Concept 5.1: Macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers
1/6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
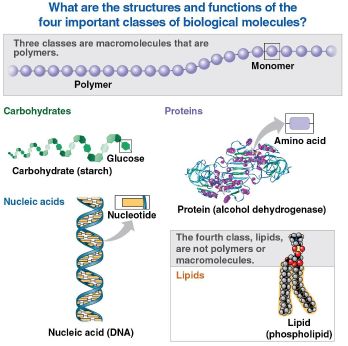
Biological molecules
Macromolecule polymers:
Carbohydrates (like glucose)
Proteins (in amino acids)
Nucleic acids (in DNA)
Non-polymer nor macromolecule:
Lipids
Macromolecules
Large polymers named for their huge size; cells have thousands and different cells have different varieties
Many can be built from just a small set of monomers
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks called monomers
Includes carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids
Monomer
The repeating units that serve as the building blocks for polymers
Enzymes
Specialized macromolecules that speed up chemical reactions such as those that make or break down polymers
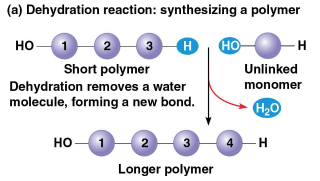
Dehydration reaction
Occurs when two monomers bond together through the loss of a water molecule, thus creating a polymer
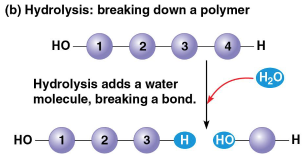
Hydrolysis
The disassembly of a polymer to a monomer, creating a reaction that is essentially the reverse of the dehydration reaction