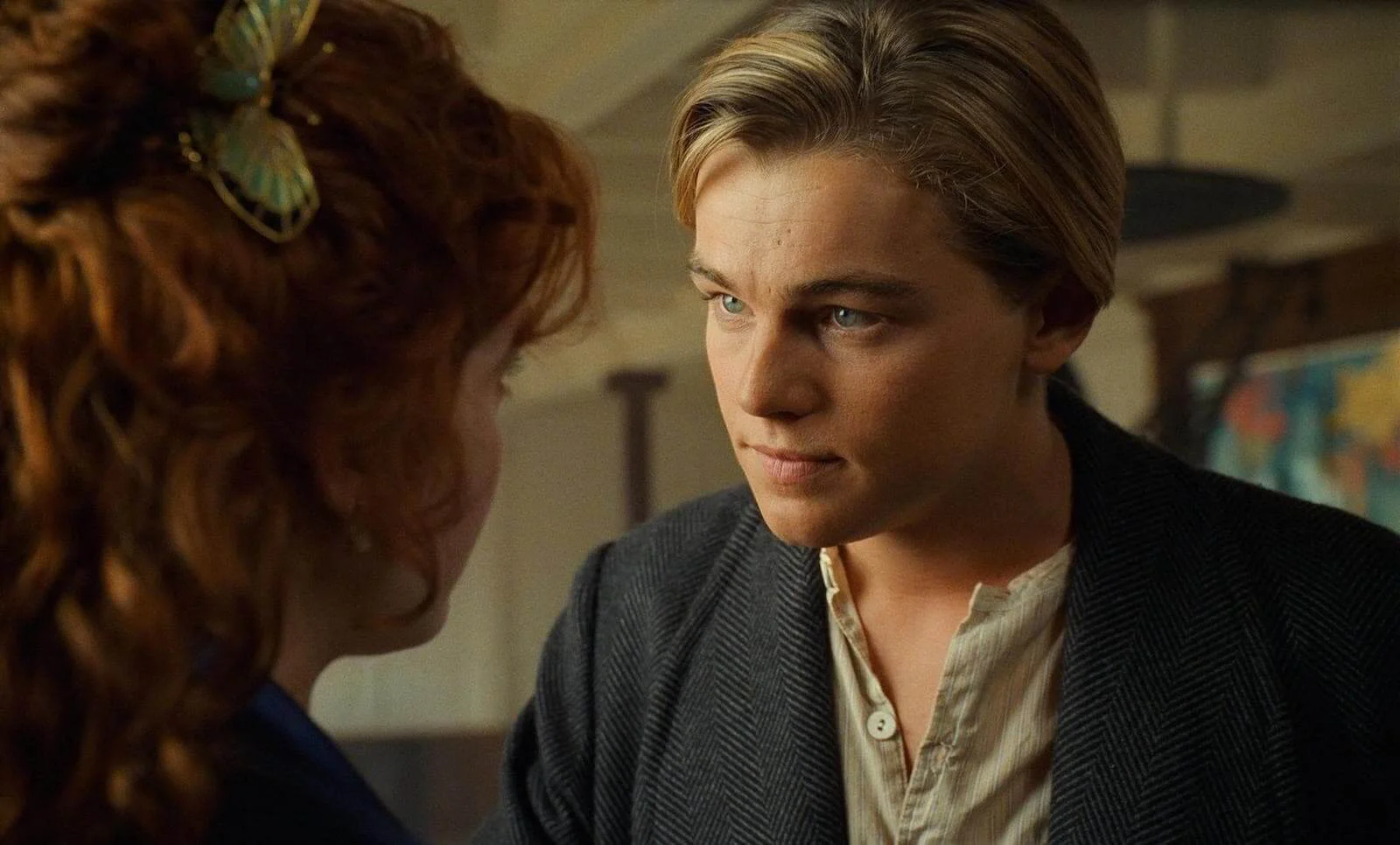
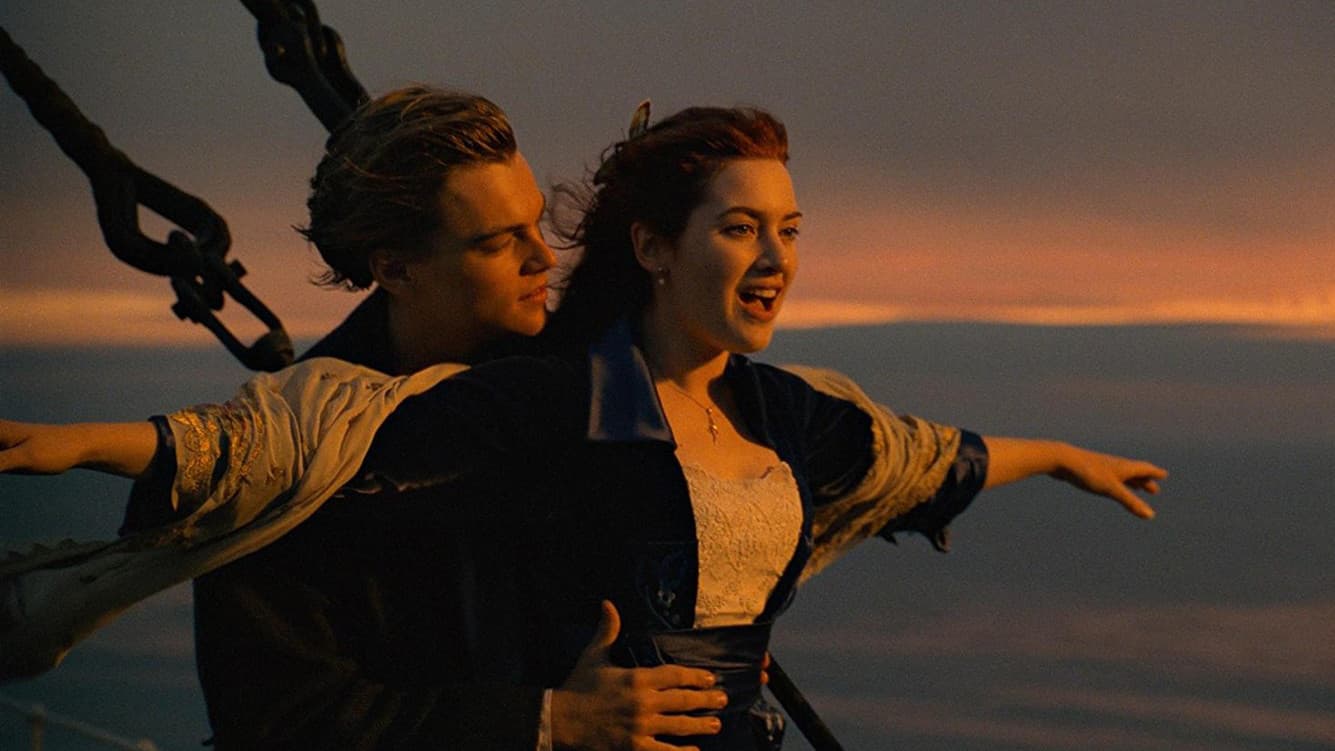
What kind of shot is this?
OVER THE SHOULDER SHOT
Often used to make the audience feel as though they are included in the conversation, a form of a POV and can also be used to create tension.
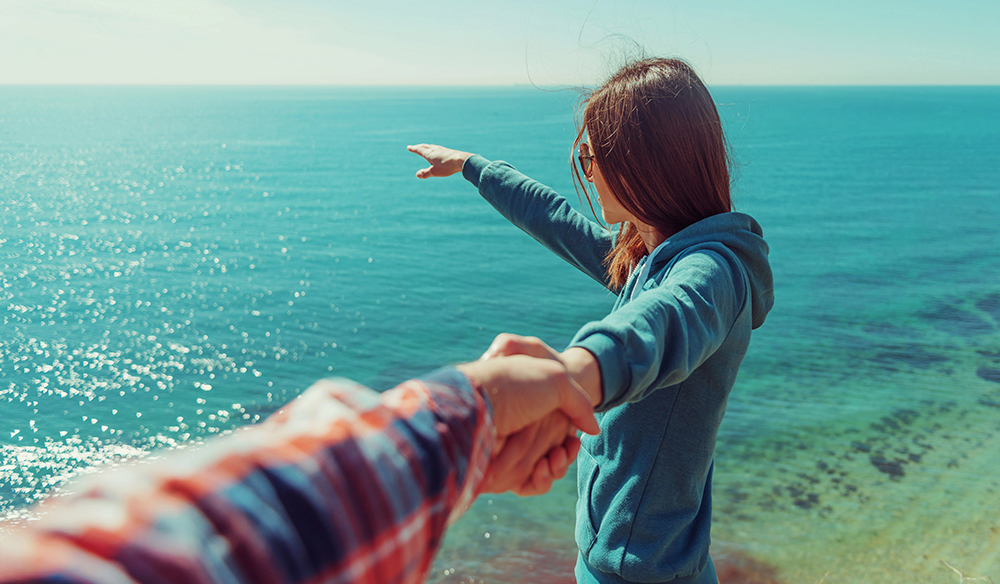
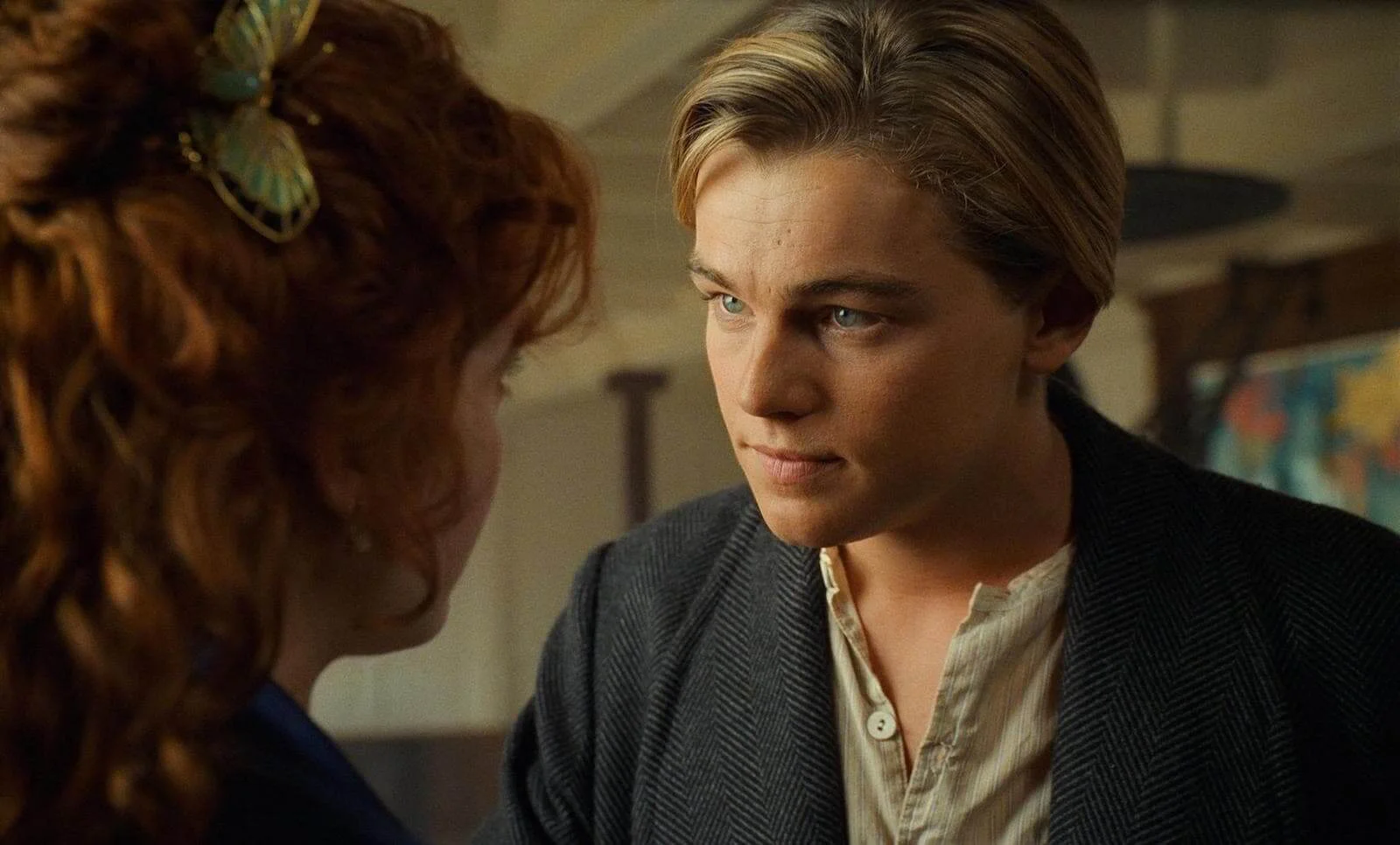

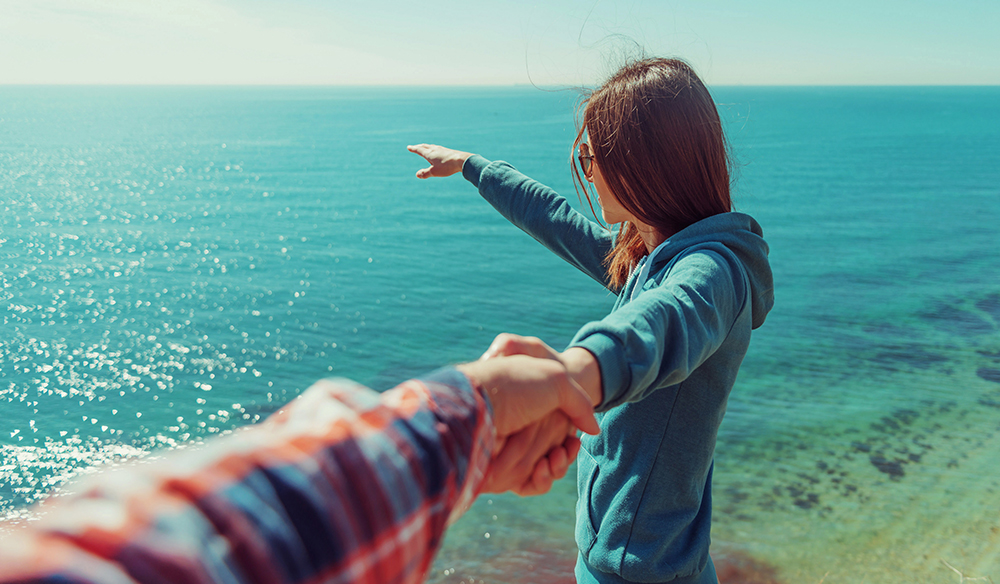
What kind of shot is this?
POINT OF VIEW SHOT
Taken from the view of the person looking/speaking.
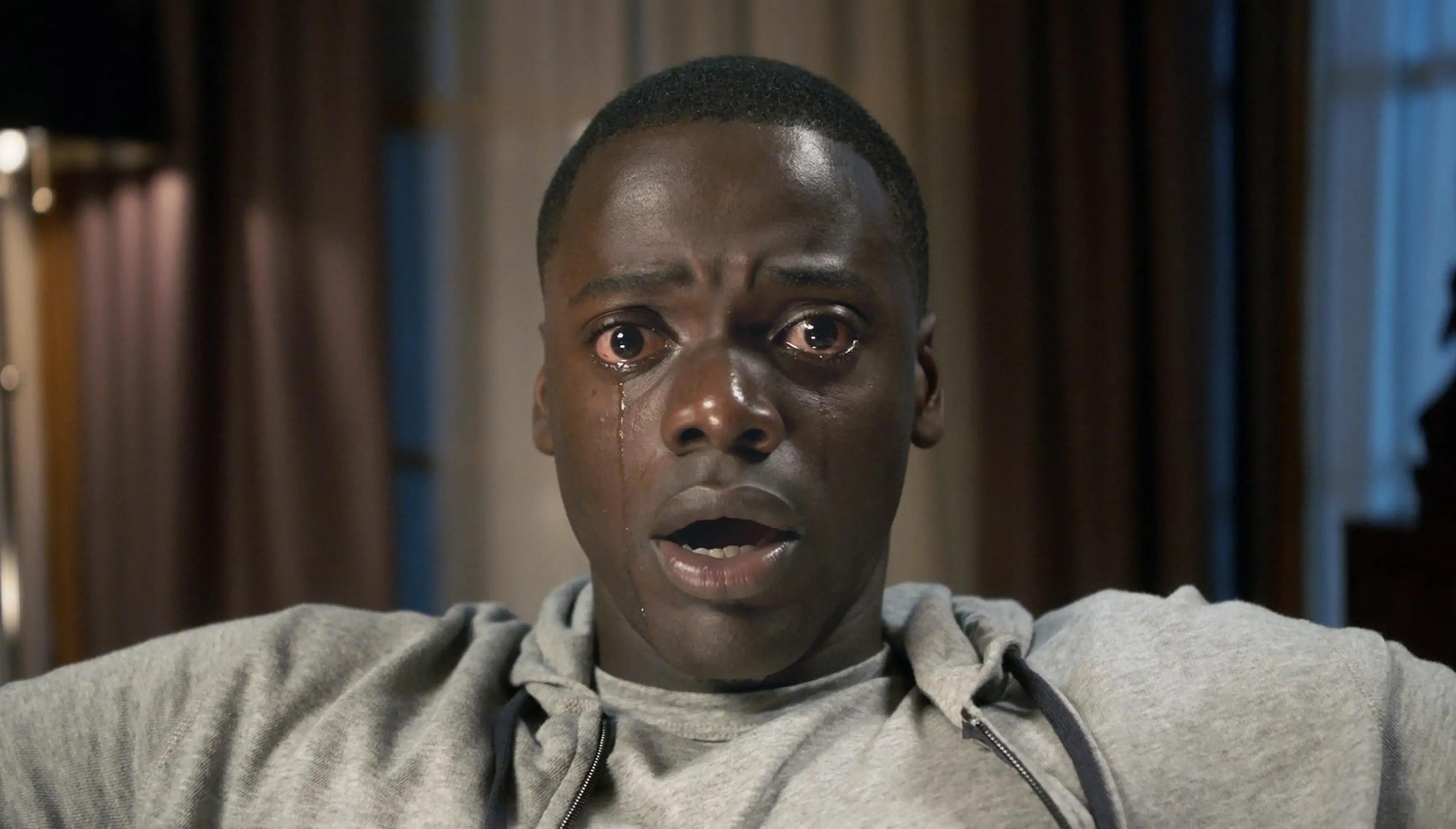


What kind of shot is this?
CLOSE UP SHOT
Shows a close range of a person or thing to draw attention to it. Typically facial expressions to show emotions.
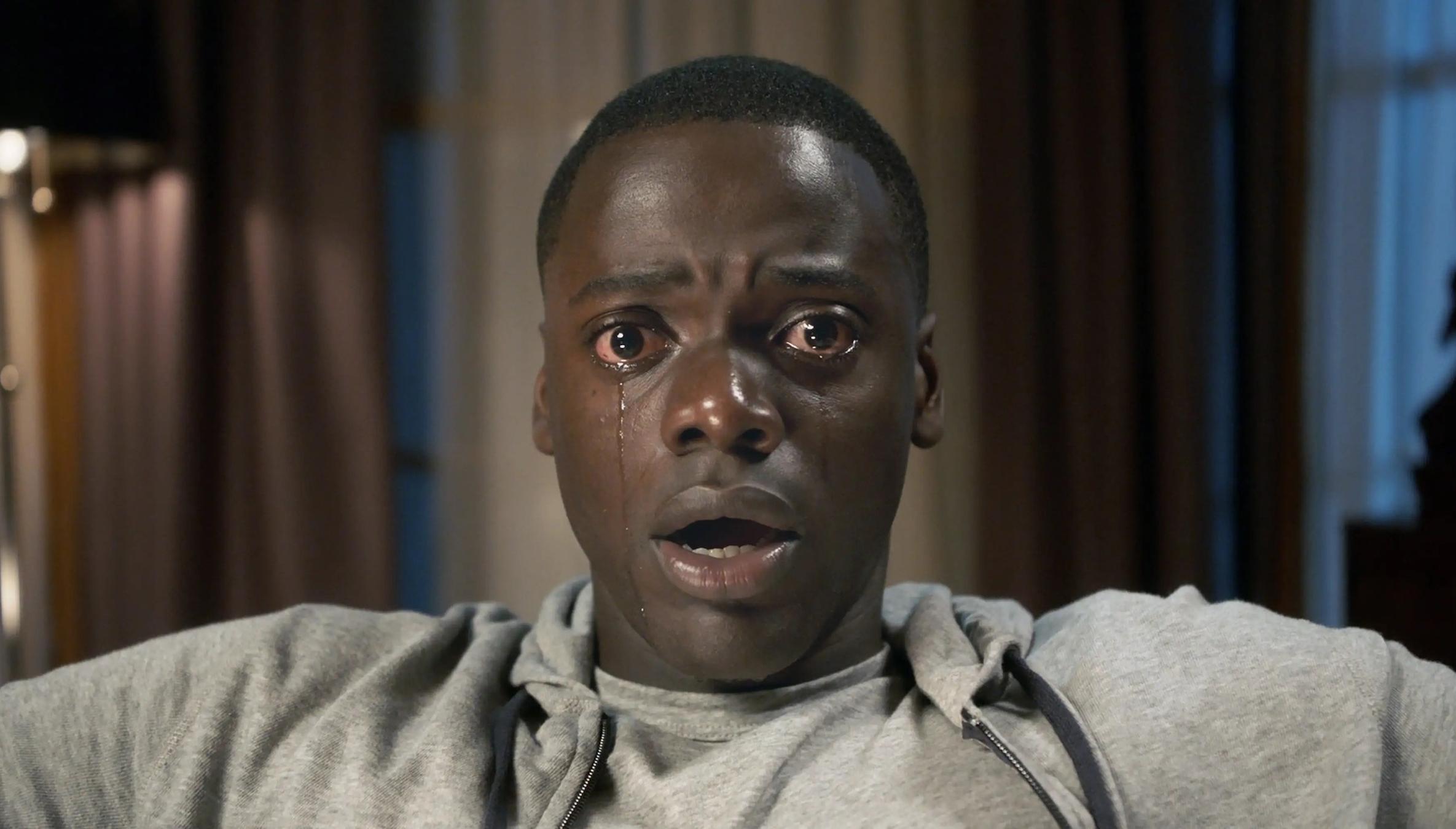


What kind of shot is this?
EXTREME CLOSE UP
Closer than a close up, an image larger than the eye would typically see.
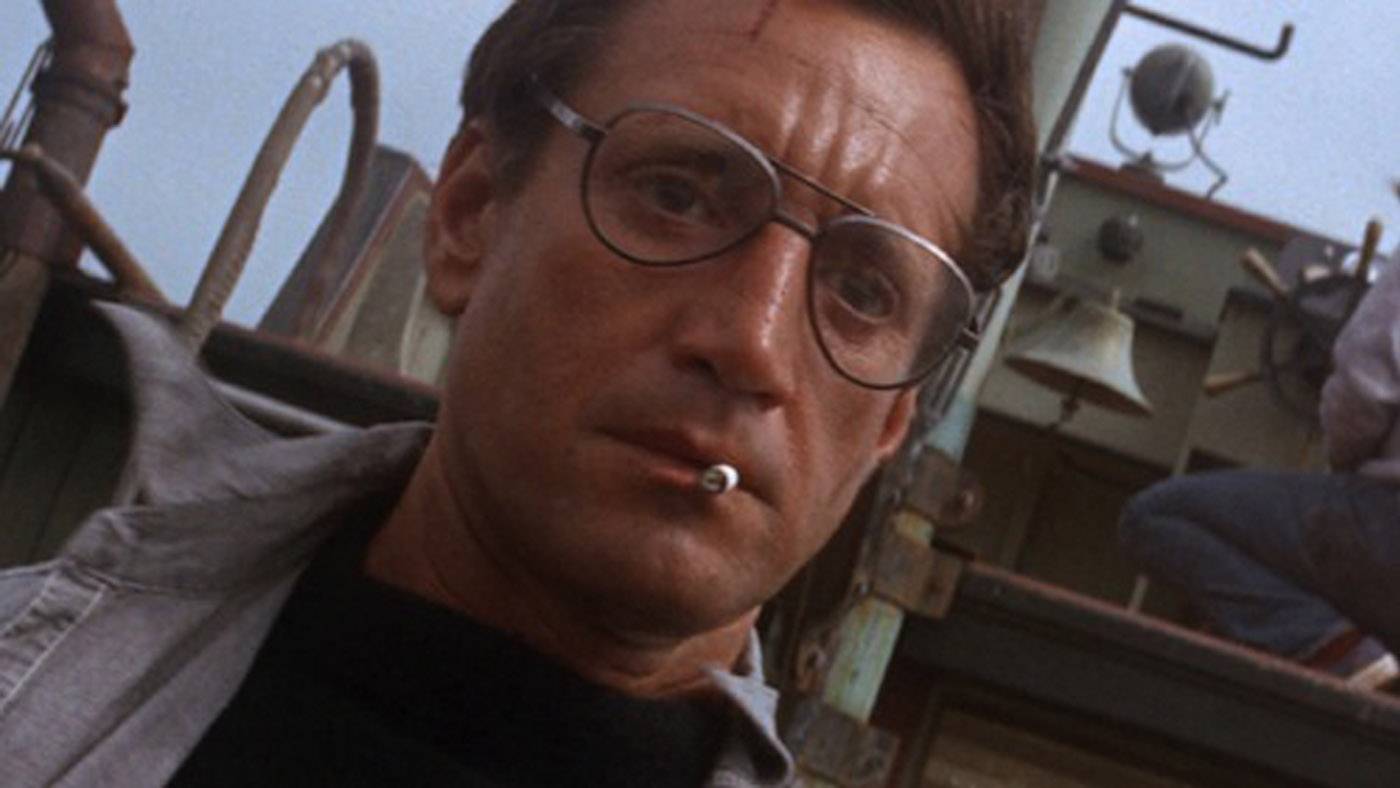


What kind of angle is this?
CANTED ANGLE / DUTCH ANGLE
Shot taken with tilted horizon, often used to signify imbalance or uncertainty, even chaos, but sometimes for aesthetic effect.
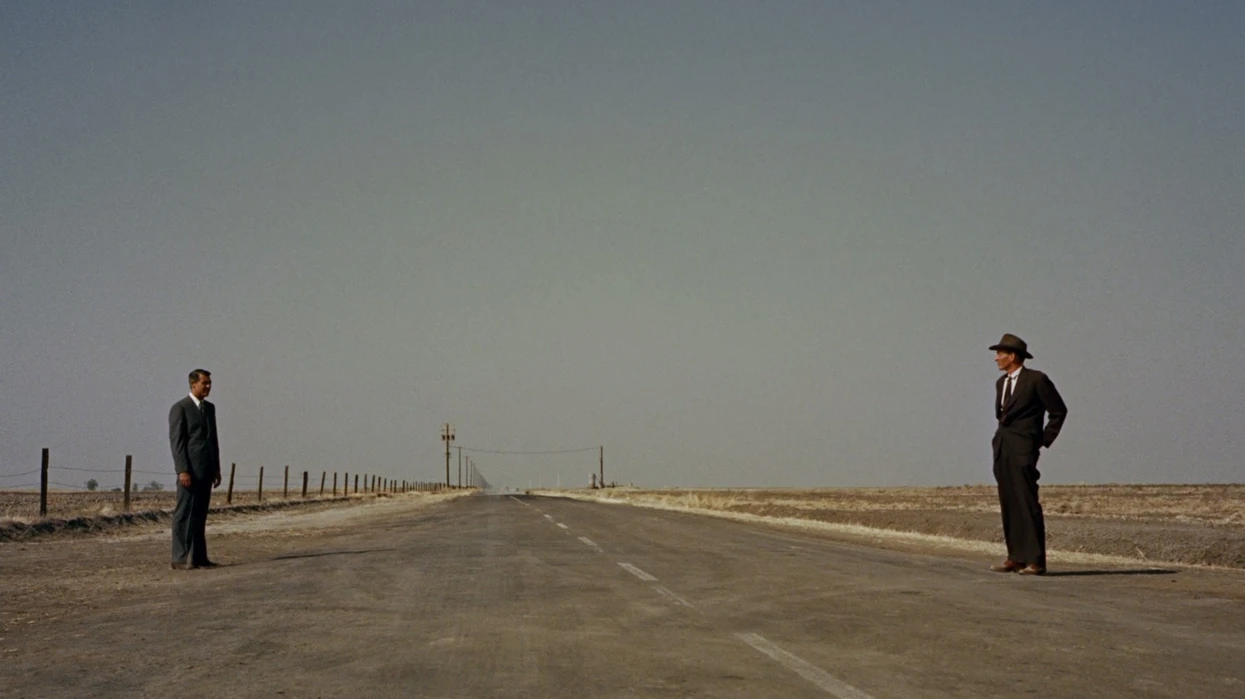


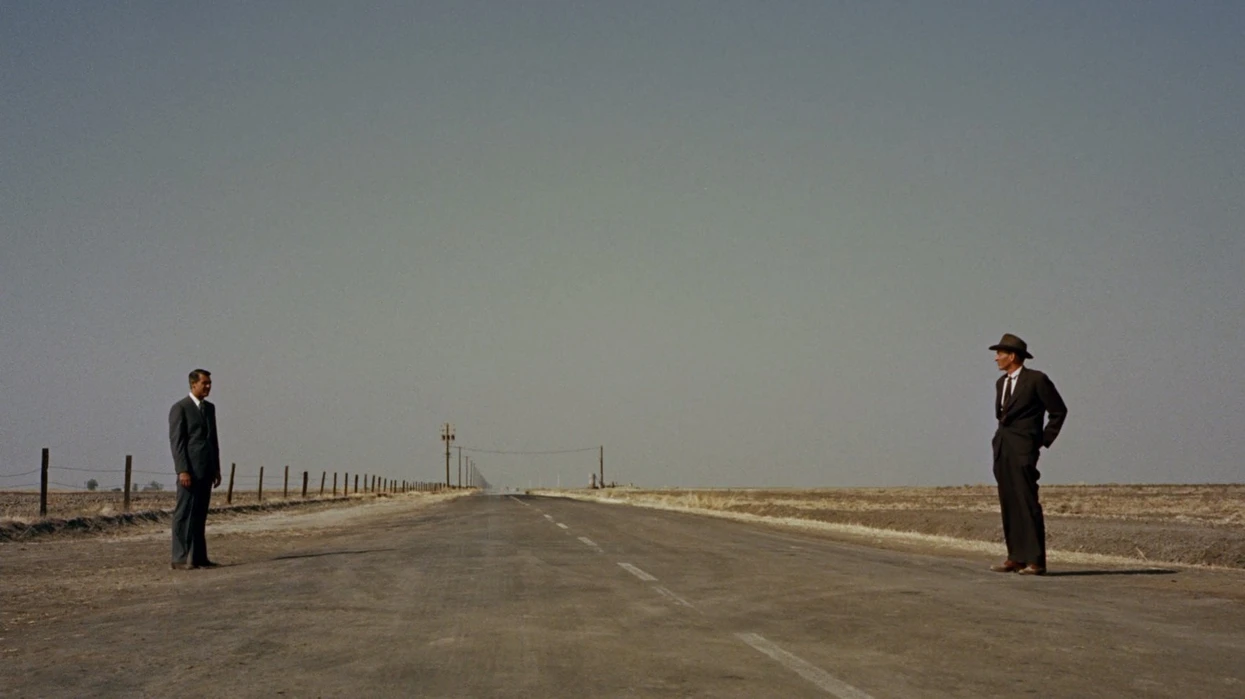
What kind of shot is this?
WIDE ANGLE
The actor may appear small against the landscape as the image as a whole to give a wide effect of the individual.
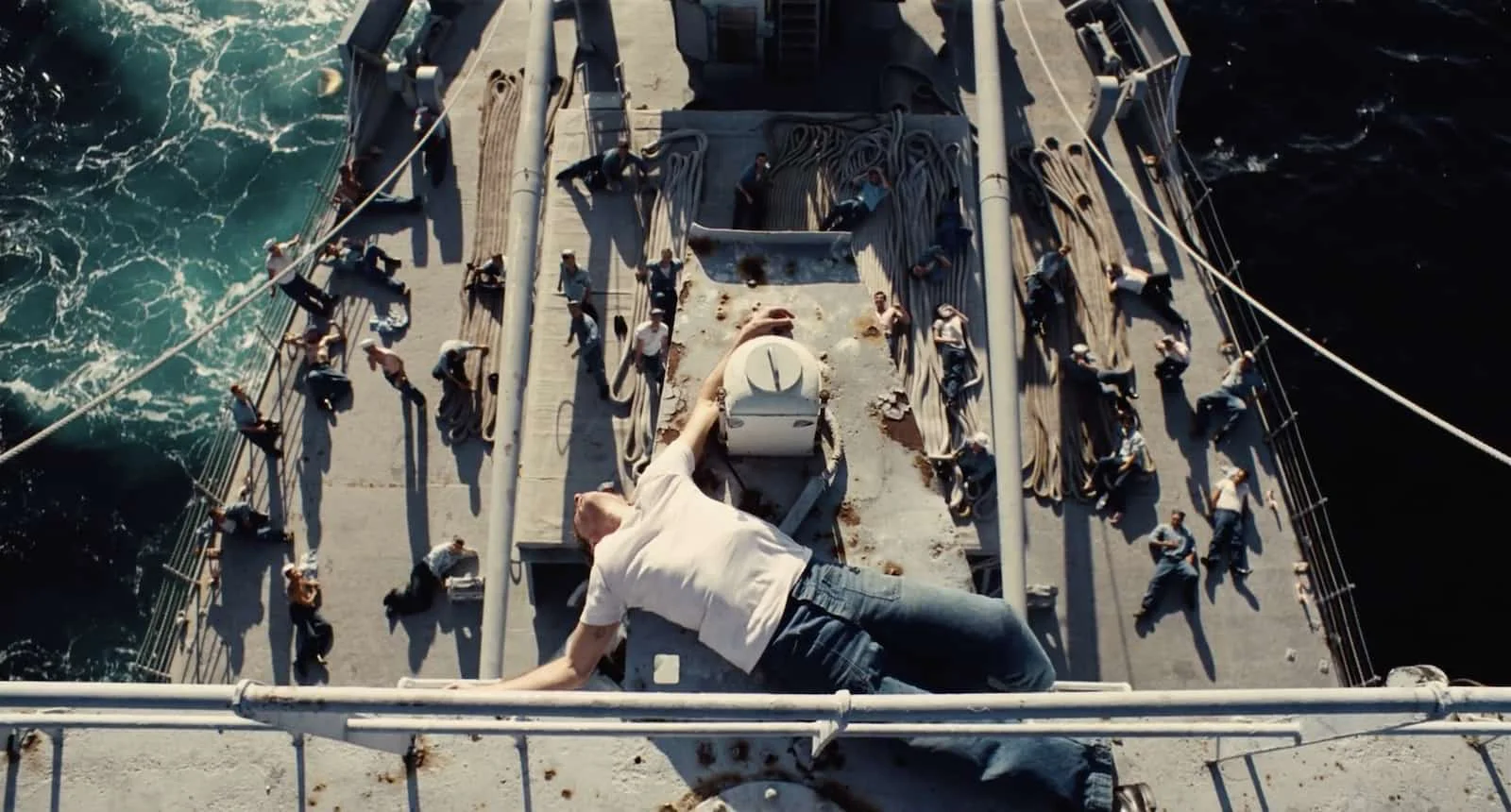


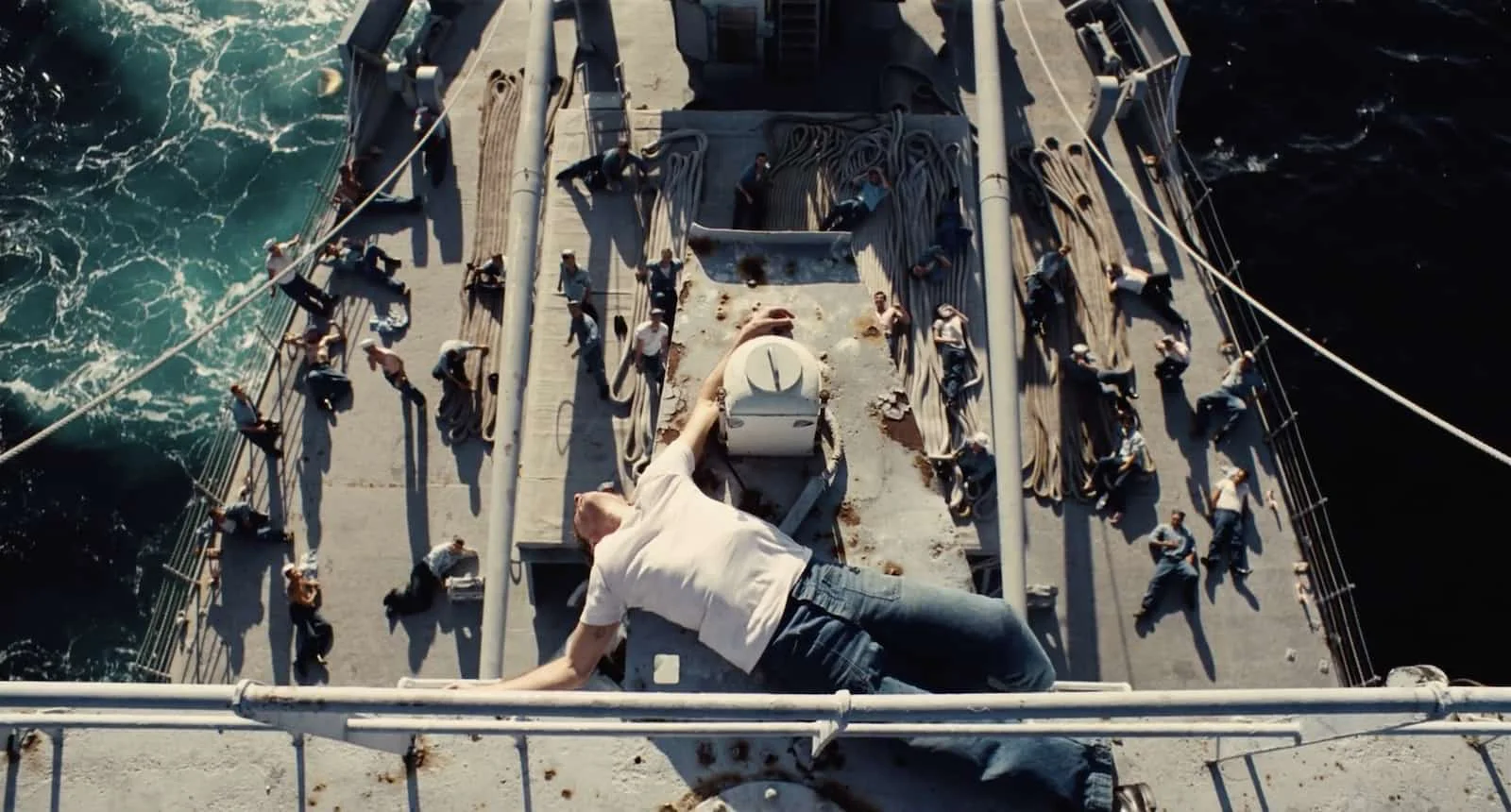
What kind of shot is this?
AERIAL SHOT
Shot taken from a high viewpoint, as though it is taken from a drone showing a bird’s eye view.


What kind of angle is this?
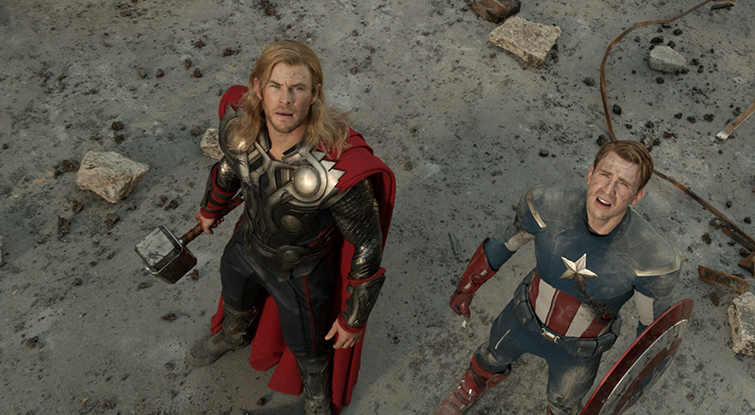
HIGH ANGLE
Shot taken above from character / setting to create a sense of empowerment for the character.


What kind of angle is this?
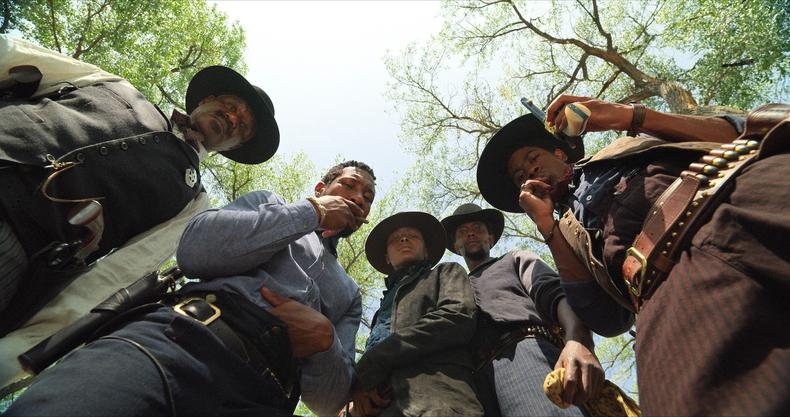
LOW ANGLE
Taken from a low angle, helping to reinforce intimidation or disempowerment for the character.

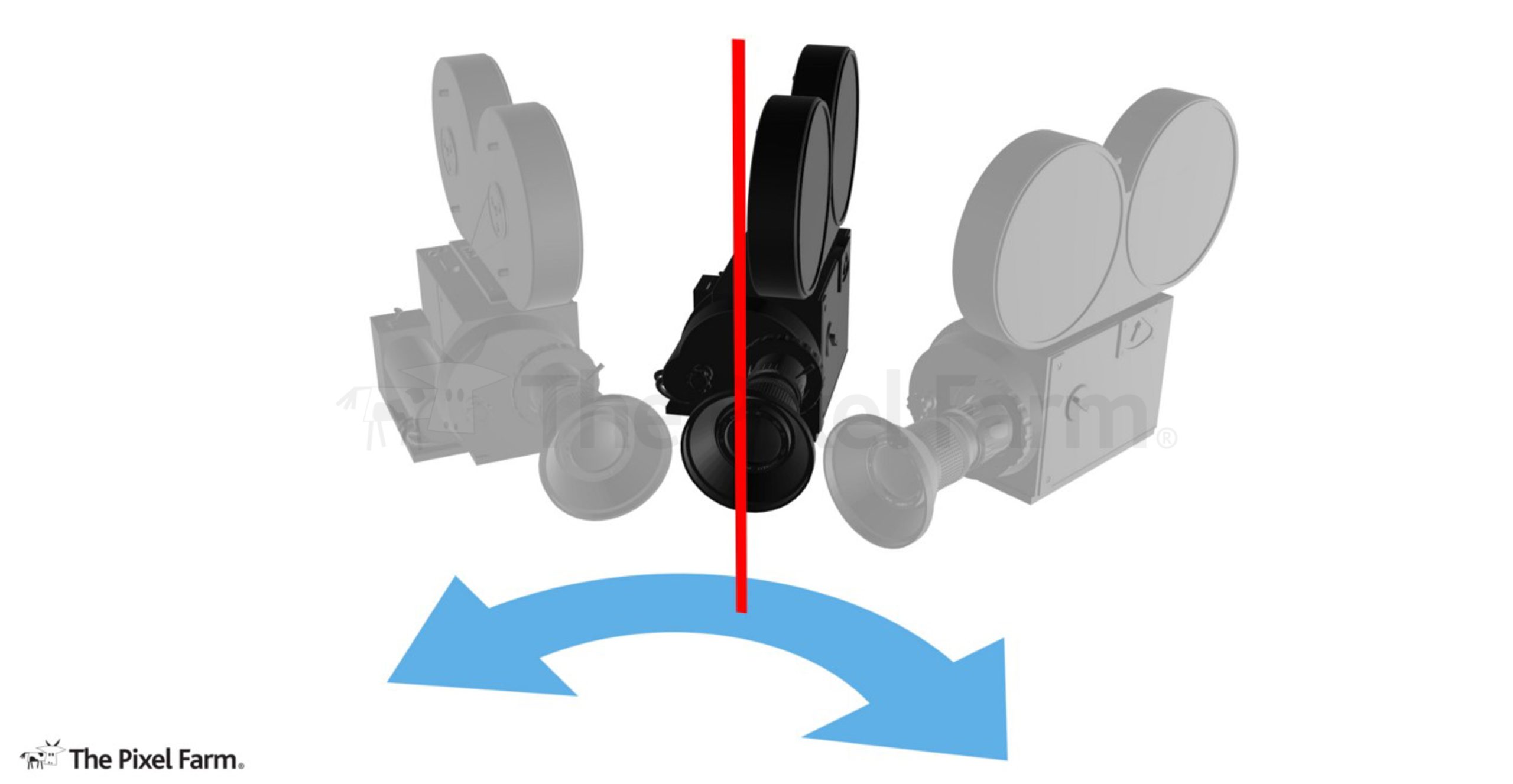
What is a pan movement?
PAN
Camera moves along the horizontal axis, with the camera body turning to the left or right on a stationary tripod.
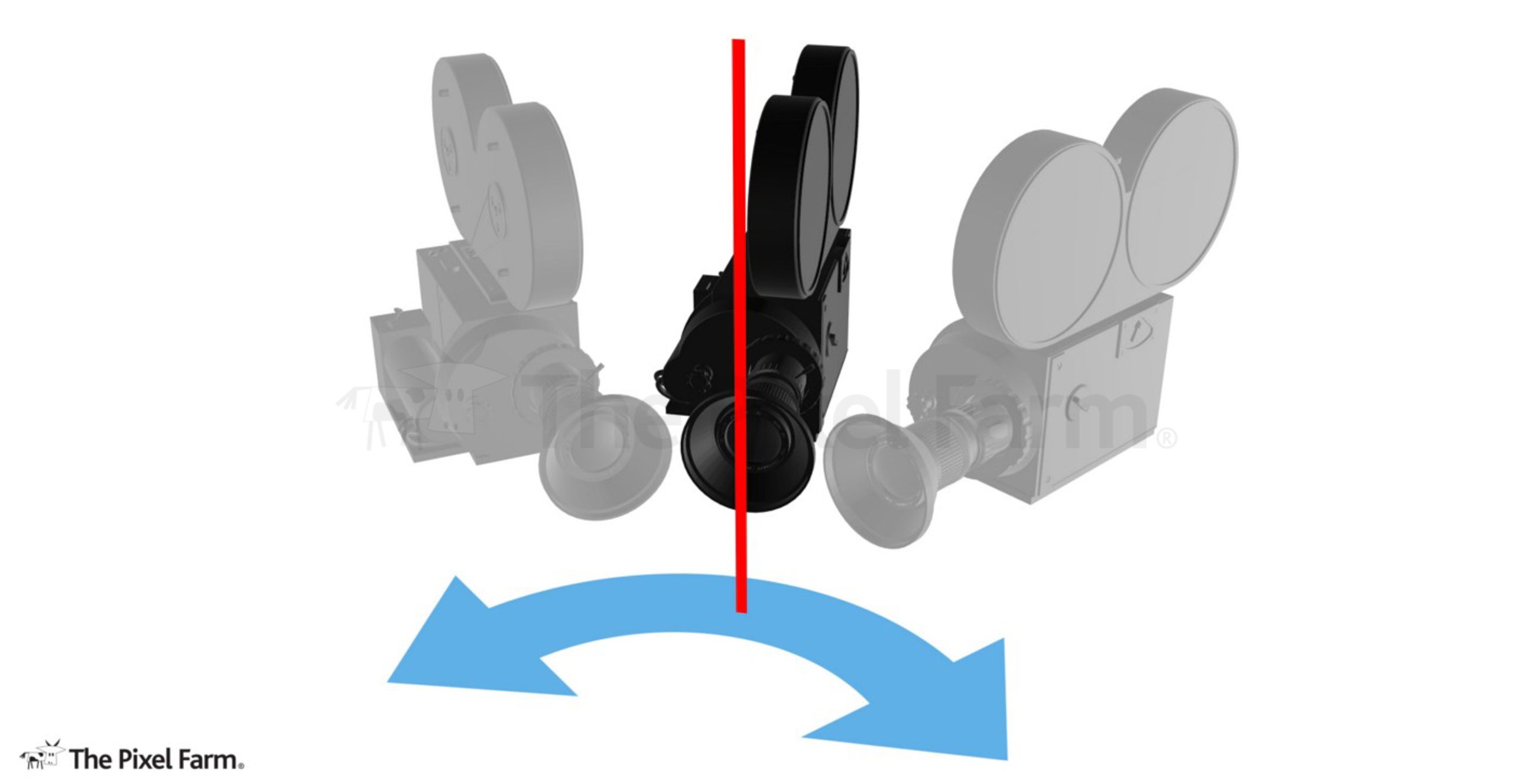
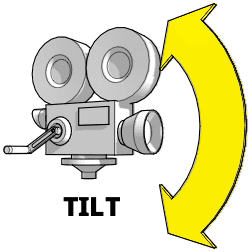
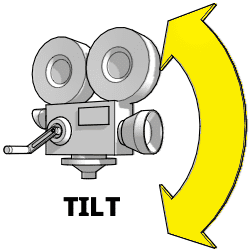
What is a tilt movment?
TILT
Camera moves along a vertical axis, with the camera turning up or down on a stationary period.
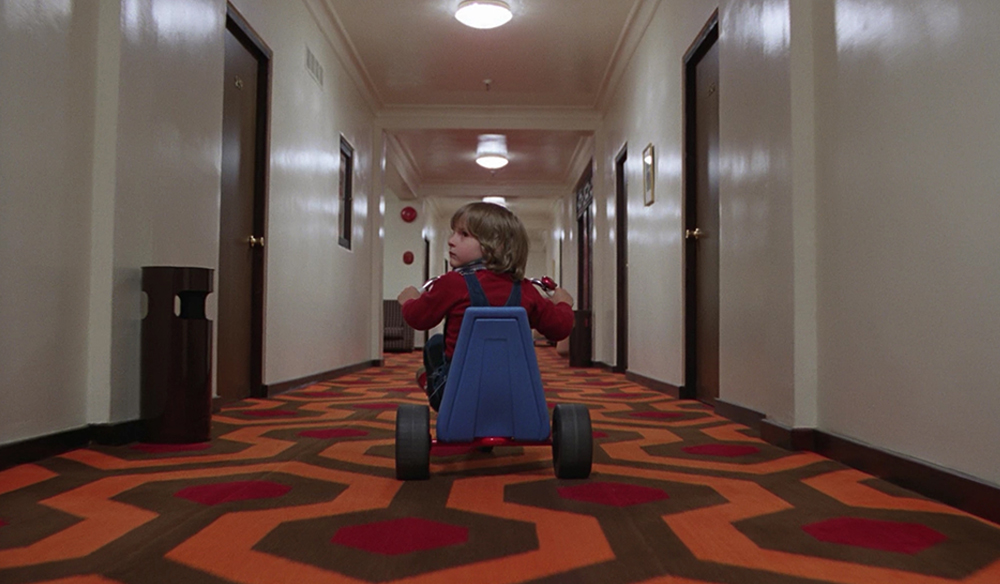

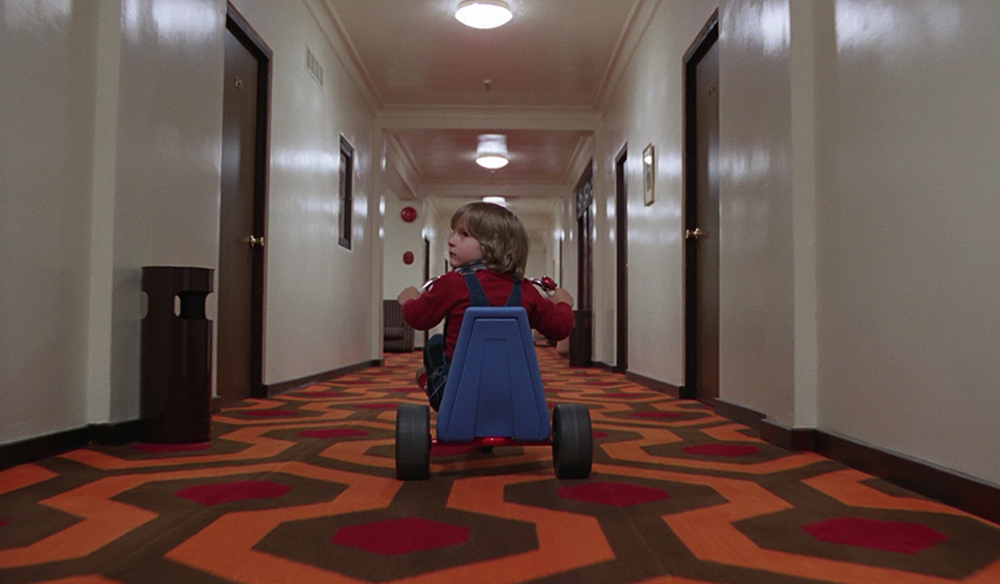
What is a tracking shot?
TRACKING SHOT
Camera moves forwards, backward, or laterally. This may be a wheeled support with a stabilization device.
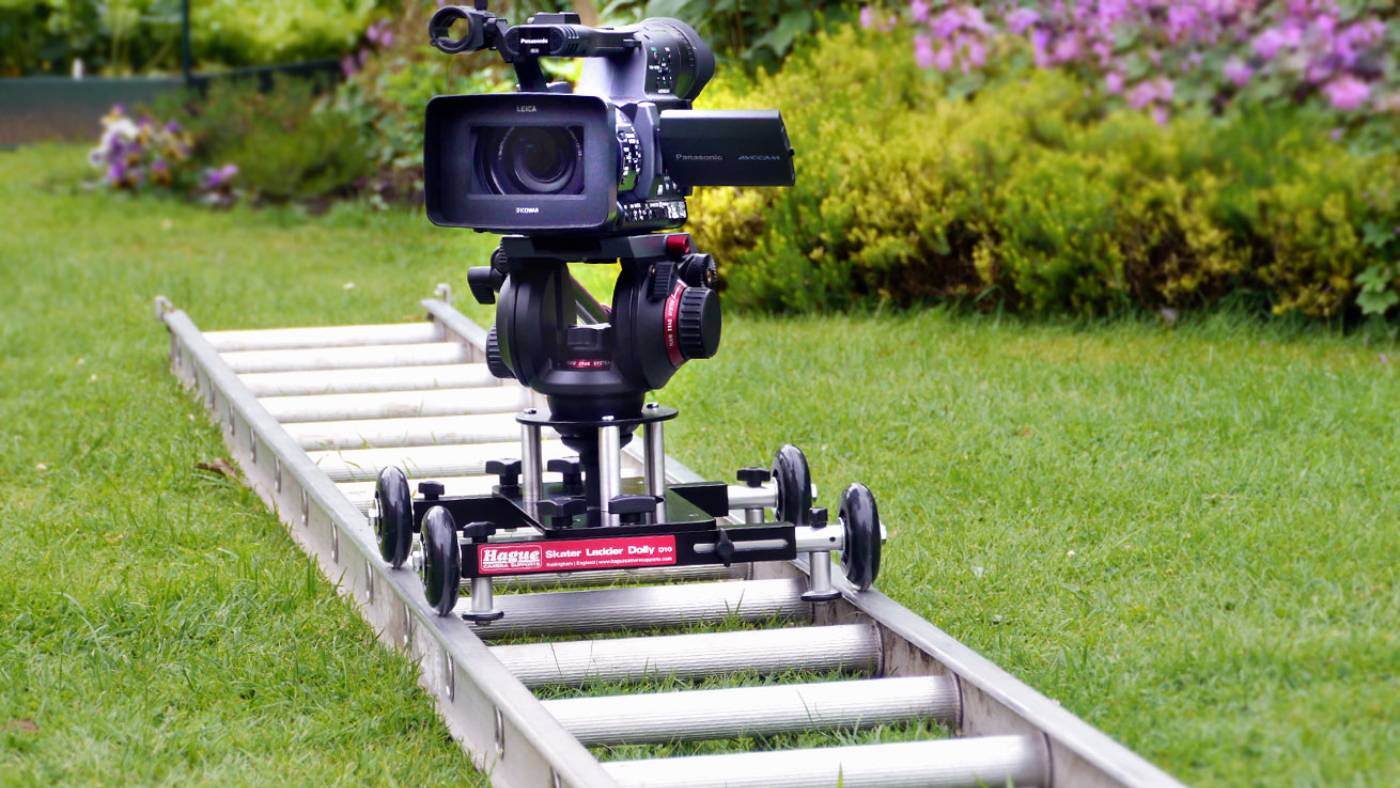


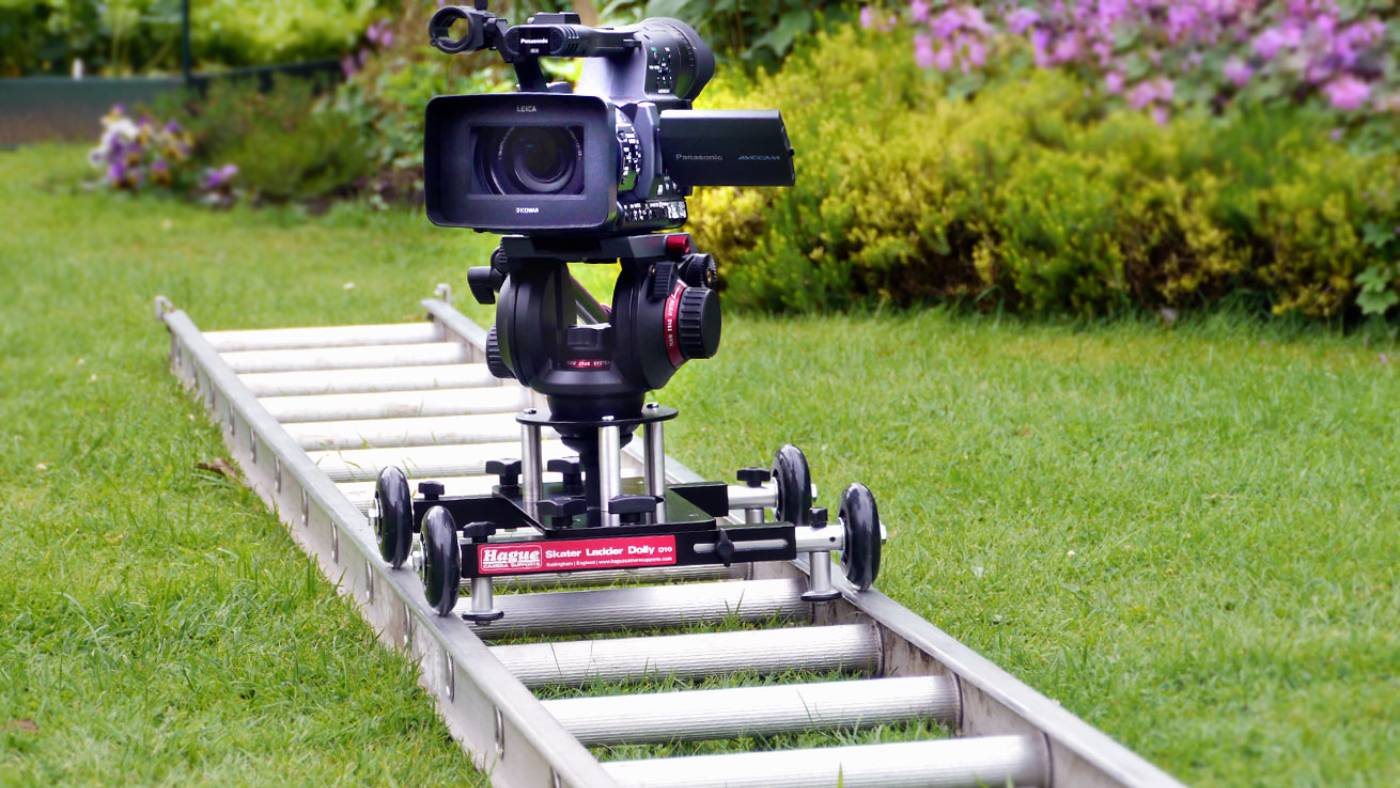
What is a dolly shot?
DOLLY SHOT
Camera supports with wheels to facilitate tracking shots. May move on tracks hence ‘dolly shot.’
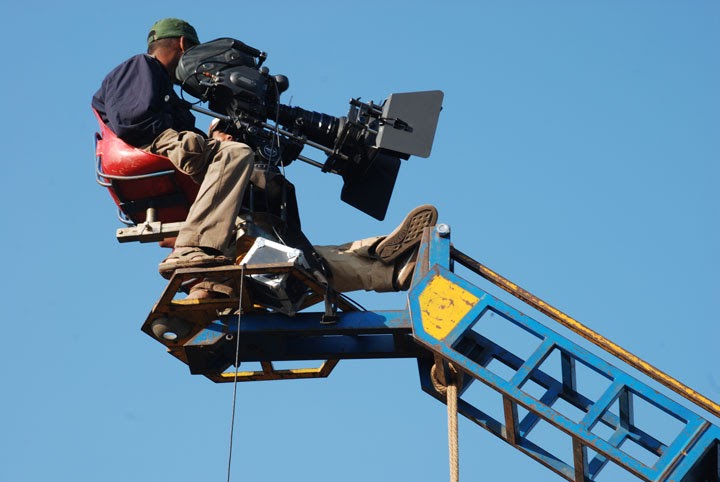


What is a crane shot?
CRANE SHOT
Camera being mounted on a crane or jib. It uses a wide, high perspective to be achieved.
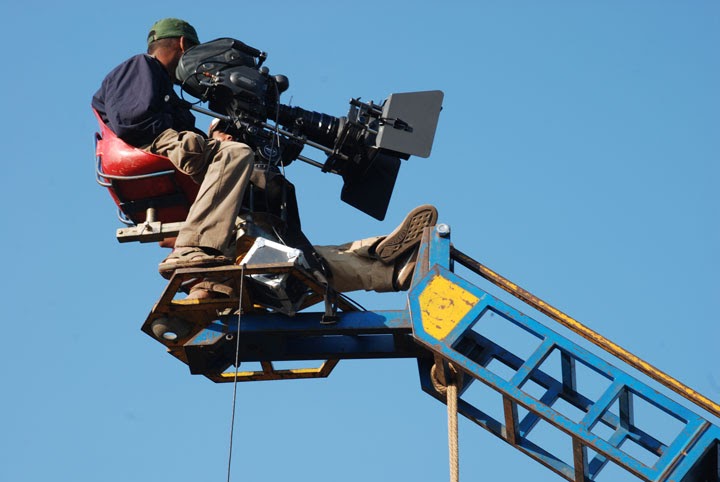


What is a steadicam?
STEADICAM
A brand name for a particular kind of camera being used to stabilization devices and enables smooth tracking shots.
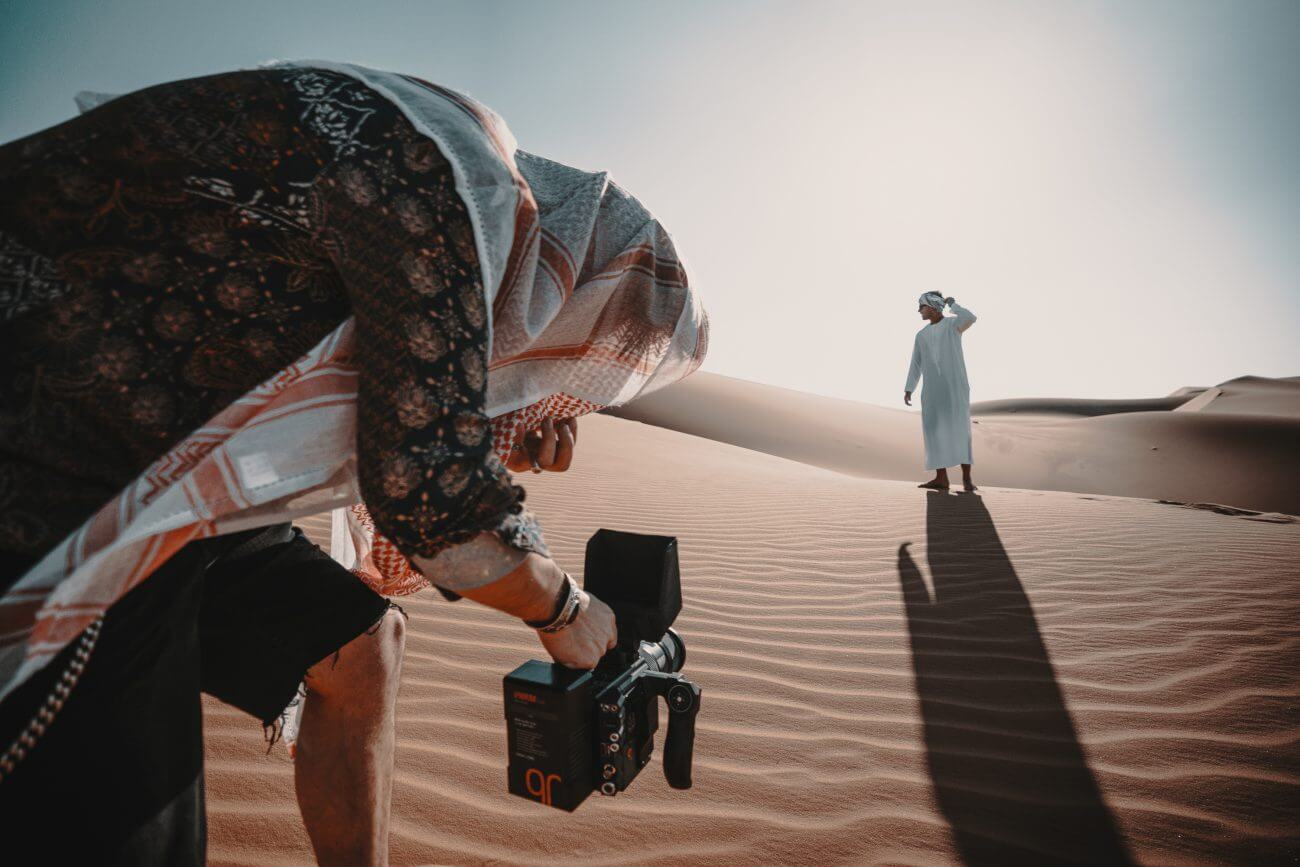


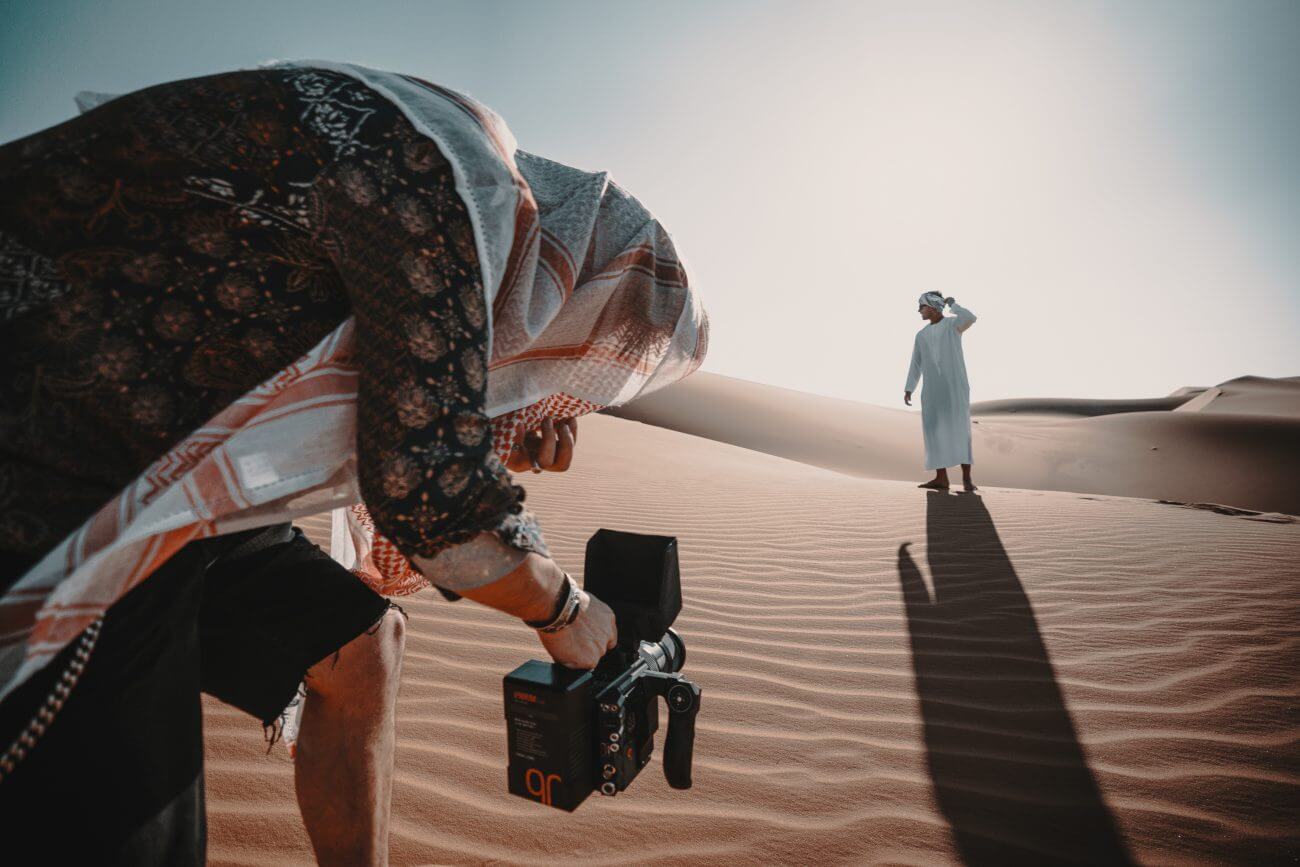
What is hand-held shot?
HAND-HELD SHOT
Characteristically ‘unpolished’ camera work. May utilize erratic movements to communicate peril or excitement

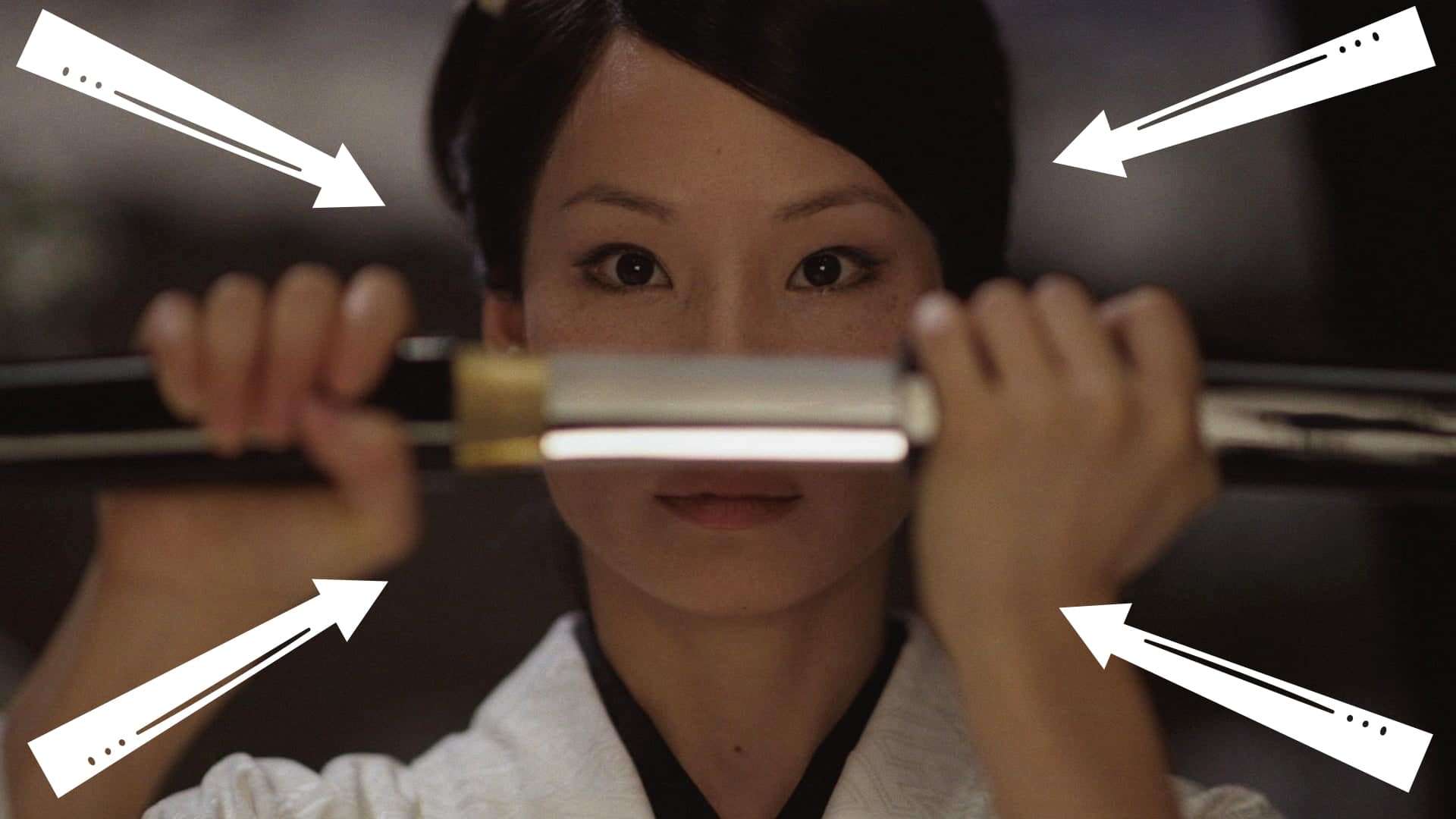
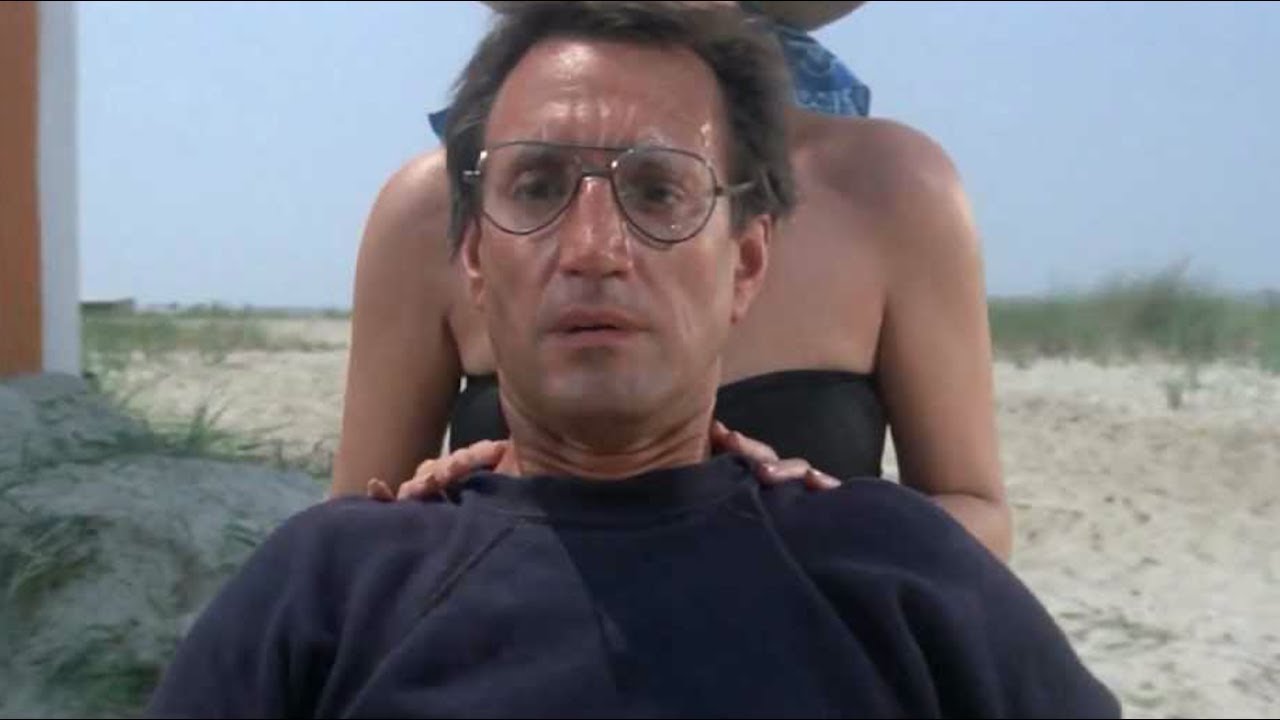
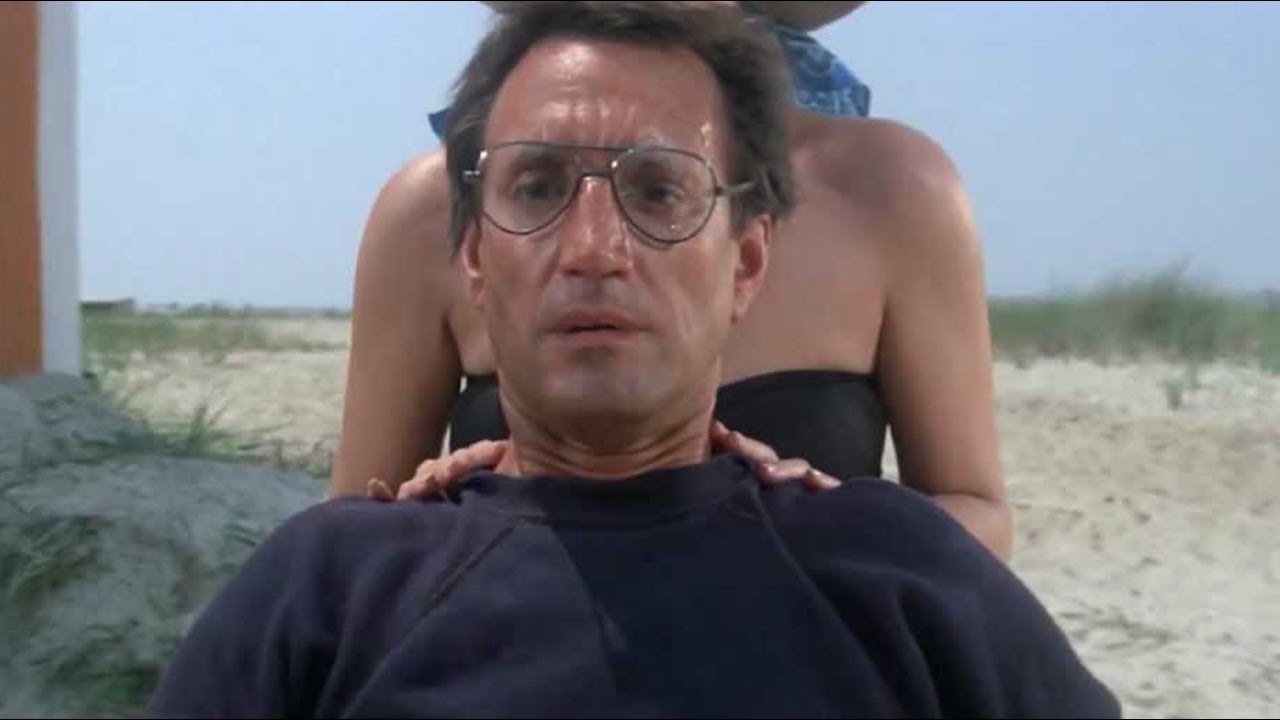
What is a zoom?
ZOOM
Unlike a tracking shot, where the camera moves in or out, a zoom is a magnification of the camera’s lens.
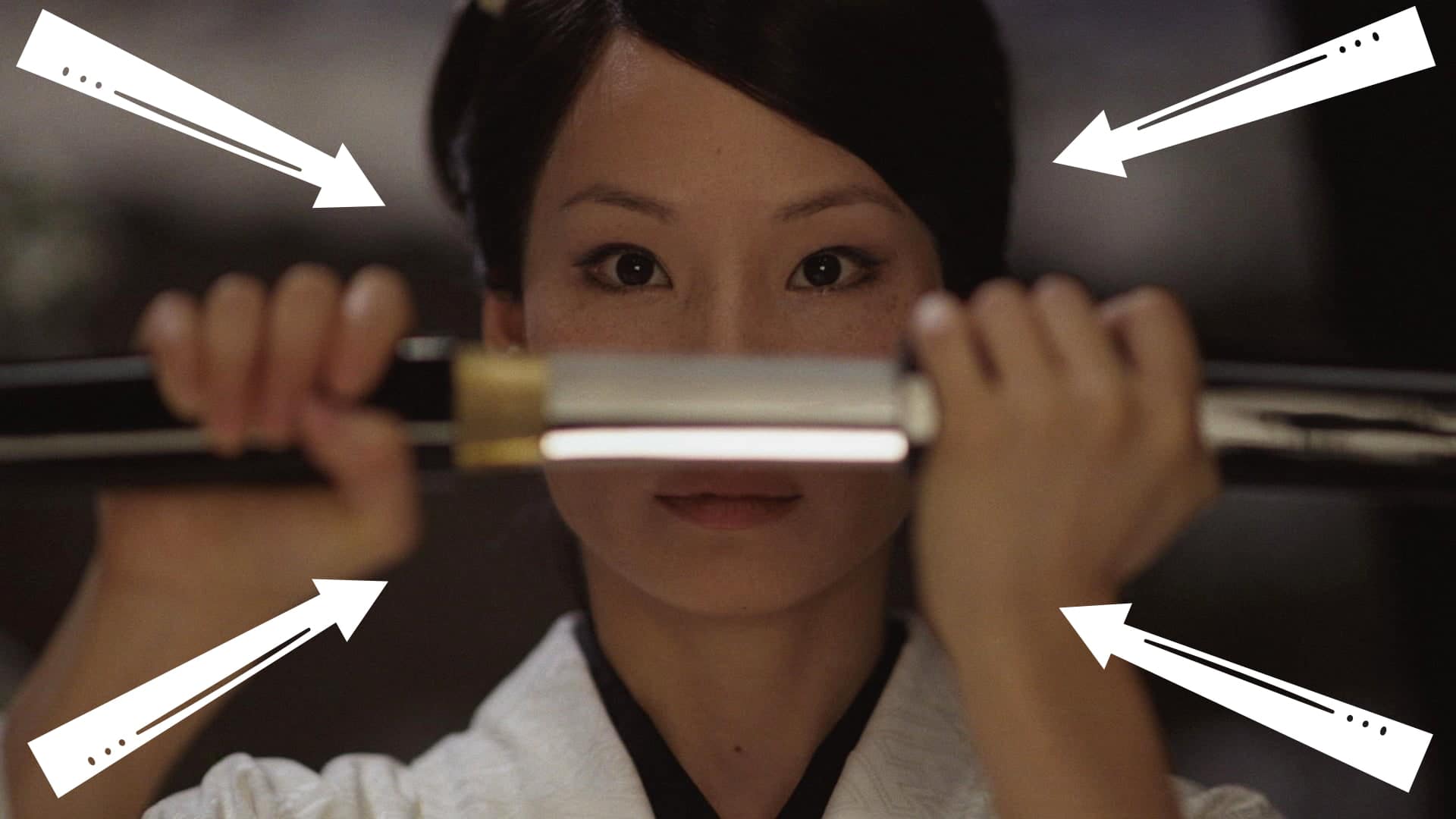

What is reverse zoom?
REVERSE ZOOM
Reverse zoom is a combination of a tracking shot and a zoom shot. The camera tracks the subject while zooming out at the same rate.

What is diegetic sound?
DIEGETIC SOUND
Sound that has its source in the scene, or ‘world of film'.’
What is non-diegetic sound?
NON-DIEGETIC SOUND
Sound that does not have its source within the world of the film. Ex) mood music
What is foley sound?
FOLEY SOUND
Sound effects produced to enhance the realism of actions in the scene. Created during post-production. Ex) Footsteps, clink of ice in glass, sound of a kiss
What is harmony?
HARMONY
Simultaneous or consecutive musical notes. They sound pleasant and may suggest all is swell in the world.
What is dissonance?
DISSONANCE
Opposite of harmony. Unpleasant music to suggest something wrong.
What is pitch?
PITCH
Frequency of a sound. High-pitched may be used to magnify aggression. Low pitches may be used for ominous moods.
What is rhythm?
RHYTHM
A recurring beat forms a pattern. Rhythms may be rapid or slow, regular or irregular, producing different emotional effects in the audience.
What is a room tone?
ROOM TONE
A recording of the sound at the location of a shoot — may be used to provide depth and atmosphere.
What is a soundscape?
Collection of background sounds that reinforce the realism of the scene. Ex) crowd murmur
What is Mise en Scene?
Costume, colors, props, setting, weather, body language
What is graphic relation editing?
Think of this editing as joining two still photos. Matching or contrasting via MeS or cinematography.
What is rhythmic relations?
Purely about shot duration. All about continuity or discontinuity.
What is spatial relations?
Whole to part, or part to whole
180 system
Eyeline match
Kuleshov effect (one shot effects perception of the next)
Cross-cutting to connect scenes
What is temporal relations?
Manipulation of time via editing
Order, frequency, duration
Flash-foward, flashback or overlap editing
What is continuity and discontinuity editing?
Continuity: Used to maintain narrative, pacing of story. Can mean many means.
Discontinuity: Broken up, does not follow a pattern intended to create unease or chaos.
What is tonal montage editing?
Editing based on emotional content (ex. cutting to facial expressions to relate reaction, slow pace for sad or tense moments)
What is a J-cut?
The audio track from the second scene overlaps the first scene's video. Looking at it from the viewer's perspective, you would hear the audio of the second scene before the video cuts in.
What is a L-cut?
A film editing transition that sees the audio from one scene or shot overlap onto the visuals from the next. (VOICEOVER, indicates narrator is person speaking).
The visuals change, but the audience still hears the audio from the previous visual.
What is internal diegetic sound?
Thoughts of the character heard
What is a rack focus?
Changing the focus without cutting the shot. Can indicate different person speaking, draws attention from one thing to another.
What is external diegetic sound?
Dialogue, effects, music
What are some basic editing transitions?
Fade, straight cut, dissolve, wipe
What is depth of field and the different forms it can take?
Depth of field: The distance between the nearest and the furthest objects that are in acceptably sharp focus in an image captured with a camera.
Shallow focus: keeps a small area of your photo in focus and blurs the rest. Draws attention to a specific person or object.
Soft focus: a technique where the entire image is slightly blurred to give it a dreamy and ethereal quality.
Deep depth of field: maintains focus all throughout the photo to showcase all details in the setting/characters.