IB Biology - Plants: gas exchange and transport
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
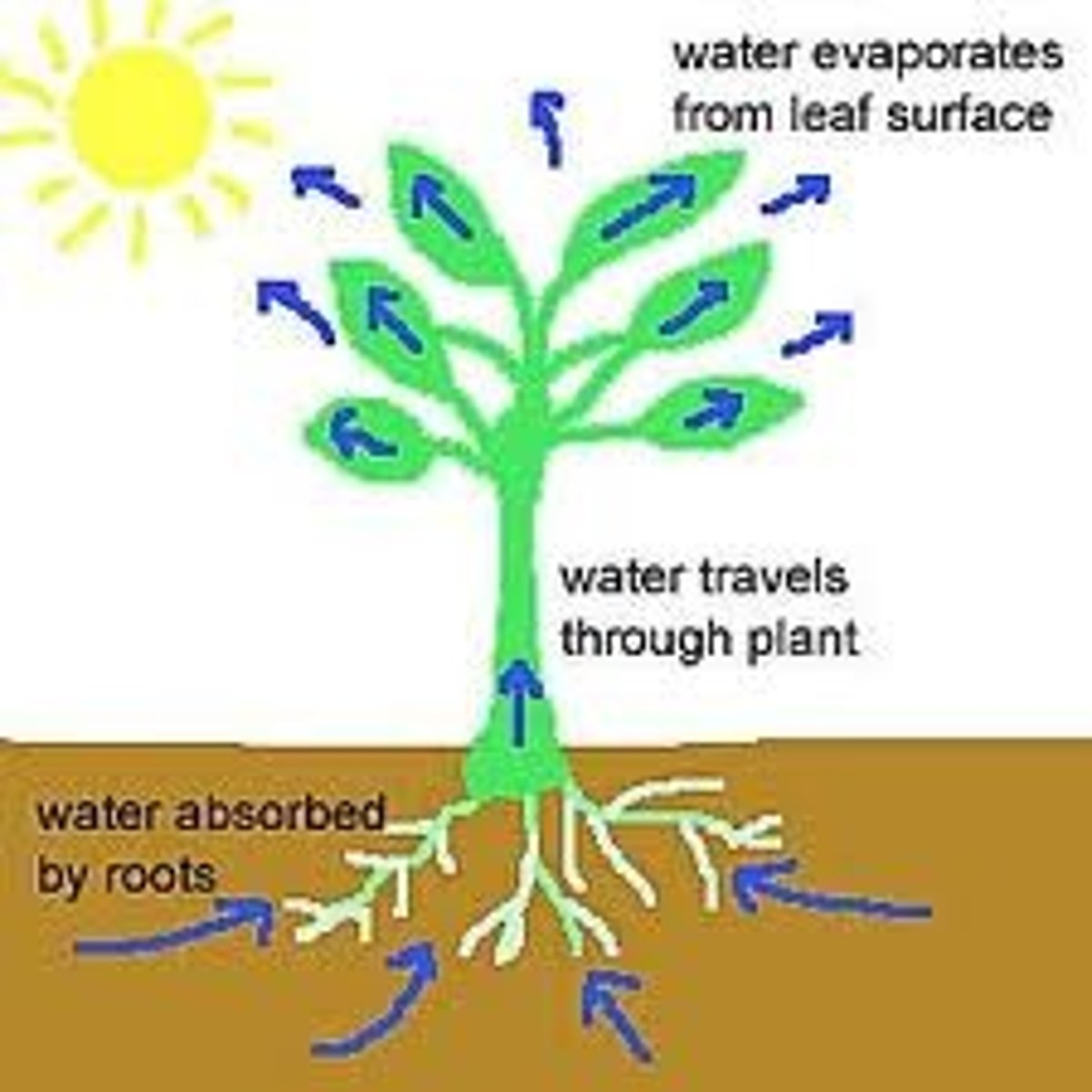
Transpiration
the passive movement of water through the plant and evaporation from leaves
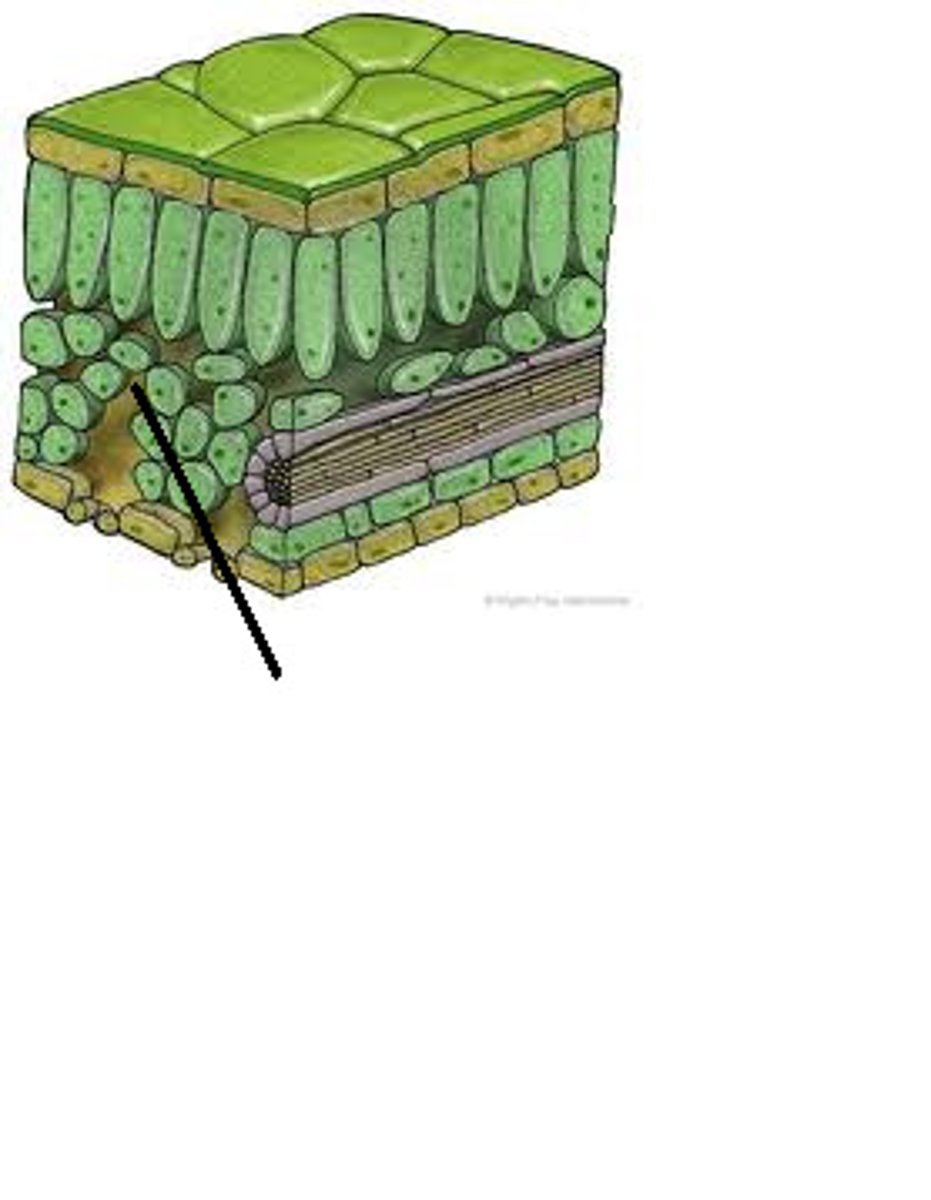
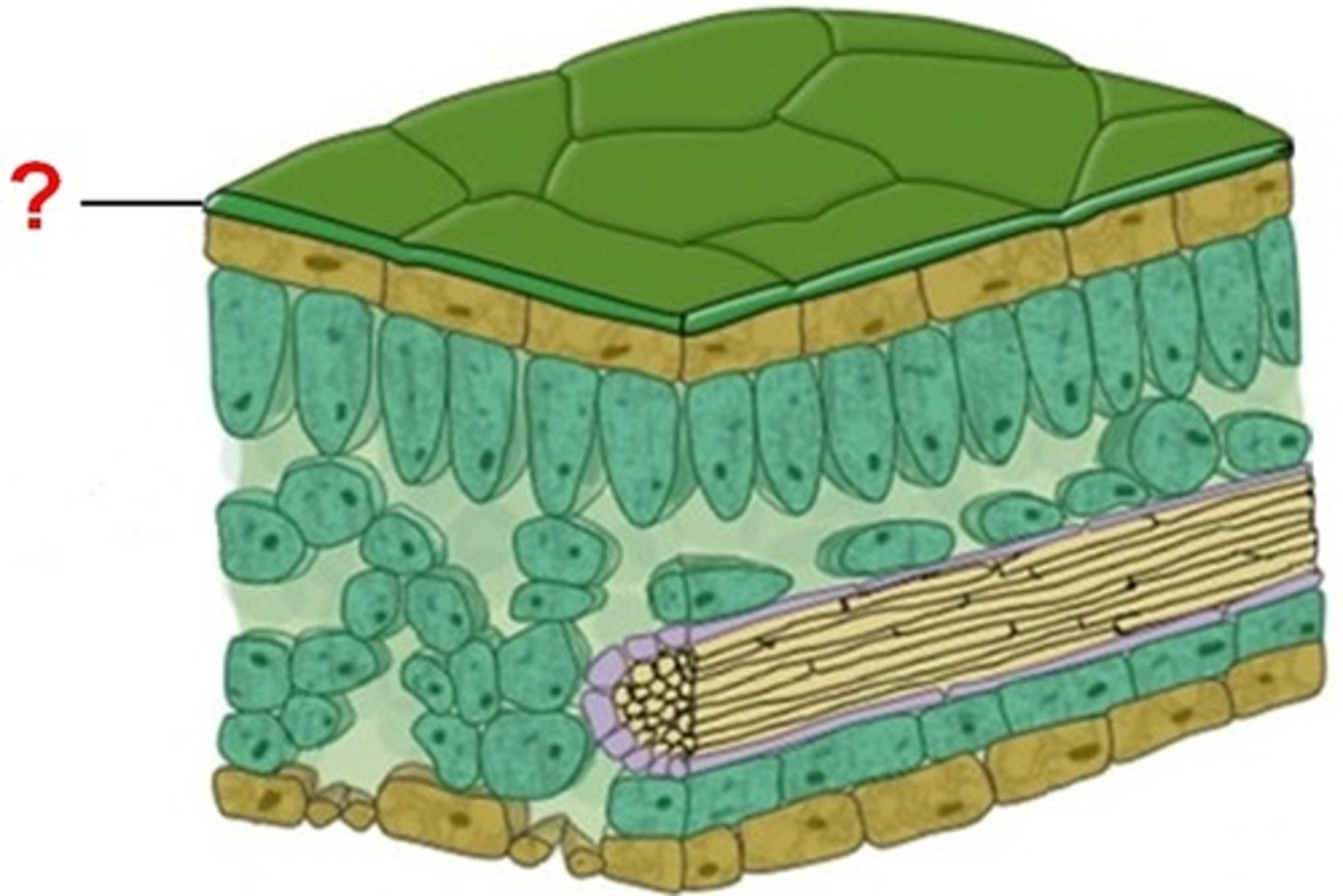
Epidermal tissue:
forms outer boundaries
Mesophyll tisue:
internal structure
Vascular tissue:
transports the subtances between the leaf and plant
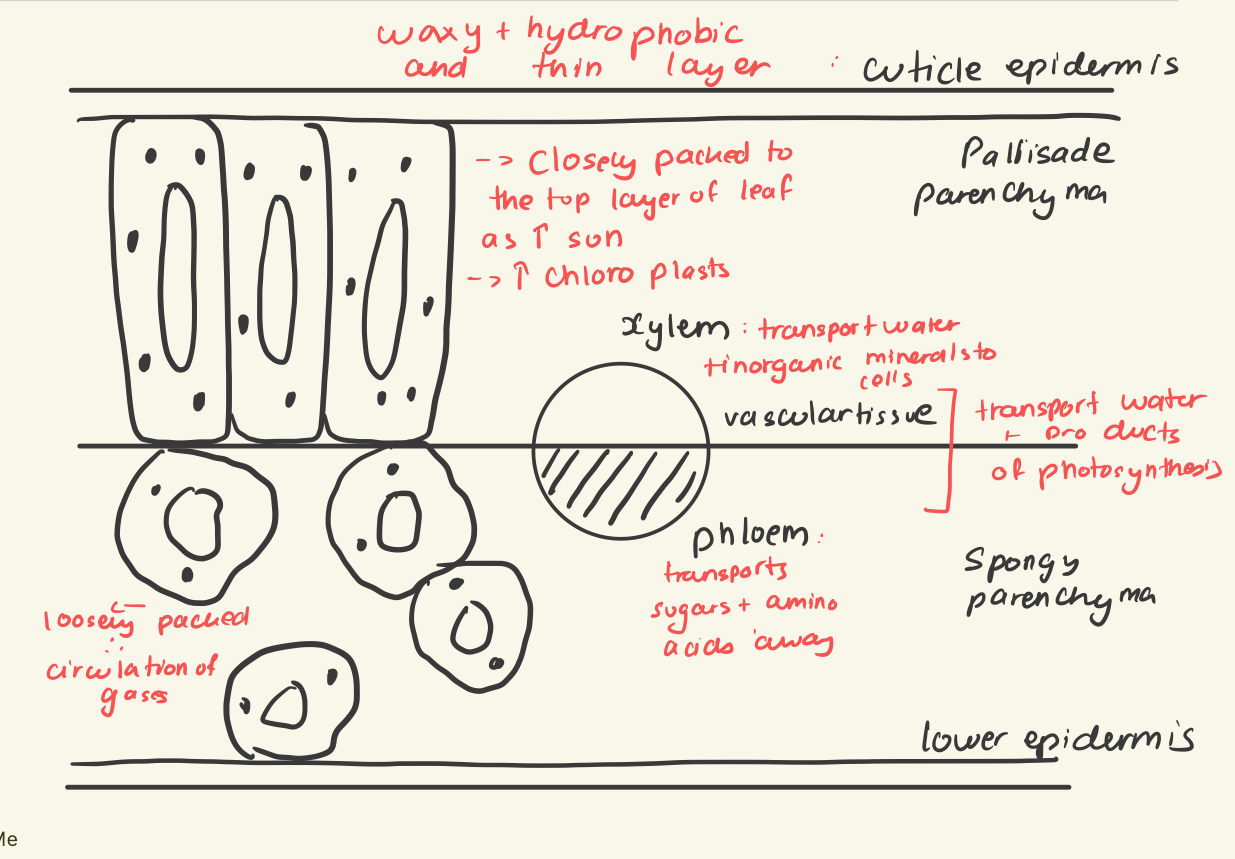
spongy mesophyll
Loose tissue beneath the palisade layer of a leaf; has many air spaces between its cells
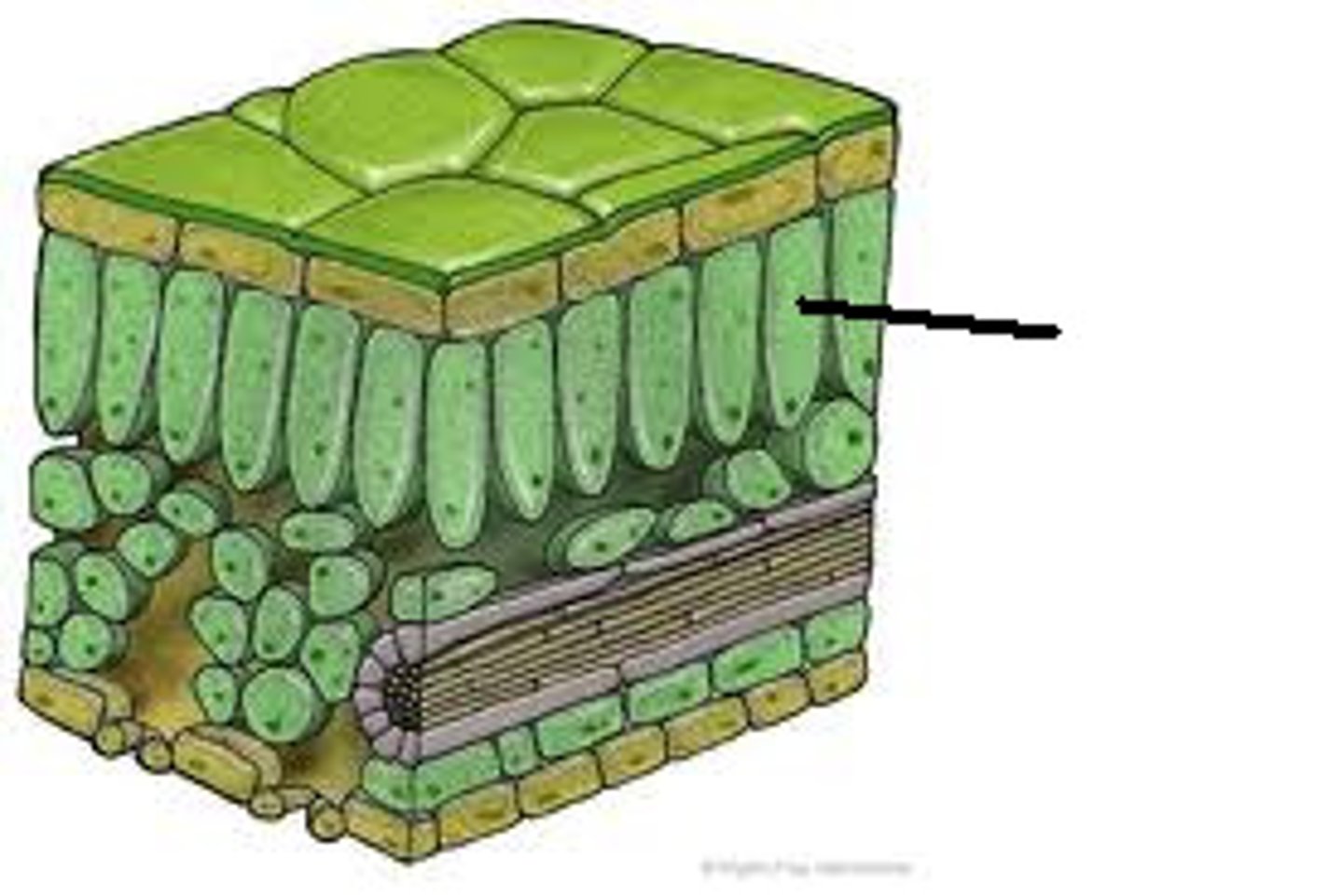
palisades mesophyll
tightly packed cells in the leaf containing chloroplasts
Draw a cross-section of a leaf:
Functions of trasnpiration stream:
supplies water for photosynthesis
carries Mineral ions dissolves
water for tugor
evaporation which cools the plants
Xylem
vascular tissue that carries water upward from the roots to every part of a plant through capillary action (cohesion and adhesion)
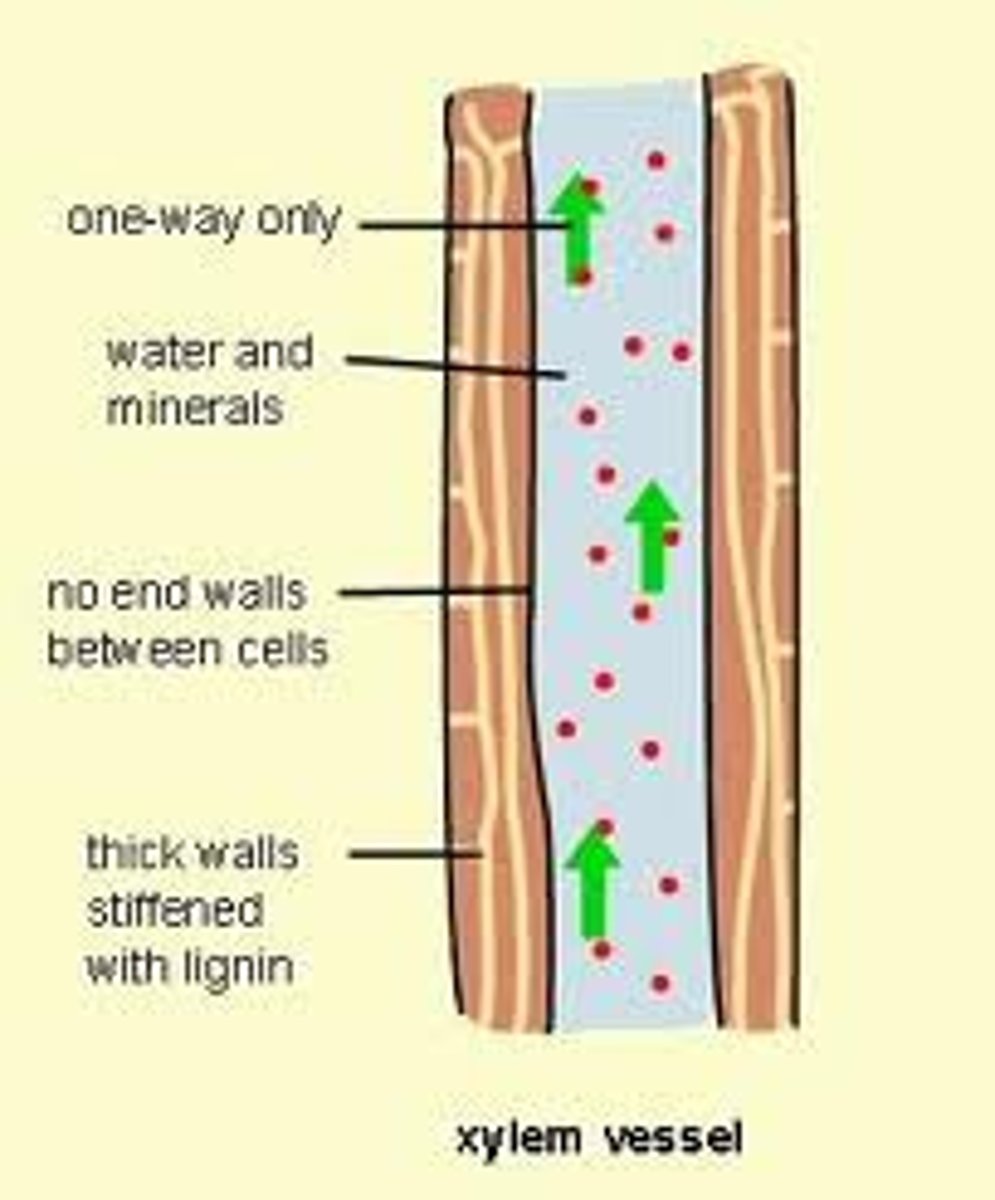
Xylem adaptations
Lignin walls: can withstand very low internal pressures
Broken down cell wall + now cell contents: continous flow of water
Pits: pores that allow water to neter and move sideways between vessels
Phloem
the vascular tissue in plants that conducts sugars and other metabolic products downward from the leaves.
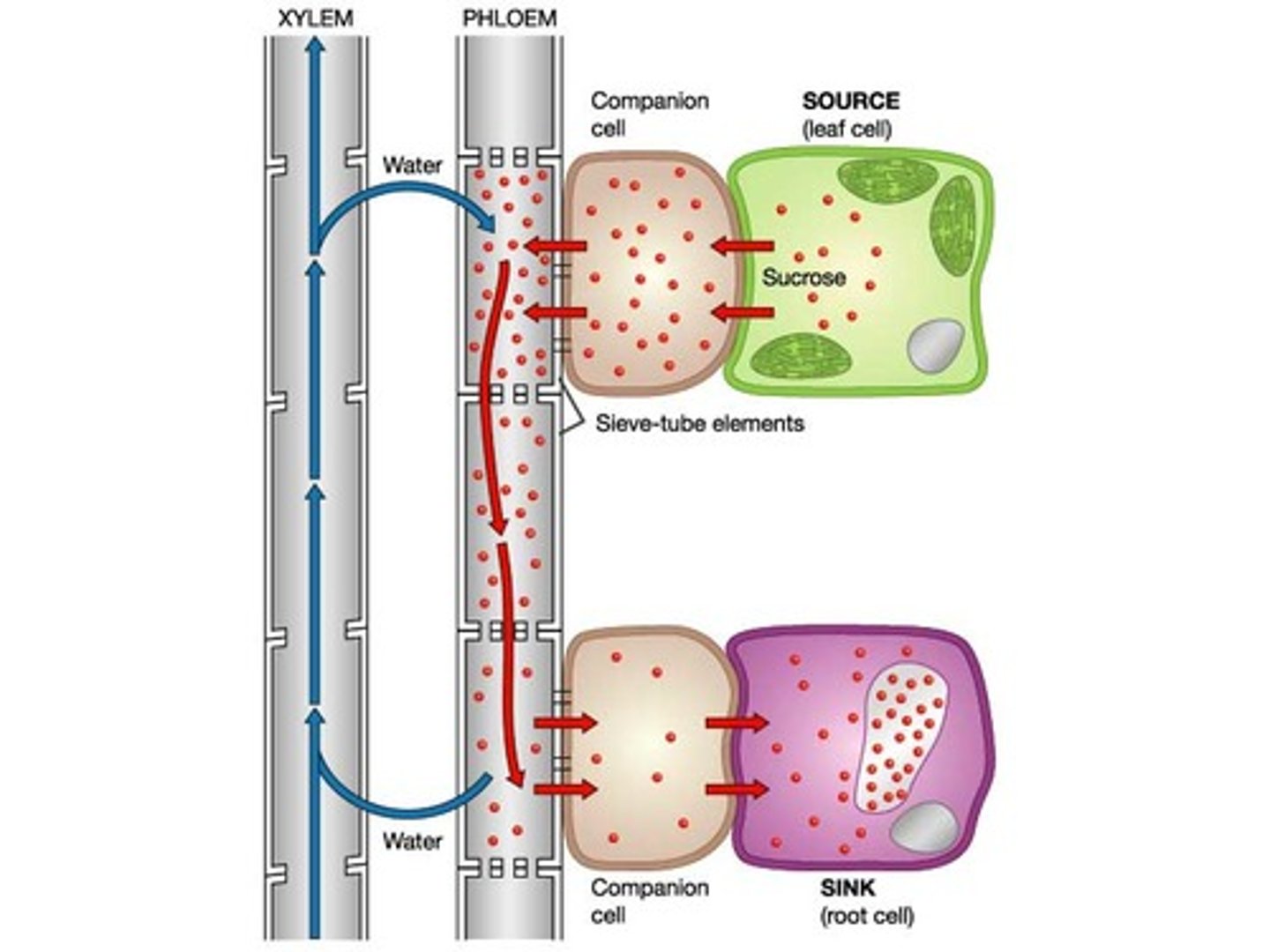

Phloem adaptations:
sieve plates: allows for the continous movement of the organic compounds between cells + ↑ resistance so pressure gradient maintained
Cellulose cell wall: strengthens the wall to wwithstand the hydrostatic pressures that move assimilates
↓ organelles in mature cells: maximises the space for the translocation of assimilates
Thin cytoplasm: reducesfriction to facilitate the movement of assimilates
Companion cell structure:
Nucleus and other organelles: Provides metabollic support to sieve tube elements
Transport proteins in plasma membrane: moves assimilates into and out of the sieve tube elements
Mant Mitochondria: provide ATP for the active transport of assimilates into or out of the companion cells
Plasmodesmata: link with sieve tube elements to allow assimilates to move from the companion cells into the sieve tubes

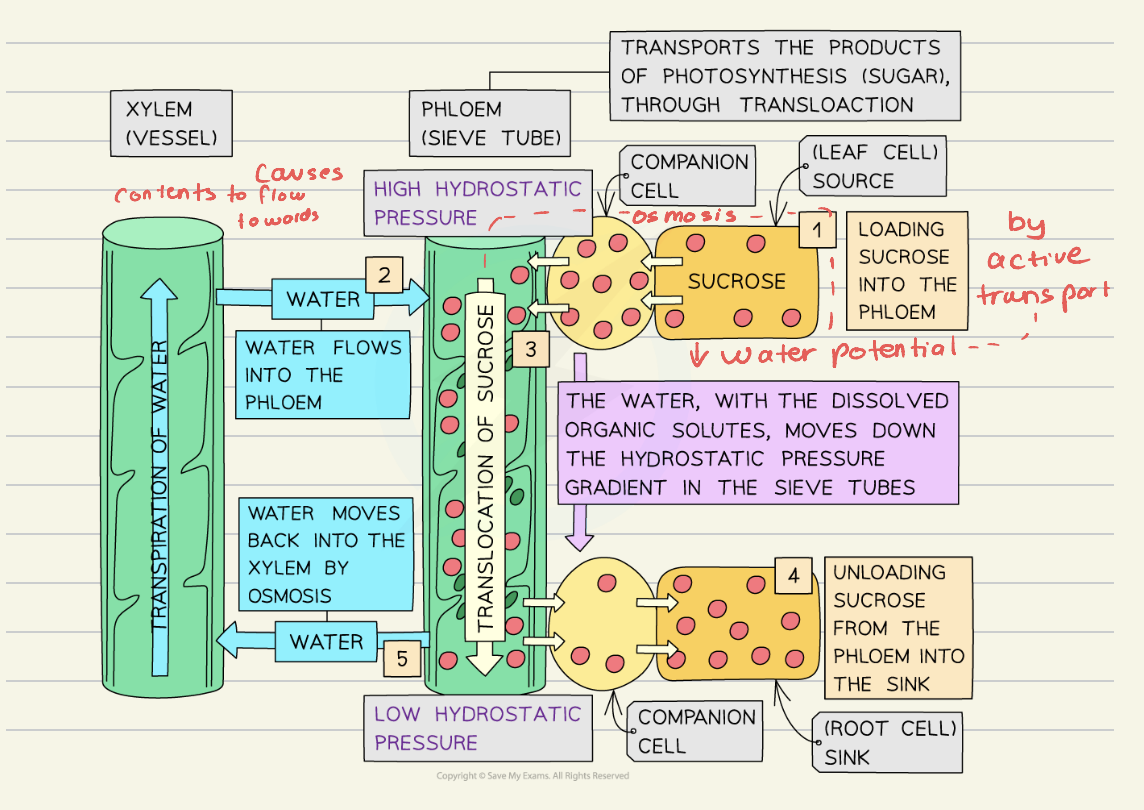
Describe how trasnlocation takes place:
The source loads sucrose into the companion cell by active transport
The high conc. of solute lowers the water potential →water from xyelm flows into plhoem by osmosis
↑ water so ↑ hydrostatic pressure ↑ pressure gradient
water + contents flow down the ploem to the sink where contents unload from companion cell to sink by difussion

dicotyledons (dicots)
two cotyledon, broad leaf, network of veins, vascular bundles in a ring, floral parts in multiples of 4 or 5

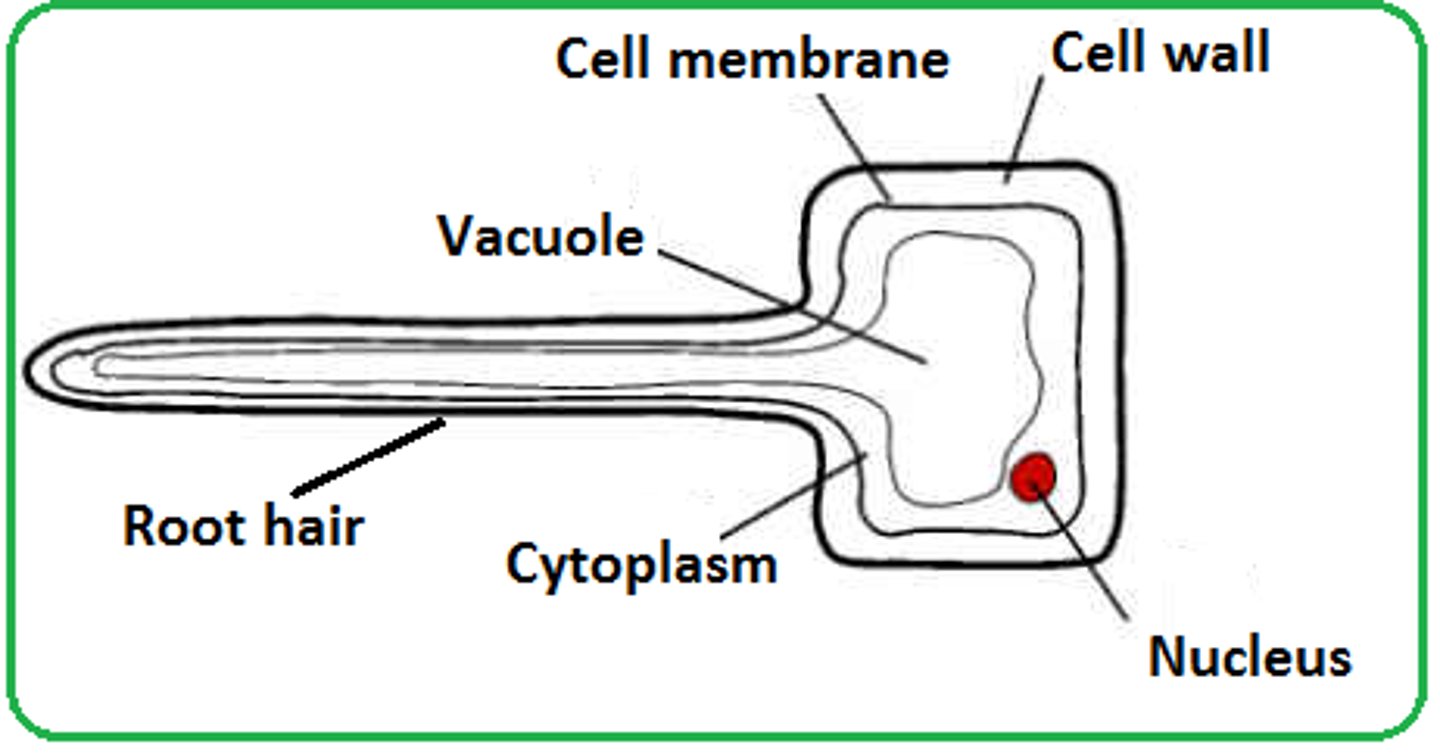
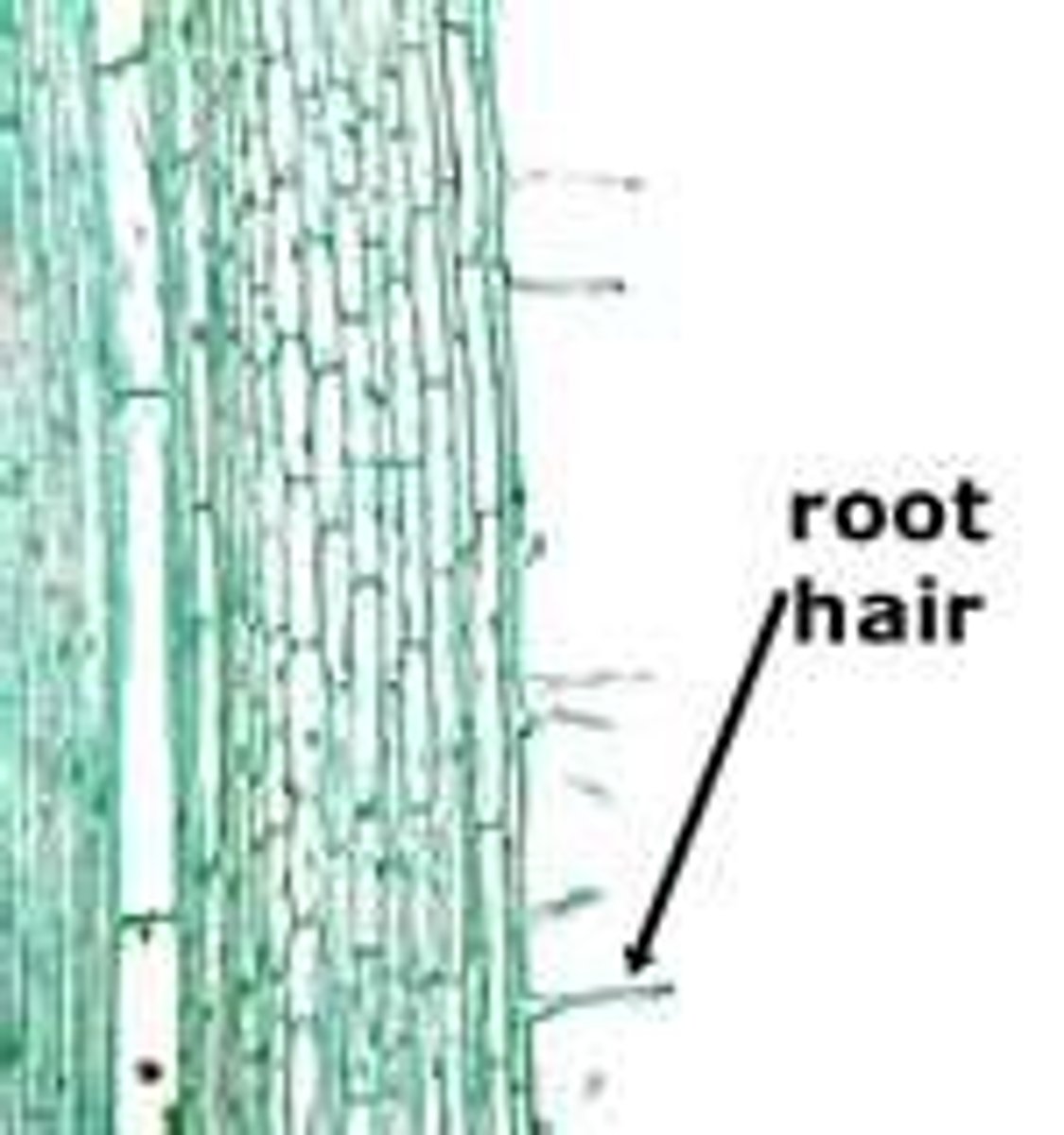
root hairs
tiny hair-like extensions that increase the surface area of the root allowing it to absorbs more water and nurtients
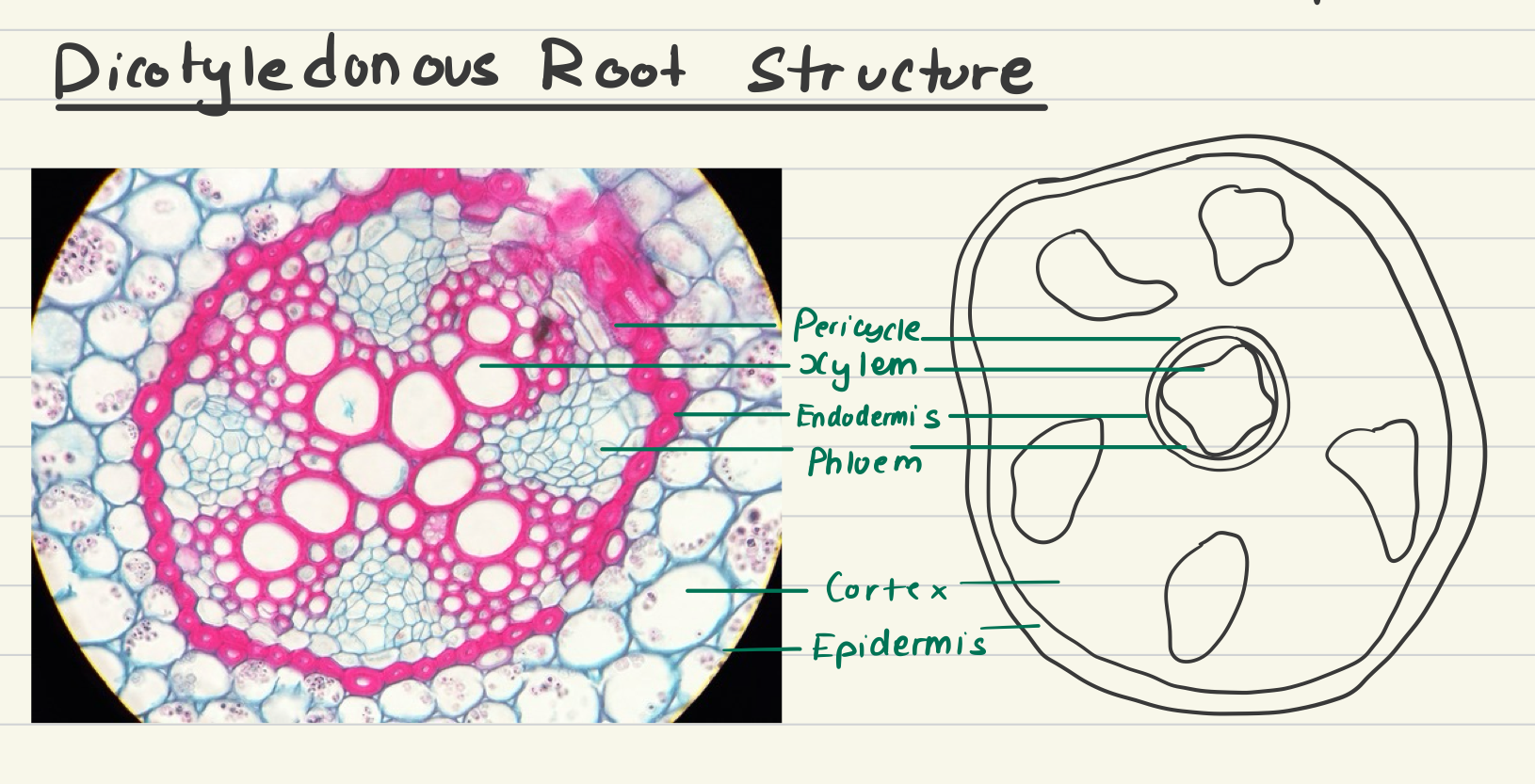
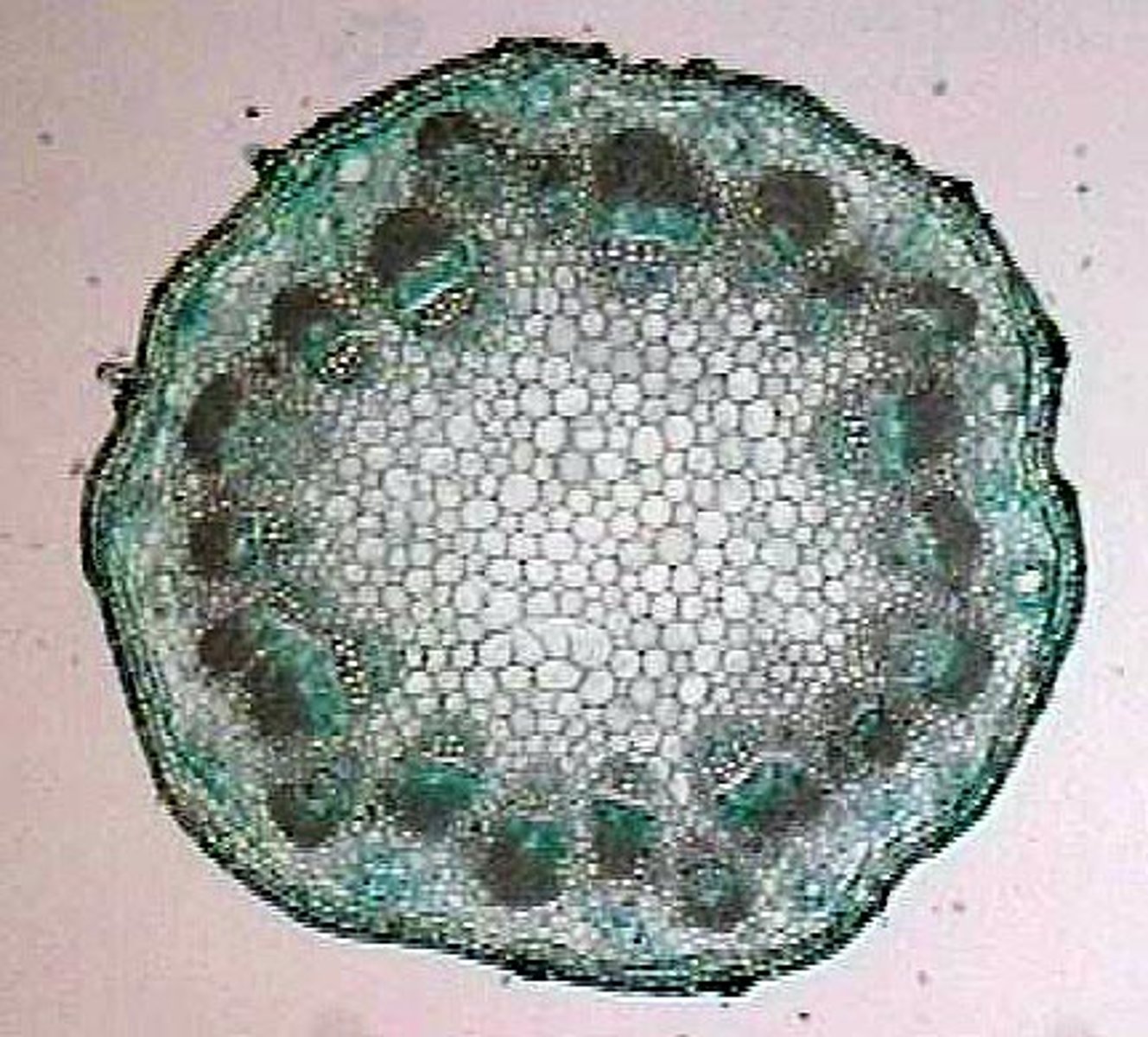
dicot root cross section
An X of xylem, and phloem is between the lines in the X.

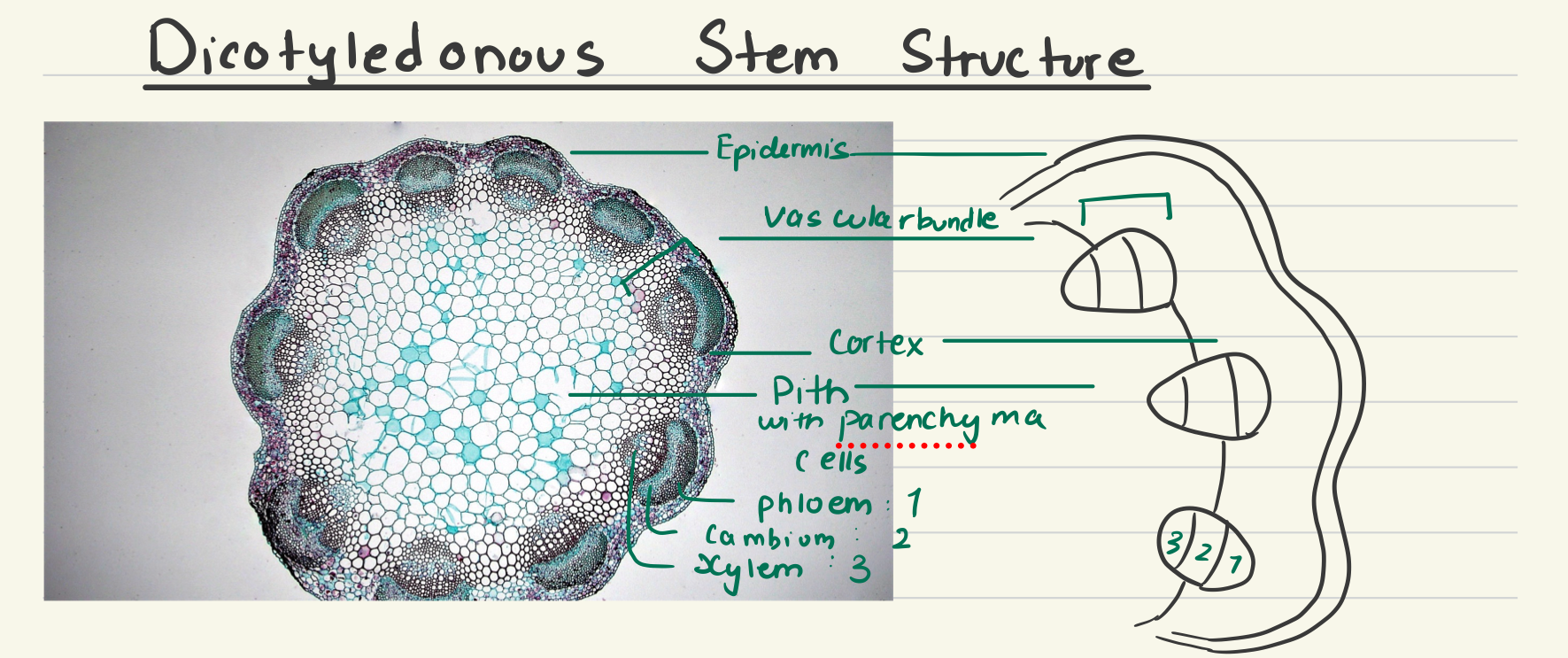
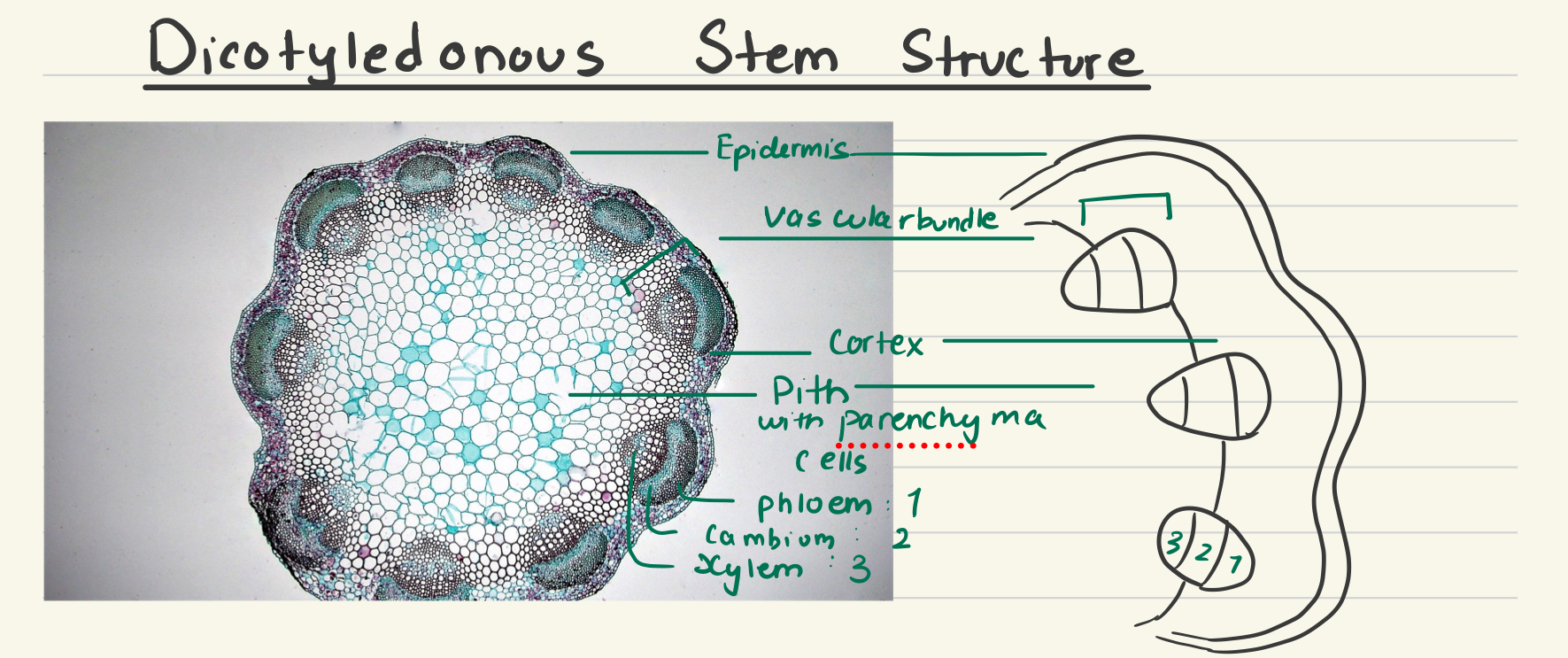
dicot stem cross section
has a circular arrangement of vascular bundles with primary xylem pointing towards the center and primary phloem pointing out, has a central pith and an outer cortex
epidermis (root)
the outermost part of the root that protects the root
cortex (root)
Very extensive in the root
Serves as the main physical barrier for water
Forces water to travel around the cells, blocking out certain things, like a sieve
root hairs
tiny hair-like extensions that increase the surface area of the root allowing it to absorbs more water and nurtients
indirect active transport
Occurs when hydrogen ions are pumped out of the root hair, bind to negatively charged clay in the soil and then release K+ and Mg2+ as free chemicals to go into the root hair
root pressure
The upward push of water within the stele of vascular plants, caused by active pumping of minerals into the xylem by root cells
pith
ground tissue internal to the vascular tissue
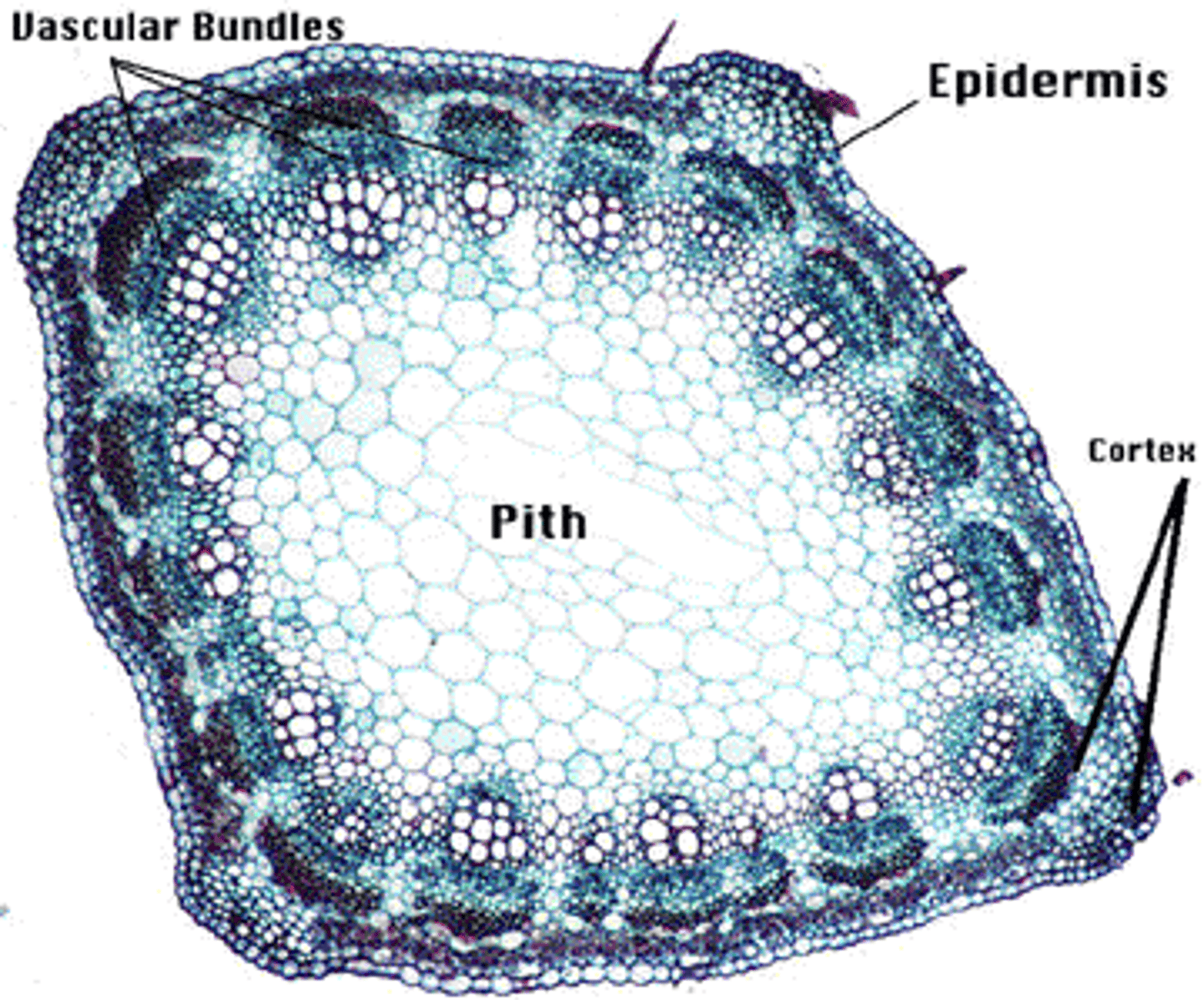
cortex (dicot stem)
corklike parenchyma cells after hypodermis that store carbohydrates & other nutrients (oils, resin, etc.)
plant capillary action
Occurs in a plant through cohesion and adhesion in the xylem.
transpirational-pull cohesion tension
water moves from roots to leaves without energy
Cellulose in xylem tubes
Hydrophilic - water adheres to it during transpiration in xylem
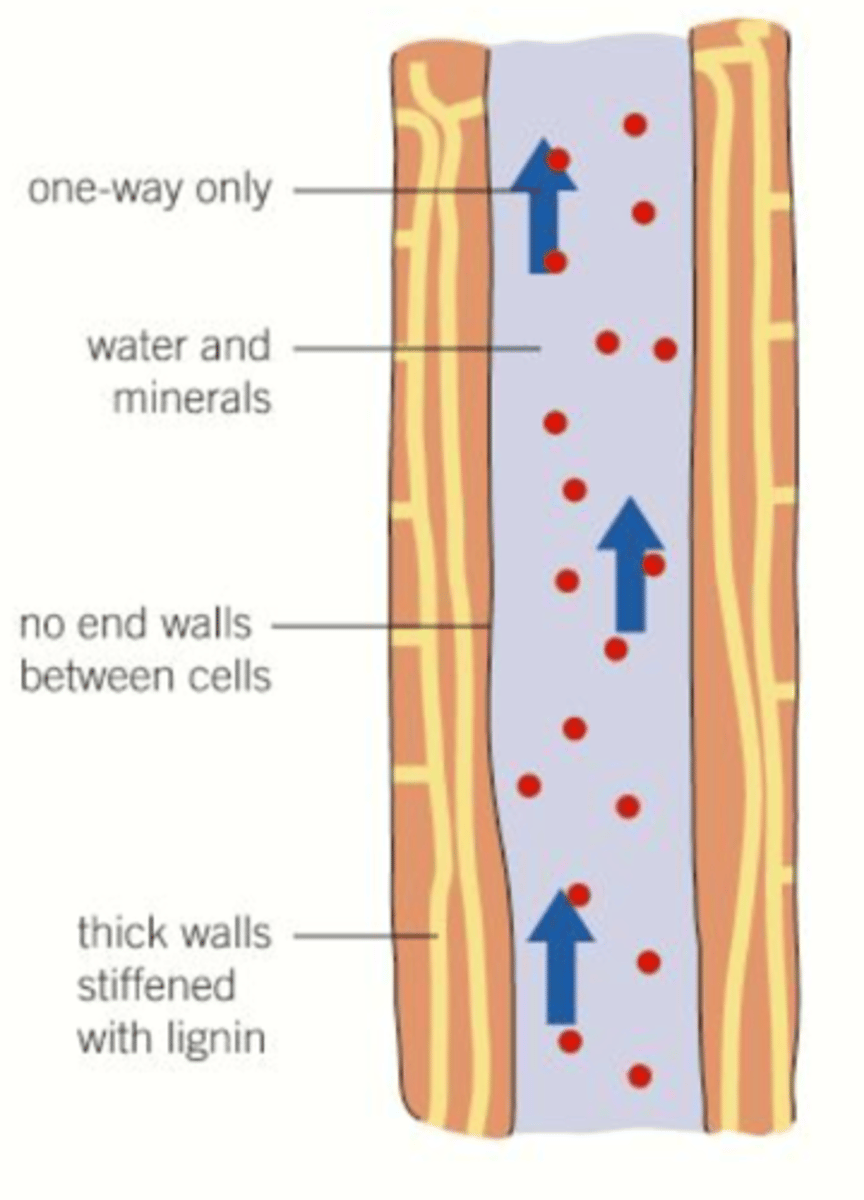
Lignin
complex polymer that hardens cell walls of some vascular tissues in plants
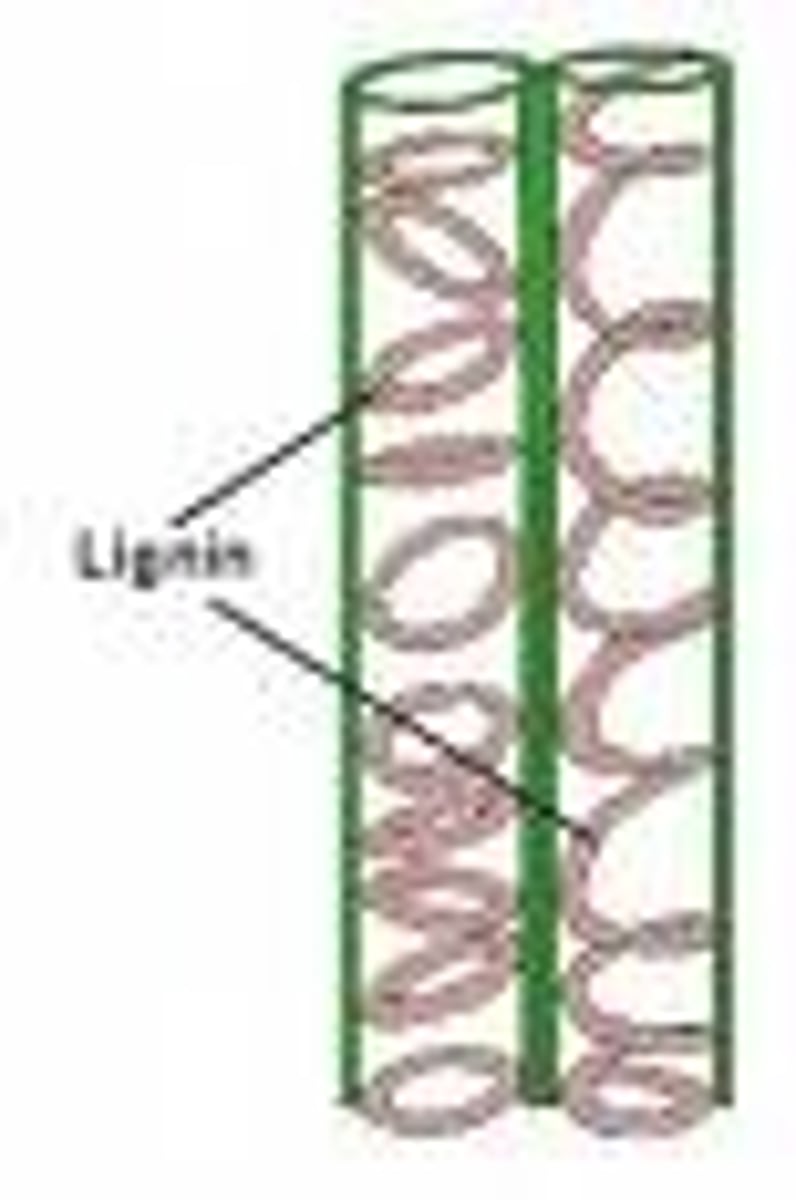
pits
openings in the lateral walls of xylem cells allowing water and nutrients to leak into surrounding tissues.
sieve tube cells
Living cells without nuclei that conduct phloem in plants
Sieve tube plate
Pore in the end wall of a sieve-tube member through which phloem sap flows
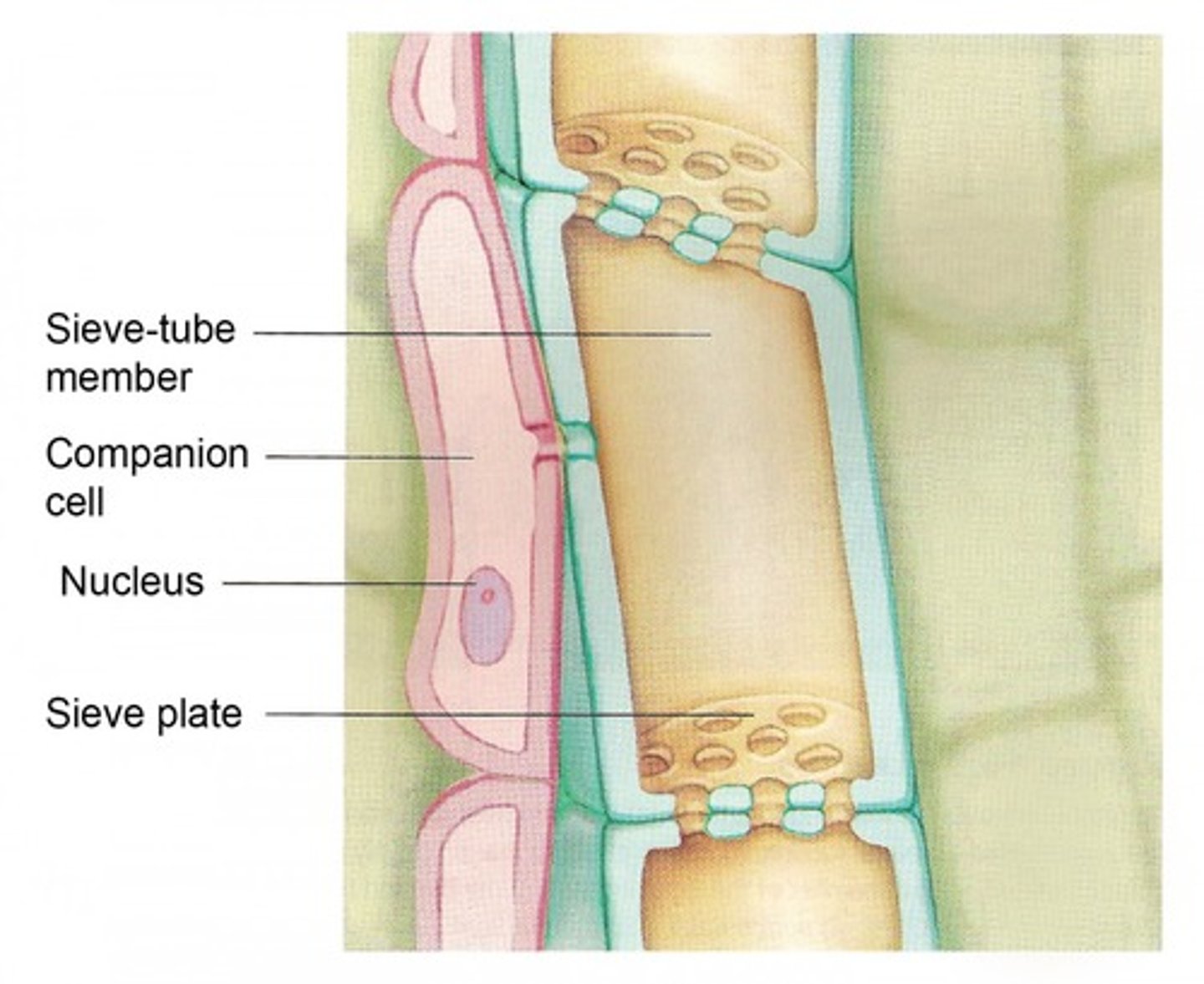
companion cells
the active cells found next to sieve tube elements that supply the phloem vessels with all of their metabolic needs
hydrostatic pressure
Pressure exerted by a volume of fluid against a wall, membrane, or some other structure that encloses the fluid.
parenchyma cells
play a role in storage, secrection, and photosynthesis in cells
Sink (in a plant)
where oranic compounds are needed and stored for growth
roots, young leaves
source (plant)
where organic solutes originate
mature green leaves, green stems
tap roots
food stores in seeds
translocation in phloem
1. active and passive loading of carbon by sources
2. water follows by osmosis, increasing hydrostatic pressure
3. at sink, sugar is unloaded
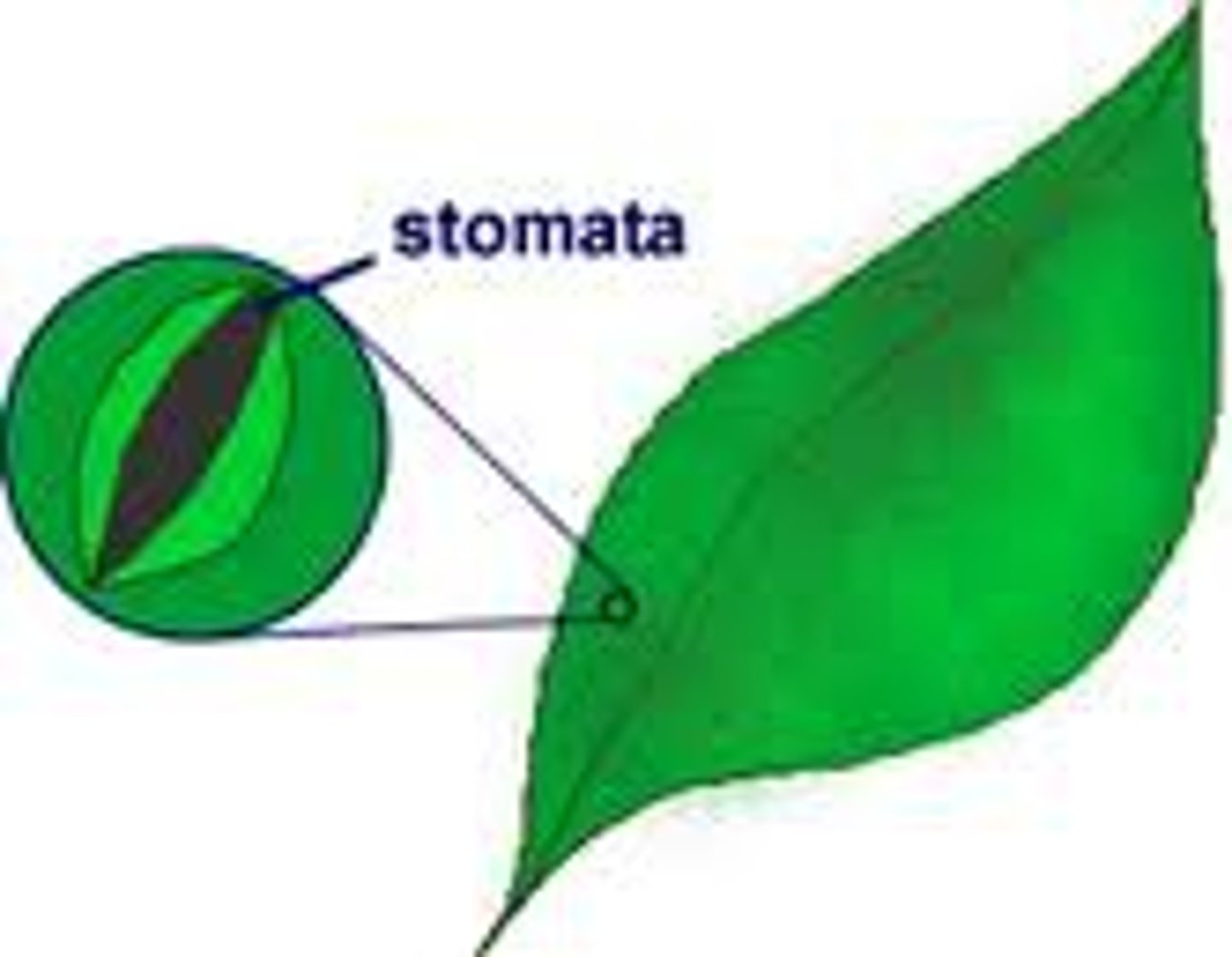
Stomata
Small openings on the underside of a leaf through which oxygen and carbon dioxide can move
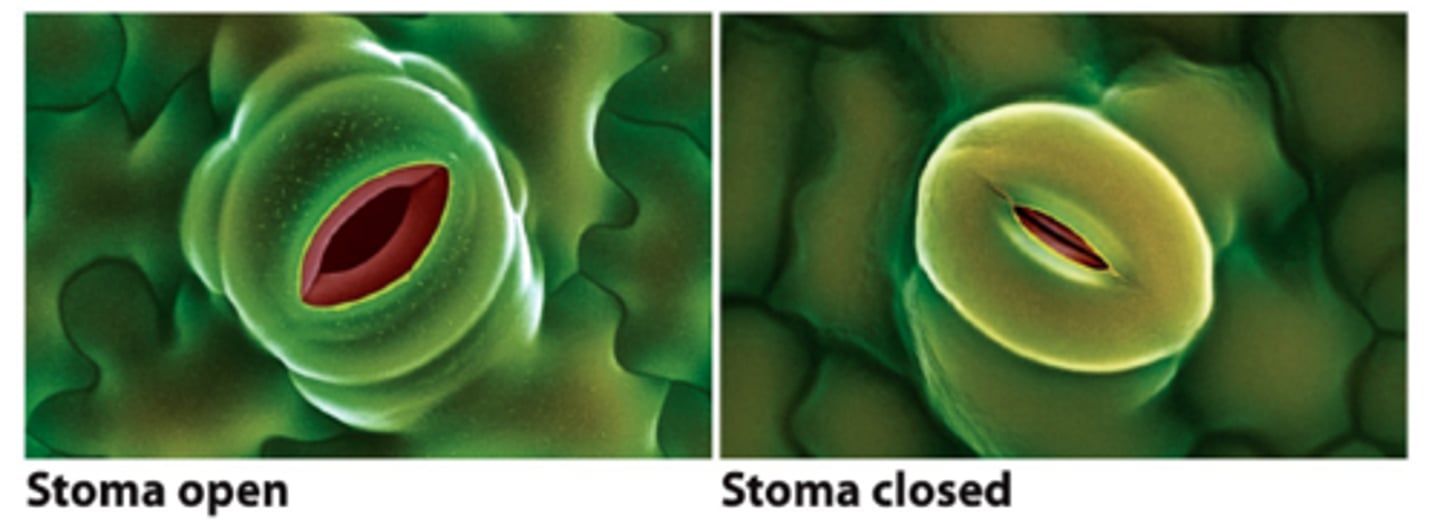
when low hydrostatic pressure: flaccid: close
when high hydrostatic pressure: turgid:open
guard cells
control the opening and closing of stomata
Cuticle
A waxy covering on the surface of stems and leaves that acts as an adaptation to prevent desiccation in terrestrial plants.
CAM pathway
a water-conserving, carbon-fixing process; CAM plants take in carbon at night and fix it into various organic compounds and release it during the day
Xerophytes
plants with adaptations that enable them to survive in dry habitats or habitats where water is in short supply in the environment.
Halophytes
plants that live in highly saline (salty) soil
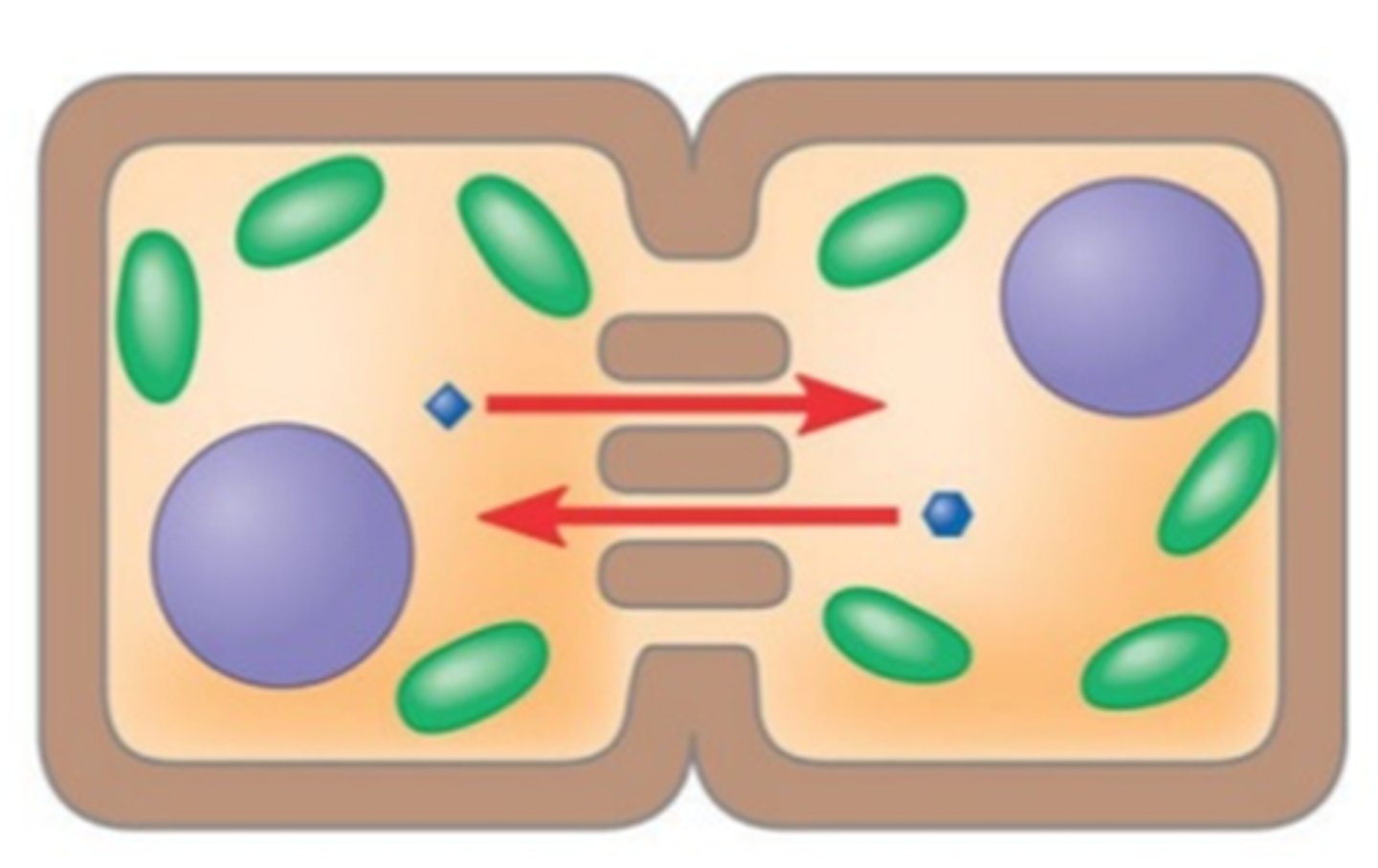
Plasmodesmata
channels through cell walls that connect the cytoplasms of adjacent cells
Factors affecting rate of transpiration;
air movement: ↑ wind, ↑ transpiration ↓ H2O in air so ↑ conc. gradient for diffusion
Light: ↑ light ↑ transpiration ↑ photosynthesis → ↑ stomata opening
temperature: ↑ temp↑ kinetic enrgy ↑ evaporation
Humidity: ↑ humid ↑ water in surroundings↓ conc. gradient ↓ transpiration
How does transpiration occur(stream):
water uptake from soil to roots hairs by osmosis
water moves from root hairs to the xylem vessel
adhesion with the xylem wall + coheison between water molecules create a continous column of water that moves up by capillary action
the pulling force is caused by the evaporation of water → root pressure ≠ leaves pressure → causes tension pressure (Pv=Pv)