ECCB 302 LAB herp
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
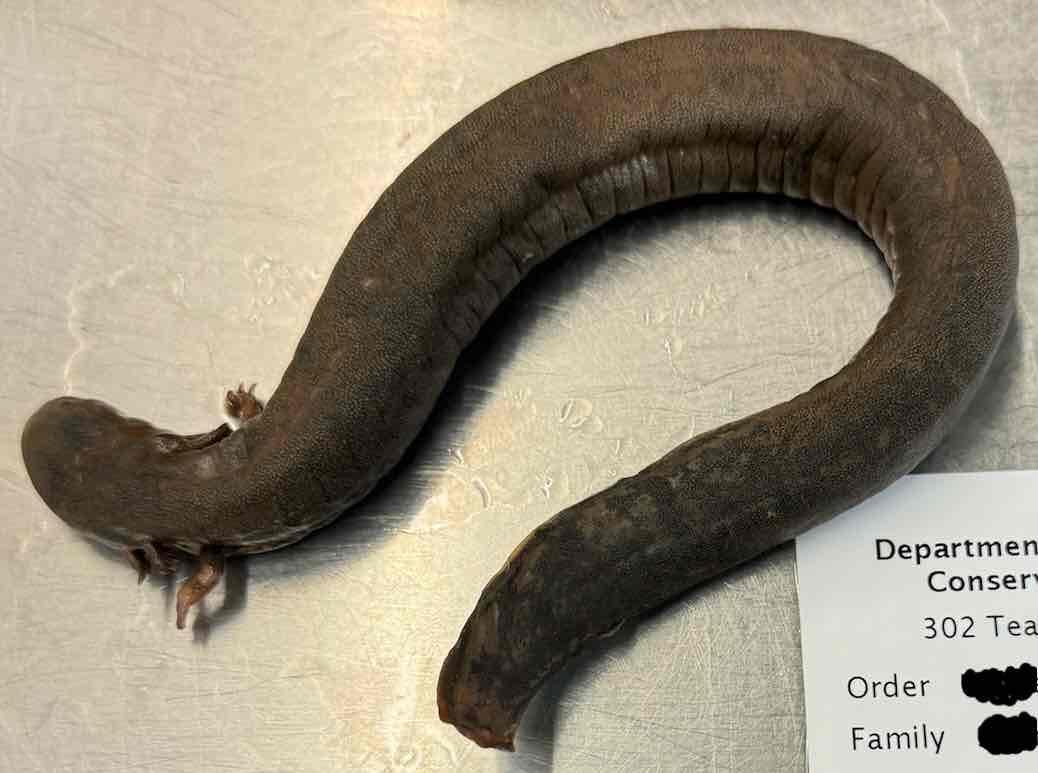

- Siren intermedia
- family: Sirenidae
- order: Urodela
Characteristics of Siren intermedia
-slender, eel like
- small forelimbs, no hind limbs
- adults have external gills and 1-3 pairs of gill slits
- no eyelids
- costal grooves on body above ribs
- said fertilization is external females lack spermatheca and males reproductive glands in cloaca( lack of being observed)
- predators
- live in aquatic vegetation
- commonly feed on crayfish
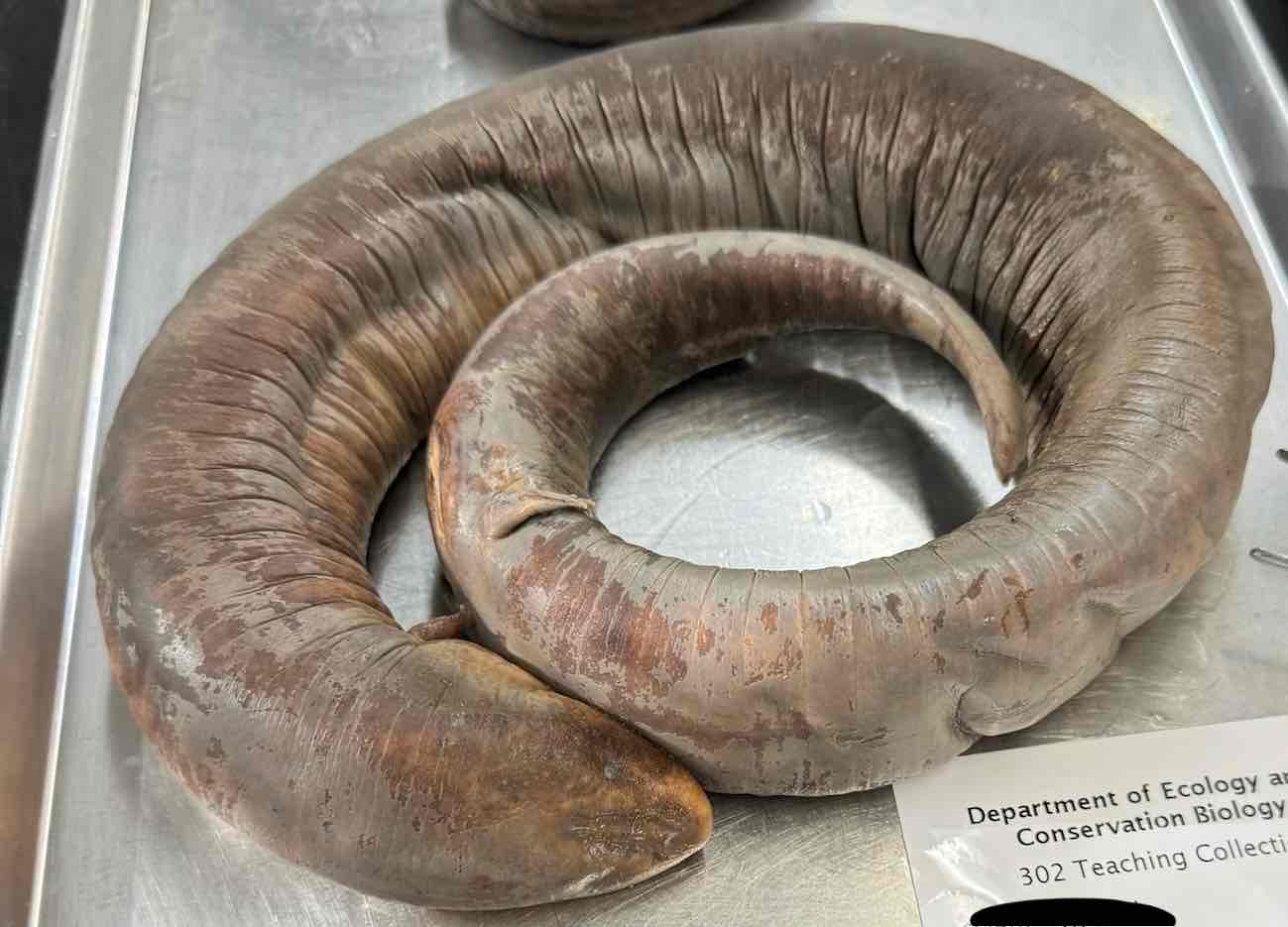

- Amphiuma tridactylum
Family: Amphiumidae
Order: Urodela
Characteristics of Amphiuma tridactylum
- aquatic predators
- heavy bodied, eel like salamanders
- tiny limbs
- internal gills
- gill slits
- eye lids and tongue absent
- fertilization internal females have spermatheca and males have reproductive glands in cloaca
- Females reproduce every couple of years and stay with their clutch of 200 eggs
- males deposit a spermatophore directly in cloaca
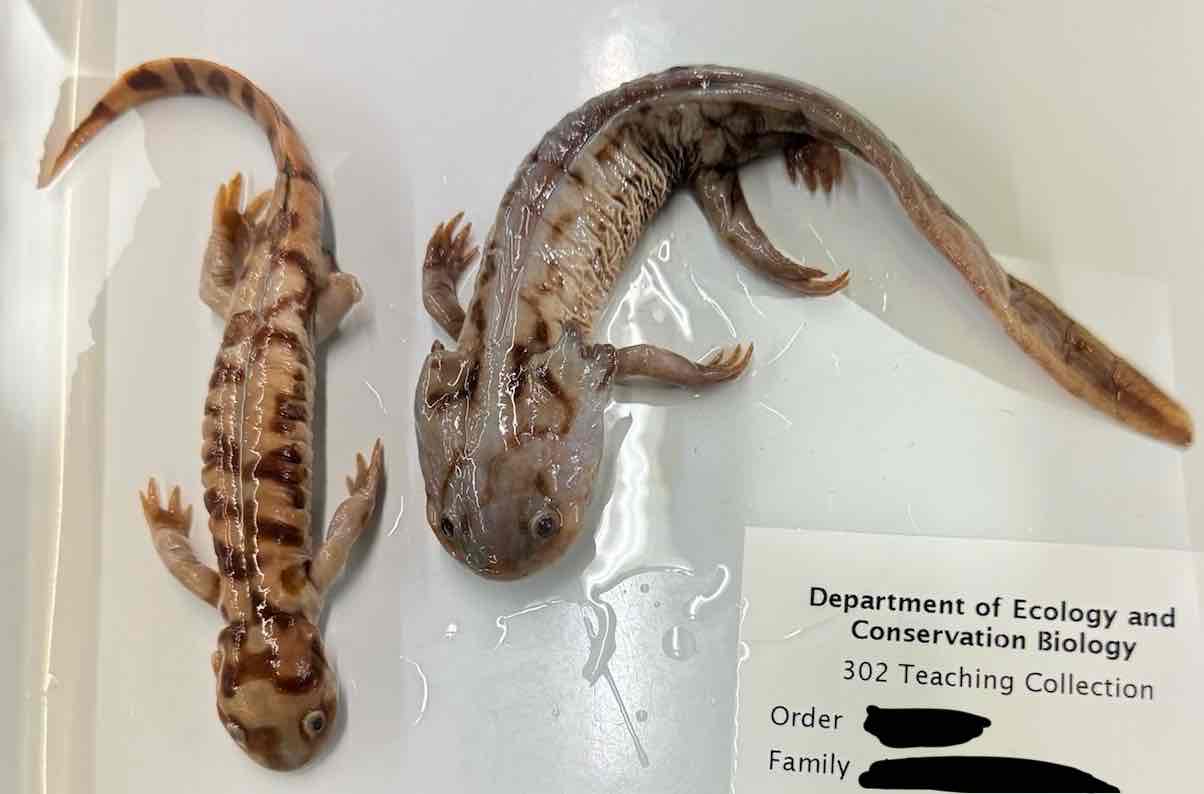

- Ambystoma tigrinum
- family: Ambystomatidae
- order: Urodela
Ambystoma tigrinum characteristics
- heavy bodied
- heavy tailed
- 4 well developed limbs
- most adult ambystomatids lack gills and gill slits
- some have eyelids
- some paedomorphic forms
- all have costal grooves and well developed lungs
- fertilization internal
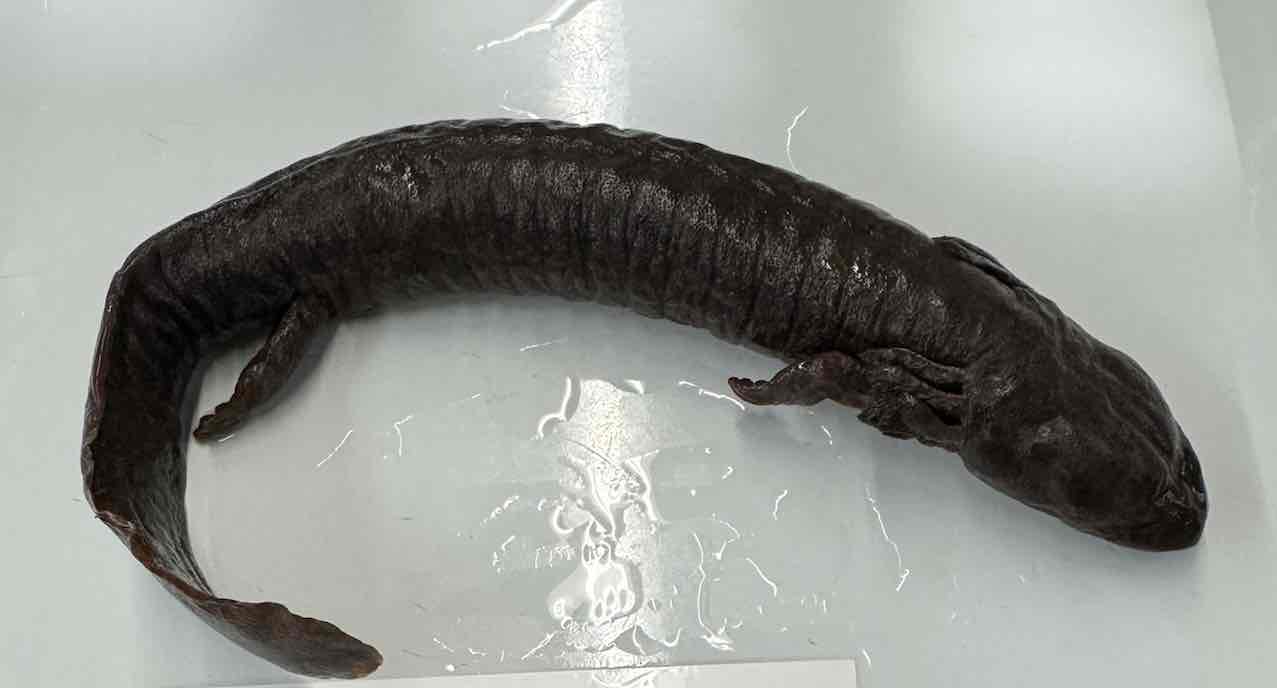

- Necturus maculosus
- family: Proteidae
- order: Urodela
Necturus maculosus characteristics
- aquatic salamanders
- robust with short well developed limbs
- compressed tails
- all proteids and paedomorphic
- have external gills, 2 pairs of gill slits
- no eyelids
- lungs present but small
- cosal grooves present on body
- fertilization internal

- Notophthalmus viridescens
- family: Salamandridae
-order: Urodela
Notophthalmus viridescens characteristics
- slender with four well developed limbs
- skin rough textured and not slimy
- costal grooves absent
- tail is finlike in aquatic forms but not terrestrial
- legs relatively long, prominent, and robust
- terrestrial and aquatic have four pairs of gill slits and large external gills
- courtship is complicated mating rituals
- life cycle is amphibious with aquatic larvae, terrestrial eft stage, and aquatic adults called newt

- Eurycea quadridigitata
- family: Plethontidae
-order: Urodela
Eurycea quadridigitata characteristics
- small, very slender
- possess distinct narrow grooves between each nostril and upper lip
- males often have protuberances on upper lip associated with nasolabial grooves and mental gland located beneath mouth
- costal grooves are pronounced
- generally have four fingers and five toes (widely separated)
- aquatic and terrestrial
- lungless
- fertilization internal
- plethodontids have elaborate mating ritual and employ chemosensory stimulants during courtship
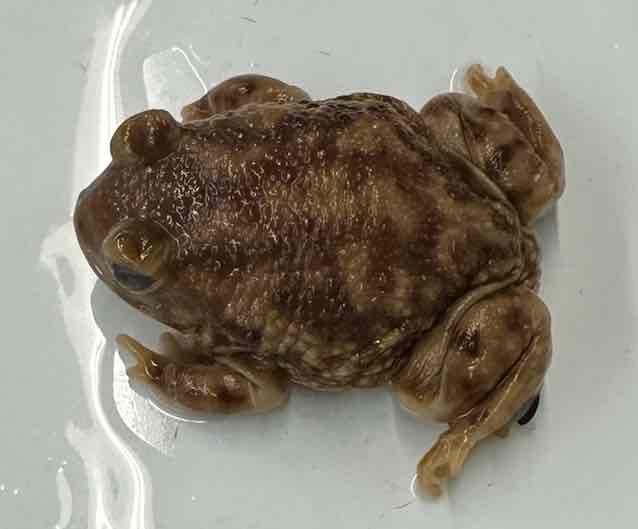

- Scaphiopus couchii
- Family: Scaphiopodidae
- order: Anura
Scaphiopus couchii characteristics
- possess a single sharp edged black spade shaped tubercle on each hind foot
- relatively smooth skin
- lack parotoid glands (poison on each shoulder)
- possess vertically elliptical pupils
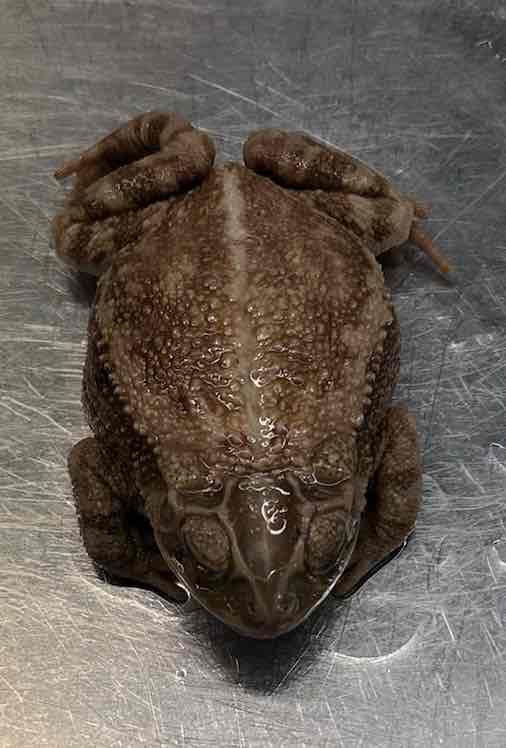

- Incilius nebulifer
- Family: Bufonidae
- Order: Anura
Incilius nebulifer
- skin is dry and warty
- body is squat and plump
- parotoid glands are very distinct and located behind the eyes
- forelimbs are shortened
- hindlimbs are used for walking or hopping
- skull highly ossified
- teeth absent from upper and lower jaws
- 2 rounded tubercles present on legs

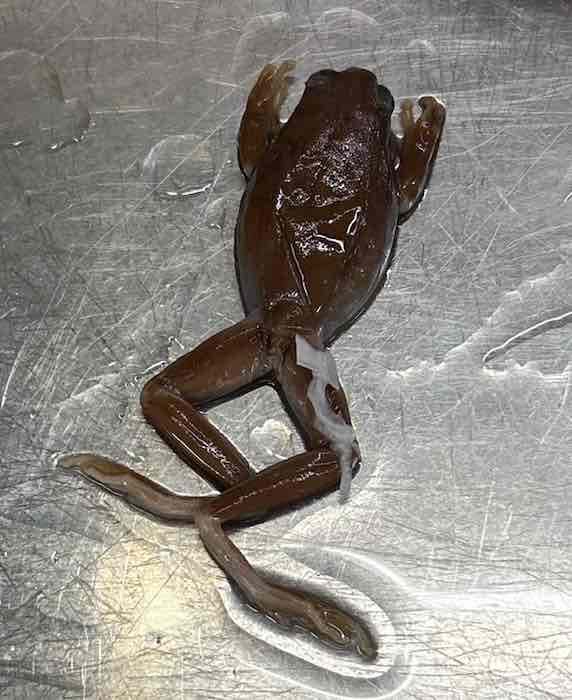
- Acris Crepitans
- Family: Hylidae
- Order: Anura
Acris crepitans Characteristics
- usually small in size
- slim waist
- long legs
- possess at least short webs between toes
- intercalary cartilage present
- arboreal species usually have enlarged discs on tip of each toe
- eyes generally forward

- Hyla cinera
- Family: Hylidae
Order: Anura
Hyla cinera
- usually small in size
- slim waist
- long legs
- possess at least short webs between toes
- intercalary cartilage present
- arboreal species usually have enlarged discs on tip of each toe
- eyes generally forward
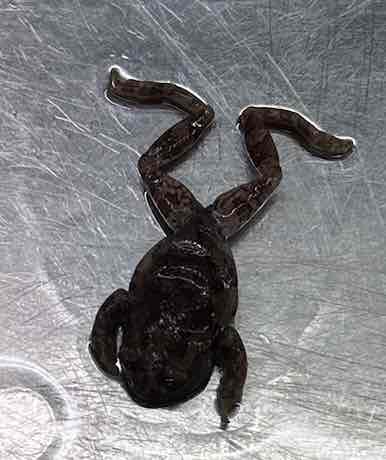
- Hyla chrysocelis (diploid)
- family: Hylidae
- order: Anura
Hyla chrysocelis (diploid)
- usually small in size
- slim waist
- long legs
- possess at least short webs between toes
- intercalary cartilage present
- arboreal species usually have enlarged discs on tip of each toe
- eyes generally forward

Great Plains Narrowmouth Toad
- Gastrophryne olivacea
- family: Microhylidae
- order: Anura
Gastrophryne olivacea characteristics
- typically small and plump
- short limbs and pointed heads
- possess a distinct fold of skin across the back of head
- all species in this widespread family have similar body plan
- possess stout hind legs
- short snouts
- globose bodies with generalized egg shape
- pupil of eye is horizontal
- toes essentially equal in diameter
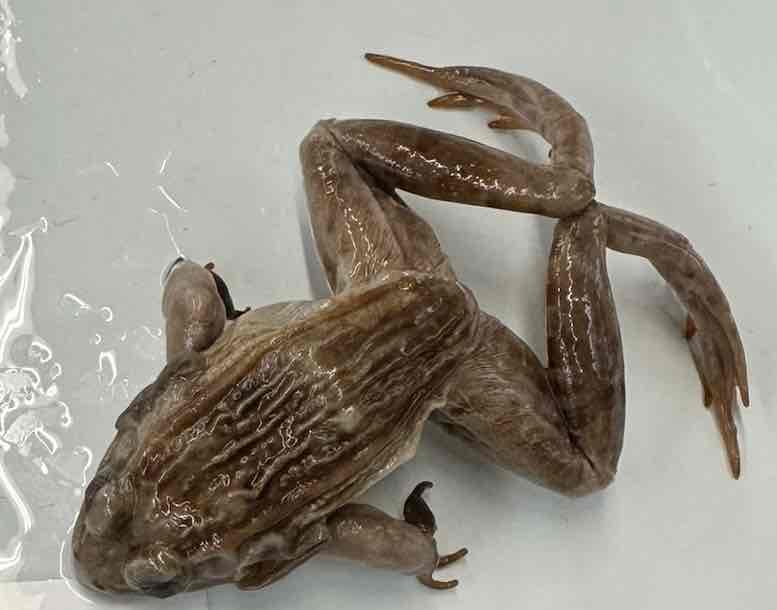

Southern Leopard Frog
- Lithobates sphenocephalus
- family: Ranidae
- order: Anura
Lithobates sphenocephalus
- posses long legs with pointed toes
- narrow waist and smooth skin
- toes joined by webbing
- typically dorsolateral folds
- upper jaw is toothed
- tongue bicornuate behind
- most are medium to large species
- Goliath is largest frog in world
- many species are typical pond breeders
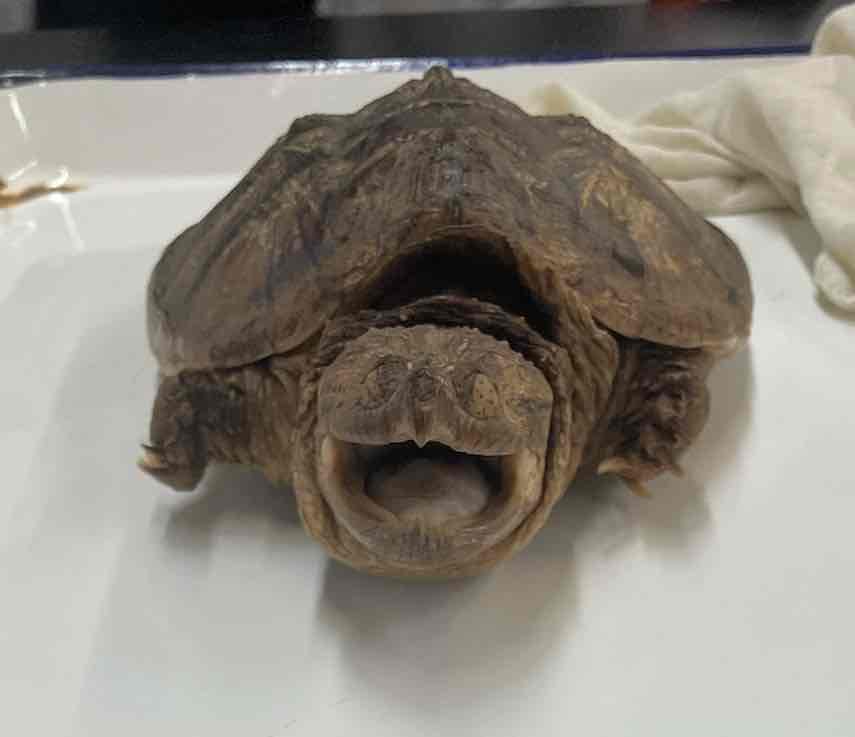

Snapping Turtles
- Chelydra serpentina
- family: Chelydridae
- Order: Testudines
Chelydra serpentina
- common in texas
- characterized by large size
- large head and limbs
- cannot fully retract into shells
- powerful jaws
- long tails
- hooked upper jaw
- carapace of adult C. serpentina is relatively smooth
- Macrochelys temminckii (protected statewide) exhibits 3 heavily keeled ridges
- opportunistic carnivores
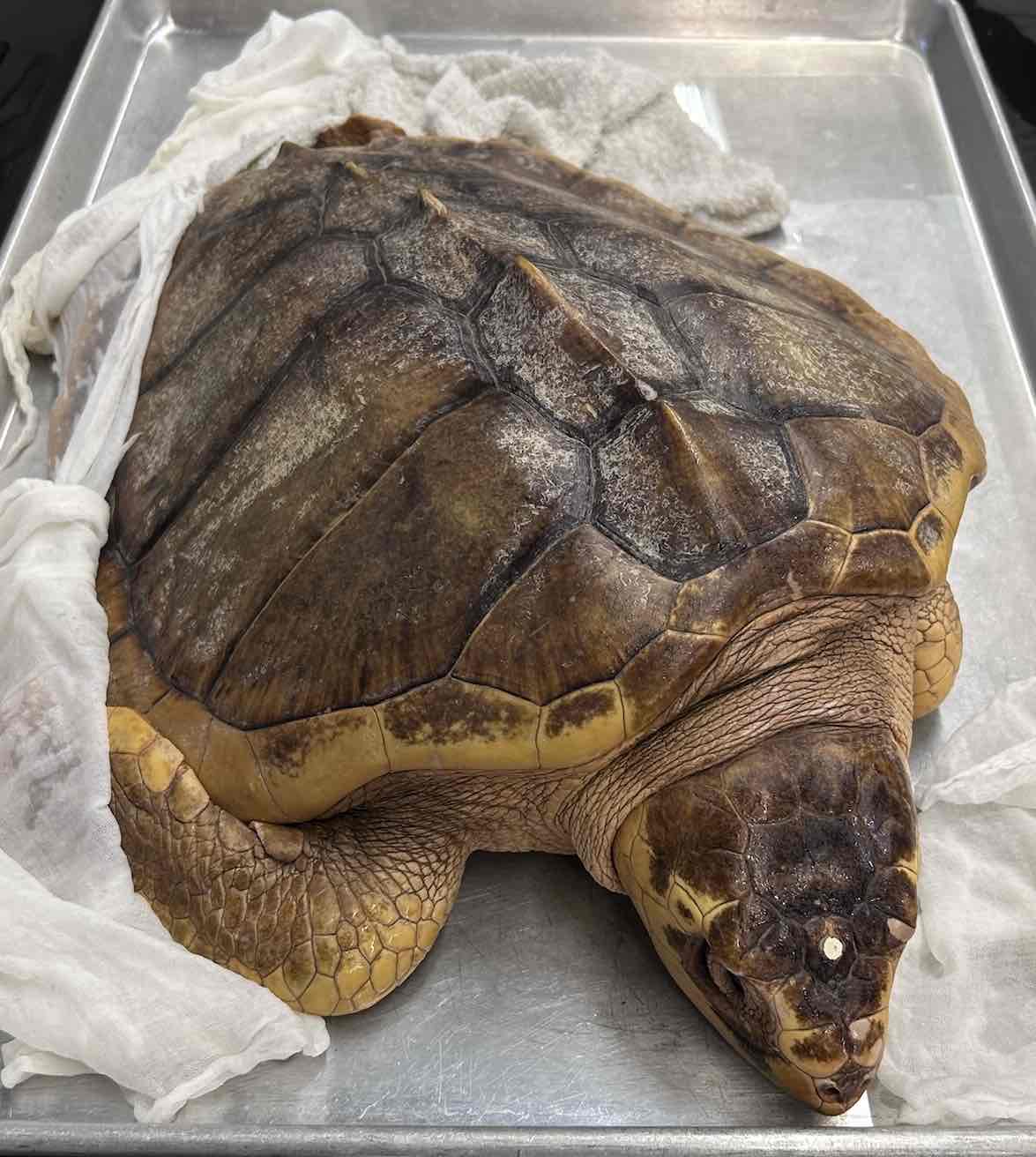

Kemp's Ridley Sea turtle
- Lepidochely kempii
- family: cheloniidae
- order: Testudines
Lepidochelys kempii Characteristics
- large sea turtles with flattened stream lined shells
- carapace is ovoid to heart shaped
- limbs modified into flippers
- cannot support weight on land
- cannot retract the head within the shell
- truly marine
- only females come ashore to nest
- basking on land is green sea turtles
- smallest and shortest lived species of sea turtle
- critically endangered
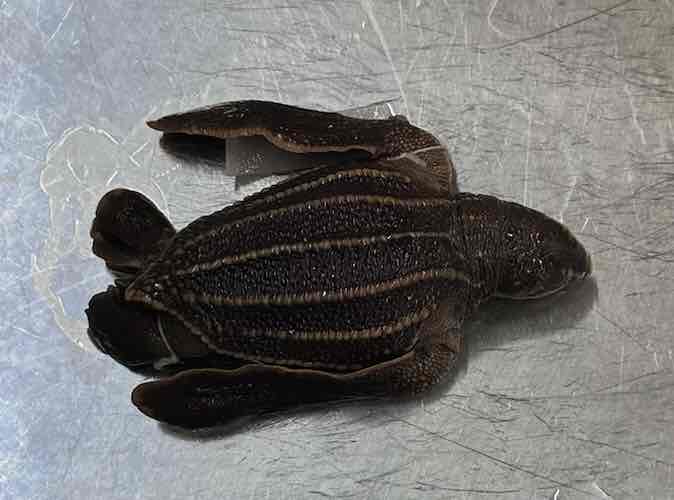

Leatherback sea turtle
- Dermochelys coriacea
- family: Dermochelyidae
- order: Testudines
Dermochelys coricea
- broad streamlined shells that lack dermal scutes
- forelimbs are large flippers and hindlimbs are strongly webbed
- highly specialized pelagic sea turtles
- only living reptile classified as an inertial endotherm
- maintain body temperatures warmer than seawater temperatures
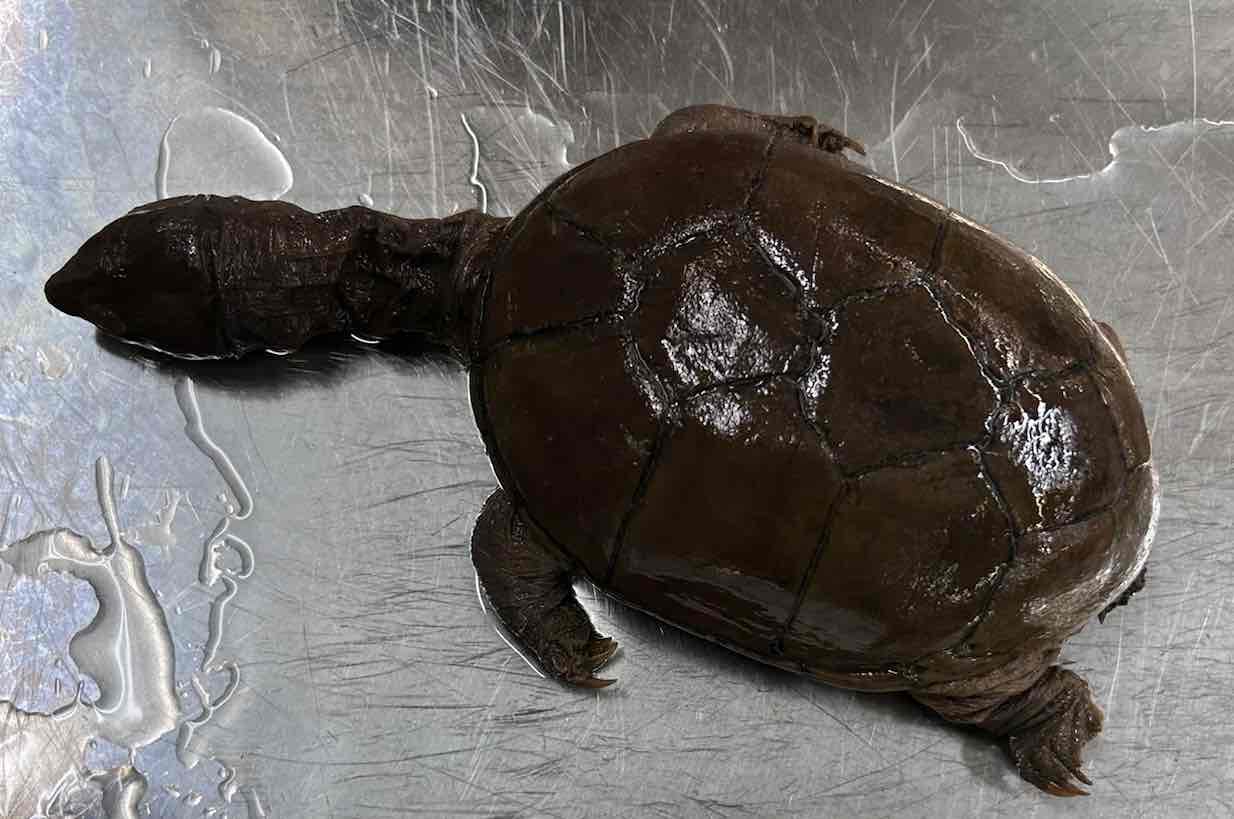

Yellow mud turtle
- Kinosternon Flavescens
- family: Kinosternidae
- order: Testudine
Kinosternon Flavescens Characteristics
- inhabit slow moving bodies of water often with soft bottoms and abundant vegetation
- variable in size
- carapace generally egg shaped (ovoid) and ranges from dusky yellow to black in color
- carapace may or may not possess keels
- plastron is often reduced and may be hinged
- musk glands are found on the bridge of shell
- plastron has 10-11 scutes
- carapace has 11 marginal scutes which are not in contact with pectoral plates
- fleshy barbels on chin and necks
- males have longer tails and two rough patches of skin on each hind leg
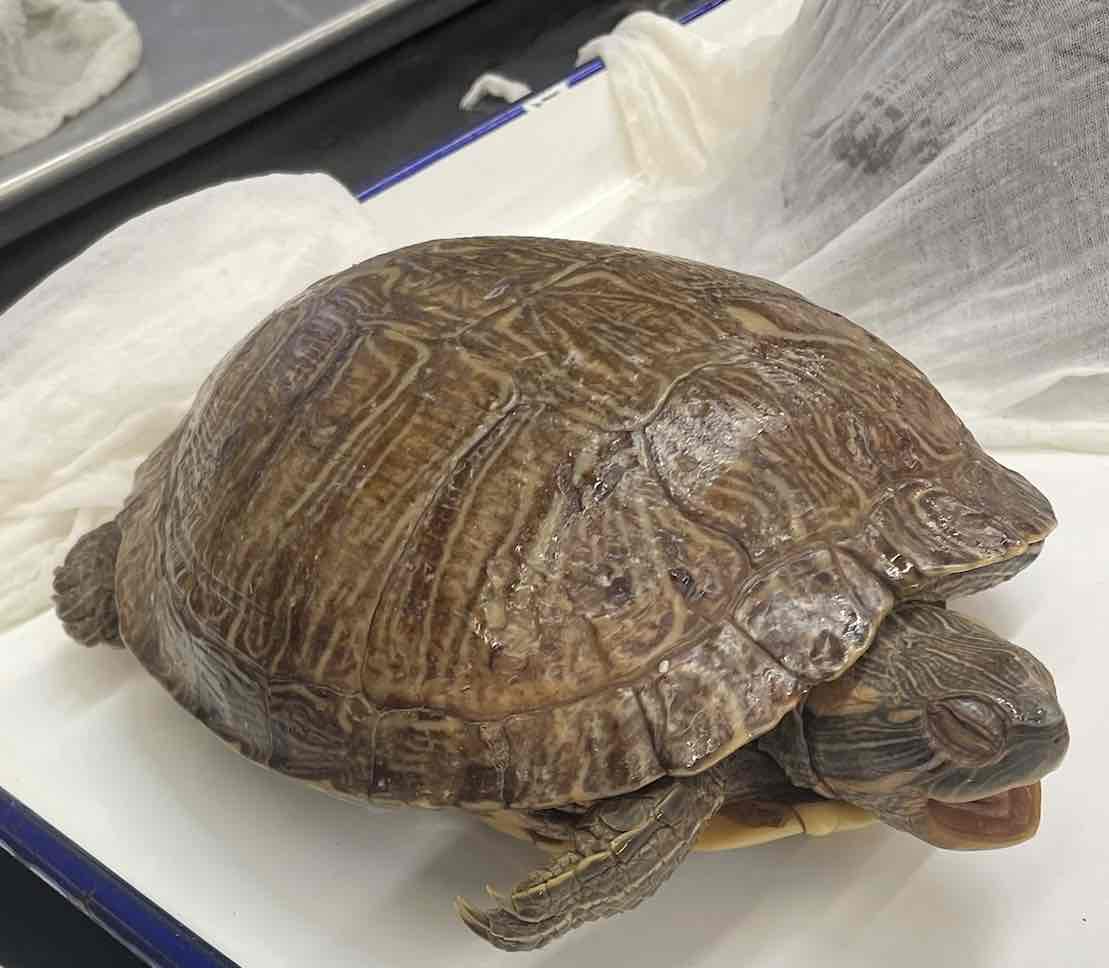

Pond slider
- Trachemys scripta
- family: Emydidae
- order: Testudines
Trachemys scripta characteristics
- primarily freshwater species though some can be in brackish waters
- variable size carapace length
- coloration variable
- some species carapace is domed and some low arching
- plastron is hinged and movable in some while fixed in others
- some unique skeletal features
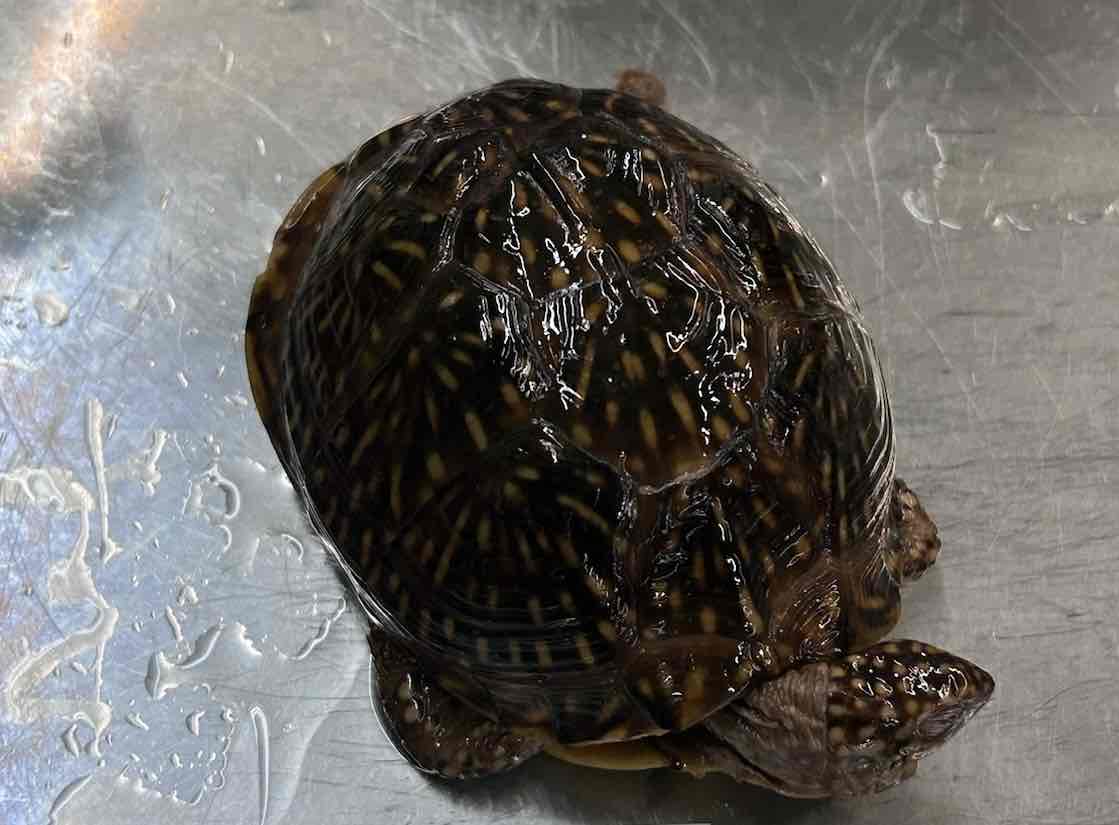

Ornate Box Turtle
- Terrapene ornata
- family: Emydidae
- order: testudines
Terrapene ornata
- primarily freshwater species though some can be in brackish waters
- variable size carapace length
- coloration variable
- some species carapace is domed and some low arching
- plastron is hinged and movable in some while fixed in others
- some unique skeletal features
- terrestrial
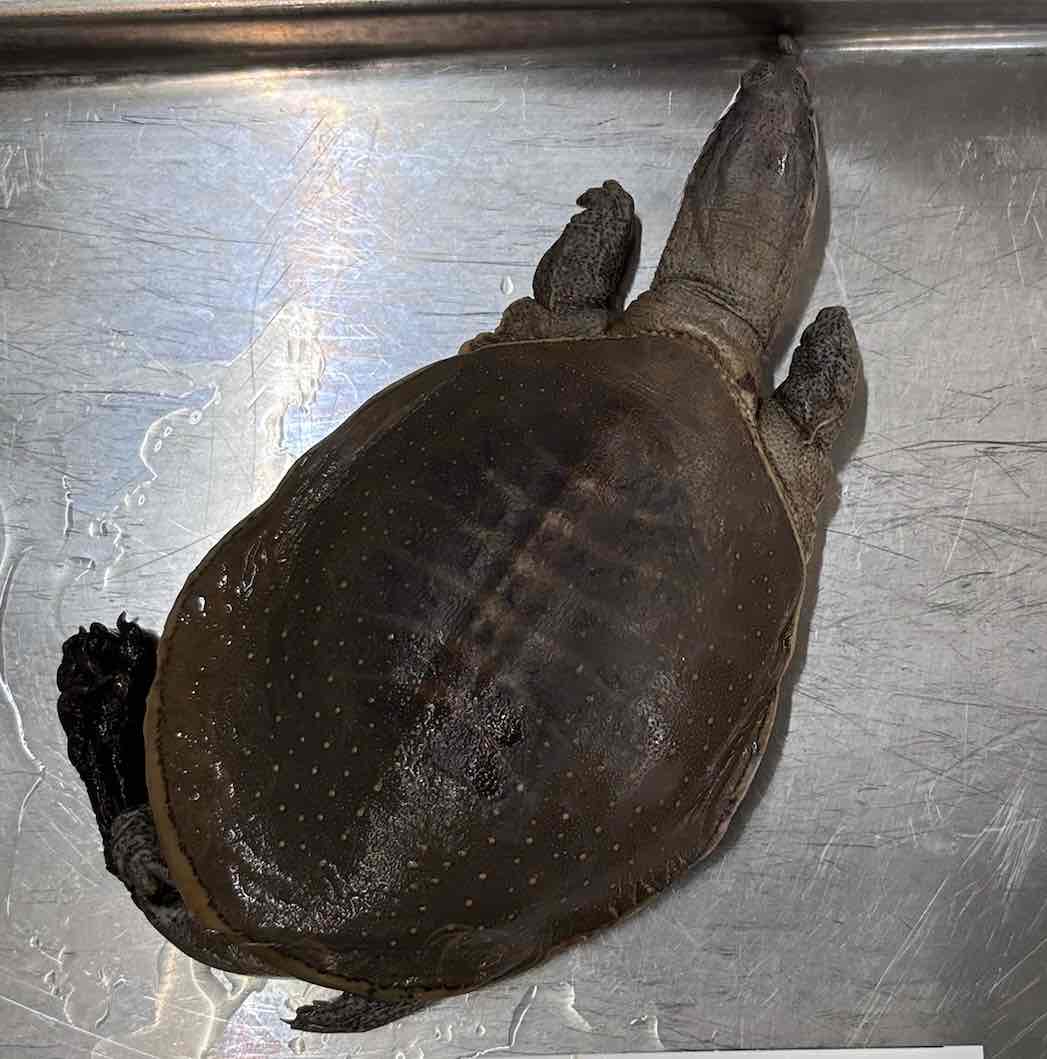

- Apalone spinifera
- family: Trionychidae
- order Testudines
Apalone spinifera characteristics
- all species are aquatic but bask near water
- carapace lacks scutes and is covered instead with leathery skin
- can be distinguished with dorsoventral compression, leathery shells, and elongated snouth
- carapace skeleton is lost resulting in ribs with free ends
- numerous characters diagnose the Trionychidae including lack of articulation between the centra of last cervical and first thoracic vertebrae, claws present on only medial three digits and fleshy lips covering usual keratin beak
- aquatic turtles able to absorb significant amounts of oxygen from water through the skin covering the carapace and their buccal cavity
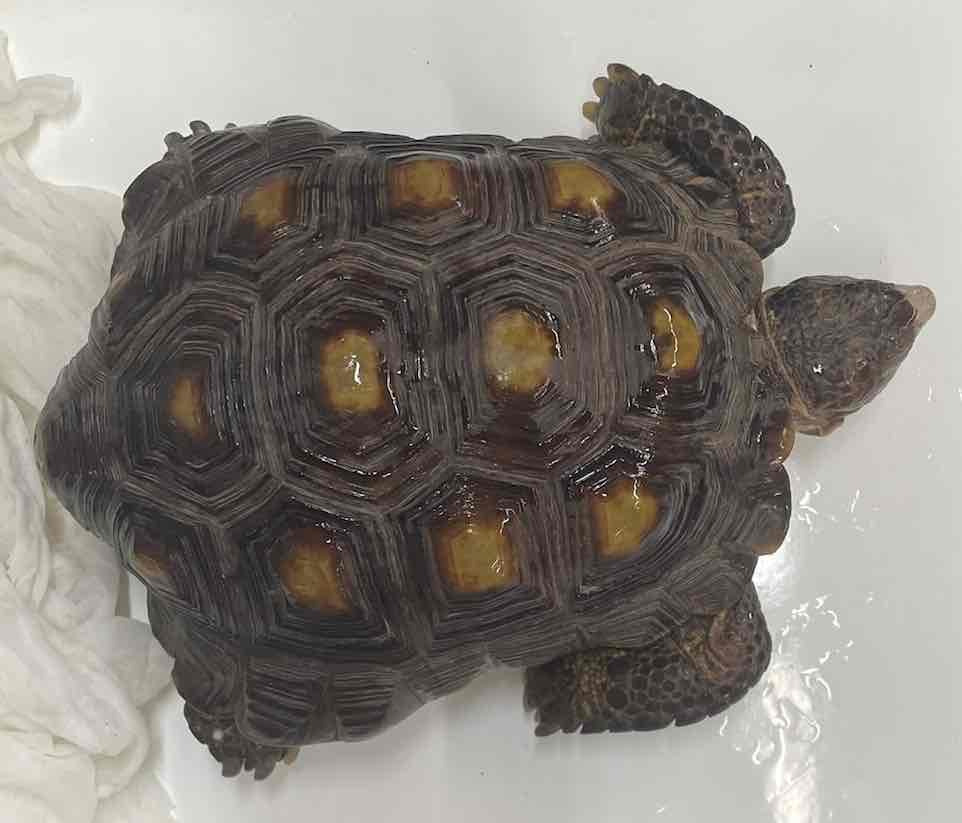

- Gopherus berlandieri
- family: Testudinidae
- order: Testudines
Gopherus berlandieri
- all terrestrial and inhabit warm areas ranging from rain forests to deserts
- range in size from carapace of less than 12 cm to 130 cm
- domed carapace
- no hinge in plastron
- only hinged found in hinge back tortoises
- adaptations to terrestrial life include thick, elephantine rear legs, short webless fee and short digits
- forelegs usually have scales on anterior surface
- lack of glands in axillary and inguinal regions
- presence of only four digits on rear feet
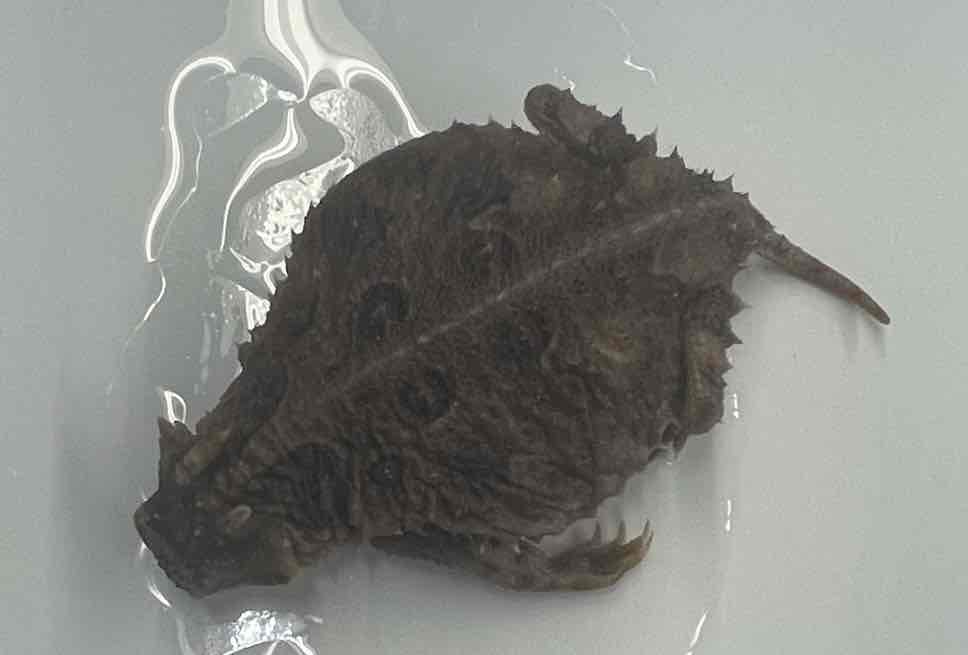

Texas Horned Lizard
- Phrynosoma cornutum
- family: Phrynosomatidae
- order: Squamata
Phrynosoma cornutum
- relatively small lizards
- diversity of forms
- pleurodont teeth
- many skeletal synapomorphies: absence of pterygoid teeth, reduction of clavicular flange, posterior process of interclavicle invested by sternum anteriorly, sink trap nasal apparatus with elongate septomaxilla, and enlarged posterior love of hemipenes
- heavily keeled scales and spines
- external ears
- femoral pores
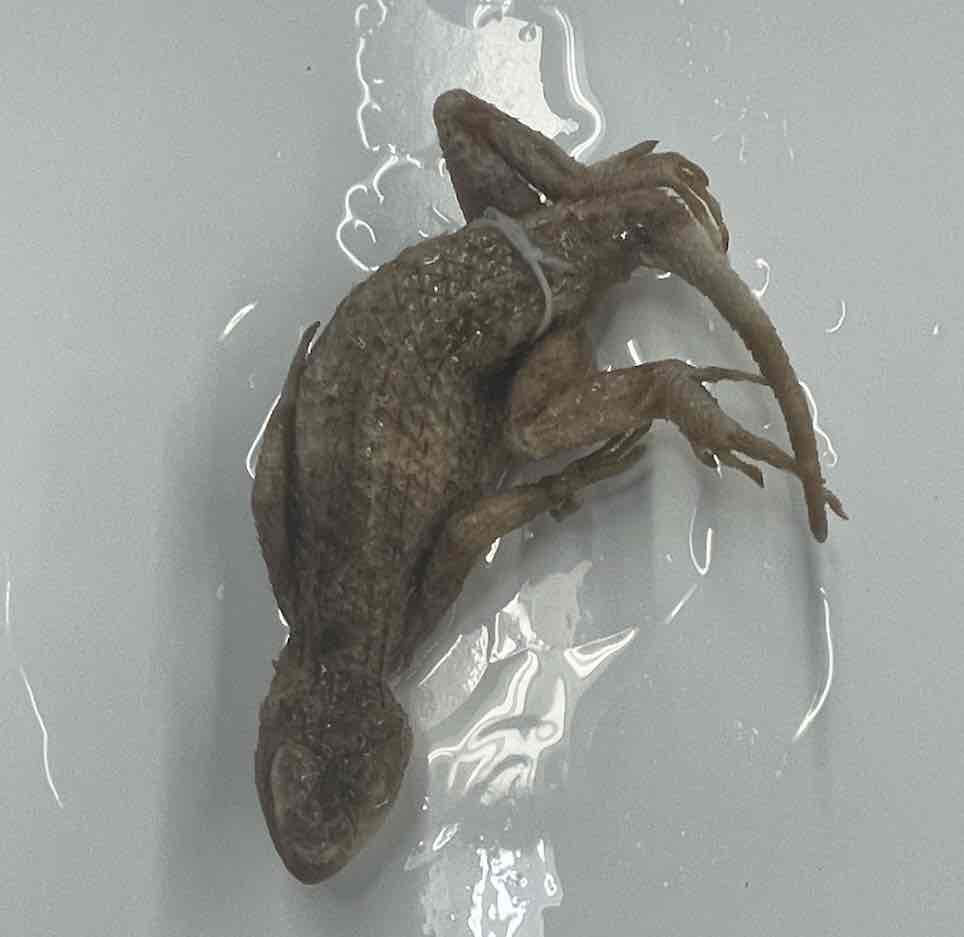

Texas Spiny lizard
- Sceloporus olivaceus
- family: Phrynosomatidae
- order: squamata
Sceloporus olivaceus
- relatively small lizards
- diversity of forms
- pleurodont teeth
- many skeletal synapomorphies: absence of pterygoid teeth, reduction of clavicular flange, posterior process of interclavicle invested by sternum anteriorly, sink trap nasal apparatus with elongate septomaxilla, and enlarged posterior love of hemipenes
- heavily keeled scales and spines
- external ears
- femoral pores
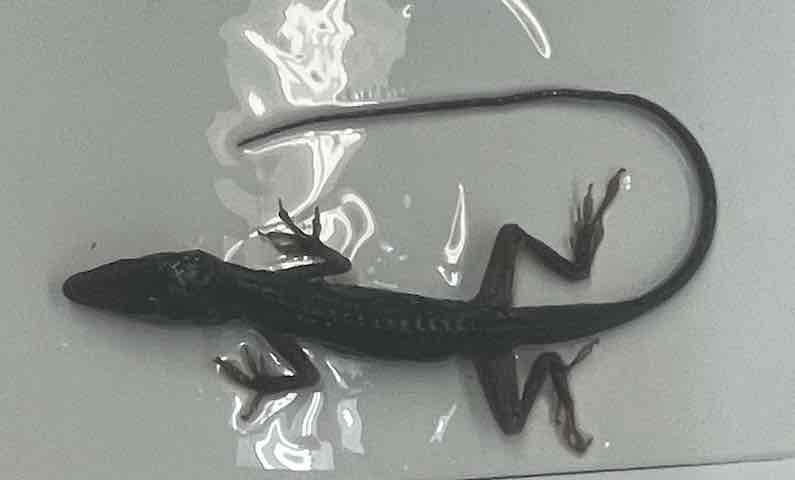

Green Anole
- Anolis carolinensis
- family: Dactyloidae
- order: squamata
Anolis carolinensis
- primarily arboreal lizards
- relatively small lizards with morphologies adapted for climbing
- pleurodont teeth which distinguished them from agamids and chameleons
- synapomorphies; endolymphatic sacs penetrating nuchal musculature, strongly bicapitate, bisulcate hemipenes, larges and most diverse reptile, posterior extensions of the dentary, reduced angular, presence of subdigital lamellae bearing setae, and reticular lingual papillae
- far posterior extension of dentary gives appearance of triangular shaped head
- external ears
- toepads expanded
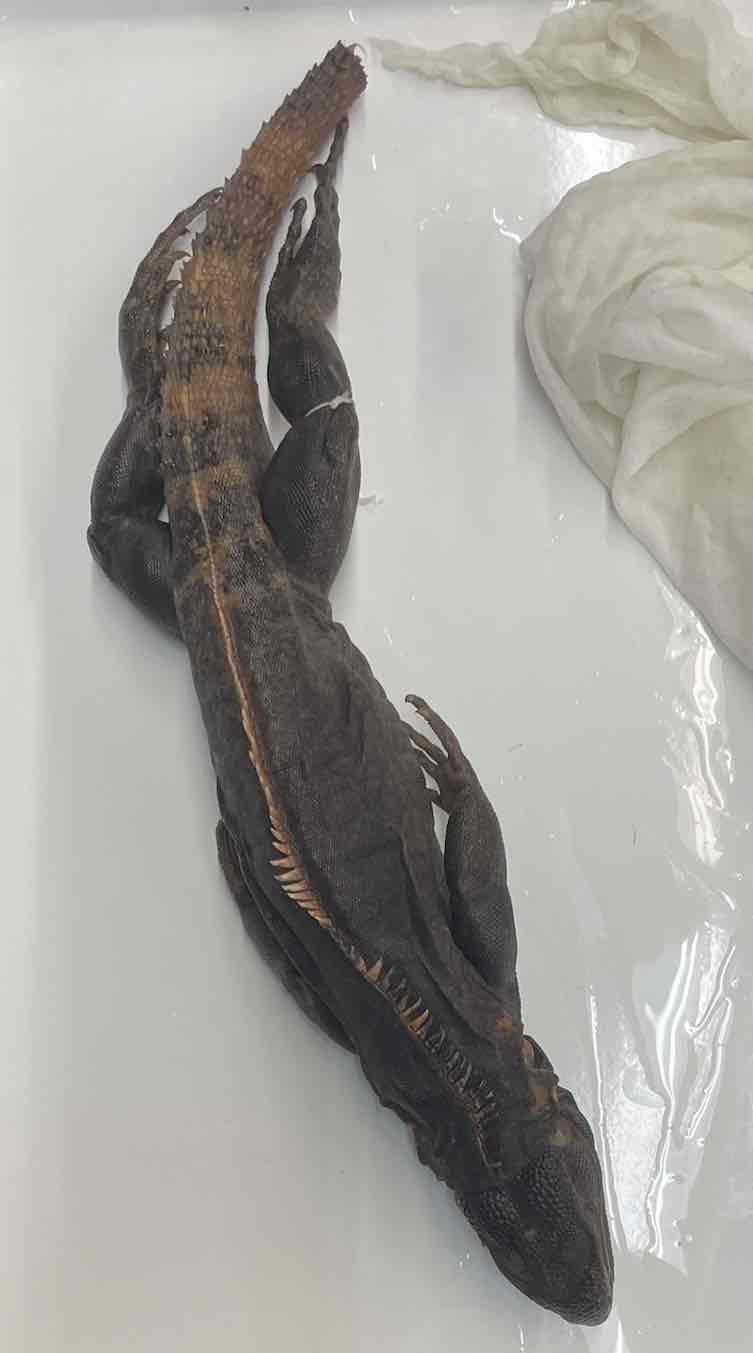

Spinytail Iguana
- Ctenosaura pectinata
- family: Iguanidae
- order: squamata
Ctenosaura pectinata
- large lizards
- predominantly terrestrial in mesic and xeric habitats
- arboreal
predominantly herbivorous
- Amblyrhyncus, marine iguana, feeds on algae
- all are oviparous and produce large clutches of eggs
- males have femoral pores
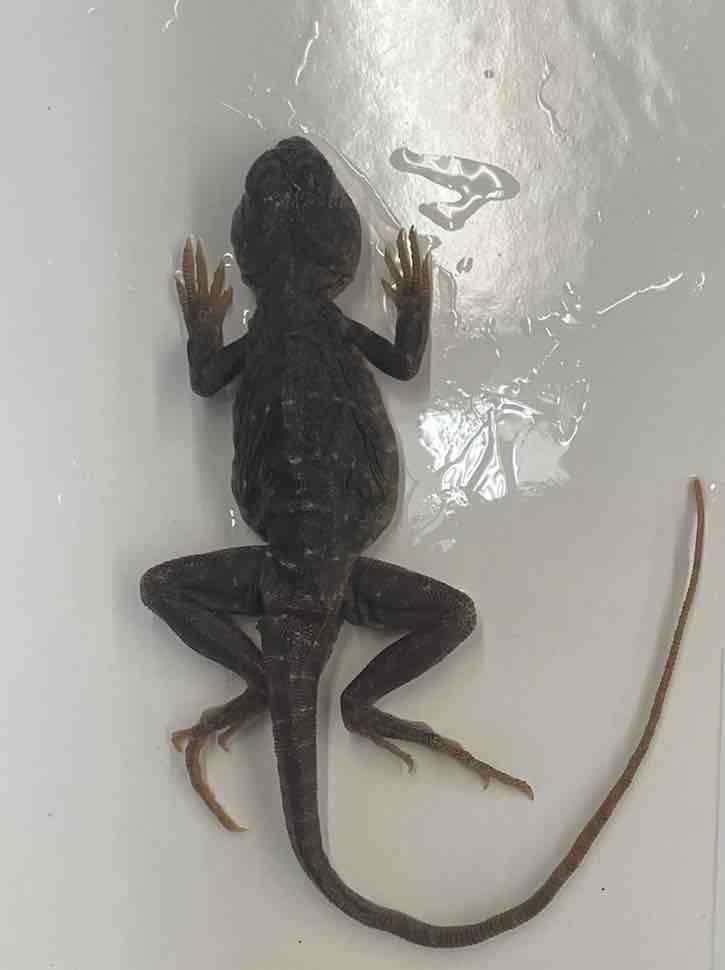

Collard lizards
- Crotaphytus collaris
- family: Crotaphytidae
- order: squamata
Crotaphytus collaris
- small group of desert dwelling lizards
- moderately large lizards
- large heads
- long limbs and tails
- pleurodont teeth, palatine teeth
- synapomorphies: may be relics of very old group
- robust head and granular scales
- external ears
- femoral pores
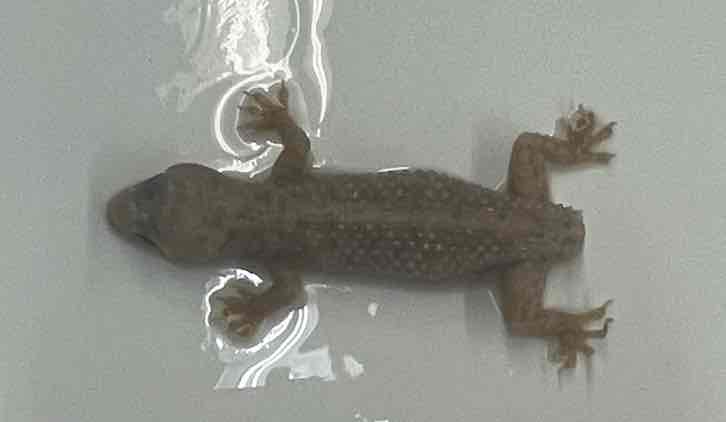

Mediterranean house gecko
- Hemidactylus turcicus
- family: Gekkonidae
- order: squamata
Hemidactylus turcicus
- nocturnal
- insectivorous
- vertical pupils and transparent scale over eye (spectacle)
- no eyelids
- skin is soft with sparse horny tubercles
- toes usually have transverse rows of hooked lamellae that permit adhesion to smooth surfaces
- tail used as fat store and capable of autotomy
- external ears
- caudal autotomy common with fracture planes in each caudal vertebra
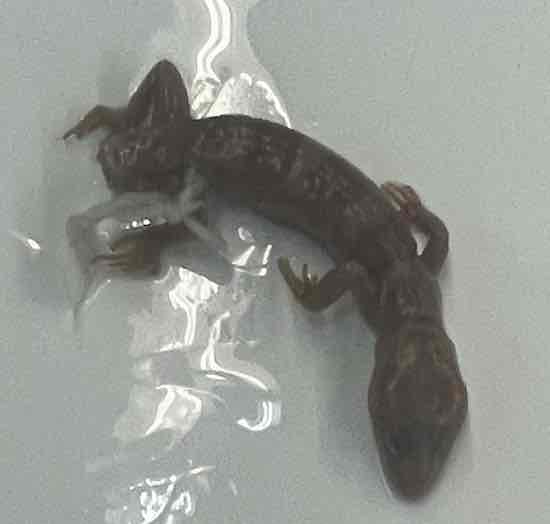

- Coleonyx brevis
- family: Eublepharidae
- order: squamata
Coleonys brevix
- skin is soft and lack tubercles
- no lamellae on toes
- external ears
- only geckos that possess true eyelids
- vertical pupil
- lay clutches of two eggs with soft shells
- ground dwellers
- nocturnal
- likely had Gondwanaland origin
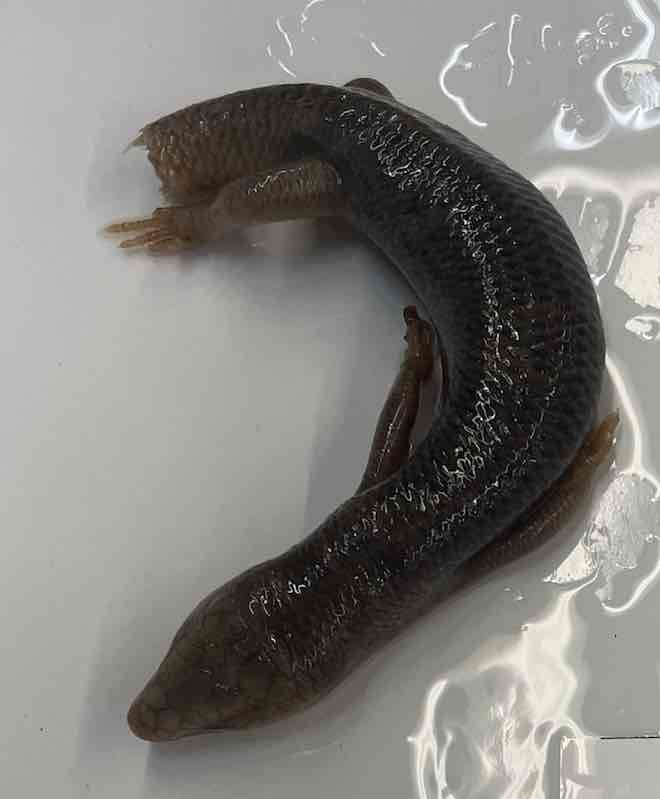

Great Plains Skink
- Plestiodon obsoletus
- family Scincidae
- order: squamata
Plestiodon obsoletus
- scales around the body equal in size, overlapping, and smooth and shiny
- size ranges from small to large
- external ears
- generally slender with relatively short limbs
- osteoderms under dorsal and ventral scales
- caudal autotomy very common but not universal
- highly diverse in behavior, reproductions and ecology
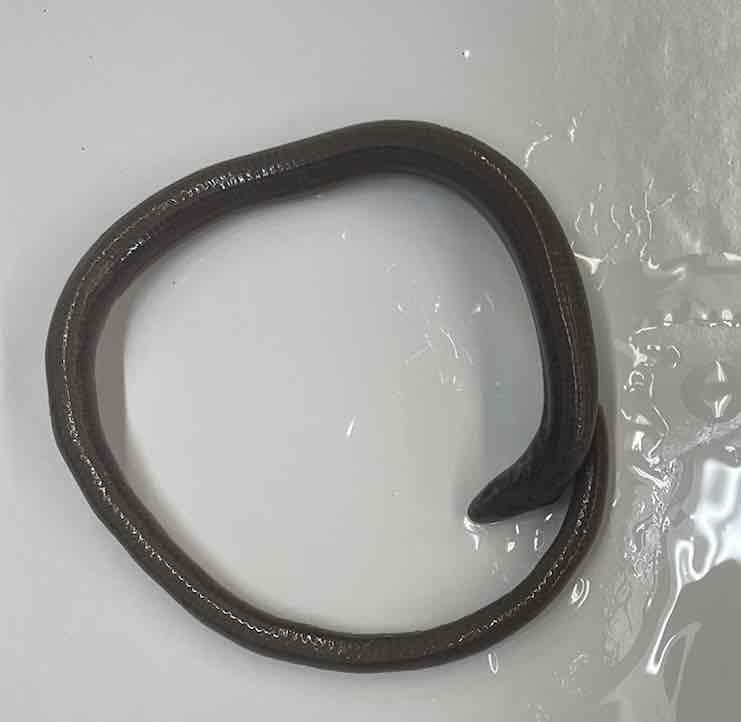

Slender Glass lizard
- Ophisaurus attenuatus
- family: Anguidae
- order: squamata
Ophisaurus attenuatus
- xeric and tropical habitats
- legless lizards and limbs are absent and reduced in many forms
- external ears
- lateral skin fold along body
- osteoderms underlie the ventral scales
- rectangular scales make skin appear armored
- several quite small and limbless others are limbless but rather long and some strong but short limbs and relatively large triangular heads with powerful jaws
- range in size less than 10 cm to 1-1.5 m
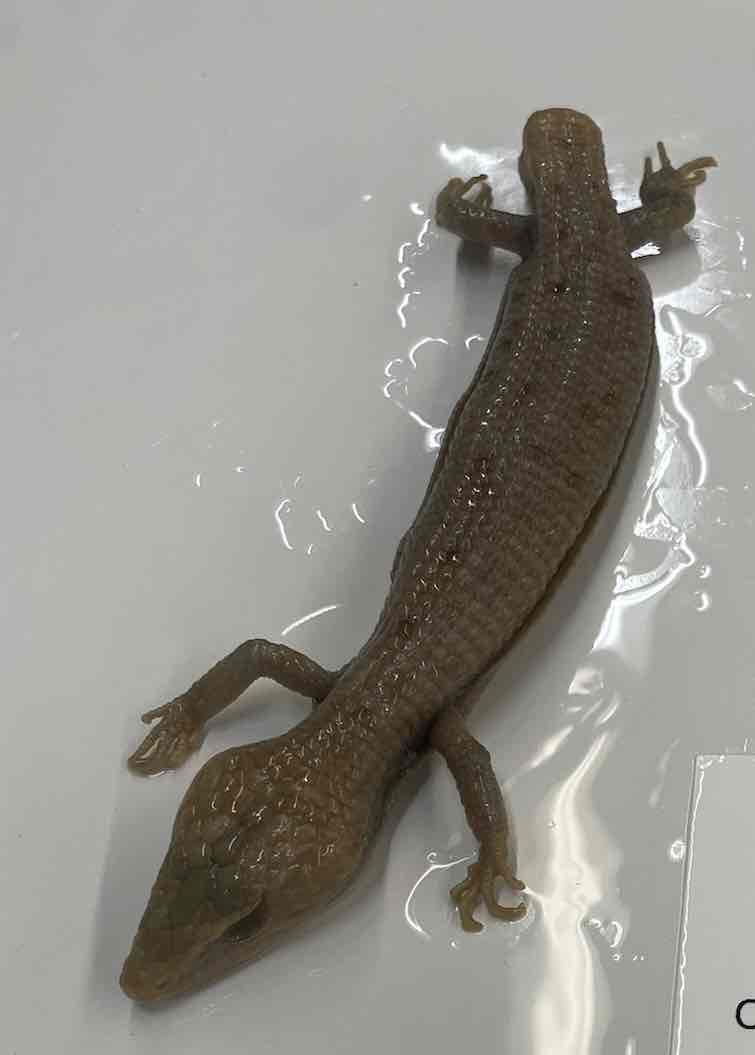

- Gerrhonotus infernalis
- family: Anguidae
- order: squamata
Gerrhonotus infernalis
- xeric and tropical habitats
- legless lizards and limbs are absent and reduced in many forms
- external ears
- lateral skin fold along body
- osteoderms underlie the ventral scales
- rectangular scales make skin appear armored
- several quite small and limbless others are limbless but rather long and some strong but short limbs and relatively large triangular heads with powerful jaws
- range in size less than 10 cm to 1-1.5 m
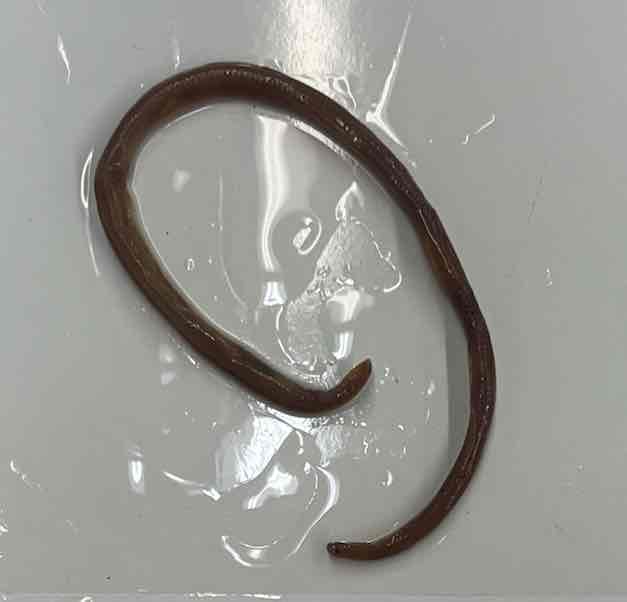

Texas blind snakes
- Leptotyphlops dulcis
- family: Leptotyphlopidae
- order: squamata
- suborder: Serpentes
Leptotyphlops dulcis
- small and very slender
- eyes vestigial and covered by scales
- ventral scales equal size as dorsal scales
- fossorial and occur in dry habitats and wet forest
- feed on soft bodies invertebrates
- they emit secretion from cloacal glands that mimics the chemosensory signals of termites and thus deceives termite soldiers from attacking
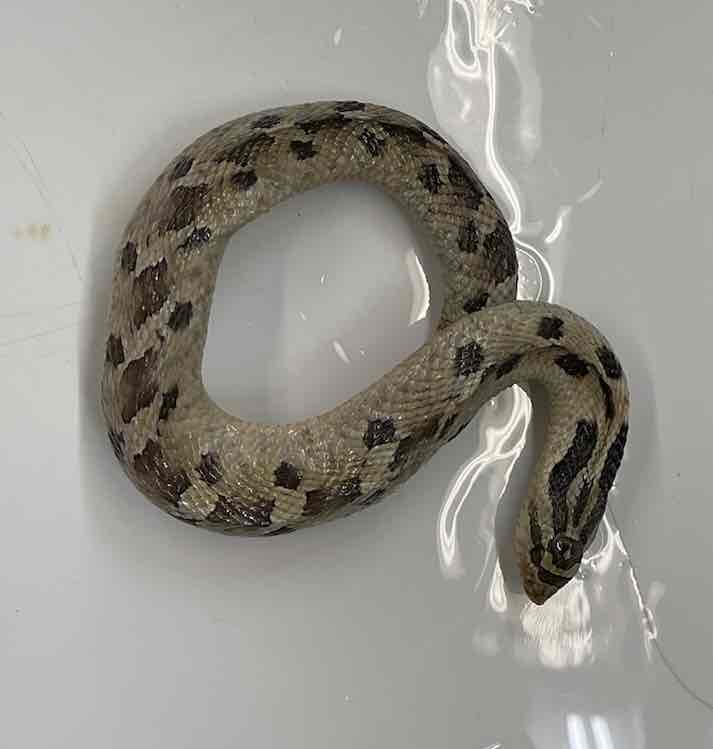

Eastern Hognose Snake
- Heterodon platirhinos
- family Colubridae
- order: squamata
- suborder: serpentes
Heterodon platirhinos
- lack limbs
- lack moveable eyelids
- lack external ears
- ventral scales transversely elongated
- left lung greatly reduced or absent

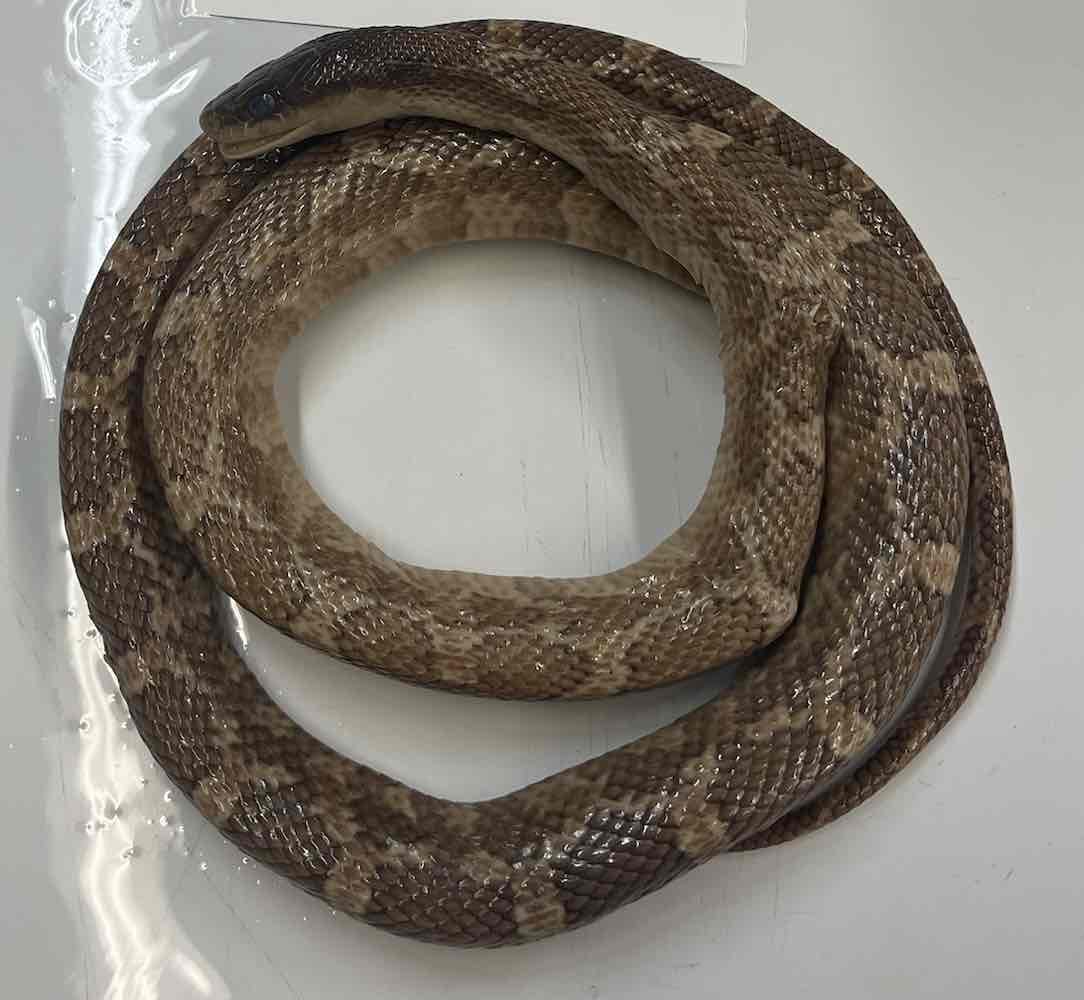
western ribbon snake
- Thamnophis proximus
- family Colubridae
- order: squamata
- suborder: serpentes
Thamnophis proximus
- lack limbs
- lack moveable eyelids
- lack external ears
- ventral scales transversely elongated
- left lung greatly reduced or absent
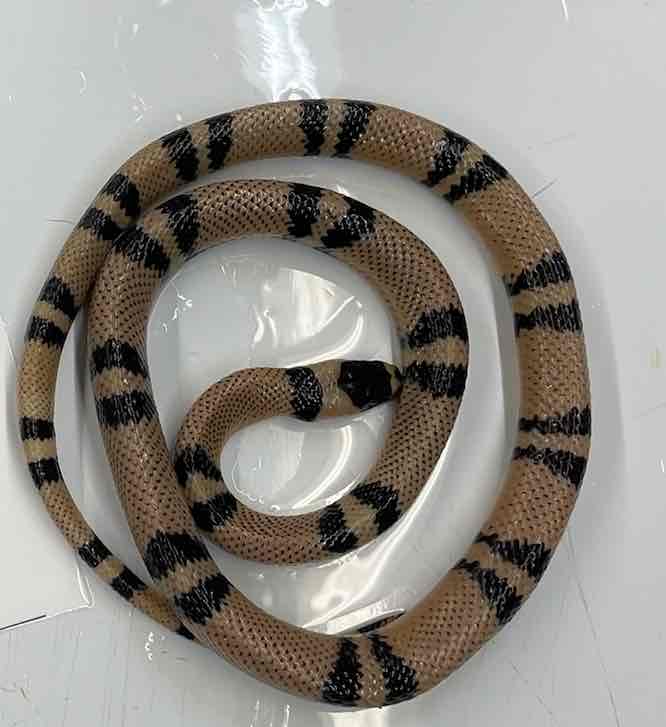

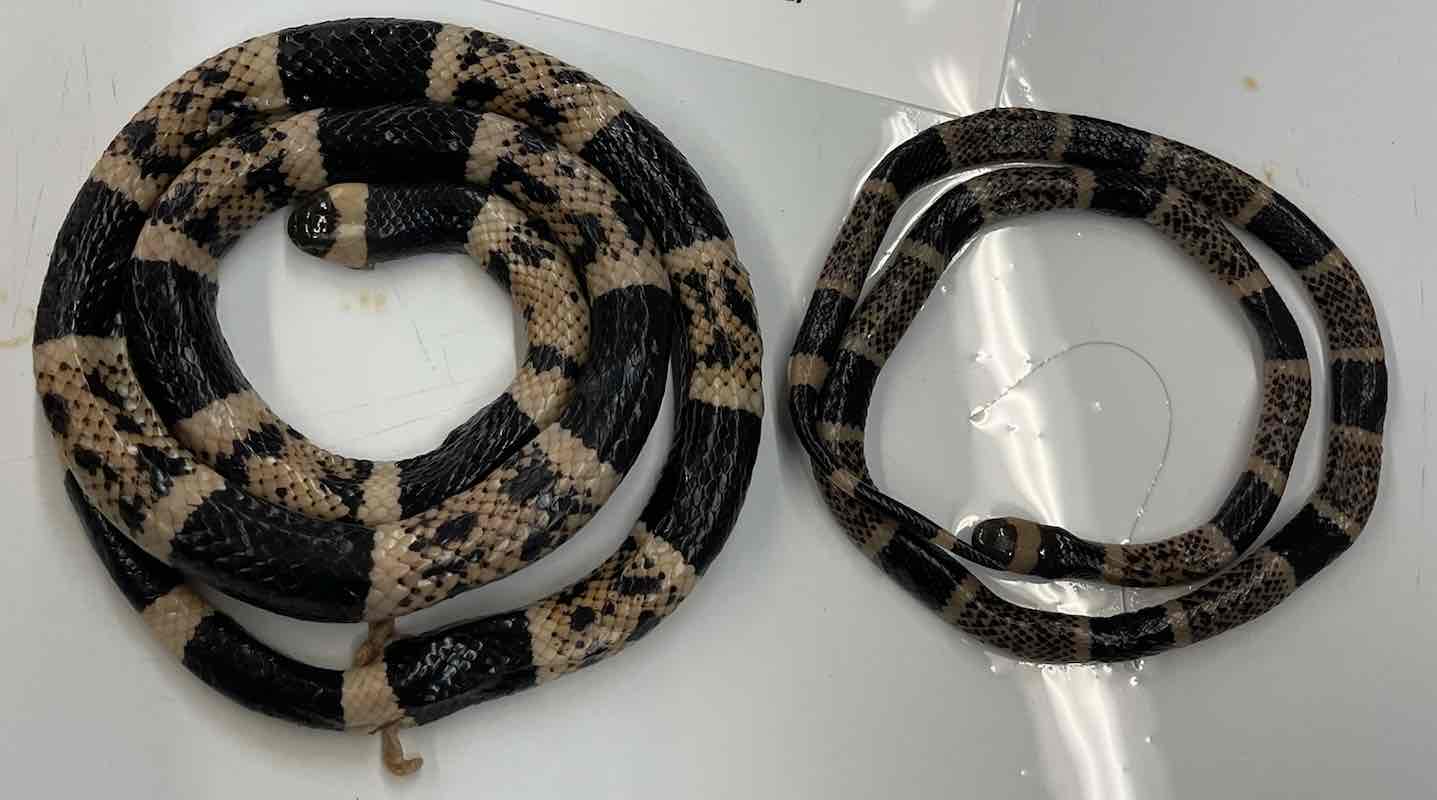
milksnake
- Lampropeltis triangulum
- family colubridae
- order: squamata
- suborder: serpentes
Lampropeltis triangulum
- lack limbs
- lack moveable eyelids
- lack external ears
- ventral scales transversely elongated
- left lung greatly reduced or absent

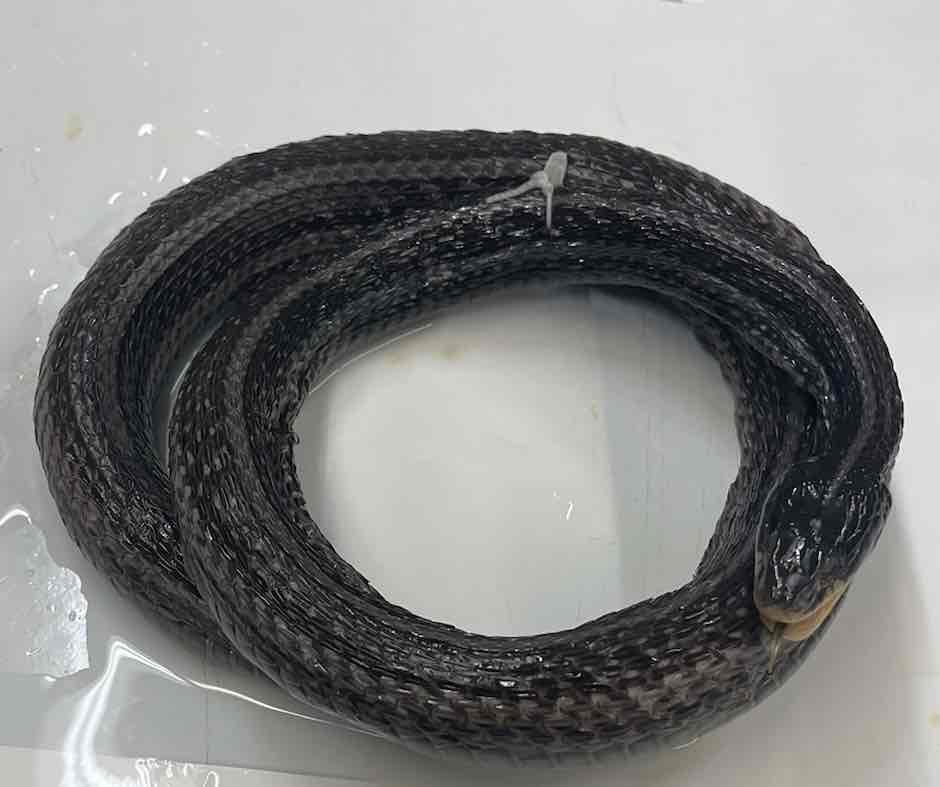
- Pantherophis obsoletus
- family: colubridae
- order: squamata
- suborder: serpentes
Pantherophis obsoletus
- lack limbs
- lack moveable eyelids
- lack external ears
- ventral scales transversely elongated
- left lung greatly reduced or absent
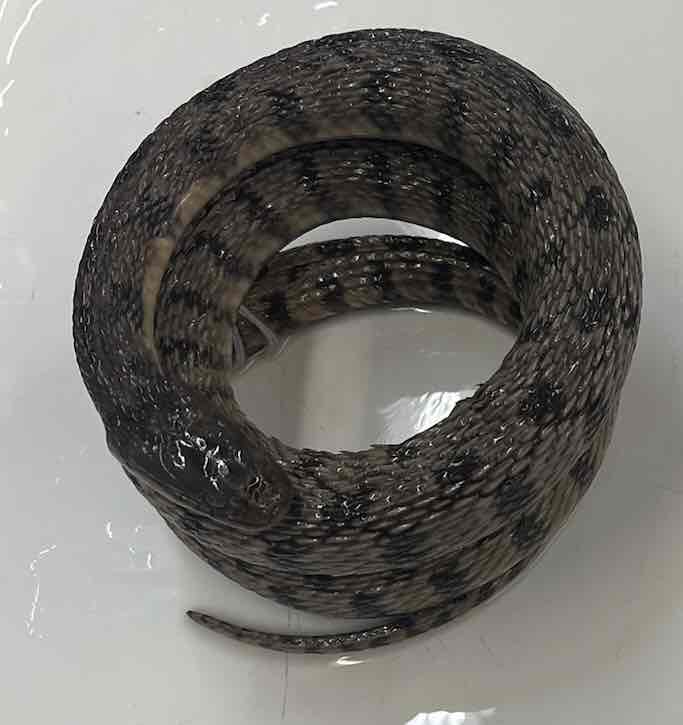

- Nerodia rhombifer
- family: colubridae
- order: squamata
- suborder: serpentes
Nerodia rhombifer
- lack limbs
- lack moveable eyelids
- lack external ears
- ventral scales transversely elongated
- left lung greatly reduced or absent

- Micrurus tener
- family: Elapidae
- order: squamata
- suborder: serpentes
Micrurus tener
- venomous with erect fangs
- left lung is reduced or absent
- ventral scales transversely elongated
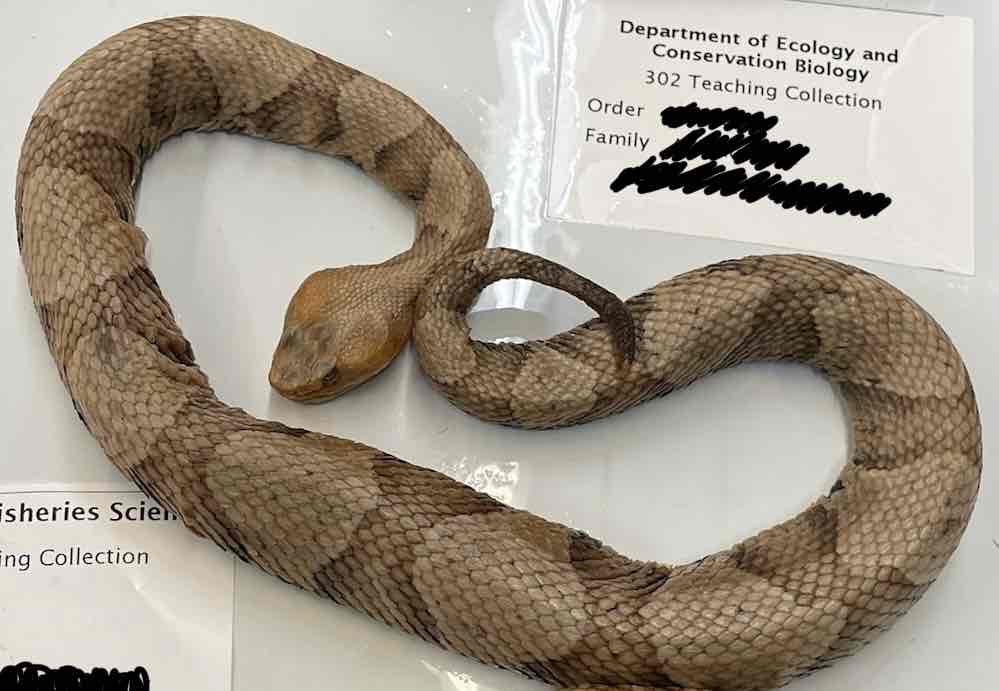

copperhead
- Agkistrodon contortrix
- family: Viperidae
- order: squamata
- suborder: serpentes
Agkistrodon contortrix
- venomous with rotating fang apparatus that allows long fangs that are erected when biting fold against palate when mouth is closed
- most have robust bodies and distinctly triangular heads
- infrared receptors (pits)
- left lung is usually absent or reduced when present
cottonmouth
- Agkistrodon piscivorus
- family viperidae
- order: squamata
- suborder: serpentes
Agkistrodon piscivorus
- venomous with rotating fang apparatus that allows long fangs that are erected when biting fold against palate when mouth is closed
- most have robust bodies and distinctly triangular heads
- infrared receptors (pits)
- left lung is usually absent or reduced when present
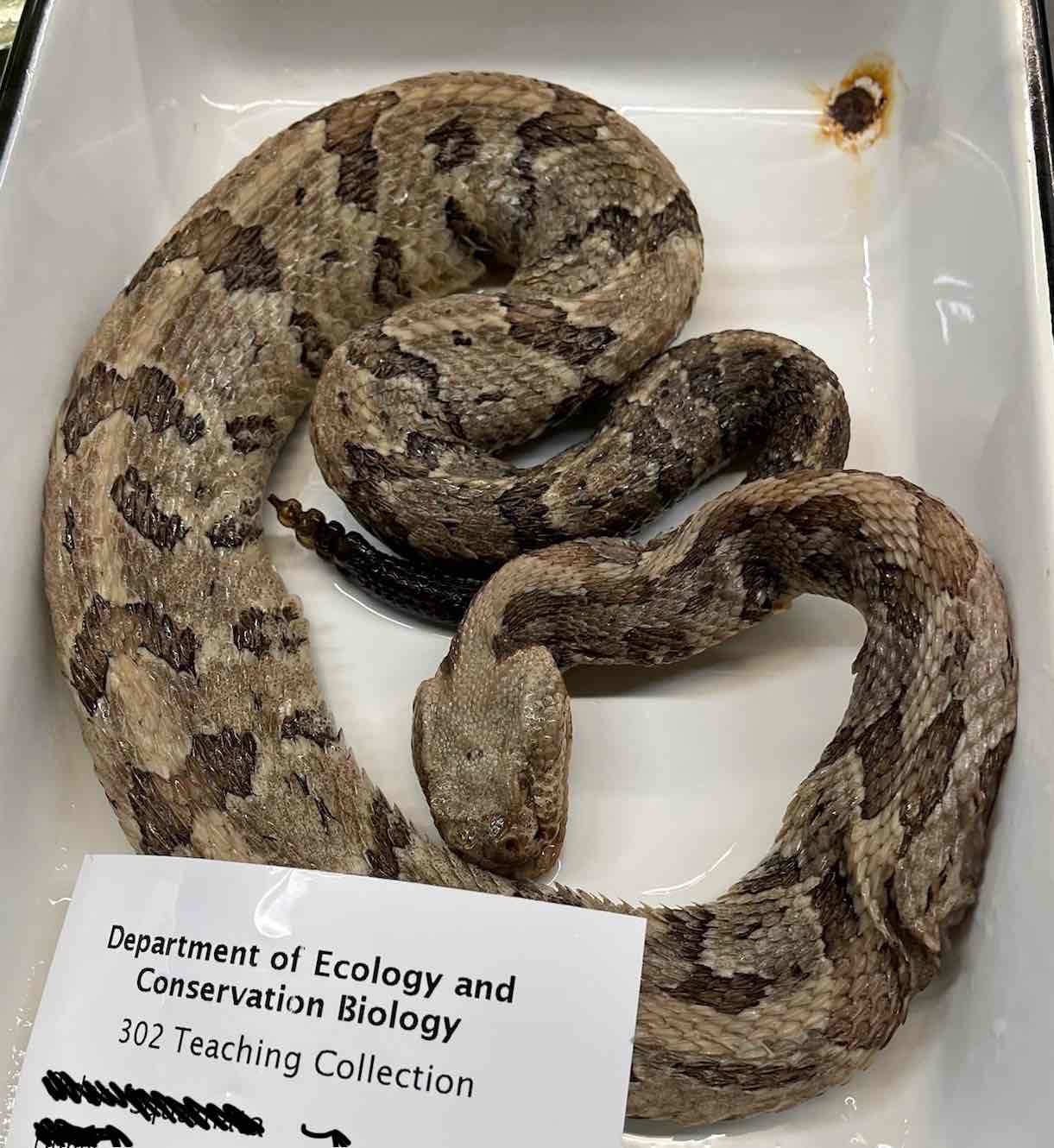

Canebrake rattlesnake
- Crotalus horridus
- family viperidae
- order: squamata
- suborder: serpentes
Crotalus horridus
- venomous with rotating fang apparatus that allows long fangs that are erected when biting fold against palate when mouth is closed
- most have robust bodies and distinctly triangular heads
- infrared receptors (pits)
- left lung is usually absent or reduced when present
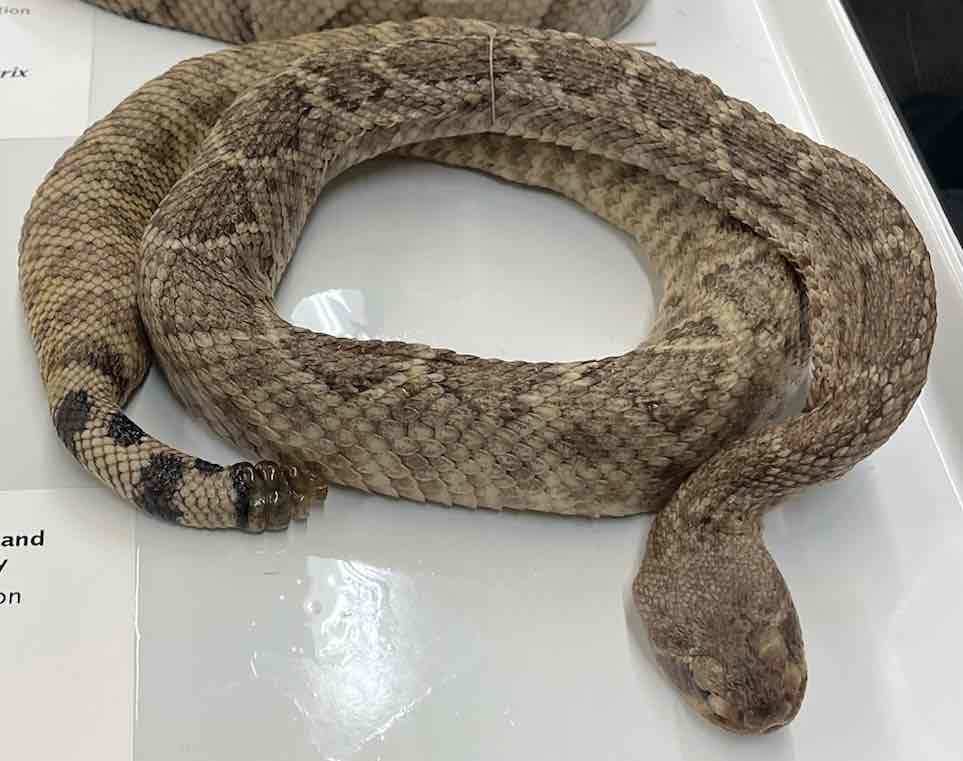

Western diamondback rattlesnake
- Crotalus atrox
- family viperidae
- order squamata
- suborder: serpentes
Crotalus atrox
- venomous with rotating fang apparatus that allows long fangs that are erected when biting fold against palate when mouth is closed
- most have robust bodies and distinctly triangular heads
- infrared receptors (pits)
- left lung is usually absent or reduced when present
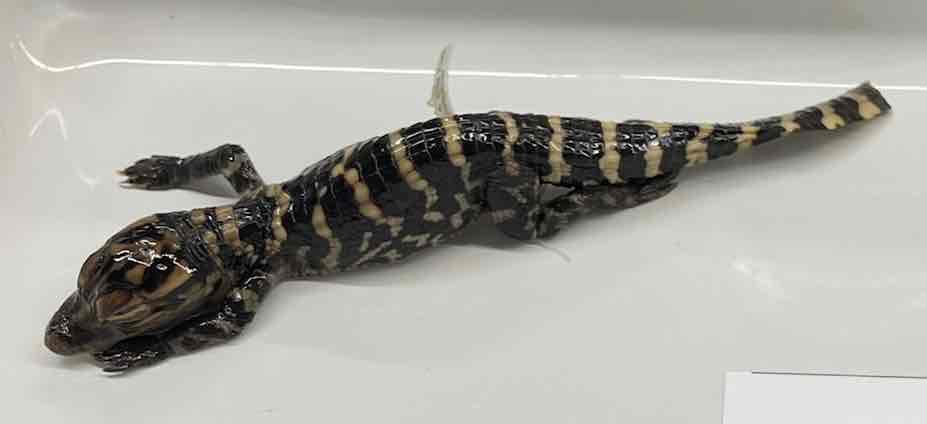

American Alligator
- Alligator mississippiensis
- family: Alligatoridae
- order: Crocodylia
Alligator mississippiensis
- broad snout
- teeth of lower jaw fit into pits inside upper jaw
- osteoderms in skin
- external tympanum
- longitudinal opening for the cloaca
- functionally four chambered heart
- nostrils dorsally located at tip of snout with valves to shut them while diving
- secondary palate separates buccal cavity and nasal passages
- webbed feet
- keeled tail
- ability to adjust peripheral and core blood flow in response to need of diving and thermoregulation
- temperature- dependent sex determination