GI Exemplar Pts
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
- proteins
- carbohydrates
- fats
What are the macronutrients?
Kwashiorkor -- malnutrition of ONLY proteins
[1. correction of fluid and electrolyte imbalances (phosphorus, potassium, and magnesium); 2. phase of repleting calories, protein, and micronutrients gradually (not too rapidly to prevent refeeding syndrome)].
Weaning infant whose sibling was just born and has a recent burn presents with edema of legs and feet, light-colored thinning hair, anemia, ascites in abdomen, and shiny skin. On PE: growth restriction, vital capacity and tidal volume are depressed. Labs: serum albumin + other micronutrients.
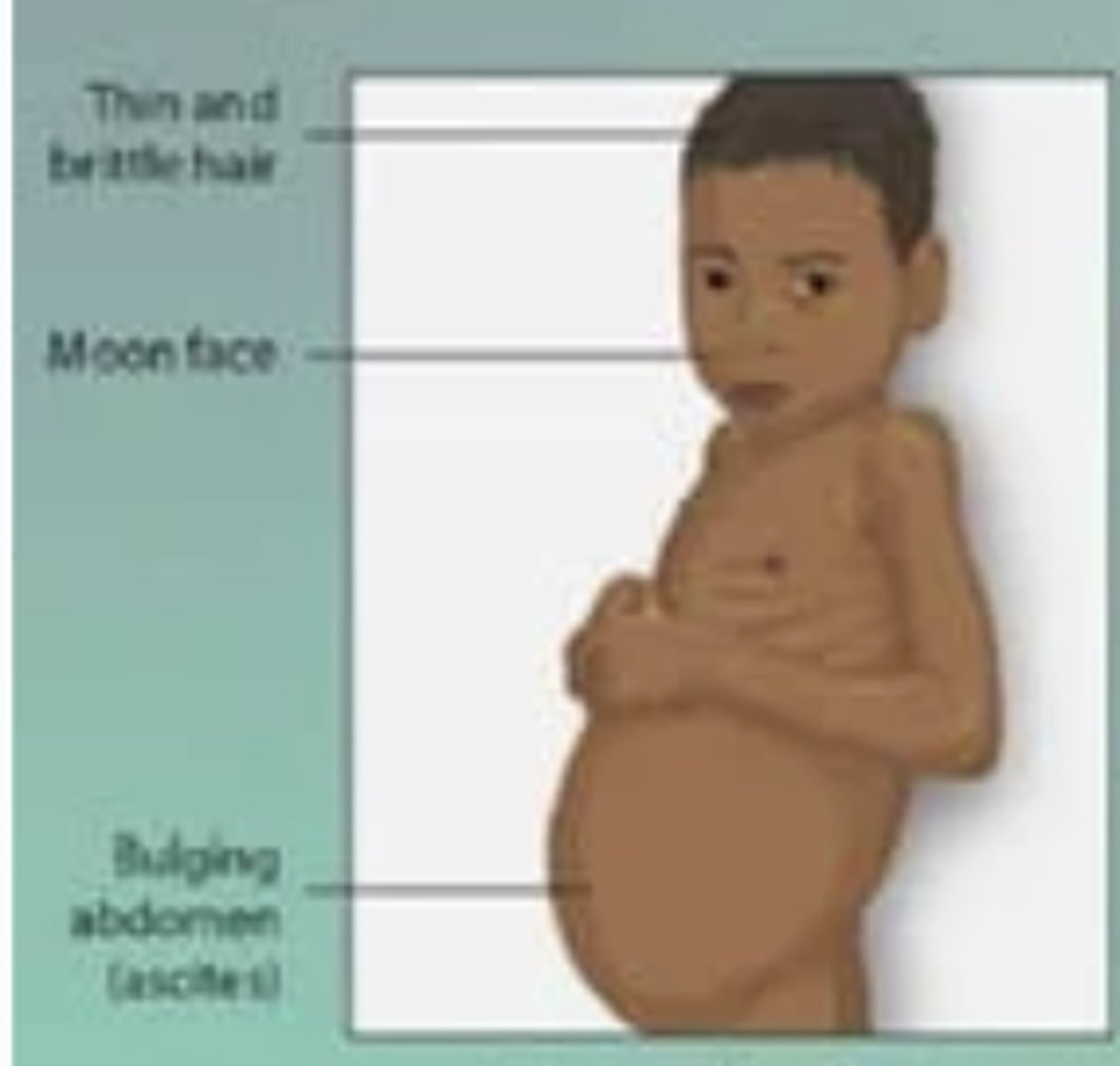
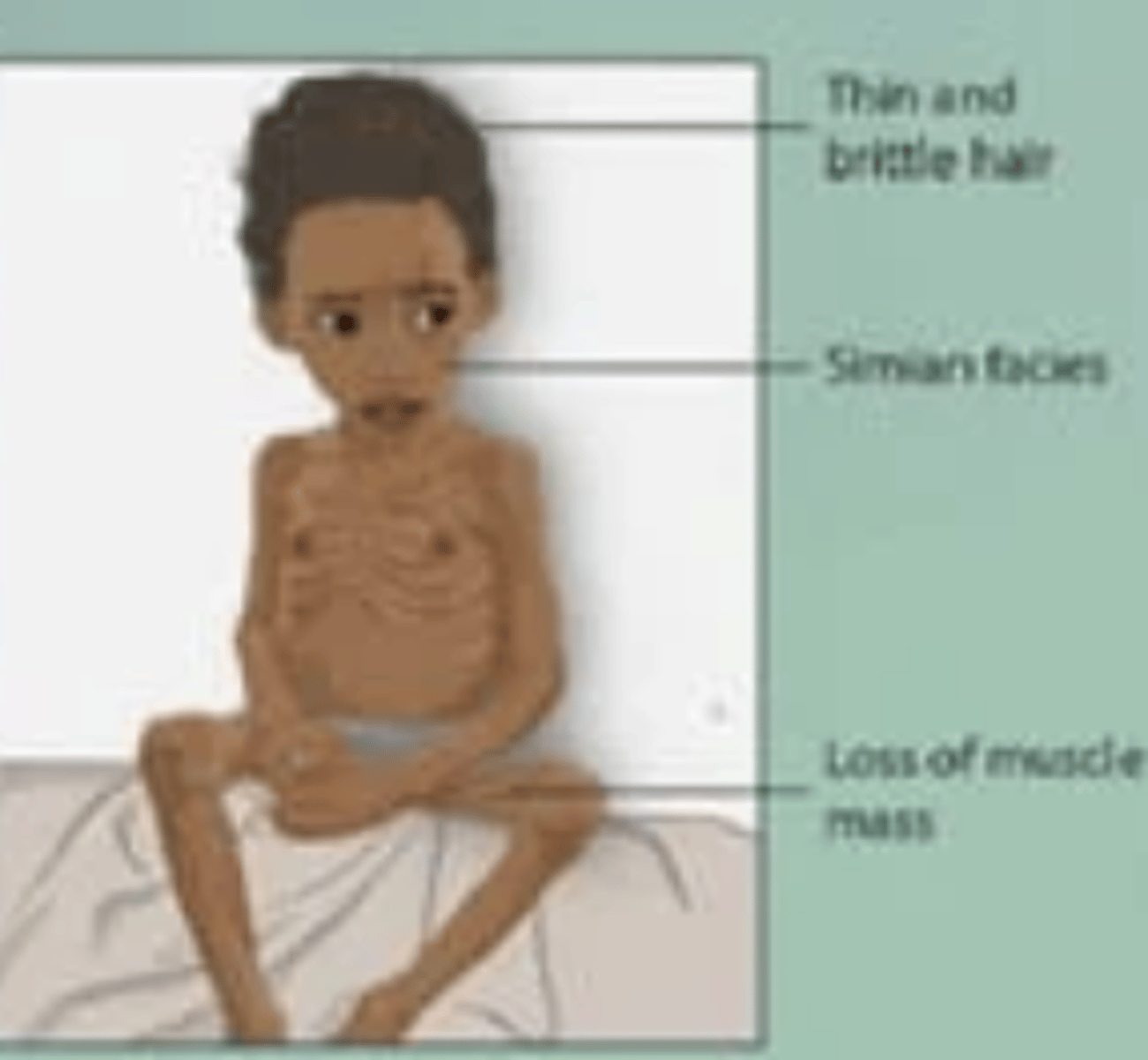
Marasmus -- malnutrition of ALL macronutrients
[1. correction of fluid and electrolyte imbalances (phosphorus, potassium, and magnesium); 2. phase of repleting calories, protein, and micronutrients gradually (not too rapidly to prevent refeeding syndrome)].
Pt who does not have access to adequate quantities of food and PMHx of COPD, HF, cancer, AIDS presents with muscle wasting and stunted growth. PE: Cachexia, poor wound healing, muscle mass depletion at temples, clavicles, shoulders, scapula, hands, thighs, and calves. Labs: serum albumin + other micronutrients
Pt 1 = excess carbohydrate
Pt 2 = carbohydrate deficiency
What macronutrient abnormality do these pts have?
- Pt 1 presents with: weight gain, high blood sugar, constipation, bloating, and sugar cravings
- Pt 2 presents with: hypoglycemia, low energy, fatigue, headache, weight loss, bad breath and ketosis
Pt 1 = excess fat
Pt 2 = fat deficiency
*linoleic acid for Tx
What macronutrient abnormality do these pts have?
- Pt 1 presents with: bloating, gas, loose stools/steatorrhea, high cholesterol, and obesity.
- Pt 2 presents with: weight loss, hair loss, weakened immune system, dry skin, lanugo, rashes, fatigue, cognitive impairment, and vitamin deficiencies (K,A,D,E).
Supplementing those who do not need them may be harmful - more particularly in regards to fat-soluble vitamins (they have a toxicity range) that are stored in adipose tissue vs water-soluble vitamins
*they have a toxicity range and are stored in adipose tissue vs water-soluble vitamins, so toxicities can last a long time!
Supplementing those who do not need them may be harmful - more particularly in regards to ___________ (they have a toxicity range) that are stored in adipose tissue vs water-soluble vitamins
pts with malnutrition typically present with multiple micronutrient deficiencies
pts with malnutrition typically present with multiple ____________
- vitamins (A, C, B12, D)
- iodine
- zinc
- folate
- iron
Name some examples of micronutrients.
Pt 1 = iodine deficiency
Pt 2 = iodine toxicity
What micronutrient abnormality do these pts have?
- Pt 1 presents with: goiter and elevated TSH
- Pt 2 presents with: abdominal pain, n/v/d, CV Sx then developed thyroiditis, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism
- Pt 1 = zinc deficiency
- Pt 2 = zinc toxicity (Tx: chelators to remove zinc from blood)
What micronutrient abnormality do these pts have?
- Pt 1 presents with: hypogonadism, impaired taste, cheilitis, reduced nerve condition, brittle hair, eczematous rash, and impaired immune system.
- Pt 2 presents with: N/V, epigastric pain, and lethargy
iron deficiency
[iron supplements - may cause constipation/stomach upset].
Patient presents with fatigue, lightheadedness, SOB, spoon nails, and tachycardia. Labs confirms Dx.
KADE
- Vitamin K
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin D
- VItamin E
What are the fat-soluble vitamins?
- Vitamin B
- Vitamin C
What are the water-soluble vitamins?
- Pt 1 = vitamin A deficiency
- Pt 2 = vitamin A toxicity
What micronutrient abnormality do these pts have?
- Pt 1 presents with: night blindness, xerosis, and blindness.
- Pt 2 presents with: hypercalcemia, bone/joint pain, significant organ damage of liver, CNS and skin.
- Pt 1 = vitamin D deficiency
- Pt 2 = vitamin D toxicity
What micronutrient abnormality do these pts have?
- Pt 1 presents with: hypocalcemia/hyperparathyroidism with bone pain, muscle weakness, and osteomalacia. Ca, phosphorous, Mg labs done.
- Pt 2 presents with: hypercalcemia, constipation, polydipsia, polyuria, and confusion. Ca, phosphorous, Mg labs done.
- Pt 1 = vitamin C deficiency
- Pt 2 = vitamin C toxicity
What micronutrient abnormality does this pt have?
- An older patient with alcohol use disorder, anorexia, food allergies, and kidney dz presents with weight loss, diarrhea, swollen/bleeding gums, loss of teeth, poor wound healing, and easy bleeding.
folate (B9) deficiency
What micronutrient abnormality does this pt have?
- Patient with PMHx of chronic alcoholism, malabsorptive disorders, hemolytic anemia mucosal cell changes leading to glossitis, vague GI, anorexia, and diarrhea. NO neurological symptoms. Labs: macrocytic megaloblastic anemia with normal MMA levels
B12 deficiency
What micronutrient abnormality does this pt have?
Patient presents with chronic use of H2 Blockers/ PPI mucosal cell changes leading to glossitis, vague GI, anorexia, and diarrhea and neurological symptoms (paresthesias). Labs: macrocytic megaloblastic anemia with elevated MMA levels.
echinacea

st. john's wort

valerian

gingko biloba

melatonin

BMI >30
What is the BMI cut off for obesity?
central obesity
Which type of obesity has greater health risks?
- central obesity
- lower body obesity
obesity
[multidisciplinary approach: dietary strategies, physical activity, behavioral modifications, and Rx: Phentermine, Orlistat, contrave, GLP-1 agonist/semaglutide, Bariatric surgery)].
Patient presents with BMI >30 at risk for HTN, DM, Sleep Apnea presents to clinic. We review medications for steroids, contraceptives, SSRIs, antipsychotic. BP, waist circumference, fasting glucose, CMP, lipid panel, and A1C completed.
anal fissure
- Pt = acute anal fissure, off midline presentation needs further work up
- Partner = chronic anal fissure, midline presentation doesnt need work up
Tx: [fiber supplementation, sitz bath, +/- OTC topical anesthetics, for chronic: topical CCBs +/- lidocaine, topical nitroglycerin, botulinum injection]
Pt and partner with previous anal trauma presents with pain during and after defecation with tearing sensation and bright red blood per rectum on toilet tissue.
- Pt has had Sx for <6 weeks. PE shows cracks in epithelium off the midline distal to dentate line. Clinical Dx. Work-up done for Crohn disease, HIV/AIDs, tuberculosis, syphilis or anal carcinoma.
- Partner has had Sx for >6 weeks. PE shows cracks in epithelium in posterior midline distal to dentate line and sentinel pile on anus. Clinical Dx.
External hemorrhoids
Tx: [W.A.S.H. – Warm water, Analgesics, Stool softener, High-fiber diet; external thrombosed: can give nifedipine + lidocaine and office excision]
Older, pregnant pt with IBD and sedentary lifestyle presents with painful, bright red blood, pruritus, mucoid discharge, fecal incontinence. On PE: palpable mass upon DRE in lateral decubitus position at rest and straining. Presence of squamous epithelium overlying vessel distal to dentate line. Clinical Dx. Proctosigmoidscopy/colonscopy done to r/o rectum/sigmoid colon dz.
internal hemorrhoids
Tx: [W.A.S.H. – Warm water, Analgesics, Stool softener, High-fiber diet; referral to GI for rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, excision]
Group of older, pregnant pts with IBD and sedentary lifestyle presents with painless, bright red blood, pruritus, mucoid discharge, fecal incontinence. On PE: anoscopy in lateral decubitus position shows presence of mucosa overlying vessel proximal to dentate line. Clinical Dx. Proctosigmoidscopy/colonscopy done to r/o rectum/sigmoid colon dz.
Pt 1: lesion protrudes into anal canal, but does not prolapse
Pt 2: lesion prolapses but reduces spontaneously
Pt 3: lesion prolapses and requires manual reduction
Pt 4: irreducible reduction
pruritus ani
Tx: [depends on etiology, proper hygiene, gentle cleansers, keep region dry, barrier cream, topical steroid, oral hydroxyzine for itching.]
Pt with PMHx of skin irritants, dermatologic conditions, dietary irritants and STIs presents with perianal itching and discomfort. PE shows erythema, excoriations, lichenified, eczematous skin of anus. Bx done to r/o SCC.
constipation
Tx: [empiric tx okay for child: increase fluids/fiber, biofeedback (kegels), surgery if severe. Rx laxatives = rare → fiber supplements, stool surfactants, osmotic laxatives (polyethylene glycol), stimulant laxatives, enemas]
Older (>45 y/o) AFAB pt and child (<50 y/o) with PMHx of psychiatric disorders, hypothyroidism, DM, neurologic dz, opioid use, anorectal disorders presents with 2 or fewer bowel movements per week and excessive difficulty and straining at defecation. Abdominal pain, bloating, distention, decreased appetite, n/v present. CBC, electrolytes, calcium, glucose, TSH, FOBT, colonoscopy, anorectal manometry and colon transit time done on older at risk pt.
uncomplicated perianal abscess
Tx: [I&D, +/- antibiotics]
30-50 y/o AMAB with PMHx of trauma, Crohn's, tobacco use presents with perianal pain, fever, sensation of fullness, +/- drainage. PE shows erythematous fluctuant perianal area. Clinical Dx.
complicated perirectal abscess
Tx: [referral to GI for surgical drainage and antibiotics]
30-50 y/o immunocompromised AMAB with PMHx of trauma, malignancy, radiation, Crohn's, HIV, TB and tobacco use presents with perianal pain, fever, sensation of fullness, +/- drainage. PE shows overlying area of cellulitis in perirectal regions. MRI/CT confirms Dx.
perirectal fistula
Tx: [referral to GI for drainage with surgery under general anesthesia (high risk for incontinence). Abx.]
30-50 y/o immunocompromised AMAB with PMHx of trauma, malignancy, radiation, Chrons, HIV, TB, tobacco use, who recently had an abscess drained, presents with perianal pain, fever, sensation of fullness and purulent drainage. Work up for Crohn’s, lymphogranuloma venereum, rectal tuberculosis, cancer done given connecting to the rectum.
Minor fecal incontinence
Tx: [increase bulk of stool, biofeedback (Kegels), scheduled toileting; procedures: collagen-enhancing injectables, sacral neuromodulation, sphincteroplasty]
Pt with local anal problems, IBS, fecal impaction secondary to constipation and laxative misuse/abuse states that they are finding slight soilage of undergarments when they cough. DRE during relaxation and squeezing shows decreased anal sphincter tone. “Anal wink” not present. Anorectal manometry, pudendal nerve terminal motor latency, endocanal ultrasound, proctosigmoidoscopy done.
Major fecal incontinence
Tx: [increase bulk of stool, biofeedback (Kegels), scheduled toileting; procedures: collagen-enhancing injectables, sacral neuromodulation, sphincteroplasty]
Older pt who recently gave birth with PMHx of rectal prolapse, dementia, DM, CVA, MS, spinal cord injury, cauda equina syndrome, presents with complete uncontrolled loss of stool. DRE during relaxation and squeezing shows decreased anal sphincter tone. “Anal wink” not present. Anorectal manometry, pudendal nerve terminal motor latency, endocanal ultrasound, proctosigmoidoscopy done.
rectal prolapse
Tx: [referral to GI for surgical repair, increase fiber, fluids, attempts to control seepage]
Grandma and grandchild (0-4 y/o) with PMHx of pelvic floor dysfunction, excessive straining and dementia/surgical complication in grandma presents with fecal incontinence, rectal bleeding, seepage, feeling of a mass and incomplete bowel evacuation. Clinical Dx.
Fecal impaction
Tx: [enemas, digital disruption, maintaining soft stools and regular bowel movements, disimpaction under anesthesia if severe]
Pt with PMHx of severe psychiatric dz, prolonged bed rest and neurogenic disorders of colon and spinal cord presents with decreased appetite, n/v, abdominal pain and distention and paradoxical “diarrhea.” PE shows palpable firm feces on DRE in the rectal vault. Clinical Dx. Pt did not treat and developed large bowel obstruction.
Dyspepsia
[empiric H. Pylori tx (PPI, tetracycline, metronidazole, bismuth) for everyone except >60 y/o, alarm Sx—> if negative or refractory then empiric PPI trial +/- tricyclic antidepressant, lifestyle/diet changes. If pt 3 is refractory to all these Tx, then = functional dyspepsia]
3 pts present with epigastric pain/discomfort, heartburn, nausea, postprandial fullness and vomiting. Pt 1 is >60 y/o. Pt 2 has weight loss, persistent vomiting, constant/severe pain, progressive dysphagia, hematemesis, melena. Pt 3 has been having Sx for at least 1 month. Pt 1 (due to age) and Pt 2 (due to alarm Sx) gets an endoscopy/CT. CBC, CMP, TSH done. Pt 3 tested for H. Pylori (fecal antigen immunoassay, urea breath test).
Irritant peptic ulcer disease
Tx: [DISCONTINUE NSAID. PPI x 8 weeks, H2 blockers (not as effective). Surgical emergency with perforation]
Pt with long term NSAID use, presents with episodic epigastric pain/dyspepsia, gnawing, dull aching abdominal pain exacerbated with eating, nausea, anorexia. PE shows mild epigastric tenderness. FOBT positive. Upper endoscopy confirms gastric ulcer in the antrum of stomach. Ulcer Bx to r/o malignancy. Pt did not treat and developed melena, coffee ground emesis, perforation and obstruction.
Infectious peptic ulcer disease
Tx: [EITHER: bismuth/tetracycline/PPE/metronidazole OR omeprazole/rifabutin/amoxicillin.]
Pt with Hx of Helicobacter pylori infection presents with episodic epigastric pain/dyspepsia, gnawing, dull aching abdominal pain relieved with eating, nausea, anorexia. PE shows mild epigastric tenderness. FOBT positive. Upper endoscopy confirms duodenal ulcer. Fecal antigen, breath urea and serum antigen positive. Pt did not treat and developed melena, coffee ground emesis, perforation and obstruction.
Gastritis
Tx: [depends on etiology. NSAIDs: discontinue, PPI 2-4 weeks; H. pylori: bismuth/tetracycline/PPE/metronidazole OR omeprazole/rifabutin/amoxicillin; portal HTN: propranolol/nadolol; alcohol: discontinue, PPI or H2 blockers, sucralfate; stress: prophylaxis with PPI or H2 blockers]
Pt with PMHx of H. pylori infection, portal HTN, alcohol use, long term NSAID use and under a lot of stress was asymptomatic and is now experiencing epigastric pain, anorexia, n/v, mild coffee ground emesis, mild melena. Clinical Dx. Upper endoscopy positive for definitive Dx. CBC, vitamin B12, stool antigen/urea breath testing to r/o iron deficiency anemia, pernicious anemia, H. pylori.
hiatal hernia — stomach protrudes through diaphragm via esophageal hiatus
Tx: [PPI, H2 blockers, surgical management for refractory or severe cases]
Pt presents asymptomatic but has developed worsening GERD Sx. PE shows bowel sounds in the chest. CXR/CT confirms Dx (stomach sliding out of esophageal hiatus).
gastric cancer
[refer to GI for surgical resection, chemo/radiation, vitamin B12 supplement after gastrectomy.]
2 pts present asymptomatic at first, but then developed dyspepsia leading to weight loss and occult blood in stool leading to iron deficiency anemia. Pt 1 >40 y/o AMAB with PMHx of H. Pylori infection. Pt 2 is young with FHx of condition. PE normal. CBC shows anemia, FIT/FOBT shows occult blood. Elevated LFTs. Upper endoscopy + biopsies confirm Dx.
Assess hemodynamic status:
- Orthostatic BP (systolic drops 10mmHg = significant change)
- pulse (drop in 20BPM)
- use volume status to determine severity of blood loss
Source of bleed:
- UGI: hematemesis (BRB, "coffee grounds"), melena
- LGI: hematochezia, BRBPR
What are PE findings to evaluate when you suspect a GI bleed?
Upper GI Bleed
[PPI, refer to GI for endoscopic therapy (thermal coaptive therapy, epinephrine injection, endoscopic clip)]
Pt with hx of NSAID use and peptic ulcer dz presents with hematemesis (BRB, “coffee-ground” colored) and black, tarry stool. On PE, hemodynamic status assessed (orthostatic BP, pulse, volume status) and mild epigastric tenderness. CBC, PT/INR, serum creatinine, LFTs done. Endoscopy confirms Dx.
Lower GI Bleed
[refer to GI for colonoscopy therapy (thermal coaptive therapy, epinephrine injection, endoscopic clip), surgical resection if endoscopic therapy fails]
>50 y/o pt with PMHx of diverticulosis, IBD, ischemic colitis and angiodysplasia presents with hematochezia and BRBPR. On PE, hemodynamic status assessed (orthostatic BP, pulse, volume status) and mild epigastric tenderness. CBC, PT/INR, serum creatinine, LFTs done. Colonoscopy confirms Dx.
diverticulosis
[High-fiber diet/fiber supplements, Exercise, Avoidance of red meat/NSAIDs]
>60 y/o with PMHx of connective tissue dz (Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Marfan syndrome) was asymptomatic and then developed chronic constipation and fluctuating bowel habits. On PE: LLQ tendernes with thickened palpable sigmoid descending colon present. Colonoscopy confirms Dx.
diverticulitis
- Pt 1 = mild diverticulitis
- Pt 2 = severe diverticulitis
[- Mild: clear liquid diet, anaerobic ABx [amox/clav OR metronidazole] + [ciprofloxacin OR bactrim].
- Severe: NPO, IV fluids, NG tube suction if ileus, IV aerobic + anaerobic ABx [cephalosporin, pip-tazo, ticarcillin clav] OR [(metronidazole, clindamycin) + (aminoglycoside, cephalosporin)].
- Procedures: percutaneous catheter drainage of abscess + surgical resection of diseased segment of colon.]
2 pts > 40 y/o pt presents with acute, aching abdominal pain in LLQ with constipation/loose stools, n/v. On PE: LLQ mass and tenderness. Stool occult blood test positive. Endoscopy and CT colonography done once pt is stabilized and confirms Dx. Pt 1 has low-grade fever. Pt 2 has high fever, leukocytosis and peritoneal signs. Pt 1 did not treat and developed Sx similar to Pt 2.
esophageal varices
[refer to GI, fluid resuscitation. Rx: terlipressin/octreotide (reduce portal pressure), PPI, prophylactic ceftriaxone. +/- vitamin K for low INR. Procedures: Endoscopic therapy (banding, sclerotherapy), transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts (TIPS)]
Pt with hx of chronic ETOH use, liver cirrhosis, and portal HTN presents with dyspepsia, retching and hematemesis. Pt then worsened and developed orthostatic hypotension, hypovolemia and shock. CBC, PT/INR, LFTs, creatinine, BUN done. Upper endoscopy confirms Dx.
Mallory-Weiss Syndrome -- nonpenetrating mucosal tear at the gastroesophageal junction due to sudden raise in transabdominal pressure
[self-limiting, fluid resuscitation, blood transfusions. Refer to GI for: endoscopic hemostatic therapy for active bleeding (epinephrine injection, cautery, mechanical compression), angiographic arterial embolization for severe cases]
Pt with alcohol use disorder presents with hematemesis, retching and vomiting. CBC, PT/INR, LFTs, creatinine, BUN done. Upper endoscopy confirms Dx and shows linear mucosal tear at/below the gastroesophageal junction/gastric mucosa.
colorectal cancer
- Pt 1 = proximal colon cancer
- Pt 2 = distal colon cancer
- Pt 3 = left sided colon cancer
- Pt 4 = rectal colon cancer
[refer to GI/oncologist for surgical resection/chemotherapy/radiation. Screening: 45-75 y/o colonoscopy Q10yrs OR FIT test Qyr. If FHx of colon cancer: colonoscopy starting at age 40 or 10yrs before family member diagnosed Q5 yrs for high risk or Q10yrs for lower risk. F/u after resection: visit/labs Q3-6 months —> Q6months x 5 yrs. CT with contrast Q6-12 months x 5 yrs, Colonoscopy Q3-5 yrs]
4 pts who are older, obese, AMAB with family Hx of dz and serrated/adenomatous polyps, who eats lots of red meat, smokes, drinks a lot of alcohol and has a sedentary lifestyle present with:
- Pt 1 has fecal occult blood, anemia.
- Pt 2 has change in bowel habits, hematochezia.
- Pt 3 has colicky abdominal pain.
- Pt 4 has rectal tenesmus (persistent feeling of needing to poo) and urgency to poo
PE is normal. Anemia, elevated ALP, FOBT/FIT positive, elevated serum carcinoembryonic antigen. Colonoscopy + Biopsy confirms Dx.
everyone: 45-75 y/o
- colonoscopy = Q10yrs
- FIT test = Qyr
- fecal DNA test = Q1-3yrs
- flexible sigmoidoscopy/CT = Q5yrs
if first degree relative >60y/o at Dx:
- colonoscopy Q10yrs at 40 y/o
if first degree relative <60y/o at Dx/multiple relatives Dx:
- colonoscopy Q5yrs at 40 y/o or 10yrs before family member Dx
What is the screening criteria for colon cancer?
intestinal polyps -- discrete flat or protruding mass lesions in the intestinal lumen
[colonoscopy polypectomy (removal of ALL polyps on colonoscopy). Increase routine colonoscopy frequency based on the number of polyps found.]
Older pt with familial polyposis syndrome presents asymptomatic and then chronic occult blood loss lead to iron deficiency anemia. Large lesions ulcerate and cause intermittent hematochezia. FIT, FOBT and fecal DNA tests positive. CT colonography shows large lesions. Colonoscopy confirms Dx.
acute non-inflammatory diarrhea
[self-limiting, focus on rehydration, antidiarrheal okay if no blood in stool, no abx at this time].
Patient who recently visited a daycare, nursing home, went on a cruise, presents with NONbloody watery diarrhea x <2 weeks (>3 BM per day or liquid feces), with periumbilical cramps, and no fever. Dx: labs: hypokalemia, metabolic acidosis. No need for stool culture if under 7 days.
acute inflammatory diarrhea
[No antidiarrheals, abx dependent on stool sample/etiology; supportive care and tx underlying cause].
Patient visited a nursing home, school, cruise ship and ate raw meat presents with bloody diarrhea x <2 weeks (>3 BM per day or liquid feces) and fever. They have LLQ cramping pain. Fecal leukocytes and lactoferrin present. Stool culture done.
- severe dehydration
- worsening bloody diarrhea
- severe abdominal pain
- signs of severe infection/sepsis
- worsening diarrhea + >70 y/o OR immunocompromised
- hemolytic uremic syndrome
When should you admit someone with acute diarrhea?
chronic osmotic diarrhea -- water retention in intestine due to presence of poorly absorbed solutes
[tx underlying cause, loperamide].
Pt with PMHx of celiac dz, carbohydrate malabsorption syndrome, laxative abuse presents with >4 weeks of diarrhea, the stool volume decreases with fasting and resolves with fasting. Increased osmotic stool gap >75 mOsm/kg present, routine labs (CBC, CRP, anti-tissue transglutaminase IgA, total IgA, BMP), +/- endoscopic exam.
chronic secretory diarrhea -- reduced water absorption
[tx underlying cause, loperamide].
Pt with PMHx of endocrine tumors, bile acid malabsorption, microscopic colitis, hyperthyroidism, IBD presents with >4 weeks of large volume watery diarrhea and which persists at night and during fasting. Normal <50 osmotic gap, 24-hour stool collection. Hyponatremia and non-anion gap metabolic acidosis present. routine labs (CBC, CRP, anti-tissue transglutaminase IgA, total IgA, BMP)
chronic inflammatory diarrhea -- presence of fecal leukocytes, lactofarrin/calprotectin or blood
[tx underlying cause, NO antidiarrheal/motility due to blood].
Patient with PMHx of IBD, C. Diff, Amebiasis, colorectal cancer, colitis, helminth infection presents with >4 weeks bloody/purulent diarrhea with abdominal pain, and fever. Anemia, hypoalbuminemia and increased ERS/CRP. Colonoscopy done. routine labs (CBC, CRP, anti-tissue transglutaminase IgA, total IgA, BMP)
chronic malabsorptive diarrhea -- fatty diarrhea
[tx underlying cause, loperamide].
Patient with PMHx of celiac dz and Giardiasis presents with >4 weeks of diarrhea with steatorrhea, weight loss and nutritional deficiencies. Anemia and hypoalbuminemia present. 24 hr stool collection of fecal fat >10 g/24hr. routine labs (CBC, CRP, anti-tissue transglutaminase IgA, total IgA, BMP)
Chronic motility disorder diarrhea -- rapid transit/stasis of chyme leads to bacterial overgrowth and malabsorption
[tx underlying cause, loperamide]
Patient with PMHx of prior abdominal surgery and IBS presents with >4 weeks of diarrhea, lower abdominal pain, altered bowel habits, with NO: weight loss, GI bleeding, or nocturnal diarrhea. routine labs (CBC, CRP, anti-tissue transglutaminase IgA, total IgA, BMP)
chronic infection diarrhea
[abx for parasites: metronidazole].
Immunocompromised pt with PMHx of AIDS presents with >4 weeks of diarrhea. They recently went hiking and had well water. Dx: stool sample of ova and parasites.
celiac disease -- immunologic response to gluten that causes diffuse damage to mucosa and malabsorption of nutrients
- Mom: Type I: normal lymphocyte population
- Children: type II with loss of surface expression of CD3/CD8 and T Cell receptors
[Refer to dietitian. Strict gluten-free diet, avoid dairy products till symptoms improve, supplements, if acute: all the above plus IV nutrition or corticosteroids short-term as gluten-free diet is initiated ]
A family presents with chronic diarrhea. The mother has a PMHx of depression, amenorrhea/reduced fertility, osteoporosis and iron deficiency anemia; current s/sx are weight loss. Her adolescent child presents with growth retardation, flatulence, dyspepsia, and variable weight loss. Her infant (<2yrs) presents with steatorrhea, weight loss, weakness, muscle wasting, and growth retardation. On PE they all have distension with hyperactive bowel sounds and dermatitis herpetiformis. Tissue transglutaminase IgA is positive. Upper endoscopy with duodenal bx definitively confirms Dx. CBC, Vit K, serum albumin, iron, folate, B12, Vit A/D, and Ca2+ were ordered. Children did not treat and developed T-cell lymphoma
Crohn's disease
[diarrhea: loperamide. Terminal ileum/ascending colon dz: budesonide. Left-sided/diffuse colitis: oral corticosteroids, sulfasalazine, oral 5-ASA agents. Biologic therapies. Surgery if needed. B12 supplement for terminal ileus dz.]
20-30 y/o smoker with FMHx of disease and Hx of antibiotic use in childhood, appendectomy, vitamin D deficiency presents with intermittent bouts of low-grade fever, diarrhea, RLQ pain, weight loss, malnourishment and perianal fistulas, fissures and abscesses. On PE: RLQ tenderness and mass [inflammation] with postprandial bloating and loud borborygmi [strictures]. Other Sx include arthralgia, pyoderma gangrenosum, erythema nodosum. CBC, ESR/CRP, fecal calprotectin, stool specimens done. Endoscopy shows transmural, non-continuous, “skip lesions” ulcerations with strictures and fistulas of terminal ileum and proximal ascending colon. Bx shows granulomas.
Ulcerative colitis -- diffuse mucosal inflammation of colon, resulting in friability, erosions and ulcers with bleeding
[5-ASA, oral corticosteroid, biologics, total proctocolectomy curative]
NONsmoker/former smoker with PMHx of primary sclerosing cholangitis, presents with bloody diarrhea, increased fecal urgency, LLQ pain. On PE: BRB on DRE. Anemia, hypoalbumeia, elevated CRP. Stool culture done. Sigmoidoscopy confirms Dx with erythematous superficial, continuous, circumferential erosions/ulcers with friability with bleeding in the colon (rectosigmoid region, splenic flexure, extensive colon involvement). Other Sx include oral ulcers, erythema nodosum, pyoderma gangrenosum. Pt did not treat and developed toxic megacolon and colon cancer.
microscopic colitis
[loperamide, budesonide, bile salt binding agents, immunosuppressive agents. stop offending medication and should subside within 30 days]
50-60 y/o AFAB on NSAID and PPI presents with chronic/intermittent non-bloody watery diarrhea. Endoscopy shows normal-appearing mucosa. R/o celiac dz (IgA anti-tissue transglutaminase antibody). Colonoscopy + Biopsy confirms Dx and shows chronic inflammation in lamina propria and increased intraepithelial lymphocytes.
Jaundice + coagulopathy WITHOUT hepatic encephalopathy
What Sx suggest acute liver injury?
liver injury, as opposed to cholestatic injury
AST/ALT >>> ALP indicates what?
acute liver injury + HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY
What Sx suggest acute liver failure?
LIVER TRANSPLANT + N-acetylcysteine
What is the treatment for acute liver failure?
acute liver injury
These are etiologies for what condition?

alcoholic hepatitis
[reversible with alcohol cessation. cravings: Acamprosate, naltrexone. Nutrient supplements. Corticosteroids.]
20-29 y/o pt with alcohol use disorder (80 g/d in men and 30-40 g/d in women), presents initially asymptomatic but then developed anorexia, nausea, fever, jaundice and RUQ pain after 5 years of drinking. On PE: RUQ tenderness and hepatomegaly. AST >>> ALT. Increased ALP. Elevated serum bilirubin. Decreased serum albumin. Anemia, leukocytosis. Decreased folate. US done to r/o ascites and biliary obstruction. CT/MRI done to r/o cancer, pancreas dz. Liver Bx confirms Dx with Mallory bodies, hepatic necrosis/fibrosis.
toxin related hepatitis / drug induced liver injury
[REMOVE OFFENDING AGENT, liver transplant if acute liver failure. N-actelycystine for acetaminophen overdose.]
Older pt who took a bunch of acetaminophen presents to the clinic with nausea, vomiting, anorexia, and jaundice. Increased AST/ALT. Elevated INR. NIH LiverTox website used to assess causality.
1. steatosis = fat deposits
2. steatohepatitis = fat deposits + fibrosis
3. cirrhosis = severe fibrosis of liver
4. liver cancer
What is the progression of liver disease?
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease / Steatohepatitis (AKA "Metabolic Associated Steatotic Liver Disease")
Tx: [treat Sx (fibrosis is permanent). vitamin E, obeticholic acid, semaglutide, ACE, liver transplant if liver failure. lifestyle modifications. bariatric surgery. LFT/US monitoring.]
>60 y/o pt with PMHx of obesity, DM, hypertriglyceridemia with metabolic syndrome (insulin resistance) presents mostly asymptomatic with mild RUQ discomfort. On PE: hepatomegaly and acanthosis nigricans (from metabolic syndrome). Elevated ALT>AST. Elevated serum ferritin. US shows steatosis +/- inflammation/fibrosis. Liver Bx confirms Dx.
Wilson Disease -- autosomal recessive disorder of too much copper in liver and brain
[refer to gastroenterologist/hepatologist. Oral D-penicillamine (excretes copper). Restrict dietary copper. Screen all first degree relatives.]
Young adult brother and adolescent sister present with corneal kayser-fleischer rings on PE. Young adult brother has neurologic and psychiatric abnormalities (Parkinsonism Sx, ataxia, dysphagia, behavioral changes). Adolescent sister has hepatitis, cirrhosis and portal HTN. Both have: decreased ceruloplasmin, increased urinary excretion of copper and increased hepatic concentration of copper. Coombs-negative hemolytic anemia. LFTs, ratio to exchangeable copper to total copper in serum and MRI done. Molecular analysis of ATP7B pathogenic variants confirms Dx.
cirrhosis
[refer to GI/hepatologist, encourage abstinence from alcohol, vitamin supplementation, vaccines (HAV, HBV, pneumococcal vaccines, influenza vaccine, COVID), carvedilol (reduce frequency of decompensation), large-volume paracentesis, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Liver transplant curative. Tx Sx as needed.]
Pt with hepatic cell dysfunction, portosystemic shunting, portal HTN and alcohol use disorder was asymptomatic and then developed fatigue, weight loss, jaundice. On PE: hepatomegaly, splenomegaly ascites, spider telangiectasis, palmar erythema, dupuytren contractures, terry nails, glossitis, cheilosis and dilated superficial veins. Pt did not treat and developed massive ascites, variceal bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy [DECOMPENSATION]. CBC shows thrombocytopenia, prolongation of prothrombin time, increased LFTs, decreased serum albumin, vitamin D deficiency. US/CT/MRI, esophagogastroduodenoscopy, liver Bx and wedged hepatic vein pressure measurement done.
hepatic encephalopathy -- CNS dysfunction resulting from failure of liver to detoxify noxious agents (mostly ammonia) of gut due to hepatocellular dysfunction and portosystemic shunting
- friend = covert hepatic encephalopathy
[Refer to gastroenterologist/hepatologist. Magnesium citrate, lactulose, polyethylene glycol to purge GI tract. Oral Abs: rifaximin, metronidazole, neomycin sulfate for ammonia producing flora. Oxazepam for agitation. Oral zinc sulfate for zinc deficiency. Lactulose for maintenance. Dietary protein restriction.]
Pt and friend with cirrhosis, GI bleed, hepatic/systemic infection, portosystemic shunt. Pt presents with day-night reversal, asterixis, tremor, dysarthria, delirium, drowsiness, stupor, coma. Friend presents with mild cognitive and psychomotor deficits. Clinical Dx: asterixis + elevated serum ammonia + exclusion of other causes of delirium. Friend did Stoop test. Staged based on mental status.
cholelithiasis -- gallstones in gallbladder
[if asymptomatic: no Tx needed. NSAIDs for pain relief, consider elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy if persistent symptoms. lifestyle mod: low carb, mediterranean, low-fat, high fiber, Physical activity, and coffee is protective].
AFAB >40 y/o of hispanic descent with PMHx of obesity, DM, and hx of tobacco and OCP use presents with episodic epigastric/RUQ that radiates to the right scapula lasting up to 30 min-3 hours with n/v, most commonly at night and after fatty foods/large meals. LFTs are normal and US confirms Dx.
acute cholecystitis -- gallstone in cystic duct with inflammation
[IV abx, stabilize → laparoscopic cholecystectomy, lifestyle mod: low carb, mediterranean, low-fat, high fiber].
Pt presents with acute persistent epigastric pain localized at RUQ and radiating to the right scapula. PE: Fever, Murphy signs positive, and rebound tenderness. Leukocytosis present. CMP LFTs normal. US confirms Dx.
chronic cholecystitis -- fibrosis of gallbladder due to chronic inflammation
[laparoscopic cholecystectomy, lifestyle mod: low carb, mediterranean, low-fat, high fiber].
Pt presents with episodic epigastric/RUQ pain and nausea that is worse after meals. PE: Murphy signs positive, rebound tenderness, NO fever present. US confirms Dx with thickening/fibrosis. CBC normal.
choledocholithiasis -- gallstone in common bile duct
[NSAIDs for pain relief, elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy. lifestyle mod: low carb, mediterranean, low-fat, high fiber, Physical activity, and coffee is protective].
Older AFAB pt presents with biliary pain, jaundice, RUQ pain, N/V. PE: NO fever present. hepatomegaly, RUQ/epigastric tenderness. ECRP/endoscopic US confirms Dx and shows biliary dilation. Elevated bilirubin, amylase, and lipase. Elevated WBC.
cholangitis -- infection within biliary tree due to obstruction (from choledocholithiasis)
[ALWAYS ADMIT. Mild/mod: cipro metronidazole or ampicillin sulbactam, Severe/hospital acquired: Pip/tazo; severe: aminoglycosides. Refer: surgery for endoscopic sphincterotomy and stone extraction].
Older patient with a hx choledocholithiasis presents with Reynolds Pentad: RUQ pain, jaundice, fever, hypotension, altered mental status, plus N/V. PE: hepatomegaly and RUQ tenderness. ERCP/endoscopic US confirms Dx and shows biliary dilation. Elevated bilirubin, evaluated WBC, and elevated LFTs.
irritable bowel syndrome -- disconnect from brain to stomach
- Friend 1 = IBS-D (diarrhea)
- Friend 2 = IBS-C (constipation)
- Friend 3 = IBS-M (mixed)
- Friend 4 = IBS-U (unspecified)
[reassurance, avoid triggers, FODMAP diet (AVOID fermentable, oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides and polyols) – refer to dietician, exercise, treat underlying psychosocial issues. peppermint oil Rx: antispasmodics (hyoscyamine, dicyclomine, methscopolamine), TCA/SNRI for pain. Antidiarrheals (loperamide), anti-constipations (miralax)]
Group of friends 20-39 y/o AFAB with FMHx of condition, recent infection and psychosocial disorders presents with chronic, recurrent abdominal pain (2-3 features: increase or decrease of pain with defecation, associated with change in frequency of stool, associated with change in form of stool). Sx present for >1 day/week for at least 3 months.
- Friend 1 has diarrhea (Bristol Stool Chart Type 5-7).
- Friend 2 has constipation (Bristol Stool Chart Type 1-2).
- Friend 3 has mixed constipation and diarrhea.
- Friend 4 has uncategorizable stools.
Clinical Dx. PE +/- mild abdominal tenderness on palpation. Rectal exam done in Friend 2 with constipation. CBC done in all friends. Celiac and IBD workup done in Friend 1 with diarrhea.
Eosinophilic esophagitis
[PPI BID x 2 months then repeat endoscopy + biopsy, topical corticosteroids, budesonide/fluticasone, food elimination diets (wheat, milk), esophageal dilation.]
AMAB white child with Hx of allergies and atopy presents with dysphagia, food impaction, heartburn, chest pain. Also because he is a child he has abdominal pain, vomiting and failure to thrive. Labs show eosinophilia, elevated IgE levels. Skin testing for food allergies done. Barium swallow shows small caliber esophagus with tapered strictures. Endoscopy + Multiple Biopsies confirms Dx. Shows REEFS = concentric Rings + Edema + Exudates + Furrows + Strictures.
Infectious esophagitis
- Friend 1 = candida albicans
- Friend 2 = CMV
- Friend 3 = HSV
[candida albicans = empiric fluconazole, CMV = ganciclovir then valganciclovir, HSV = acyclovir/famciclovir; referral to gastroenterologist if empiric Tx is not working]
Group of immunosuppressed friends with HIV presents with odynophagia, dysphagia and substernal chest pain.
- Friend 1 was asymptomatic.
- Friend 2 has infections at other sites (colon, retina).
- Friend 3 has oral ulcers. Endoscopy + Biopsy + brushings confirms Dx.
pill-induced esophagitis
[take pills with water, remain upright for 30 mins after ingestion, avoid offending agents].
Pt who took alendronate and NSAID without water while supine presents with severe retrosternal chest pain, odynophagia and dysphagia. Clinical Dx. Endoscopy shows ulcers, esophagitis with strictures, hemorrhage, perforation.
diffuse esophageal spasm
[esophageal acidification: PPI, H2 antagonists; smooth muscle relaxants: nitrates, CCB; procedure: per oral endoscopic myotomy]
Pt presents with episodic dysphagia, chest pain and regurgitation. Barium esophagography shows “corkscrew esophagus.” Manometry confirms Dx (pressure and constriction of muscle in esophagus diminished). Endoscopy done to r/o other causative conditions. Pt did not treat and developed achalasia.
gastroesophageal reflux disease
[lifestyle mods: decrease meal size, weight, triggering foods. Mild: PRN antaids, H2 antagonists. Mod: oral PPI QD. Severe: Oral PPI BID +/- TCA. Refer to GI for procedures: surgical/laparoscopic fundoplication. Barrett esophagus: therapeutic endoscopy + screening endoscopy Q3-5 years. Peptic stricture: endoscopic dilation.]
Pregnant pt with impaired salivation (Sjogren syndrome, anticholinergics, oral radiation therapy), delayed gastric emptying (gastroparesis), obesity who is stress consuming acidic, fatty foods, peppermint chocolate, alcohol and cigarettes, presents today with heartburn and regurgitation 30-60 minutes after meals, upon reclining and has relief from antacids. Other Sx: dysphagia, dyspepsia, belching, hoarseness. PE is normal. Clinical Dx. Endoscopy done in severe cases (anemia, difficulty swallowing, weight loss, frequent bloody emesis/stools, refractory to Tx, >50 y/o with GERD x 5 years with RF for gastric cancers). pH testing in refractory/atypical GERD. R/O CARDIAC EVENT! Pt then developed Barrett esophagus and peptic stricture. Endoscopy + Biopsy done in Barrett esophagus.
esophageal cancer
- Friend 1 = SCC
- Friend 2 = adenocarcinoma
[refer to GI/oncologist, neoadjuvant chemoradiation, esophagectomy, lymphadenectomy. Screenings: white males, obesity, smoking, FHx; adenocarcinoma – endoscopic surveillance, SCC – eliminate cigarette smoking]
50-70 y/o AMAB, obese friends with family Hx of condition presents with progressive dysphagia to solid food, odynophagia and significant weight loss.
- Friend 1 has Hx of ingestion of caustic substances (smoking).
- Friend 2 has Hx of chronic GERD with Barrett metaplasia.
PE is normal, lymphadenopathy and hepatomegaly present. Anemia, elevated LFTs and hypoalbuminemia present. Barium esophagogram shows polypoid, obstructive, ulcerative lesion. Endoscopy with biopsy confirms Dx. Lymph node biopsy done. Bronchoscopy r/o tracheobronchial extension. Laparoscopy r/o occult peritoneal carcinomatosis. After Dx established, CT chest, abdomen pelvis and PET r/o metastasis.
esophageal web
[passage of bougie or endoscopic balloon dilators to disrupt web. endoscopic electrosurgical incision curative, PPI]
Pt with congenital version of condition, eosinophilic esophagitis and iron deficiency anemia [Plummer-Vinson syndrome] was asymptomatic and now presents with intermittent solid-food dysphagia. Barium esophagogram with full esophageal distention shows diaphragm-like membranes (“cling wrap”) of squamous mucosa in mid/upper esophagus.
esophageal ring
[passage of bougie or endoscopic balloon dilators to disrupt web. endoscopic electrosurgical incision curative, PPI]
Pt with hiatal hernia and GERD was asymptomatic and now presents with intermittent solid-food dysphagia. Barium esophagogram with full esophageal distention shows circumferential structures in distal esophagus.
achalasia
[Refer to GI, CCB for Sx, procedures: modified Heller cardiomyotomy of LES and cardia, per oral endoscopic myotomy, complete esophagectomy, PEG tube, botulinum toxin injection, pneumatic dilation.]
Older pt presents with progressive (months-years) dysphagia to solids and liquids and regurgitation of undigested food. PE normal. Barium esophagogram shows smooth, symmetric “bird’s beak” tapering at distal esophagus. Esophageal manometry confirms Dx with complete absence of normal peristalsis of esophagus and incomplete LES relaxation with swallowing. CXR shows enlarged, fluid-filled esophagus. Endoscopy r/o distal stricture or infiltrating carcinoma.
Zenker Diverticulum
[ASx: observation, Sx: cricopharyngeal myotomy, giant diverticula: surgical transcervical myotomy with diverticulectomy]
AMAB pt presents with progressive dysphagia and regurgitation. Initially started as vague dysphagia with coughing progressing to halitosis, spontaneous regurgitation of undigested food, nocturnal choking, gurgling and protrusion in throat. Video esophagography confirms Dx with protrusion of pharyngeal mucosa. Pt did not treat and developed aspiration pneumonia, bronchiectasis, lung abscess.
acute pancreatitis
[fluid resuscitation, NPO, pain and nausea control, ABx if lots of necrotizing pancreatitis; Tx underlying etiology. alcohol cessation, procedures: cholecystectomy]
AFAB pt who drinks alcohol and with PMHx of gallstones and hypertriglyceridemia presents with ⅔ criteria: steady, severe LUQ abdominal pain radiating to back, elevated lipase >3x upper limit of normal, and pancreatic inflammation on CT. ASx: n/v, worse with eating, tachycardia, fevers, epigastric tenderness. On PE: Grey Turner’s sign (flank ecchymoses), Cullen’s Sign (periumbilical ecchymoses. LFT, serum Ca and triglyceride levels done. First line imaging: US then CT. Ranson’s Criteria and BISAP Score done to determine risk. Pt did not treat and developed pseudocyst, necrotizing pancreatitis, acute tubular necrosis, pseudoaneurysm, splenic vein thrombosis, chronic pancreatitis and DM.
chronic pancreatitis
[Tx etiology: alcohol cessation, low fat diet; exocrine insufficiency: pancreatic enzymes, endocrine insufficiency: insulin, pain: NSAIDs, neuromodulators. Procedures: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatoscopy for dilation of ducts or obstructions]
Pt with PMHx of alcohol use disorder, recurrent acute pancreatitis and DM [endocrine dysfunction] presents with chronic epigastric pain radiating to the back. Steatorrhea [exocrine dysfunction] and weight loss present. CT/MRI confirms Dx and shows pancreatic calcifications. Endoscopic US used to assess pancreatic ductal dilation/strictures, fluid collections and atrophy. Amylase/lipase are normal. Low fecal elastase suggests pancreatic insufficiency. Pt did not treat and developed pseudocysts, biliary obstruction, duodenal obstruction, splenic vein thrombosis and pancreatic cancer.
pancreatic cancer
[refer to oncologist. surgical resection → Head lesion: Whipple surgery (pancreas attached to small intestine). Tail/body lesion: distal pancreatectomy. chemo/radiation.
supportive care: celiac plexus blocks/neurolysis, ERCP with biliary stenting, surgical bypass or enteral stenting for gastric outlet obstruction. Screening: family members with pancreatic cancer, certain genetic mutation and Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (polyps in abdomen)]
>60 y/o AMAB with PMH significant for smoking, obesity, chronic pancreatitis, new onset DM and pancreatic cysts presenting with painless jaundice, steatorrhea, weight loss and abdominal pain. On PE: Courvoisier’s sign (palpable gallbladder), and trousseau syndrome (migratory superficial thrombophlebitis). CT/MRI shows mass on imaging with double duct sign (dilation of biliary and pancreatic duct). LFT done. Genetic testing for CA 19-9 done. Endoscopic US guided fine-needle biopsy/aspiration confirms Dx.
small bowel
These pathogens typically effect which part of the GI tract?
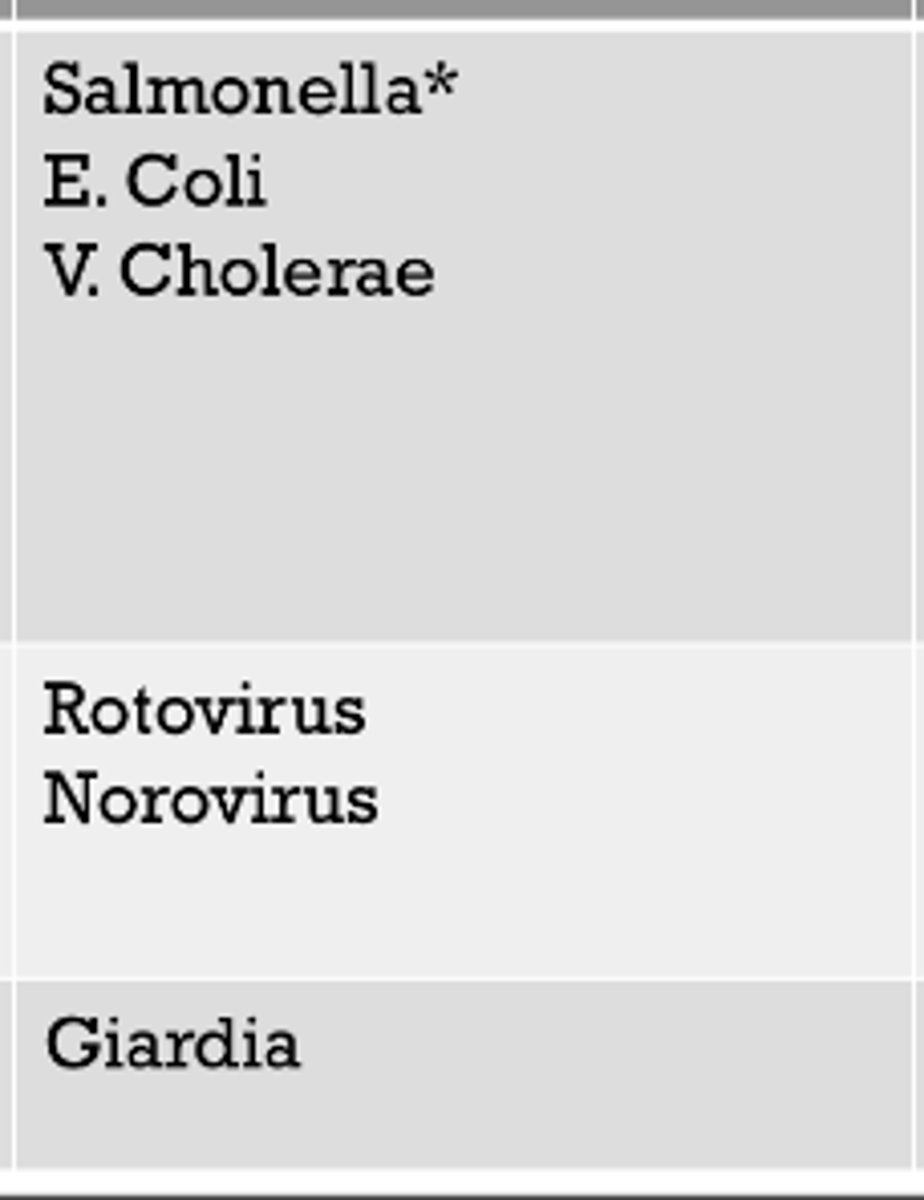
large bowel
These pathogens typically effect which part of the GI tract?
