EXAM 2- Corso
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
based on yellow points and stuff said in cell
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
What is the product of carbohydrate/starch digestion?
simple sugar (glucose, fructose, galactose)
What is the product of Triglyceride/fat digestion?
fatty acids and glycerol
What is the product of protein digestion?
amino acids
Where does digestion take place in the body? (organs)
mouth
stomach
small intestine
What’s the difference between catabolism and anabolism? Which take place during fed/fasting state?
catabolism- breakdown of molecules to release energy- FASTING state
anabolism- synthesis of molecules, costing energy- FED state
Catabolism of proteins release ___kcal/g.
4
Catabolism of carbs release ___kcal/g.
4
Catabolism of fats release ___kcal/g.
9
Catabolism of alcohol release ___kcal/g.
7
Which sugar molecules are essential for out diet?
none are needed
Which 4 fat molecules are ESSENTIAL for our diet?
a-linoleic— an OMEGA 6
a-linolenic—- an OMEGA 3
eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)—- an omega 3
docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)—- an omega 3
SUMMARY: OMEGA 6 and OMEGA 3
What’s the difference between essential and nonessential amino acids?
non-essential amino acids are made from essential amino acids
What digestive enzymes are found in the mouth? What macromolecule (fat, carb, protein) do they digest?
salivary amylase- carbs
lingual lipase- fats
salivary amylase breaks what bonds?
KNOW
glucose alpha 1-4 bonds
(note: HAS TO be alpha, has to be 1-4)
Lingual lipase breaks triglycerides into ___________ and ____________ in the mouth.
diglycerides and free fatty acid
What digestive enzymes are found in the stomach? What macromolecule (fat, carb, protein) do they digest?
gastric lipase- fats
pepsin- proteins
acid
Why is there no carb digestion/ stopped carb digestion in the stomach?
acid degrades/inactivates amylase coming from the mouth
What are the products of TG/fat digestion in the stomach?
same as in the mouth- diglycerides and fatty acid
Pepsin in the stomach breaks down _________ to AAs.
proteins
What are proton pumps? What do they do to proteins and bacteria?
PP’s: H+/K+ ATPase
denature proteins, kill bacteria by producing HCl
What are zymogens?
“pro-enzymes”
enzymes that aren’t active yet
What cells secrete pepsinogen?
Chief cells
Why is pepsinogen released, not pepsin?
so chief cells aren’t degraded
What is the difference between glucose and fructose?
glucose- aldehyde
fructose- ketone
What is the difference between glucose and galactose?
galactose is an epimer of glucose at C-4
What is the common feature of aldose sugars? name the key ones?
common- ALDEHYDE
names- glyceraldehyde, erythrose, ribose, glucose, mannose, galactose
What is the common of ketose sugars? name the key ones?
common- KETONE
names- dihydroxyacetone, fructose
Why do we usually draw glucose as a ring?
bc aldehydes are very reactive, they don’t stay as chain long and form a ring
In the intestine, what enzymes are used to break down PROTEINS? What type of enzymes are these?
zymogens (inactive enzymes)
amino peptidase (brush border cell enzyme)
What are the names of the zymogens and their active enzyme in the intestine?
trypsinogen—> trypsin
chymotrypsinogen—→ chymotrypsin
proelastase—> elastase
procarboxypeptidases —> carboxypeptidase
What is bile needed for? Where is bile made? Where is bile stored?
needed to polarize non-polar molecules like FATS
made in the liver
stored in the gallbladder
In the intestines, what enzymes are found to break down TGs/fats?
intestinal LIPASE
In the intestines, 72% of triglycerides are broken down into ____________________+ FFA.***
2-mono-acylglycerol
What enzymes are found in the intestine that digest CARBS!
pancreatic a-amylase
brush border enzymes: maltase, isomaltase, lactase, sucrase
Summarize carb, protein, lipids in the mouth, stomach, and intestine:
Macromolecule | Mouth | Stomach | Intestine |
Carbs | Salivary amylase | none |
|
Proteins | none |
|
|
Lipids | Lingual lipase | gastric lipase |
|
How are amino acids absorbed into the cell after digestion?
an AA-Na+ symporter using secondary active transport
(Using Na+ from Na+/K+ ATPase to drive aa in)
How are monosaccharides absorbed into the cell after digestion?
mainly through GLUT or Na+/glucose symporter
into cell from intestinal lumen: GLUT5 or symporter
(FYI: into blood from the intestinal cell: GLUT2)
Why aren’t the Na+/glucose symporter or GLUT Transporters considered active transport?
doesn’t use ATP directly
Which GLUT transporters require insulin?
GLUT 4
Where is each GLUT transporter found?
Corso said could be a “matching question” on the test
GLUT1- RBCs, and most other cells
GLUT2- intestine, b-cells, liver
GLUT3- brain
GLUT4- muscle, fat
GLUT5- lumen of intestine
TGs are digested into fatty acids and glycerol. How are they absorbed and how are they transported from intestine to target organ?
absorption: fatty acids are absorbed into the cell (by a micelle)and then TURNED BACK INTO TGs
These TGs are then packed into CHYLOMICRONS and transported to where they need to go
(summary: digested fatty acids/micelle—> back to TGs—→ chylomicron)
What lipids are found within a chylomicron? SATA
a. LDLs
b. apolipoproteins
c. TGs
d. phospholipids
e. cholesterol esters
c, e
What is the function of chylomicrons?
What are the fxn of the surface proteins?
Where do chylomicrons deliver TGs?
fxn of chylo- transport fats in the body
fxn of surface proteins- protein markers
WHERE DO THEY DELIVER? muscle or fat
How are sugars, fats, and amino acids transported in the blood? (think about hydrophilicity)
sugars and amino acids- dissolve in plasma/ don’t need carrier
fats- transported using chylomicrons
In the fed state, which organs use glucose almost exclusively?
RBCs MUST use glucose exclusively
Brain ALMOST uses glucose exclusively
Why is glucose absorbed into the muscle ONLY during the fed state?
What does the muscles do with glucose when it’s not active?
What does the muscle do with glucose when it’s active?
bc GLUT transported are only active/on cell surface during fed state
stores it as glycogen
uses it for energy
What does the liver do with glucose when its not active?
Why does the liver only make glycogen in the fed state?
What does the liver do with excess glucose when it is full of glycogen and has enough ATP?
store as glycogen
bc the conversion to off glucose to glycogen is insulin dependent, and insulin is only secreted during the fed state
excess glucose converted into TGs (fat)
Why do adipose cells only take up glucose during the fed state?
What does adipose do with glucose?
What do adipose cells do with VLDLs and Chylomicrons?
bc GLUT transported are only active/on cell surface during fed state (like muscle)
fat synthesis
converts it back into TG for storage
What are the 2 FATES of amino acids when a cell is growing?
use amino acids to make proteins
burn for energy
Describe the main differences between the fed and fasting state:
insulin/glucagon
glycogen
fat
protein
brain
muscle
Fed | Fasting |
Insulin High | Glucagon High |
Glycogen synthesis | Glycogen breakdown |
Fat synthesis | Fat utilization |
Protein synthesis | Protein breakdown |
Brain uses glucose | Brain uses glucose |
Muscle uses glucose | Muscle uses fat |
When are ketone bodies used to meet energy needs? What’s the problem with ketone bodies?
use when we’re STARVING
the problem—> drops blood pH—> ACIDOSIS
What is the benefit of creatine in the muscle?
energy boost—>can give a little more ATP when working out
What is lactose intolerance? Where is the enzyme found? What can cause it?
SAID will be test question on this topic
lactase enzyme deficiency
enzyme found in intestinal brush border
causes: injury, excess alcohol, genetics/born with it
What are triglycerides? what bond connects? What are diglycerides?
3 fatty acids, 1 glycerol, joined by ester bonds
2 fatty acids, 1 FFA, 1 glycerol, joined by ester bonds
How does the drug Orlistat work?
said POSSIBLE test question
LIPASE INHIBITOR!!!!!
blocks digestion of fat
What are the “big steps” of fat synthesis? How does Acetyl CoA get of the mitochondria during fat synthesis?
gets out by converting to CITRATE (happens before step 1 of synthesis)

Does insulin inhibit or promote fat synthesis in the liver?
promote
WHAT IS THE RATE LIMITING STEP OF FAT SYNTHESIS?
Malonyl CoA
Why is biotin needed for fat synthesis?
needed for rate limiting step!!
conversion of Acetyl CoA to Malonyl CoA
Fat synthesis takes place in the cytoplasm of the __________.
liver
What is an Eicosanoid? What is arachidonic acid?
eicosanoid- 20 C fatty acid
arachidonic acid- conditionally essential fatty acid
How do TGs made in the liver move to fat and muscle?
TGs are made into VLDLs and reach tissues using Lipoprotein lipase (LPL)
WHATS THE DIFFERENCE between VLDL’s and chylomicrons?
Chylomicron | VLDL |
TGs are from DIETARY TGs (fats we eat) | TGs are made from EXCESS CARBs |
WHAT IS THE ENZYME USED IN THE RATE CONTROLLING STEP OF CHOLESTEROL SYNTHESIS?
said will be on test.
HMG-CoA reductase (converts HMG-CoA to Mevalonate)
What drugs are HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors?
statins
Where do LDL particles come from?
What is the main function of LDLs?
What is the main function of HDL?
“downstream products of VLDL remnants”
carry cholesterol to arteries
carry cholesterol back to liver
WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS MOSTLY TGs? (POSSIBLE TEST Q)
a. chylomicron
b. LDL
c. HDL
d. VLDL
a
WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS MOSTLY CHOLESTEROL? (POSSIBLE TEST Q)
a. chylomicron
b. LDL
c. HDL
d. VLDL
b
Isoprenoid is a precursor to ___________ and ____________.
dolichol and coQ10
What important molecules are made from cholesterol?
vitamin D
bile acid
steroids
Which of the following is the largest particle? which of the following is the smallest particle?
chylomicron
VLDL
LDL
HDL
biggest- chylomicron
smallest- HDL
When we need to use fatty acids for energy because free fatty acids are not water soluble it is carried with __________ in the blood.
albumin
For the release and transport of lipids from fat tissue you have to have:
______ insulin (high/low)
______ glucagon (high/low)
and what NT?
low insulin, high glucagon, EPI
Once the free fatty acid makes it to the mitochondria and is ready to be used for energy… what happens?
said “fair game test question”
binds to protein on the mitochondria CALLED CARNITINE ACYLTRANSFERASE
For beta-oxidation in the mitochondria (using lipids for energy), what happens during each of the 4 steps?
corso said, “If I put a test question on this it will be pictures”
corso said, “I might ask show you a picture of the molecule and ask what is the product”
alkane- alkene
alkene- alcohol
alcohol- ketone
cut off 2 carbons
RECOGNIZE THE PICTUREEEEEEE
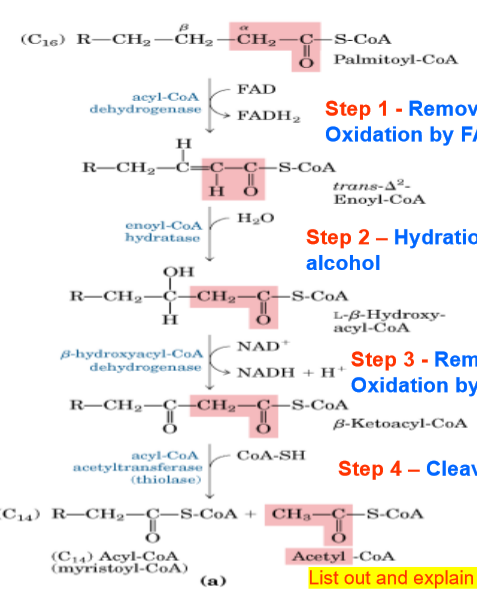
MCAD deficiency is a defect of _____________________.
fatty acid metabolism
What are the most common pharm tx for reducing stomach acid?
antacids (Tums, Milk of Mag, Maalox, Alka-Seltzer)
H2RAs (Famotidine (Pepcid), “-tidines”
PPIs (“-prazoles”)
Describe pancreatitis and how it can come about:
inability to digest proteins, lipids, sugars (lead to diabetes)
can be caused by gallstones, alcoholism, cystic fibrosis
zymogens can become active and destroy the pancreas
What is Hartnup disease?
said “more likely to be on the test than cystinuria”
defect in neutral AMINO ACID TRANSPORTER
What is cystinuria?
too much cystine
can cause kidney stones
What are the 3 fates of ingested amino acids?
protein synthesis
converted to glucose
converted to fat
What is the most abundant AA in the body?
glutamine
What is the only organ that can get rid of ammonia without breaking it down?
kidney
Where does the urea cycle take place?
LIVER (NOT THE KIDNEYS)
What is the purpose of the urea cycle? What are the 2 sources of nitrogen for urea synthesis?
purpose: get rid of waste nitrogen
2 sources: AMMONIA AND ASPARTATE (an AA)
Through ___________ reactions we move nitrogen around without making urea.
know this
TRANSAMINATION
(FYI: basically we remove N from AA by transferring it to another molecule)
Glutamine is the #1 way to move nitrogen around the body. What is #2?
alanine
What are the names of all the enzymes in the urea cycle? 😑
corso said “recognize the enzyme names”
arginase
argininosuccinate lyase
argininosuccinate synthetase
ornithine transcarbamoylase
carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPSI)
FYI: a deficiency in any of these enzymes results in high ammonia

Which of the following is an intermediate in the urea cycle:
a. Tyrosine
b. Tryptophan
c. Arginine
d. Alanine
c
liver transaminases are measured in the blood as _____ and _____. Are they normally high or low in the blood?
test q on this topic
ASTs and ALTs
NORMALLY NOT IN THE BLOOD
If the liver has a lot of transaminases, ALT or AST, what is that an indication of?
test q on this topic
LIVER DAMAGE
WHAT 2 DRUGS CAN REMOVE NITROGEN FROM THE BODY? How do they work?
SAID ON TEST
benzoic acid (instead of urea converts to hippuric acid)
phenylbutyrate (converts to glutamine and takes it right outta the blood)
What is a symptom of urea cell defect? How would you treat it?
said on the test
symptom- HIGH AMMONIA
tx- benzoic acid, phenylbutyrate