Schizophrenia (Paper 3)
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AQA A-LEVEL PSYCHOLOGY - There are NO named researchers/ studies in this paper but there is at least one study with each topic.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
1
New cards
What is psychosis?
A severe mental disorder where thoughts and emotions are so impaired contact is lost with external reality
2
New cards
How much of the population does schizophrenia affect?
1% of the population
3
New cards
At what ages is schizophrenia most commonly diagnosed at?
15-35
4
New cards
Who is affected more, men or women?
Men and women are affected equally
5
New cards
Who is **most** likely to be affected?
Working Class young men who live in **urban** areas
6
New cards
What are the two most common symptoms of schizphrenia?
Delusions and Hallucinations
7
New cards
What is a **delusion**?
False beliefs that are firmly held despite being completely illogical, or for which there is no evidence
8
New cards
What is a **delusion of persecution**?
The belief that others want to harm, threaten or manipulate you
9
New cards
What is a **delusion of grandeur**?
This is the idea that you are an important individual, even god-like and have extraordinary powers
10
New cards
What is a **delusion of control**?
Individuals may believe that they are under the control of an alien force that has invaded their mind and/or body.
11
New cards
What is a **Hallucination**?
Disturbances in perception (rather than disturbances in thought). They are false perceptions that have no basis in reality. Many schizophrenics report hearing voices that instruct them to do something that could be harmful to themselves and others.
12
New cards
What is **Speech Poverty?**
Lessening of speech fluency and productivity
13
New cards
What is **Avolition?**
The reduction of, or inability to initiate or persist in goal directed behaviour (i.e completing tasks)
14
New cards
What iis **Catatonic Behaviour?**
When someone is awake but does not seem to respond to other people and their environment
15
New cards
What is meant by **positive symptoms of schizophrenia?**
Reflecting an @@excess or distortion@@ of ‘normal’ functions
16
New cards
What is meant by **negative symptoms of schizophrenia?**
@@Loss@@ of ‘normal’ functioning
17
New cards
Give **3** examples of positive symptoms of schizophrenia
* Delsusions
* Hallucinations
* Disorganised Speech/ behaviour
* Hallucinations
* Disorganised Speech/ behaviour
18
New cards
Give **3** examples of negative symptoms of schizophrenia
* Avolition
* Speech Poverty
* Catatonic Behaviour
* Speech Poverty
* Catatonic Behaviour
19
New cards
\
There are two main classification systems for mental illnesses: the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) and the ________?
There are two main classification systems for mental illnesses: the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) and the ________?
ICD
20
New cards
What is meant by **reliability** (in context to schizophrenia)?
The **consistency** of a measuring tool i.e the DSM or other tests used in diagnosis - @@a test@@ @@must be valid to be reliable@@
21
New cards
What is **test-retest** reliability?
Doctors must be able to reach the same conclusions about a patient at **two different points in time**
22
New cards
What is **inter-rater** reliability?
Doctors must reach the same conclusion about a patient’s diagnosis when assessed independently.
23
New cards
Outline **Cheniaux et al. (2009)** study into reliability
* Two psychiatrists independently diagnosed 100 patients using the DSM and the ICD
* Doctor 1 diagnosed @@**26** patients with schizophrenia according to the DSM and **44** accoring to the ICD@@
* Doctor 2 diagnosed @@**13** according to the DSM and **24** according to the ICD.@@
* Doctor 1 diagnosed @@**26** patients with schizophrenia according to the DSM and **44** accoring to the ICD@@
* Doctor 2 diagnosed @@**13** according to the DSM and **24** according to the ICD.@@
24
New cards
What does **Cheniaux et al. (2009)’s** study suggests about reliability in schizophrenia diagnoses?
This suggests that the **inter-rater** reliability of classification systems are unreliable. Firstly using the same classification system (DSM), Doctor 1 diagnosed twice the number of pts and between the ICD and DSM, more pts are classed according to the ICD.
25
New cards
What are the **cultural differences** in diagnoses of schizophrenia?
* *Copeland* found that 69% of US psychiatrist diagnosed a pt description compared to just 2% of Bristiish psychiatrists
* *Luhrmann* found that there was a difference in hearing voices across cultures. In Ghana and India, the voices where seen as @@‘playful’,@@ possibly due to the high spirituality in these cultures. In the US however, the voices were @@violent and agressive@@
* *Luhrmann* found that there was a difference in hearing voices across cultures. In Ghana and India, the voices where seen as @@‘playful’,@@ possibly due to the high spirituality in these cultures. In the US however, the voices were @@violent and agressive@@
26
New cards
What is meant by **validity,** in terms of schizophrenia?
The extent to which a diagnosis is accurate and meaningful - the DSM must measure schizophrenia accuartely.
27
New cards
What does **Cheniaux et al. (2009)’s** study suggests about validity of schizophrenia diagnoses?
It **undermines the validity** of the current classification systems to diagnose schizophrenia due to the fact that results vary so much, that neither can possible be accurate
28
New cards
What is **gender bias,** in terms of schizophrenia?
**When the diagnosis is dependent on the gender of an individual.** This may be due to gender-biased diagnostic criteria or clinicians basing diagnoses on stereotypes about gender
29
New cards
What is **symptom overlap** in terms of schizophrenia?
Many of the symptoms of schizophrenia are **also found in other disorders** such as depression and bipolar disorder.
30
New cards
What is **Co-Morbidity** in terms of schizophrenia?
**The extent to which two or more conditions co-occur.** Schizophrenia often occurs alongside substance abuse, anxiety and depression.
31
New cards
Outline **Rosenhan (1973)’s** study ‘**Sane in Insane Places’** about?
* He went to US psychiatric hospitals, getting 8 ordinary people to claim they could hear voices - **7 of the 8 were admitted**
* In the second experiment, he called the psychiatric hospital warning them some fake patients would be coming in. In fact, there were non but around **10% were suspected as fakes**
* In the second experiment, he called the psychiatric hospital warning them some fake patients would be coming in. In fact, there were non but around **10% were suspected as fakes**
32
New cards
What does **Rosenhan (1973)’s** study ‘**Sane in Insane Places’** show, in terms of the validity and reliability of schizophrenia diagnoses?
This shos there is low validity in schizophrenia diagnoses, as the criteria is easily manipulated to be a measure of certain ‘symptoms’
↳ @@A test must be valid for it to be reliable@@
↳ @@A test must be valid for it to be reliable@@
33
New cards
Evaluate **Rosenhan (1973)’s** study ‘**Sane in Insane Places’**
%%Strengths%%
↳ High Value Study
↳ Representative sample
==Weaknesses==
↳ Low Temporal Validity
↳ Unethical: Hospital staff not informed
↳ High Value Study
↳ Representative sample
==Weaknesses==
↳ Low Temporal Validity
↳ Unethical: Hospital staff not informed
34
New cards
Explain what is meant by **Heredity** in relation to schizophrenia?
Genetics as an explanation for schizophrenia
35
New cards
True or False: Schizophrenia tends to run in families?
True
36
New cards
What are candidate genes?
Genes which, through research, have been **implicated in the development of schizophrenia**
37
New cards
Schizophrenia is thought to be __*polygenic*__. What does this mean?
It’s development is determined by many genes
38
New cards
What are the **three** main ways to study the genetic explanation?
1. Family Studies
2. Twin Studies
3. Adoption studies
39
New cards
What is the purpose of family studies?
To investigate whether biological relatives of someone with schizophrenia are more likely to be affected by it than non-biological relatives
40
New cards
What is the purpose of Twin Studies?
If MZ (identical twins) are more concordant than DZ twins, this suggests the greater similarity is due to genetics.
41
New cards
What is the purpose of Adoption studies?
Tienari (2000) found that **6.7%** of adoptees who had biological schizophrenic mothers also received a diagnosis, compared to **2%** of those born to nonm-schizophrenic mothers
42
New cards
What is a limitation of the genetic explanation?
Joseph (2004) explains **MZ twins are treated similarly** and encounter similar environments - often causing **Identity Confusion**
43
New cards
What is an **issue/debate** with the genetic explanation of schizophrenia?
%%Nature/Nurture%%
↳ Genetic explanation falls on the **nature** side of the n/n debate. Ignores environmental, social and psychological factors
↳ Genetic explanation falls on the **nature** side of the n/n debate. Ignores environmental, social and psychological factors
44
New cards
What is the **dopamine hypothesis**?
@@**Excess dopamine in the brain is associated with the** ***positive*** **symptoms of schizophrenia.**@@ Messages from neurons that transmit dopamine fire too easily, leading to hallucinations and delusions
45
New cards
What is **Leucht et al. (2012)’s study?**
* @@**Leucht et al. (2012)**@@
↳ They carried out a ***meta-analysis of 65 studies***
* Some patients had their antipsychotic drugs replaced with a placebo
* **64%** of those with the placebo relapsed, compared to **27%** of those on the antipsychotics
↳ They carried out a ***meta-analysis of 65 studies***
* Some patients had their antipsychotic drugs replaced with a placebo
* **64%** of those with the placebo relapsed, compared to **27%** of those on the antipsychotics
46
New cards
How does **Leucht et al. (2012)** show research support for the dopamine hypothesis?
**Antipsychotics block dopamine activity,** showing reduced dopamine activity = reduced symptoms and more effective schizophrenia treatment
47
New cards
What is an **issue/debate** with the dopamine hypothesis?
%%Nature/Nurture%%
↳ The dopamine hypothesis falls on the **nature** side of the n/n debate. Ignores environmental and psychological factors + an interactionist approach would be better
↳ The dopamine hypothesis falls on the **nature** side of the n/n debate. Ignores environmental and psychological factors + an interactionist approach would be better
48
New cards
What are **neural correlates**?
**changes in neuronal events** and mechanisms that result in schizophrenia
49
New cards
What **3 correlates** do those with schizophrenia show?
* Reduced Brain Volume
* Reduced grey matter volume
* Ventricular enlargement
* Reduced grey matter volume
* Ventricular enlargement
50
New cards
How do changes to the **ventral striatum** affect the **development of schizophrenia**?
The ventral striatum is linked with **the anticipation of reward**. Abnormality results in a lack of motivation (avolition)
51
New cards
What **empirical evidence** can be used to support the neural correlates explanation?
@@**Suddarth et. al (1990)**@@
↳ - MRI of MZ twins where one was schizophrenic
- The **difference in ventricle size was so large**, the schizophrenic twin could be detected in **12 out of 15 twins**
↳ - MRI of MZ twins where one was schizophrenic
- The **difference in ventricle size was so large**, the schizophrenic twin could be detected in **12 out of 15 twins**
52
New cards
What **correlational evidence** can be used to support the neural correlates explanation?
@@**Tilo et al. (2001)**@@
↳ - fMRI scans done on 6 non-schizophrenics + 6 schizophrenics looking at inkblots
- Those with schizophrenia had a negative correlation between **thought disorder** and activity in **Wernicke’s area**
↳ - fMRI scans done on 6 non-schizophrenics + 6 schizophrenics looking at inkblots
- Those with schizophrenia had a negative correlation between **thought disorder** and activity in **Wernicke’s area**
53
New cards
What is an **issue/debate** with the neural correlates explanation?
%%Nature/Nurture%%
↳ The neural correlates explanation falls on the **nature** side of the n/n debate. Ignores environmental and psychological factors + an interactionist approach would be better
↳ The neural correlates explanation falls on the **nature** side of the n/n debate. Ignores environmental and psychological factors + an interactionist approach would be better
54
New cards
There are two drugs used in drug therapy: _______ antipsychotics?
Typical and Atypical
55
New cards
How do **typical antipsychotics** treat schizophrenia?
They bind to dopamine receptors, blocking around **75%** of D2 Receptors - this reduces positive symptoms like hallucinations and delusions @@e.g chlorpromazine@@
56
New cards
Give an advantage of **typical antipsychotics**
They are **cheaper** and **easier** than atypical antipsychotics
57
New cards
Give a disadvantage of **typical antipsychotics**
They can lead to undesirable side effects - **sedation** + **anhedonia**
58
New cards
How do **atypical antipsychotics** treat schizophrenia?
They block D2 receptors **but** they rapidly dissociate to allow normal dopamine transmission resulting in less side effects - **e.g clozapine**
59
New cards
Give an advantage of **atypical antipsychotics**
They have a **stronger affinity for serotonin receptor**s and are suitable for **treatment-resistant patients**
60
New cards
Give a disadvantage of **atypical antipsychotics**
**More expensive** than typical antipsychotics
61
New cards
Give an example of **research support** for drug therapy
@@**Leucht et al. (2012)**@@
↳ They carried out a ***meta-analysis of 65 studies***
* Some patients had their antipsychotic drugs replaced with a placebo
* **64%** of those with the placebo relapsed, compared to **27%** of those on the antipsychotics
↳ They carried out a ***meta-analysis of 65 studies***
* Some patients had their antipsychotic drugs replaced with a placebo
* **64%** of those with the placebo relapsed, compared to **27%** of those on the antipsychotics
62
New cards
Give an **limitation** of drug therapy
**Side effects -** Typical antipsychotics can cause *Tardive Dyskinesia* which cause involuntary movements of the tongue, face and jaw
63
New cards
What is an **issue/debate** with the drug therapy?
%%Biological Reductionism%%
↳ Drug Therapy as a treatment of schizophrenia r**educes the cause of schizophrenia down to a biological issue** which then has a purely biological treatment. It needs to be approached **more holistically,** taking into account every aspect of the person’s circumstance.
↳ Drug Therapy as a treatment of schizophrenia r**educes the cause of schizophrenia down to a biological issue** which then has a purely biological treatment. It needs to be approached **more holistically,** taking into account every aspect of the person’s circumstance.
64
New cards
What is a **psychological** explanation of schizophrenia?
Family Dysfunction
65
New cards
What is **double bind theory** in terms of schizophrenia?
@@**Double bind theory suggests that conflicting messages from parents can contribute to schizophrenia**@@
* When a parent sends mixed messages that are invalidate each other, it prevents an ***internally coherent idea of reality***
This later manifests into *flattened affect* and *withdrawl*
* When a parent sends mixed messages that are invalidate each other, it prevents an ***internally coherent idea of reality***
This later manifests into *flattened affect* and *withdrawl*
66
New cards
What is **Expressed Emotion?**
Family members of the schizophrenic patient talk about them in a critical/hostile manner
↳ This is **over-concern and over-involvement** w/ the patient
↳ This is **over-concern and over-involvement** w/ the patient
67
New cards
Do **high levels of EE** increase or decrease relapse rates?
Increases (*Linszen et al. (1997))*
68
New cards
**Why** does EE affect schizophrenic patients?
They often have a l**ower tolerance for intense interactions**, leading to **stress beyond their internal coping mechanisms**
69
New cards
Give a **limitation** of family dysfunction
@@**Inconclusive Support**@@
↳ *Berger (1965)* found that schizophrenics having high double bind situation than non- schizophrenics
* However, *Liem (1974)* found **no difference** compared to ‘normal’ families
↳ *Berger (1965)* found that schizophrenics having high double bind situation than non- schizophrenics
* However, *Liem (1974)* found **no difference** compared to ‘normal’ families
70
New cards
What are **cognitive explanations**?
That **dysfunctional thought processing** can explain delusions and hallucinations
71
New cards
What are **cognitive explanations** of delusions?
They have **egocentric bias** meaning they see themselves as the central component of every event
72
New cards
What are **cognitive explanations** of hallucinations?
People with schizophrenia **focus excessive attention on auditory stimuli (hypervigilance)** + they often **missatribute their inner voice** as from an **external source**
73
New cards
What is research support for **cognitive explanations**?
@@**Sarah and Wallin (2014)**@@
↳ Delusional patients showed dysfunctional thinking such as **jumping to conclusions** and **lack of reality testing**
↳ Likewise those with hallucinations were found to **experience their own thoughts as voices**.
↳ Delusional patients showed dysfunctional thinking such as **jumping to conclusions** and **lack of reality testing**
↳ Likewise those with hallucinations were found to **experience their own thoughts as voices**.
74
New cards
How does CBT therapy support the cognitive explanation?
The NICE review found that compared to antipsychotics alone, **CBT was effective reducing hospital rates up to 18 months** (CBT and Antipsychotics)
75
New cards
What is an issue/debate with the cognitive explanation?
%%Nature/Nurture%%
↳ The cognitive explanation of schizophrenia falls on the **nurture** **side of the debate as it only focuses on learned/gained ways of thinking.** An interactionist approach which takes into account both sides of the argument would be better.
↳ The cognitive explanation of schizophrenia falls on the **nurture** **side of the debate as it only focuses on learned/gained ways of thinking.** An interactionist approach which takes into account both sides of the argument would be better.
76
New cards
What does CBTp stand for?
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for psychosis
77
New cards
What is the purpose of CBTp?
* To help patients identify and correct faulty interpretations of events
* To help patients trace the origin of their symptoms
* To challenge the patients hallucinations/delusions with logic
* This reduces distress and improves functioning
* To help patients trace the origin of their symptoms
* To challenge the patients hallucinations/delusions with logic
* This reduces distress and improves functioning
78
New cards
CBT can be used **without** antipsychotics. True/False?
**False**
79
New cards
How is Leucht et al. (2012)’s study evidence that CBTp is not the sole answer to schizophrenia?
If CBTp was the sole answer, antipsychotics would not be **so effective**
80
New cards
What is an issue/debate with the **CBTp**?
%%Nature/Nurture%%
↳ CBTp suggests falls on the **nurture** side of the nature/nurture debate, as it suggests the problem solely stems from the environment, so can be cured using therapies
This ignores biological causes. A better approach would be an **interactionist** one, which takes into account both environment and biological causes.
↳ CBTp suggests falls on the **nurture** side of the nature/nurture debate, as it suggests the problem solely stems from the environment, so can be cured using therapies
This ignores biological causes. A better approach would be an **interactionist** one, which takes into account both environment and biological causes.
81
New cards
What is the aim of **family therapy**?
* to provide support for carers
* to make family life less stressful
* To reduce rehospitalisation rates
* to make family life less stressful
* To reduce rehospitalisation rates
82
New cards
**True/False:** NICE recommends family therapy should be offered to all schizophrenics living with family
True
83
New cards
Give one piece of research support for family therapy
@@**Garety et al. (2008)**@@
↳ Estimated relapse rates for those who receive **family therapy** at **25%** compared to **50%** for those who only receive **antipsychotic treatment**
↳ Estimated relapse rates for those who receive **family therapy** at **25%** compared to **50%** for those who only receive **antipsychotic treatment**
84
New cards
**True/False:** Token Economy is a form of management, not treatment
True
85
New cards
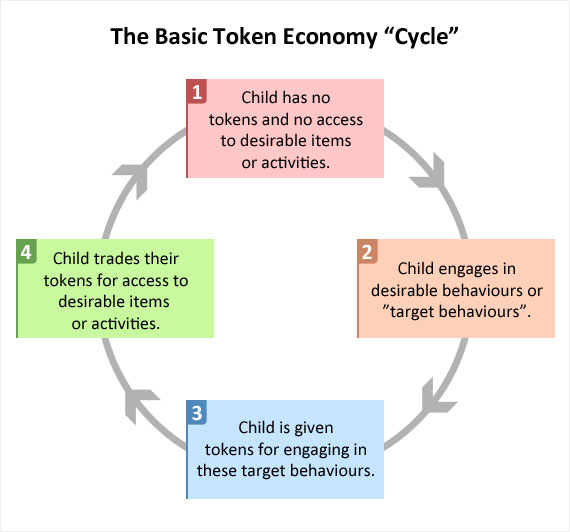
Explain Token Economy in **3** bullet points
* A form of schizophrenia management, based on the principles of operant conditioning
* Helps manage negative symptoms of schizophrenia such as **apathy** and **social withdrawal**
* Involves giving patients **tokens** for **good behaviours** which can be exchanged for rewards
* Helps manage negative symptoms of schizophrenia such as **apathy** and **social withdrawal**
* Involves giving patients **tokens** for **good behaviours** which can be exchanged for rewards
86
New cards
What are **primary** and **secondary reinforcers** in token economy?
**Primary reinforcers** - anything that give pleasure (I.e food or a blanket)
**Secondary reinforcers** - initially have no value to the patient but reinforce when paired with primary reinforcers
**Secondary reinforcers** - initially have no value to the patient but reinforce when paired with primary reinforcers
87
New cards
Do frequent exchange periods of tokens **increase** or **decrease** the likelihood of good behaviours?
Increase
88
New cards
Give a strength of Token Economy
@@Research Support - Dickerson et al. (2005)@@
↳ Meta-analysis of 13 studies - **11 studies reported beneficial effects directly attributable to the use of token economy**
↳ Meta-analysis of 13 studies - **11 studies reported beneficial effects directly attributable to the use of token economy**
89
New cards
Give a limitation of Token Economy
@@Only effective in a hospital setting@@
↳ **Only effective in hospital setting where patients receive 24 hour care** - outpatients who live in the community will only receive a few hours of care a day which means the results cannot be maintained
↳ **Only effective in hospital setting where patients receive 24 hour care** - outpatients who live in the community will only receive a few hours of care a day which means the results cannot be maintained
90
New cards
What is an **issue/debate** with Token Economy?
%%Ethics%%
↳ **Token economy gives the professionals/staff significant power over the patients**. This restricts the patients **personal freedom** and autonomy, also imposes a norm to expect perfection
↳ **Token economy gives the professionals/staff significant power over the patients**. This restricts the patients **personal freedom** and autonomy, also imposes a norm to expect perfection
91
New cards
What is the point of an interactionist approach to treating schizophrenia?
It takes into account both nature and nurture, which means there are varied treatments (CBTp, drug therapy and family therapy)
92
New cards
What is the **diathesis stress model** of explaining schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is the result if psychological/environmental and biological/genetic influences. The symptoms of schizophrenia are triggered when **significant external stressors** are **combined** with **biological vulnerability**
93
New cards
Evidence for **Diathesis**
Twin studies show that schizophrenia has a genetic component - MZ twins have a higher concordance rate than DZ twins. However, the there is a *disconcordance* rate of about 50% which shows environmental factors must also play a role in schizophrenia
94
New cards
Evidence for **Stress**
@@***Varese et al. (2012)***@@ found that children who experienced **severe trauma** before the ages of 16 were __3x__ more likely to develop schizophrenia than the general population.
95
New cards
What is meant by the additive nature of schizophrenia?
Diathesis and stress add together to produce schizophrenia i.e *low vulnerability + high levels of trauma* or *high vulnerability + low trauma levels*
96
New cards
Show research support for the additive nature of schizophrenia
* @@***Tienari et al. (2004)***@@ conducted a study on the effects of family background on the development of schizophrenia.
* **Individuals with a biological predisposition to schizophrenia were more likely to develop the disorder if they were raised in a dysfunctional family environment.**
* The risk of developing schizophrenia was higher for individuals who experienced both genetic and environmental risk factors.
* The study highlights the importance of considering both genetic and environmental factors in the development of schizophrenia.
* **Individuals with a biological predisposition to schizophrenia were more likely to develop the disorder if they were raised in a dysfunctional family environment.**
* The risk of developing schizophrenia was higher for individuals who experienced both genetic and environmental risk factors.
* The study highlights the importance of considering both genetic and environmental factors in the development of schizophrenia.
97
New cards
What is a strength of the Diathesis-Stress model?
**It takes into account both nature and nurture**. A limitation of purely biological explanations are that they don’t factor in environmental causes and therefore are limited to one treatment method, antipsychotics
98
New cards
What is a limitation of the diathesis-stress model?
It only focuses on genetic vulnerabilities when talking about biological predispositions. Increased risk may also result from brain damage - @@***Verdoux et al. (1998)***@@