Unit 0: Prologue: History before 1200 C.E. AMSCO World History
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
Part 1: Human Development to c. 600 B.C.E. The First Migrations
Define Patriarchy:
A society dominated by males in which family lines and power and passed through the male.
The Agricultural Revolution- Geography and Humans
Populations grew and people began living in larger groups becoming cities.
The Agricultural Revolution- Religion and Culture
People became more separated into classes, and the status of woman declined.
The Agricultural Revolution- Arts, Architecture, and Technology
Learned how to use irrigation systems, use the wheel in transportation, and replace stone with bronze/iron for tools, invented writing,
The Agricultural Revolution- Political Systems
More extensive governments and systems of taxes were created. Led to the development of a way of writing.
The Agricultural Revolution- Economic Systems
People started becoming skilled at one job. Ex. merchants or tool makers
The Agricultural Revolution- Social Interaction
As people developed wealth and competed for resources, gov. became a peaceful way of resolving these conflicts.
List two significant details for each of the following areas:
Mesopotamia
- Developed major City-States which would build large religious temples called Ziggurats. (They were polytheistic)
-Taxes and trade became more complex because of city-state structure, so they invented the first written language, Cuneiform. They also recorded the first written laws in this language.
Egypt
-Egypt was highly centralized under one rule, the Pharoah and they built large Pyramids to their power
- Woman were given much more power in their society, being allowed to own property and were equal to men in court.
Indus River Valley
- Performed long distance trade with Mesopotamia and developed technology like indoor plumbing and urban planning
-their language has never been deciphered so little is known about them.
China
-Patriarchal and highly centralized
-gave a lot of respect and special honor to their ancestors
Non-River Valley Civilizations
-participated in extensive trade
-Olmee in Mesoamerica and Chavin in the Andes
4. What are the major characteristics of a civilization?
Centralized government, organized religion, social classes and job specialization, Arts and Architecture, Writing
5. List key facts about Hinduism:
Aryans came from North of the Himalayan mountains into Pakistan/India and brought scriptures called the vedas
They believed that many deities existed, but it has evolved that each of these are just an expression of one supreme deitie.
Vedas teaches that people are reincarnated until they have spiritually advanced enough to stop this cycle.
Vedas taught that people should organize society into classes called castes and prohibited social mobility
Society was stratified and unified under this system.
6. What is Zoroastrianism?
Developed in Persia
Clear example of monotheism
Focused on human free will and the eternal struggle between good and evil
Part 2 The Classical Era, c. 600 B.C.E. to c. 600 C.E.
7. List key facts about Judaism:
Monotheism
Originally called Hebrews or Israelites
Developed in and around Israel, and traces origins back to abraham
Believe they have entered into a covenant with god and in return for their devotion, god will consider them his chosen people
codification of the Tenakh
1. Define Empire:
A collection of nations and people all ruled under one very large powerful person, the emperor/empress.
Name the empires that came from Western Eurasia:
the Persian, Greek, Roman, and Byzantine
Name the empires that came from Southern Asia
the Mauryan and Gupta
Name the empires that came from Eastern Asia
the Qin and Han
Name the empires that came from Mesoamerica
the Mayan
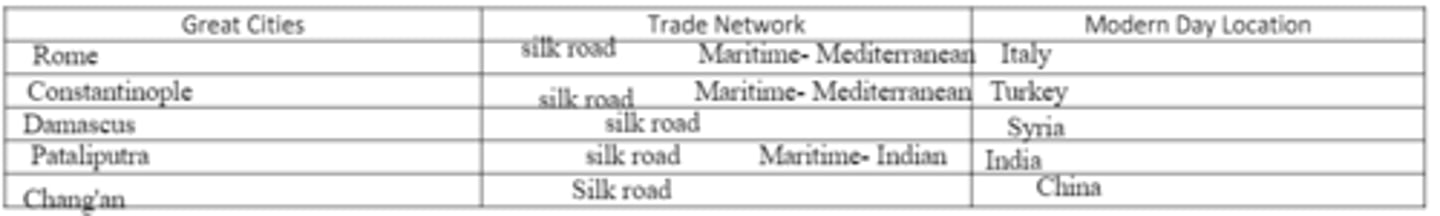
3. Great trading networks, both land and maritime, fostered the development of great cities. Name five and list what country they would be found in today:
The Beginning and Spread of Buddhism: Geography and Humans
It was not specific to an area and could be universal. It was therefore passed along the silk road
The Beginning and Spread of Buddhism: Religion and Culture
Additionally, it was monastic, allowing for monasteries to be built
The Beginning and Spread of Buddhism: Arts, Architecture, and Technology
The Beginning and Spread of Buddhism: Political Systems
The Mauryan Empire, while it existed, helped to spread Buddhism in India when it's leader converted
The Beginning and Spread of Buddhism: Economic Systems
The Beginning and Spread of Buddhism: Social Interaction
Rejected the caste system, creating more social movement in class
5. What do many historians consider the most significant legacy of the Zhou Dynasty in China?
The Mandate of Heaven, which stated that an emperor was put in place by the heavens and that if they fell out of favor from the heavens there would be a sign such as drought.
6. Discuss the ‘5 Ws’ regarding Confucianism:
Who was Confucius?
A philosopher in 551 BCE
Where did he make his mark?
He impacted Chinese beliefs and values more than any other philosopher
What were his beliefs?
education, benevolence, virtue, respect for authority, patriarchal society structure, and filial piety
When did he live?
551 BCE during the Warring States Period
Why did his beliefs become so significant during his time and/or after his death?
With the Han Dynasty, it was mandated that all students study Confucianism.
7. What is Daoism?
Daoism was also created during the warring states period and focused on how people could live in harmony with nature, emphasizing internal reflection
8. How is Daoism similar, yet different, to Buddhism?
Both Daoism and Buddhism focused on self reflection and meditation, but buddhism did so in order to stop the cycle of reincarnation and daoism did so in order to achieve harmony with nature.
9. What are some of the accomplishments of the Qin Dynasty (221 B.C.E. – 207 B.C.E.) of China?
a. Why are the Qin considered a dynasty if they only lasted fourteen years?
The Qin Dynasty re-established centralized control and brought about a lot of good change. It created a standardized chinese script, established a uniform system of weights and measurements, and built canals + roads. This would setup the Han Dynasty to expand trade vastly, and so it's considered a dynasty for all of these vast changes.
b. EXTENSION: What is legalism?
Legalism is a dependence on moral law over religious faith
The Han Dynasty - Geography and Humans
Empire of China, Capital was in Chang'an
The Han Dynasty - Religion and Culture
Students studied the principles of Confucianism in school, which all government leaders followed and knew.
The Han Dynasty - Arts, Architecture, and Technology
magnetic compass, paper, stern post rudder
The Han Dynasty - Political Systems
All students took a civil service exam on Confucianism in order to get a possible position in the government
The Han Dynasty - Economic Systems
Trade extended West into the Mediterranean Sea. Trade in luxury items and silk
The Han Dynasty - Social Interaction
the Warring State Period was over and so interactions were much more peaceful
Civilizations of Western Eurasia and Christianity
1. Discuss the ‘5 Ws’ for the Persian Empire.
Who are some of the great rulers of the Persian Empire?
Cyrus the great
Where was the epicenter of the Persian Empire using political boundaries of the twenty-first century?
Modern day Iran
What did the Persian Empire accomplish?
Gov. practiced religious toleration and had vast trading networks
When did the Persian Empire exist?
559 BCE
Why does the Persian Empire matter?
Vast trade and efficient bureaucracy
2. Discuss the ‘5 Ws’ for the Roman Republic and Empire.
Who are some of the great rulers of the Roman Republic and Empire.?
Julius Caeser
Where was the epicenter of the Roman Republic and Empire using political boundaries of the twenty-first century?
Rome
What did the Roman Republic and Empire accomplish?
representative gov, innocent until proven guilty, killed Jesus, aquaducts
When did the Roman Republic and Empire exist?
753 BCE
Why does the Roman Republic and Empire matter?
Made advances in gov. that effect govs today. And christian religion
3. Rome’s most enduring legacy was not in its military or its engineering achievements. It was in religion (xlix)
a. Why would some justify the above statement?
Their harsh policy on religion forcing others to adopt their polytheism or leave caused the spreading of Jews, and began Christianity with the death of Jesus
b. Why would some refute the statement?
The Romans themselves did not create Christianity but rather it was Jesus, and because of this not directly one of their doings.
4. Discuss the ‘5 Ws’ for the origins and spread of Christianity.
a. Who was Jesus?
A leader exiled from Rome for his refusal to accept polytheism
b. Where was the epicenter of the Christian faith during the life of Jesus using political boundaries of the twenty-first century?
Rome and Istanbul
c. What caused the division within the Christian faith?
The east had become far more wealthier and politically powerful and so the roman empire was split into two halves
d. When did the Christian belief system begin?
During the Diaspora in the 1st century CE
e. Why was the Christian faith able to spread rather easily?
It was the main religion of the roman empire and Byzantine empire which grew very far. Additionally, it was universal and so anyone could accept it anywhere.
5. Discuss the ‘5 Ws’ for the Byzantine Empire.
a. Who was the greatest ruler of the Byzantine Empire?
Justinian the great
b. Where was the epicenter of the Byzantine Empire using political boundaries of the twenty-first century?
Istanbul and Rome
c. What did the Byzantine Empire accomplish?
Justinian codes, Hagia Sophia church
d. When did the Byzantine Empire exist?
middle of 4th century
e. Why does the Byzantine Empire matter?
Created the Justinian Codes which provided legal grounds for Europe into the 19th century.
Early American Civilizations
1. Where is Teotihuacan?
Modern day Mexico City
2. Why does the city of Teotihuacan matter?
It was the largest city at the time and it's grid like structure and huge temples to the gods would influence other cultures like the aztecs
3. Discuss the ‘5 Ws’ for the Mayans.
a. Who are the Mayans?
most influential classical civilization in the americas
b. Where was the epicenter of the Mayan Civilization using political boundaries of the twenty-first century?
Guatemala
c. What were the Mayans known for?
Created calendar and most complicated writing system in americas, also had the idea of 0, something most didn't.
d. When did the Mayan Civilization exist?
as far back as 1500 BCE, peak at 900 CE
e. Why does the Mayan Civilization matter?
Understood the concept of 0 and understood how the earth moved in space
Comparisons in the Classical Age
1. What are some of the traits that empires that emerged between 600 B.C.E. and 600 C.E. shared?
Most had expansive and growing trade networks, more tech innovations, and a centralized government, which all made the lives of the people living in them much better.
2. Describe the early trading networks.
Early trading networks were made possible by the power and wealth of the empires, and then later made easier through inventions like stirrups. Sea trade was made easier through inventions that made improvements to the sail.
3. What are the major reasons why the great classical empires declined?
a. Attacks from outside groups and disease killing large sections of the urban population
b. increase in the gap between rich and poor created social strife
c. challenges collecting taxes and broad support for leadership weakened the government
d. decline of trade
Part 3: Postclassical Civilizations, c. 600-c. 1200
1. The three major trading networks listed below prospered. What areas were connected by each and what were some of the significant goods and ideas that were spread?
a. The Silk Roads:
Connected the Eastern areas of Europe to the far Western areas of China
artwork, precious stones and metals, silk, religious beliefs, disease
b. The Indian Ocean:
Connected many of the same areas as the silk road, but also connected more to africa in places like Mombasa
ivory, metal, cloth, wine, gold, silk
c. The Trans-Saharan:
Europe + Northern Africa - > sub-Saharan Africa
salt, slaves, gold
The Spread of Islam
2. Discuss the ‘5 Ws’ for the origins and spread of Islam.
a. Who was Muhammad?
Merchant living on Arabian peninsula who believed he had received revelations from god
b. Where was the epicenter of the Islamic faith during the life of Muhammad using political boundaries of the 21 century
Southern Spain, North Africa, the Middle East, and parts of India
c. What caused the division within the Islamic faith?
The death of Muhammad caused 2 different groups of the religion to disagree on who should take over. The Sunni believed it could be anyone in the Islamic community while the Shi'a believed it should be a descendant of Muhammad.