Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
1
New cards
Define: Heterochromatin
Compacted, inaccessible DNA that is not transcriptionally active
High levels of methylated C at CpG Dinucleotides (very condensed)
Low levels of Histone Acetylation (histones are immobile and do not dissociate from DNA)
\
Can be constitutive (never expressed) or facultative (can be euchromatin)
High levels of methylated C at CpG Dinucleotides (very condensed)
Low levels of Histone Acetylation (histones are immobile and do not dissociate from DNA)
\
Can be constitutive (never expressed) or facultative (can be euchromatin)
2
New cards
Define: Euchromatin
Euchromatin contains sites of transcriptional activity (open and accessible for transcription)
\
Low levels of methylated C at CpG Dinucleotides (not compacted)
High levels of Histone Acetylation (mobile histones that can dissociate from DNA)
\
Low levels of methylated C at CpG Dinucleotides (not compacted)
High levels of Histone Acetylation (mobile histones that can dissociate from DNA)
3
New cards
What factors are needed for chromatin re-modeling?
Remodeling complex: Basal transcription factors, RNA Pol II, remodeling proteins.
\
*bound to promoter*
\
*bound to promoter*
4
New cards
Which regulatory elements are cis-acting?
Promoters, enhancers, operators
5
New cards
Which regulatory elements are trans-acting?
Repressors
6
New cards
Differentiate between promoters and enhancers
Enhancers
– Located further away from the gene, either upstream or downstream (sometimes 100s or 1000s of kb away)
– function in either orientation to activate genes – A region that contains binding sites (4-8 bp) for many different TFs allowing for finely tuned transcription
– May influence expression of more than one gene over a large region
\
Promoters (RNA pol II)
– Upstream, very close to the coding region
– a TATA box: TATA-A/T – A – A/T
– Basal factors plus RNA polymerase II binding allows a low (basal) level of expression
– Define a transcription initiation site
– Typically, one promoter per protein-encoding gene but sometimes more
– Located further away from the gene, either upstream or downstream (sometimes 100s or 1000s of kb away)
– function in either orientation to activate genes – A region that contains binding sites (4-8 bp) for many different TFs allowing for finely tuned transcription
– May influence expression of more than one gene over a large region
\
Promoters (RNA pol II)
– Upstream, very close to the coding region
– a TATA box: TATA-A/T – A – A/T
– Basal factors plus RNA polymerase II binding allows a low (basal) level of expression
– Define a transcription initiation site
– Typically, one promoter per protein-encoding gene but sometimes more
7
New cards
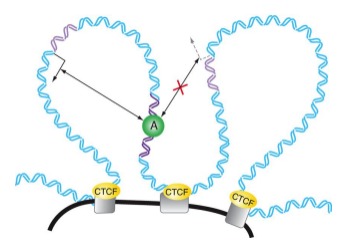
Define: Insulators
Insulator elements limit which promoters enhancers can activate by keeping enhancers/promoters within their boundaries.
\
Insulator elements bind specialized proteins (i.e. CTCF) that limit the promoters that a given enhancer can influence.
\
Insulator elements bind specialized proteins (i.e. CTCF) that limit the promoters that a given enhancer can influence.
8
New cards
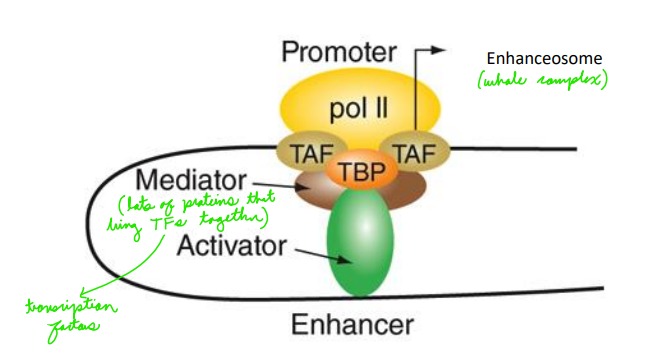
What does the activation by enhancers require?
Interaction between enhancer binding factors and promoter binding factors to form an enhanceosome
9
New cards
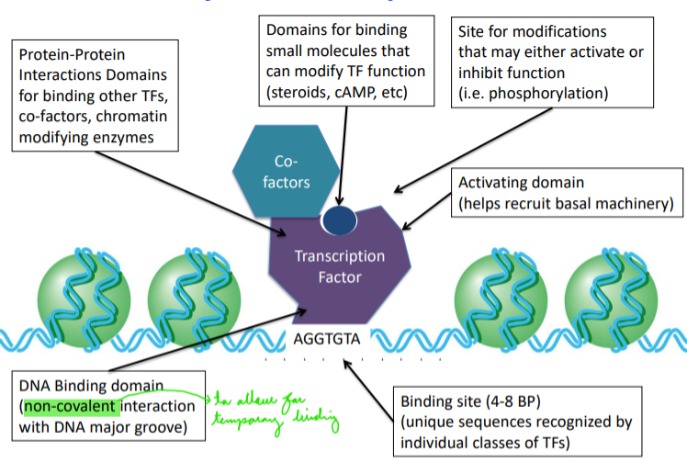
Describe: Eukaryotic transcription factors
Binding site: unique sequences recognized by individual classes of TFs
DNA Binding domain: non-covalent interaction with DNA major groove
Activating domain: helps recruits basal machinery
Protein-Protein Interaction Domains: for binding other TFs, co-factors, chromatin modifying enzymes
\
Domains for binding small molecules that can modify TF function (steroids, cAMP, etc)
Site for modifications that may either activate or inhibit function (i.e. phosphorylation
DNA Binding domain: non-covalent interaction with DNA major groove
Activating domain: helps recruits basal machinery
Protein-Protein Interaction Domains: for binding other TFs, co-factors, chromatin modifying enzymes
\
Domains for binding small molecules that can modify TF function (steroids, cAMP, etc)
Site for modifications that may either activate or inhibit function (i.e. phosphorylation
10
New cards
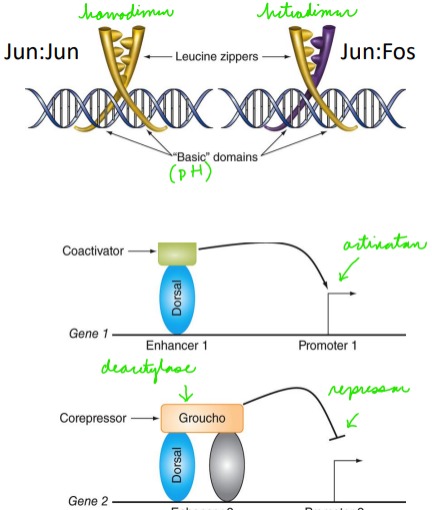
How can protein-protein interactions modify TF specificity/function?
Dimerization can change binding specificity and regulate different target genes
\
Dimerization can change which co-Factors are bound changing TF activity
\
Dimerization can change which co-Factors are bound changing TF activity
11
New cards
The association of DNA with histones to form chromatin affects transcription by:
Decreasing basal transcription rates as chromatin is tightly bound (heterochromatin)
12
New cards
What is the result of hyper-condensed heterochromatin?
Transcriptional silencing
13
New cards
Describe the interactions of trans-acting elements
Trans-regulatory factors regulate (or modify) the expression of distant genes by combining with their target sequences
14
New cards
Describe the interactions of cis-acting elements
Cis-regulatory elements are regions of non-coding DNA, which regulate the transcription of nearby genes.
15
New cards
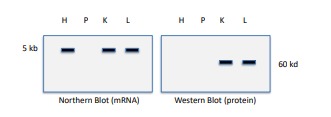
Interpret these results (heart (H), pancreas (P), kidney (K), and liver (L))
The gene of interest is not transcribed or translated in pancreas cells (no mRNA or protein present)
\
The gene of interest is transcribed in heart cells, but is not translated in heart cells. (mRNA present, but no protein)
\
The gene of interest is transcribed in heart cells, but is not translated in heart cells. (mRNA present, but no protein)
16
New cards
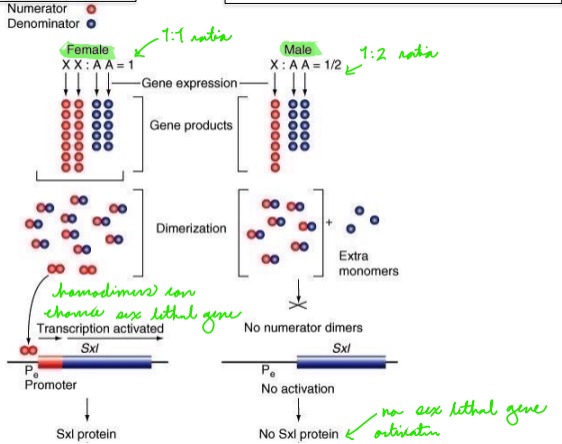
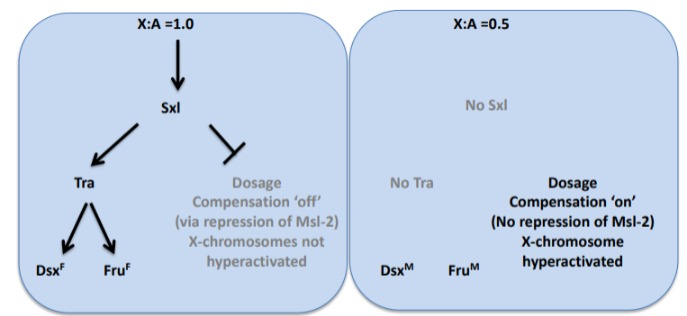
What ratio of sex chromosomes to autosomes denotes female or male Drosophilia?
Female: 1:1 (1)
Male: 1:2 (0.5)
Male: 1:2 (0.5)
17
New cards
How do the ratios of sex chromosomes to autosomes affect the production of sex lethal proteins?
The resulting homodimers from female flies enhance sex lethal genes (needed for dosage compensation), whereas male flies do not produce homodimers and do not activate the sex lethal gene.
\
The presence of sex lethal genes in female flies results in more productive splicing that results in more sex lethal protein, or a premature stop codon that results in nonsense mediated decay.
\
Sxl in females is necessary to prevent lethal overexpression of X linked genes.
Sxl in males is lethal as males need overexpressed X linked genes.
\
The sex lethal protein blocks a splice site resulting in a functional Tra protein and normal female.
\
The presence of sex lethal genes in female flies results in more productive splicing that results in more sex lethal protein, or a premature stop codon that results in nonsense mediated decay.
\
Sxl in females is necessary to prevent lethal overexpression of X linked genes.
Sxl in males is lethal as males need overexpressed X linked genes.
\
The sex lethal protein blocks a splice site resulting in a functional Tra protein and normal female.
18
New cards
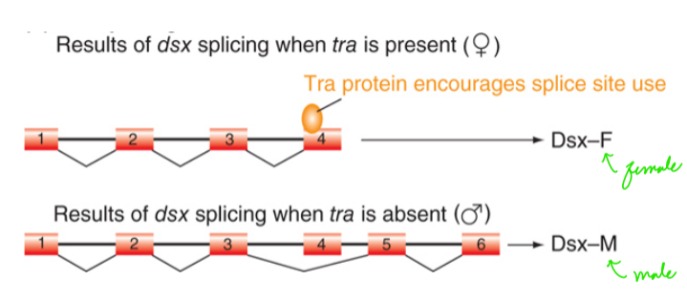
How does the presence of Tra protein affect doublesex phenotype?
Tra proteins encourages splice site use, resulting in normal females. Males do not need Tra.
\
Males with Tra are doublesex.
Females without Tra are doublesex.
\
Males with Tra are doublesex.
Females without Tra are doublesex.
19
New cards
How does the presence of Tra protein affect fruitless phenotype?
Normal fruitless function is required for proper development of several anatomical structures necessary for courtship, including motor neurons which innervate muscles needed for fly sexual behaviors.
\
Females need Tra for normal sexual behaviour, males do not. If males have the fruitless phenotype due to the presence of Tra they have abnormal courtship behaviour.
\
Females need Tra for normal sexual behaviour, males do not. If males have the fruitless phenotype due to the presence of Tra they have abnormal courtship behaviour.
20
New cards
Why do male flies with the sex lethal mutation die?
Sex lethal blocks the translation of msl-2 (male specific lethal 2) mRNA, a protein required for dosage compensation in males. X-linked genes are not over-expressed and males die.
21
New cards
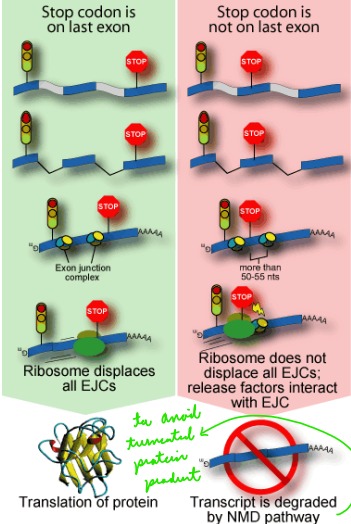
Describe: Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay
The degradation of mRNA with premature stop codons
\
\*EJC = exon junction complex
\
\*EJC = exon junction complex
22
New cards
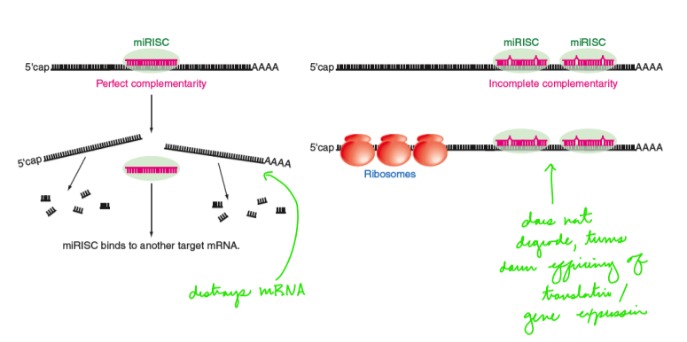
Describe: micro-RNA (miRNA) mediated RNA interference (RNAi)
miRNA
\- Small RNA molecules (21-24 nucleotides) that prevent translation of mRNA
\- Trans-acting
\- Complementary base-pairing to sequences in UTRs
\
If miRNA binds to target mRNA with perfect complementarity, the mRNA is destroyed. If miRNA binds with incomplete complementarity, it turns down the efficiency of translation and gene expression.
\- Small RNA molecules (21-24 nucleotides) that prevent translation of mRNA
\- Trans-acting
\- Complementary base-pairing to sequences in UTRs
\
If miRNA binds to target mRNA with perfect complementarity, the mRNA is destroyed. If miRNA binds with incomplete complementarity, it turns down the efficiency of translation and gene expression.
23
New cards
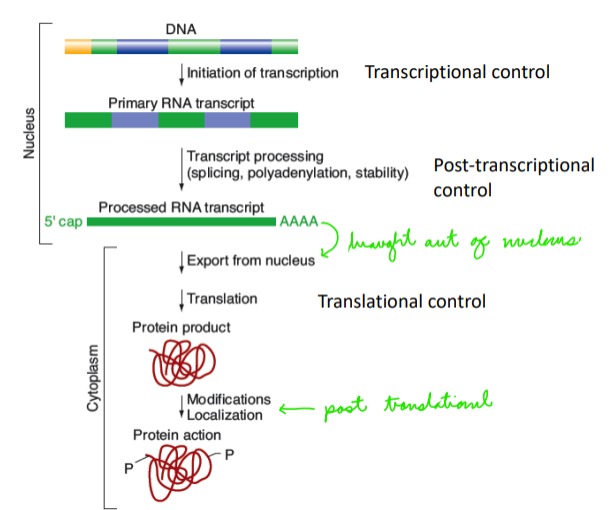
Outline the stages of gene regulation in eukaryotes
In the nucleus:
Transcriptional control
Post transcriptional control
\
Out of nucleus:
Translational control
Post translational control
Transcriptional control
Post transcriptional control
\
Out of nucleus:
Translational control
Post translational control