Physiology Exam 4 Lecture 13A [The Adrenal Glands: Miller]
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
The adrenal glands sit on top of the
kidneys
There are 2 adrenal glands (one on each kidney)
each have two layers:
Adrenal Cortex
Adrenal medulla
Adrenal cortex secretes
adrenocortical hormones
Adrenal medulla secretes
cathecholamines
The cortex is comprised of
- Zona glomerulosas: mineralocorticoids
- Zona fasciculata: Glucocorticoids > DHEA
- Zona reticularis: DHEA > glucocorticoids and androgen
Adrenocortical hormones are
steroid hormones (cholesterol backbone)
IMAGE of the Adrenal glands
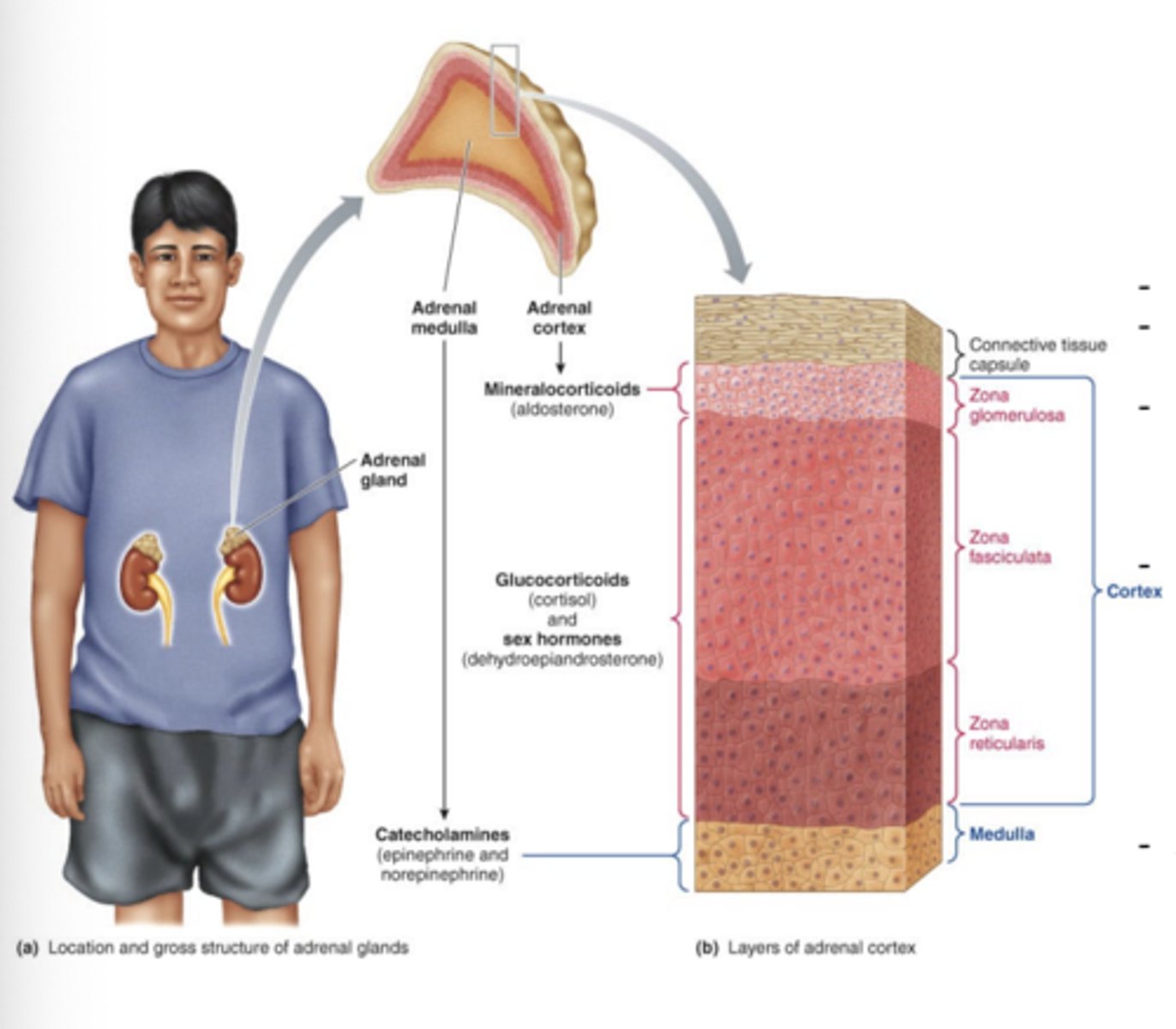
The adrenal cortex consists of three layers and secretes
adrenocortical hormones (which are steroid hormones)
Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) exclusively in the
Zona Glomerulosa
Glucocorticoids (Cortisol) Primarily in the
Zona Fasciculata
Sex steroid hormones (DHEA) primary adrenal source is the
Zona Reticularis
All steroid hormones are derived from
Cholesterol
The final steroid hormone produced depends on the
enzymes present in a given cell type
SUMMARY: The adrenal gland consists of two very different tissues
The cortex is a glandular tissue that secretes various steroids
The medulla is a nervous tissue that secretes catecholamines
SUMMARY: The adrenal cortex is comprised of 3 distinct layers
1. Zona glomerulosa is the top layer and exclusively secrets the mineralocorticoid aldosterone
2. Zona Fasciculata is the middle layer and primarily secretes the glucocorticoid cortisol
3. Zona Reticulata is the lowest layer and primarily secrets cortisol and the androgen DHEA
The rate limiting step for steroid hormone biosynthesis is the step that converts cholesterol into
pregneneolone
- this happens through an enzyme called P450-SCC
Steroid hormones are
lipophilic
Steroid hormones cannot be stored in
secretory vesicles
The rate of secretion of Steroid hormones is dictated by
the rate of synthesis
How are steroid hormones carried in the blood
extensively bound to plasma proteins
Steroid hormones bind to ________________ present in target cells - causing changes in transcription of genes. This is the primary mechanism of action of steroid hormones
intracellular receptors
SUMMARY: All steroids are derivatives of
cholesterol
SUMMARY: The conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone is the rate limiting step of steroid synthesis and involves the actions of
P450-SCC
SUMMARY: From pregnenolone one can synthesize
cortisol, aldosterone, and DHEA
SUMMARY: The steroids are lipophilic and thus can
cross the plasma membrane
SUMMARY: because of their lipophilicity steroids cannot be stored but are
synthesized as needed
SUMMARY: Steroids are highly bound to ______ ______ _____ in the blood and interact with intracellular receptors to change gene expression
plasma protein carriers
The primary mineralcorticoid in humans is
aldosterone
The principal site of action of aldosterone is on the
distal and collecting tubules of the kidney, where it promotes Na retention and enhances K elimination during the formation of urine
Promotion of Na retention secondarily induces osmotic retention of water, thereby causing
expansion of the ECF volume, which is important in the long-term regulation of blood pressure
Mineralocorticoids are essential for
life
Without Mineralocorticoids ie aldosterone
a person rapidly dies from circulatory shock because of the marked fall in plasma volume
Aldosterone secretion is increased by
Activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system by factors related to a reduction in Na and a fall in blood pressure
Direct stimulation of the adrenal cortex by elevated plasma K concentrations
Aldosterone secretion is largely independent of
pituitary control by ACTH
- ACTH plays no role in Aldosterone secretion
The primary glucocorticoid in humans is
cortisol
The overall metabolic effects of cortisol are to
increase the concentration of blood glucose at the expense of protein and fat stores
How does cortisol increase concentration of blood glucose
Stimulates gluconeogenesis in the liver and inhibits glucose uptake by tissues other than the brain
- Increase plasma concentration of glucose
Stimulates protein degradation
- Increase plasma concentration of amino acids
Facilitates the breakdown of fat stores in certain adipose tissues
- Increase plasma fatty acids that can be used as an energy source instead of glucose
Other effects of cortisol
Important in lung development in the fetus
Necessary to permit catecholamines to induce vasoconstriction
- A person lacking in cortisol may go into circulatory shock in a stressful situation that demands immediate widespread vasoconstriction
Plays a key role in adaptation to stress (or perception of stress)
When stress is accompanied by tissue injury
inflammatory and immune responses accompany the stress response
Cortisol at physiological concentrations exerts modest _____ and _______ effects to help hold these immune system responses in check
inflammatory and immunosuppressive
At pharmacological concentrations glucocorticoids exert
stronger effects
synthetic glucocorticoids have been developed that maximize
anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects while minimizing the metabolic effects
Examples of when glucocorticoids are given:
Rheumatoid arthritis, allergic disorders
Glucorticoids are used cautiously because
- A glucocorticoid- treated individual has diminished ability to resist infections
- Person can develop Cushing's syndrome
- Prolonged treatment can cause atrophy of the adrenal glands, preventing the body from producing its own cortisol
-Elevated glucocorticoids increase blood pressure
SUMMARY: The primary mineralocorticoid secreted by the adrenal cortex is
aldosterone
SUMMARY: aldosterone's primary target is the
distal convoluted tubule and the collecting ducts of the nephron to increase Na reabsorption and K secretion. Along with Na uptake this causes the additional H2O to be reabsorbed
SUMMARY: Aldosterone is crucial for
life
SUMMARY: Aldosterone secretion is stimulated by
plasma K levels and angiotensin II and is unaffected by levels of ACTH
SUMMARY: The primary glucocorticoid secreted by the adrenal cortex is
cortisol
SUMMARY: Cortisol has a variety of actions, many of which increase energy molecules in the plasma:
1. increase gluconeogenisis in the liver to release glucose
2. Increases protein breakdown to increase amino acid levels in blood
3. increases lipid breakdown to increase fatty acids in blood
4. Increases tissue sensitivity to catecholamines
5. Has slight anti-inflammatory properties at physiological concentrations
SUMMARY: Cortisol is a major
stress hormone
SUMMARY: synthetic glucocorticoids are used to
decrease inflammatory conditions like arthritis
SUMMARY: Synthetic glucorticoids must be used
sparingly and require careful use
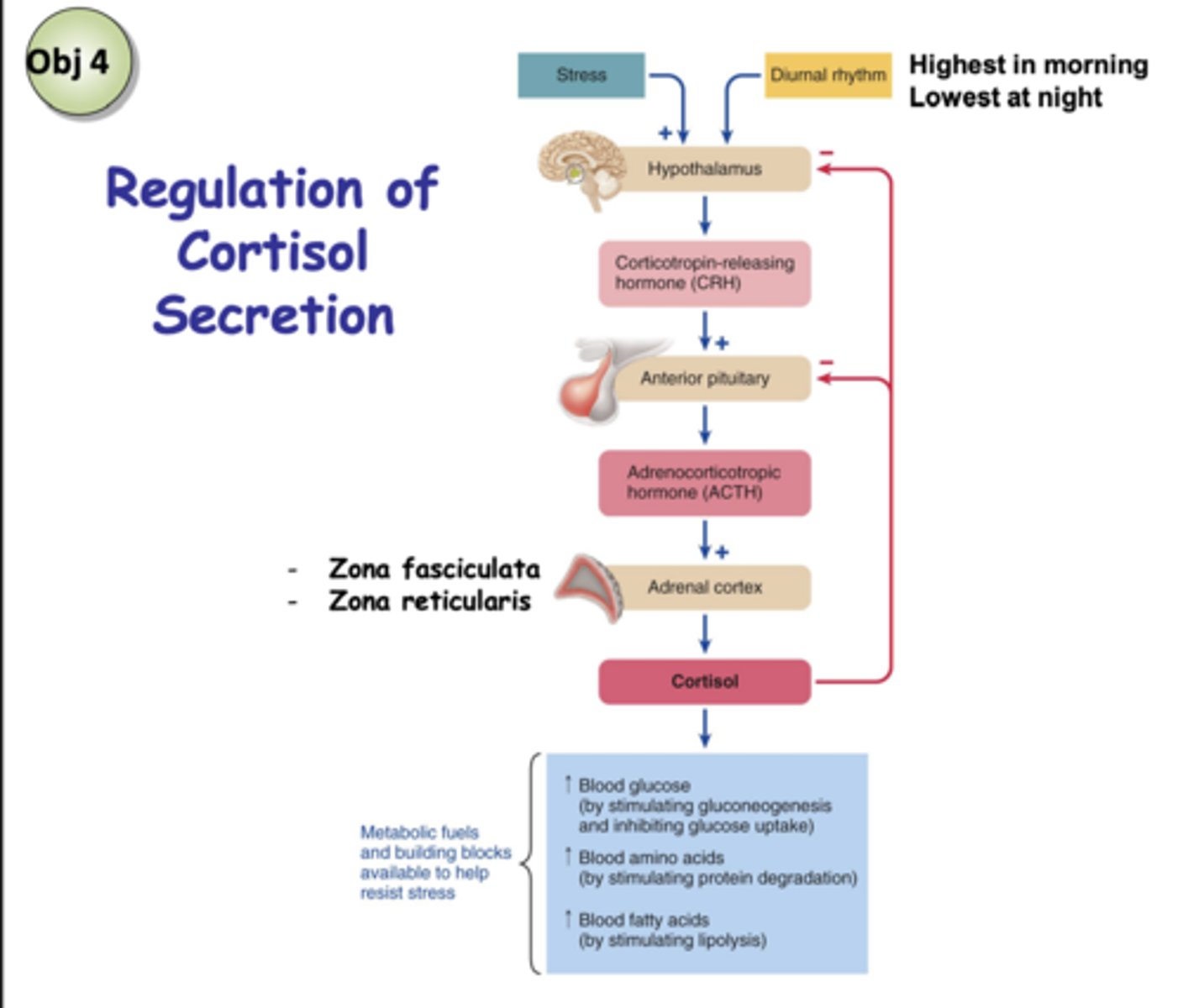
Regulation of Cortisol Secretion (IMAGE)
In both sexes the adrenal cortex secretes small levels of ____ (female sex steroid hormone)
estrogens
In females the ovaries are the main site of
estrogen synthesis
Adrenal estrogens in males and females are not abundant enough to have
effects
In both sexes the adrenal cortex secretes small levels of _____ (Male sex steroid hormones)
androgens
Androgens
Primarily dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)
Most DHEA in sulfated form (DHEA-S)
DHEA/DHEA-S are weak androgens. They can be converted to the more potent androgen ______ in peripheral target tissues
testosterone
Main site of secretion of androgens in males are the
testes (testosterone)
Role of Adrenal DHEA in females
DHEA mediates androgen-dependent processes in females during puberty:
- Grotwth of pubic and axillary hair
- Enhancement of the pubertal growth spurt
- Development and maintenance of the female sex drive
Mediated by testosterone derived from the adrenal DHEA
The secretion of adrenal sex steroid hormones (DHEA/DHEA-S) is stimulated by
pituitary ACTH
The _______ are the primary sex steroid hormone producing cells
zona reticularis
Adrenal sex steroid hormones do not feed back on the hypothalamus and pituitary to suppress
CRH and ACTH
Adrenal sex steroid hormones negatively feed back on the hypothalamus and pituitary to suppress
GnRH, LH, and FSH secretion
If abnormally elevated levels of adrenal sex steroid hormones feedback on hypothalamus and pituitary would result in
suppression of gonadal function
SUMMARY: Cortisol release is controlled by
Stimulation from the release of CRH and ACTH
A negative feedback of cortisol to the hypothalamus (CRH release) and pituitary (ACTH release)
SUMMARY: The adrenal cortex can also release very small amounts of
estrogen and a higher lover of the androgen (DHEA) - weak androgen
SUMMARY: DHEA can be converted to
testosterone in target tissues
SUMMARY: In males the level of DHEA plays
almost no role as a much larger amount of testosterone is released by the testes
SUMMARY: In the female DHEA plays an important role in
1. development of pubertal hair
2. Enhances the pubertal growth spurt
3. Maintains sex drive
SUMMARY: The secretion of DHEA by the adrenal cortex is stimulated by
ACTH
SUMMARY: The DHEA produced by the adrenal cortex does not inhibit the release of
CRH and ACTH
Primary hyperaldosteronism - Conn's disease
hypersecreting tumor of aldosterone-secreting cells of the adrenal
Symptoms of Conn's disease
Hypernatremia (excessive Na retention)
Hypokalemia (excessive K depletion)
Hypertension (high blood pressure)
Cortisol Hypersecretion - Cushing's syndrome
Primary hypersecretion of cortisol
- Hypersecreting tumor of cortisol-secreting cells of the adrenal
Secondary hypersecretion of cortisol
- Excessive stimulation of the adrenal cortex by pituitary ACTH
ACTH-secreting tumors other than the pituitary (common in the lung)
Cushing syndrome is reflective of excessive ____________ - high blood glucose and protein shortage
gluconeogenesis
Cushings: Some of the extra glucose is deposited as body fat in locations characteristic of the disease --
abdomen, face, and above shoulder blades
Characteristics:
- moon face
- buffalo hump
- thin arms and legs
Cushings: Breakdown of body proteins leads to
muscle weakness and fatigue, thinning of the skin, tendency to bruise and poor wound healing, bone weakness
Cushings: Elevated cortisol increases blood pressure due to
the body becoming more sensitive to the effects of epinephrine and norepinephrine
Primary adrenocortical insufficiency or Addison's Disease
All layers of the adrenal cortex are severely under-secreting
DHEA, aldosterone, and cortisol are insufficient
Aldosterone insufficiency, if severe enough, can be fatal due to circulatory shock
Cortisol insufficiency, if severe enough, can be very serious and even fatal due to severe hypoglycemia
Addisons: From aldosterone hypo-secretion
Hyperkalemia
- Results in disturbances in cardiac rhythm
Hyponatremia
- results in hypotension
Life threating if severe enough
Addisons: From cortisol hypo-secretion
Hypoglycemia
Lack of permissive action for many metabolic activities
Poor response to physiological stress
Life-threatening if severe enough
Secondary adrenocortical insufficiency = decreased ACTH
Results in decreased cortisol (and DHEA) secretion
- Doesn't affect aldosterone secretion because it is not regulated by ACTH
Cortisol hypo-secretion
- Hypoglycemia
- Lack of permissive action for many metabolic activities
- Poor response to physiological stress
- Life-threatening if severe enough
SUMMARY: Primary hyperaldosteronism is caused by a
hyper-aldosterone secreting tumor of the adrenal cortex (Conn's syndrome).
SUMMARY: Conn's syndrome leads to
Hypernatremia
Hypokalemia
Excessive water retention leading to hypertension
SUMMARY: Primary hypersecretion of cortisol is usually due to
a tumor of the cortex (Cushing's syndrome).
SUMMARY: Secondary hypersecretion of cortisol is usually due to
over stimulation of the adrenal cortex by ACTH which can arise from the piruitary or certain lung cancers
SUMMARY: Hypersecretion of cortisol cause
Hyperglycemia
Deposition of fat in face, abdomen, and upper back
Hypertension
Muscle wasting and fatigue
frequent infections
SUMMARY: Primary adrenocorticoid insufficiency is usually due to an
autoimmune disease where the adrenal cortex layers are attacked (Addison's Disease)
SUMMARY: Low levels of aldosterone and cortisol can be life threatening while decreased DHEA only has effects in
women
SUMMARY: Addison's disease leads to
Hyperkalemia
Hyponatremia
Hypovolemia
Hypoglycemia
decreased responses to sympathetic activation
usually severe enough to require treatment or death can occur
SUMMARY: Secondary adrenocorticoid insufficiency usually cuased by
insufficient release of ACTH
SUMMARY: Unlike Addison's Disease, in Secondary adrenocorticoid insufficiency, aldosterone secretion is
unaffected and only cortisol and DHEA are low
The innermost region of the adrenal is the
Adrenal medulla
The adrenal medulla is a modified part of the sympathetic nervous system because
Releases chemical transmitters directly into the circulation upon stimulation by the preganglionic fiber
Like sympathetic neurons, releases norepinephrine
Most secreted hormone by the adrenal medulla is epinephrine
Most secreted hormone by the adrenal medulla is
epinephrine
Epinephrine and norepinephrine are
catecholamines
Catecholamines are synthesized in
adrenomedullary secretory cells